
Android Programming Lecture 5 Intent
Android Programming Lecture 5 Intent

What is Intent From Google:An Intent object is a bundle of information. It contains information of interest to the component that receives the intent(such as the action to be taken and the data to act on)plus information of interest to the Android system(such as the category of component that should handle the intent and instructions on how to launch a target activity) 2
What is Intent • From Google: An Intent object is a bundle of information. It contains information of interest to the component that receives the intent (such as the action to be taken and the data to act on) plus information of interest to the Android system (such as the category of component that should handle the intent and instructions on how to launch a target activity) 2
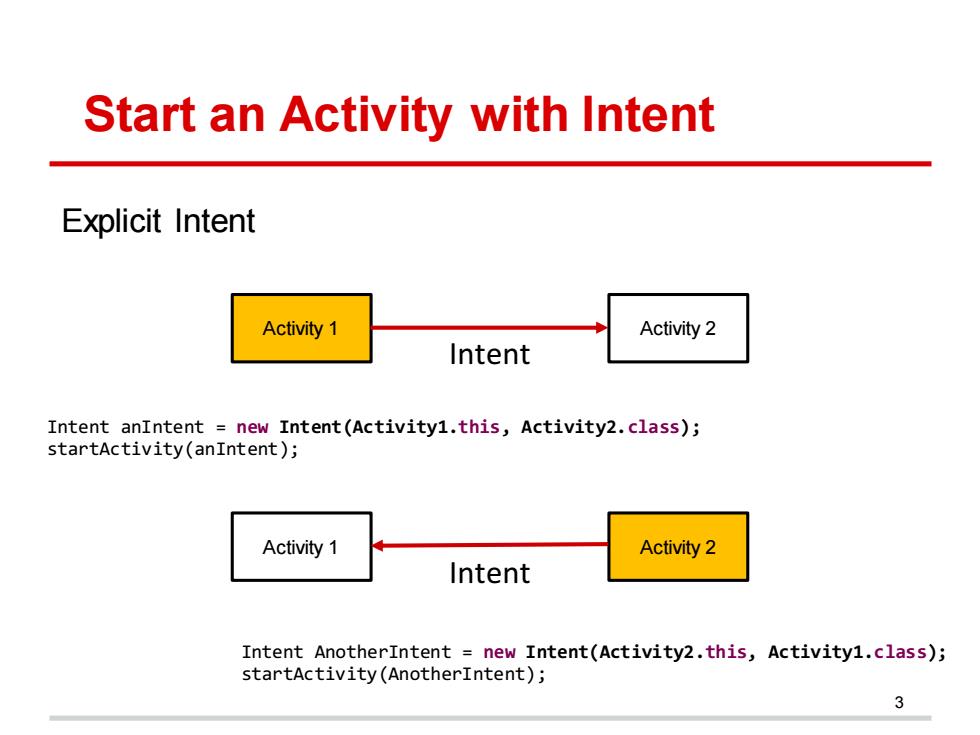
Start an Activity with Intent Explicit Intent Activity 1 Activity 2 Intent Intent anIntent new Intent(Activity1.this,Activity2.class); startActivity(anIntent); Activity 1 Activity 2 Intent Intent AnotherIntent new Intent(Activity2.this,Activity1.class); startActivity(AnotherIntent); 3
Start an Activity with Intent 3 Activity 1 Activity 2 Intent Intent anIntent = new Intent(Activity1.this, Activity2.class); startActivity(anIntent); Intent AnotherIntent = new Intent(Activity2.this, Activity1.class); startActivity(AnotherIntent); Activity 1 Activity 2 Intent Explicit Intent

