
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 19 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volume Analysis Spring,2017 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 LAAAAARA http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html 1日
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 19 Spring, 2017 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volume Analysis http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html
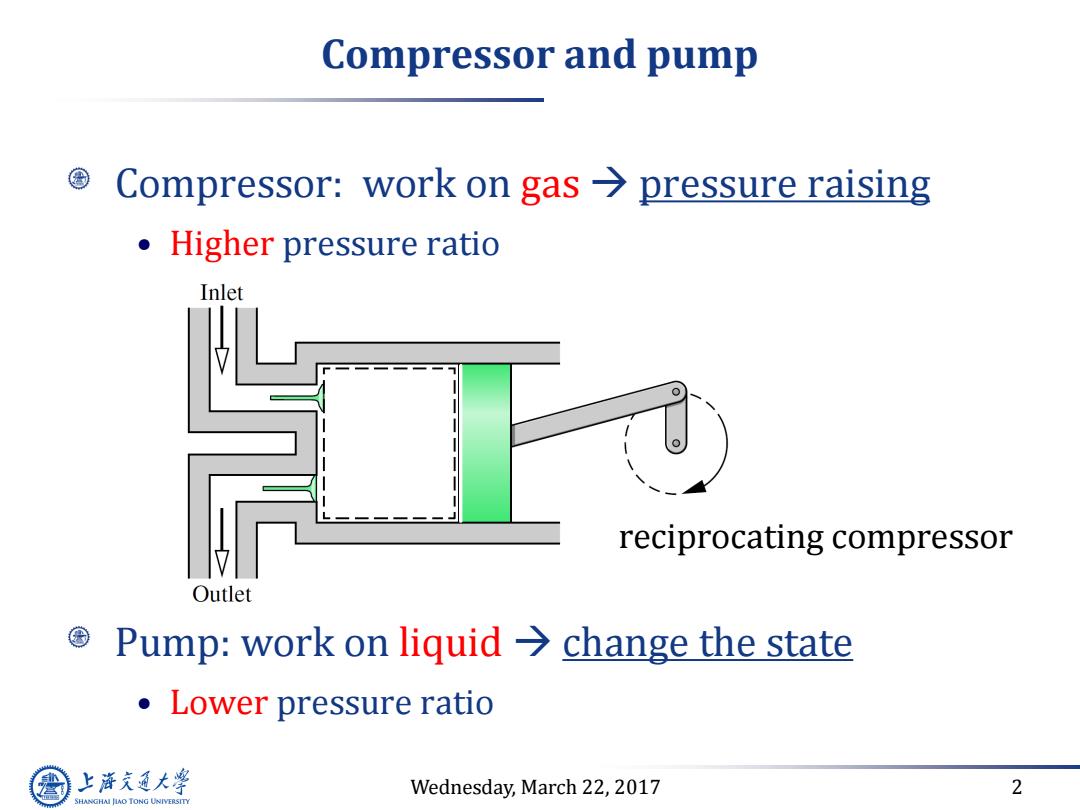
Compressor and pump Compressor:work on gas pressure raising Higher pressure ratio Inlet reciprocating compressor Outlet ©Pump:work on liquid→change the state Lower pressure ratio 上游充通大 Wednesday,March 22,2017 2 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 2 Compressor and pump Compressor: work on gas pressure raising • Higher pressure ratio Pump: work on liquid change the state • Lower pressure ratio reciprocating compressor
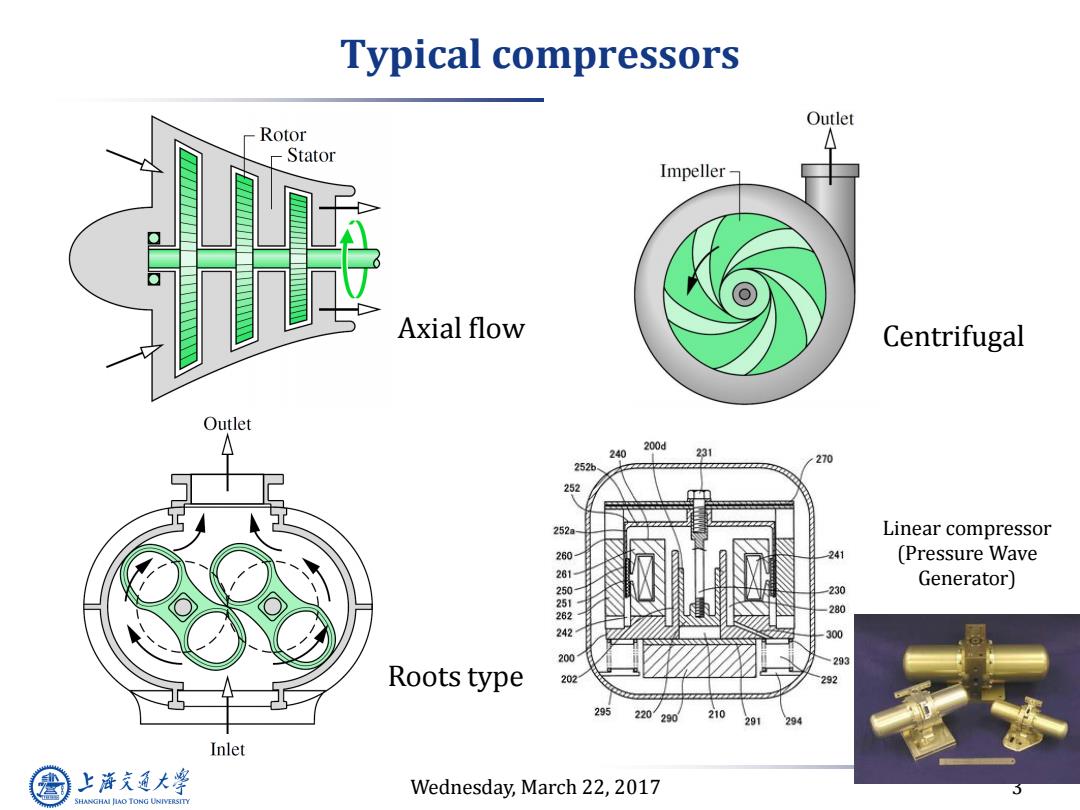
Typical compressors Outlet Rotor Stator Impeller- Axial flow Centrifugal Outlet 200d 240 231 270 252 252 252a Linear compressor 241 (Pressure Wave Generator) 230 280 242 300 200 293 Roots type 202 292 295 220 290 210 291 294 Inlet 上降通大学 Wednesday,March 22,2017 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 3 Typical compressors Axial flow Centrifugal Roots type Linear compressor (Pressure Wave Generator)
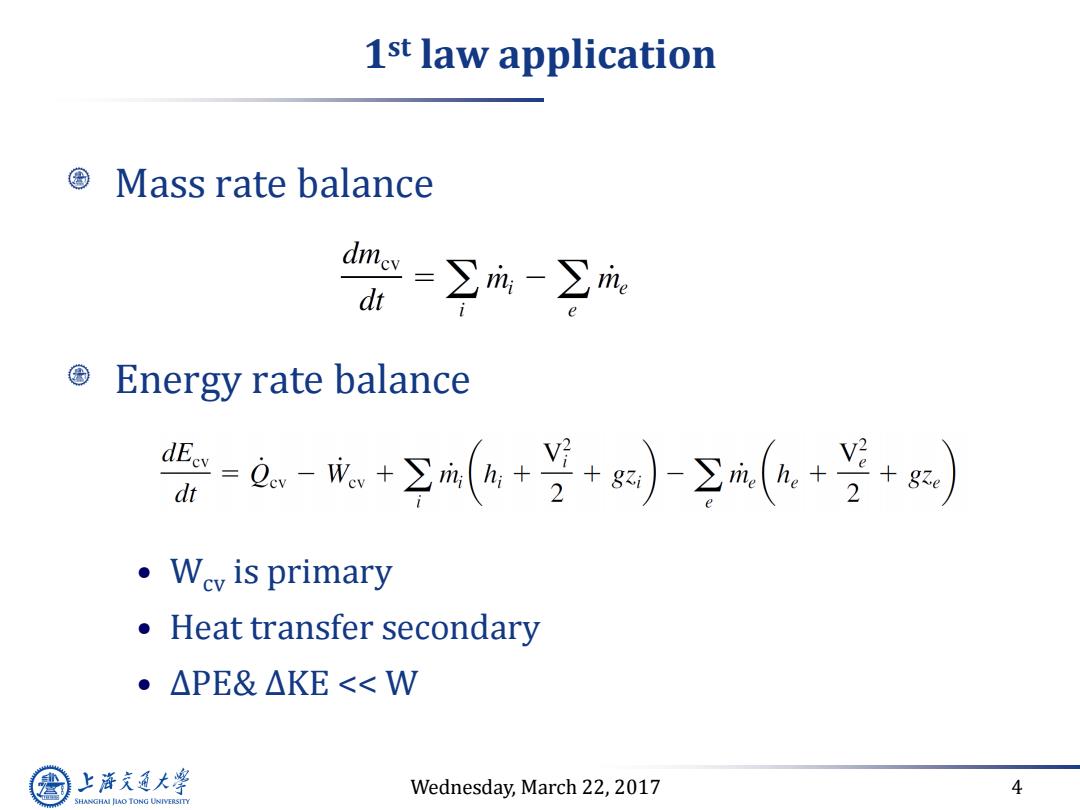