Activity Stack
Activity Stack 4
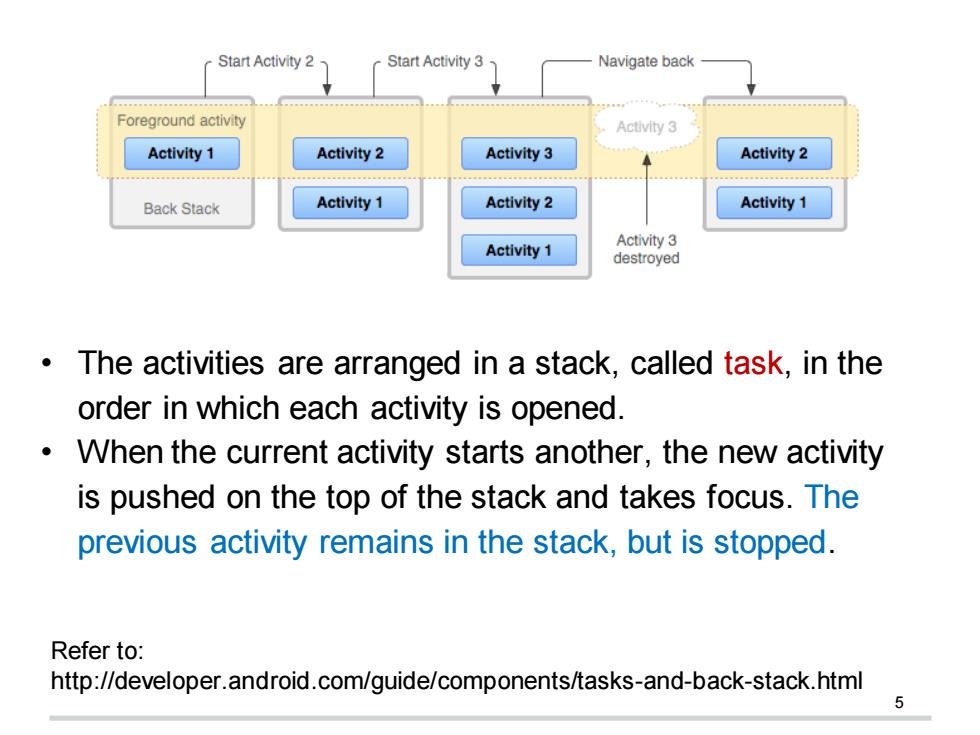
Start Activity 2 Start Activity 3 Navigate back Foreground activity Activity 3 Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity 3 Activity 2 Back Stack Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity 1 Activity 1 Activity 3 destroyed The activities are arranged in a stack,called task,in the order in which each activity is opened. When the current activity starts another,the new activity is pushed on the top of the stack and takes focus.The previous activity remains in the stack,but is stopped. Refer to: http://developer.android.com/guide/components/tasks-and-back-stack.html 5
5 • The activities are arranged in a stack, called task, in the order in which each activity is opened. • When the current activity starts another, the new activity is pushed on the top of the stack and takes focus. The previous activity remains in the stack, but is stopped. Refer to: http://developer.android.com/guide/components/tasks-and-back-stack.html
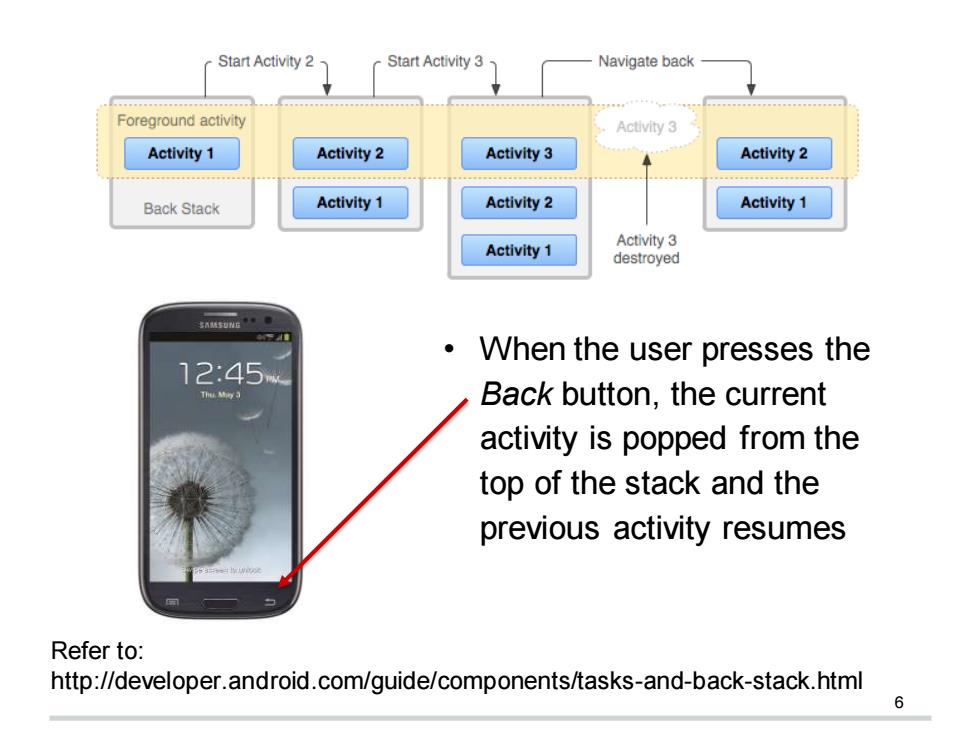
Start Activity 2 Start Activity 3 Navigate back Foreground activity Activity 3 Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity 3 Activity 2 Back Stack Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity 1 Activity 3 Activity 1 destroyed When the user presses the 12:45 Back button,the current activity is popped from the top of the stack and the previous activity resumes Refer to: http://developer.android.com/guide/components/tasks-and-back-stack.html
6 • When the user presses the Back button, the current activity is popped from the top of the stack and the previous activity resumes Refer to: http://developer.android.com/guide/components/tasks-and-back-stack.html
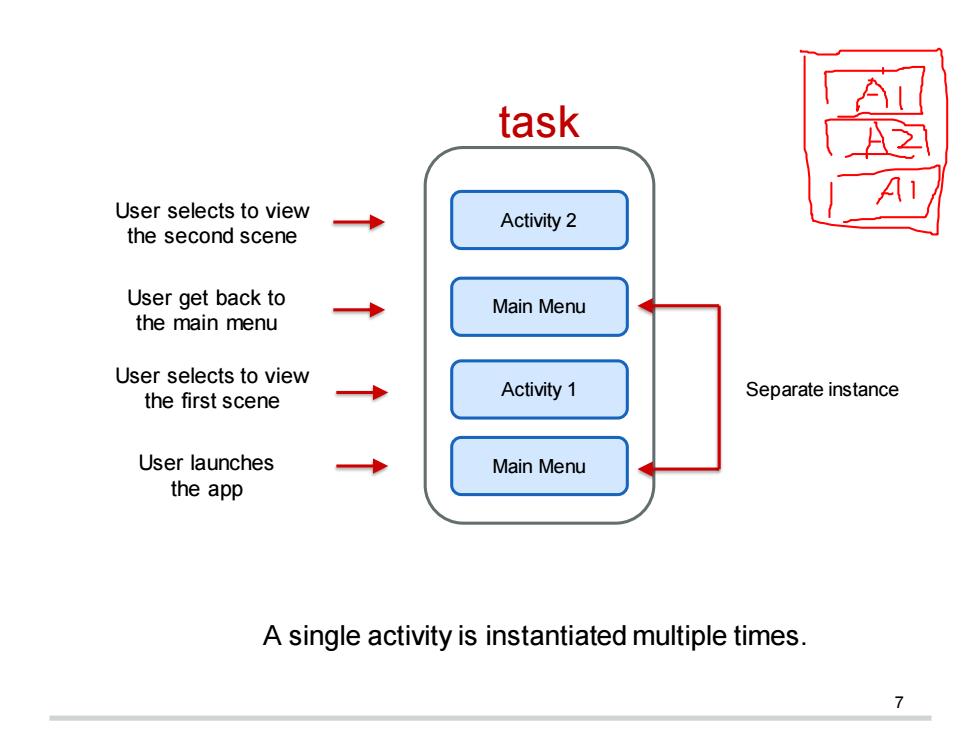