1st law application Mass rate balance =∑m-∑m: dt Energy rate balance 份-@,-成+空m(4+于+)(a+兰+) dt ·Wc is primary Heat transfer secondary ·△PE&△KE<<W 上游气通大粤 Wednesday,March 22,2017 4 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 4 1 st law application Mass rate balance Energy rate balance • Wcv is primary • Heat transfer secondary • ∆PE& ∆KE << W
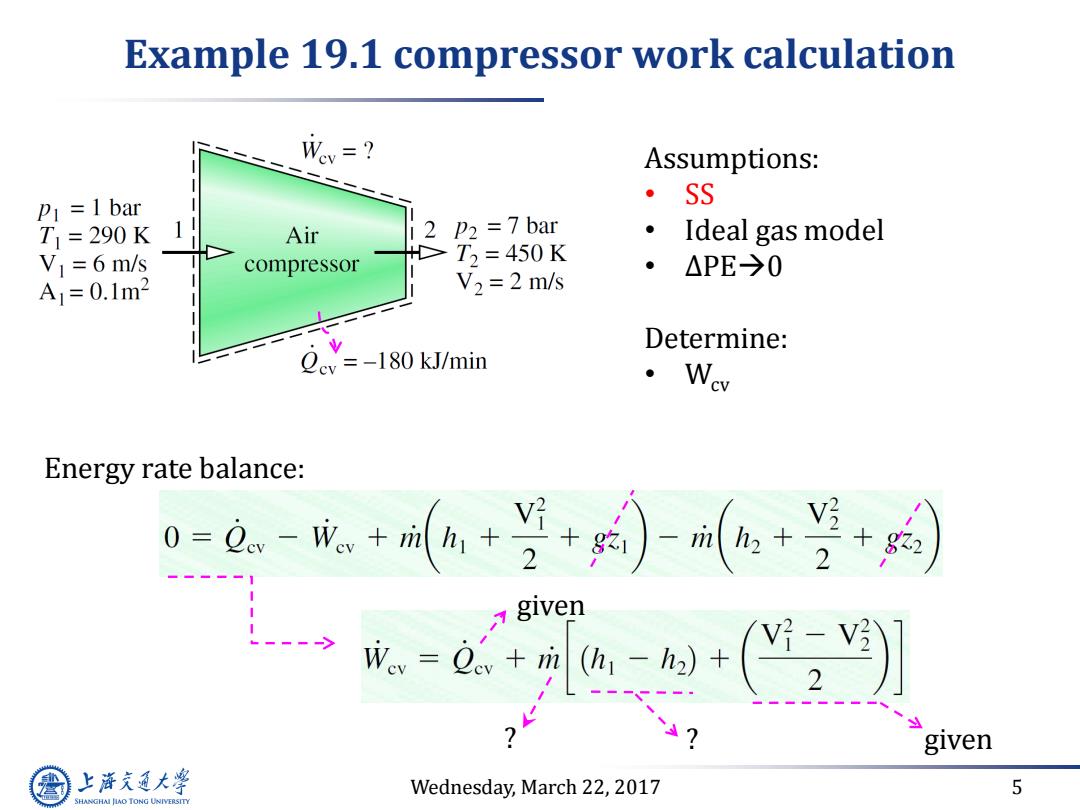
Example 19.1 compressor work calculation Wey=? Assumptions: =1 bar ·SS T =290K Air 2 p2 7 bar Ideal gas model > V=6 m/s compressor T2=450K ● △PE→0 A=0.1m2 V2 2 m/s Determine: Qev =-180 kJ/min ·Wew Energy rate balance: 0=0.-1++--+ given =-( given 上游充通大学 Wednesday,March 22,2017 5 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 5 Example 19.1 compressor work calculation Assumptions: • SS • Ideal gas model • ∆PE0 Determine: • Wcv Energy rate balance: given given ? ?
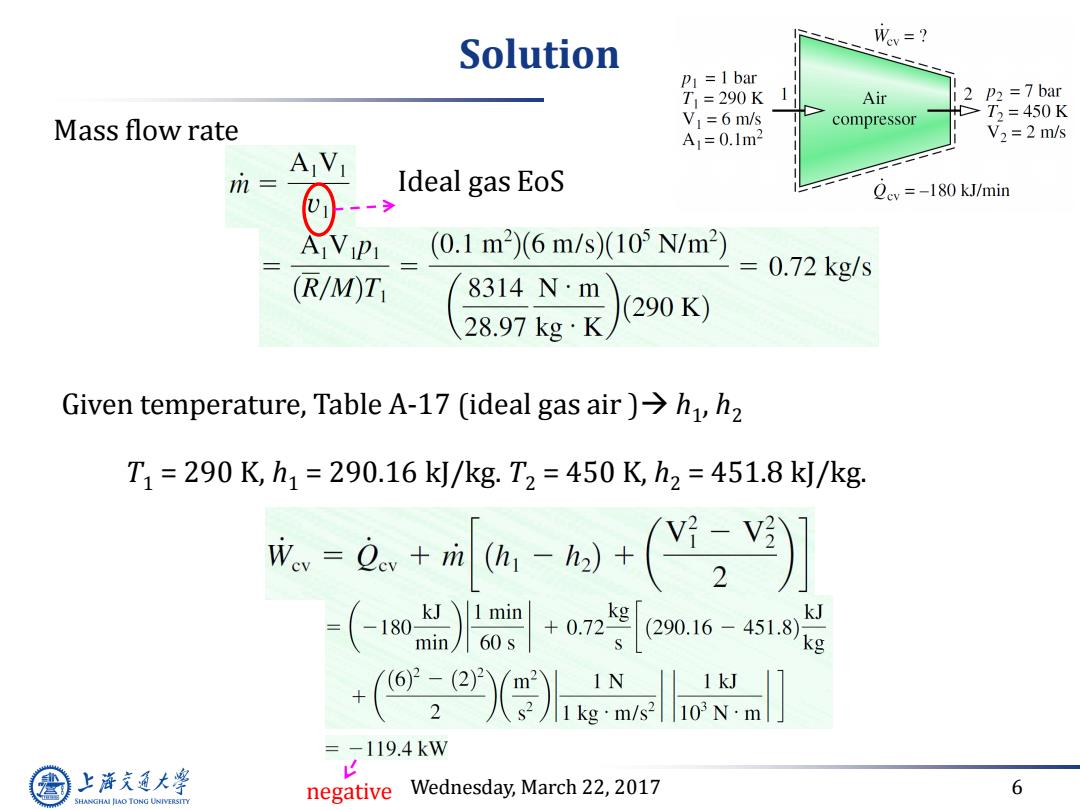
Solution Wev=? P1=1 bar T1=290K Air 2 P2=7bar Mass flow rate VI=6 m/s compressor T,=450K A1=0.1m2 V2 =2 m/s AVI m Ideal gas EoS Qcy=-180 kJ/min 1(0.1m2)6m/s)(105N/m (R/M)T 2897gR)290 8314Nm 2=0.72kgs Given temperature,Table A-17 (ideal gas air)>h,h2 T1=290K,h1=290.16k/kg.T2=450K,h2=451.8k/kg. -e.+a--(] -(-1)l+02e016-451 kJ +(:erXgndiso -119.4kW 上游充通大学 negative v Wednesday,March 22,2017 6 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 6 Solution Mass flow rate Ideal gas EoS Given temperature, Table A-17 (ideal gas air ) h1 , h2 T1 = 290 K, h1 = 290.16 kJ/kg. T2 = 450 K, h2 = 451.8 kJ/kg. negative

Pumps:Pipe and Duct Flow 2 often include pumps (or fans)and heat exchangers can have significant PE and KE changes Heater Pump or Fan Qloss pumps for liquids (water),fans for gases SSSF,Mass/Energy Balances i=PAVi=P2A2 V2 +s6y0-i Special Case: incompressible,adiabatic,isothermal flow with no work △h=A°+p4°+vAp=vp Wn-n+,Y+ge-)=0 ***Bernoulli's Equation*** 2 上游充通大学 Wednesday,March 22,2017 7 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 7 Pumps: Pipe and Duct Flow 2 Qin • often include pumps (or fans) and heat exchangers • can have significant PE and KE changes pumps for liquids (water), fans