task A User selects to view Activity 2 the second scene User get back to Main Menu the main menu User selects to view the first scene Activity 1 Separate instance User launches Main Menu the app A single activity is instantiated multiple times
7 A single activity is instantiated multiple times. Main Menu Activity 1 Main Menu Activity 2 Separate instance task User launches the app User selects to view the first scene User get back to the main menu User selects to view the second scene

Launch Modes of Activity The launchMode attribute specifies an instruction on how the activity should be launched into a task There are four different launch modes you can assign to the launchMode attribute o standard:(the default mode) o singleTop:Reuse the activity on the top o singleTask:The system creates a new task and instantiates the activity at the root of the new task. o singleInstance Refer to: http://developer.android.com/quide/components/tasks-and-back-stack.html http://inthecheesefactory.com/blog/understand-android-activity-launchmode/en 8
Launch Modes of Activity • The launchMode attribute specifies an instruction on how the activity should be launched into a task • There are four different launch modes you can assign to the launchMode attribute o standard: (the default mode) o singleTop: Reuse the activity on the top o singleTask:The system creates a new task and instantiates the activity at the root of the new task. o singleInstance 8 Refer to: http://developer.android.com/guide/components/tasks-and-back-stack.html http://inthecheesefactory.com/blog/understand-android-activity-launchmode/en

Launch Modes of Activity http://ww.intridea.com/blog/2011/6/16/android-understanding-activity-launchmode 9
Launch Modes of Activity 9 http://www.intridea.com/blog/2011/6/16/android-understanding-activity-launchmode

Pass Data using Intent 10
Pass Data using Intent 10