for gases Pump or Fan 1 Heater Qloss CV Win SSSF, Mass/Energy Balances Special Case: incompressible, adiabatic, isothermal flow with no work 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 V -V ( ) ( ) 0 2 v p p g z z m 1 1 1 A V A V 2 2 2 h u 0 p v 0 v p v p 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 V -V ( ) ( ) 2 m h h g z z Q W ***Bernoulli’s Equation***
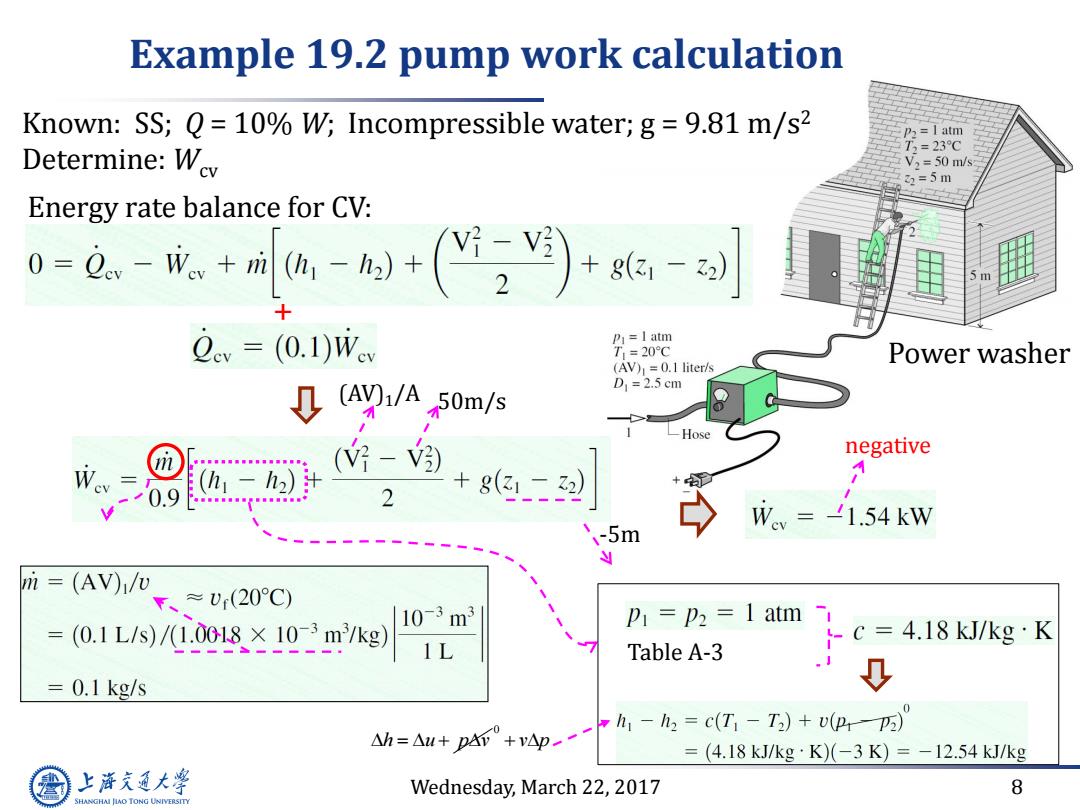
Example 19.2 pump work calculation Known:SS;Q=10%W;Incompressible water;g=9.81 m/s2 p2=I atm Determine:Wev T2=23℃ V2=50m/s 2=5m Energy rate balance for CV: 0=0。-成+刻+()+的-对 v=(0.1)Wev P=I atm T1=20C Power washer (AV)=0.1 liter/s ↓(ayi/A50m/s D1=2.5cm (好-嗡) negative -h2) + 0.9 2 +8(- Wev =-1.54 kW -5m m (AV)/v ≈U(20C) (0.1L/s)/1.0018×10-3m/kg) 10-3m3 P=p2=1 atm C= 4.18 kJ/kg K Table A-3 1 0.1 kg/s h1-h2=c(T-T2)+v(P-p) △h=△u+p4+vp一 = (4.18kJ/kg·K)(-3K)=-12.54kJ/kg 上降文通大学 Wednesday,March 22,2017 8 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 8 Energy rate balance for CV: Example 19.2 pump work calculation + -5m 50m/s (AV)1/A Table A-3 negative Power washer Known: SS; Q = 10% W; Incompressible water; g = 9.81 m/s2 Determine: Wcv h u p v 0 v p
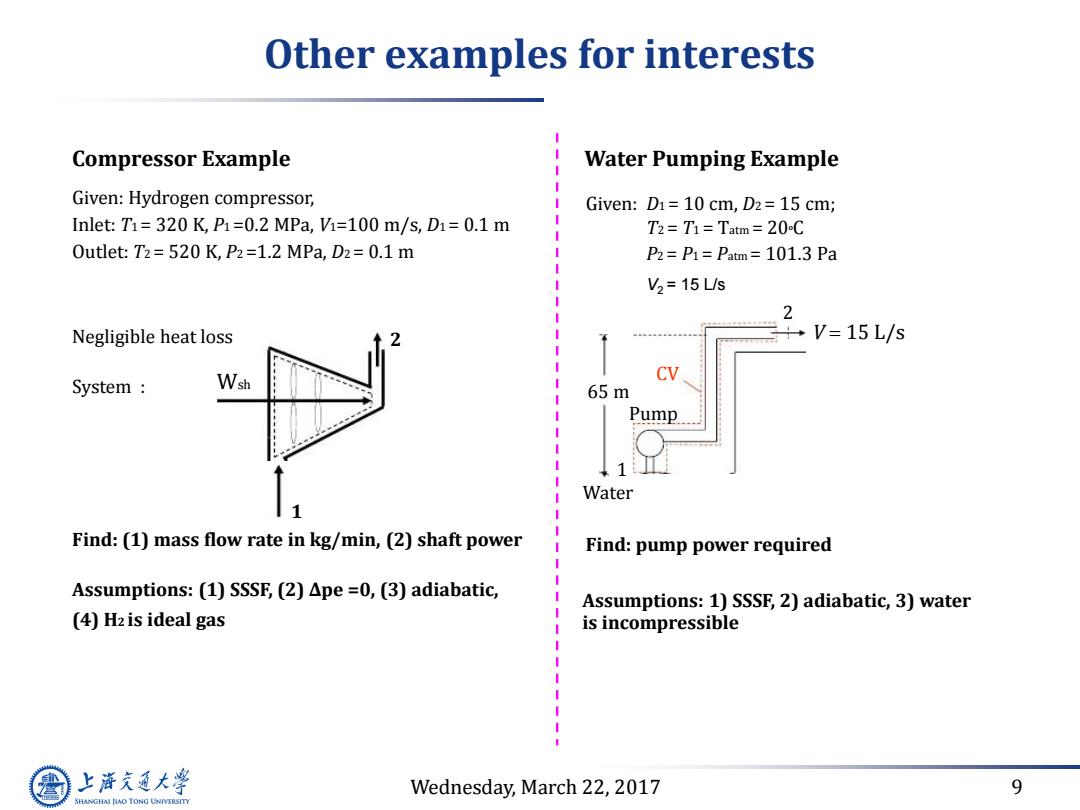
Other examples for interests Compressor Example Water Pumping Example Given:Hydrogen compressor, Given:D1=10 cm,D2=15 cm; Inlet:T1=320K,P1=0.2MPa,=100m/s,D1=0.1m T2=T1=Tatm=20C Outlet:T2=520 K,P2=1.2 MPa,D2=0.1 m P2=P1=Patm=101.3 Pa V2=15L/s 2 Negligible heat loss ÷V=15L/s System Wsh 65m Pump Water 1 Find:(1)mass flow rate in kg/min,(2)shaft power Find:pump power required Assumptions:(1)SSSF,(2)Ape =0,(3)adiabatic, Assumptions:1)SSSF,2)adiabatic,3)water (4)Hz is ideal gas is incompressible 上游充通大 Wednesday,March 22,2017 9 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 9 Other examples for interests Compressor Example Given: Hydrogen compressor, Inlet: T1 = 320 K, P1 =0.2 MPa, V1=100 m/s, D1 = 0.1 m Outlet: T2 = 520 K, P2 =1.2 MPa, D2 = 0.1 m Negligible heat loss 2 System : Wsh 1 Find: (1) mass flow rate in kg/min, (2) shaft power Assumptions: (1) SSSF, (2) ∆pe =0, (3) adiabatic, (4) H2 is ideal gas Water Pumping Example 2 CV 65 m Pump V 15 L/s 1 Water Find: pump power required Assumptions: 1) SSSF, 2) adiabatic, 3) water is incompressible Given: D1 = 10 cm, D2 = 15 cm; T2 = T1 = Tatm = 20oC P2 = P1 = Patm = 101.3 Pa V2 = 15 L/s

Homework: Problems:SP1,SP2 上游充通大学 Wednesday,March 22,2017 10 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 10 Homework: Problems: SP1, SP2