
Testing is part of quality assurance. Software Testing Chapter 5: Test Management 同海大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Software Testing Testing is part of quality assurance. Chapter 5: Test Management

Outline ·Test organization Test planning and estimation Test progress monitoring and control Configuration management ·Risk and testing ·Incident management 同将大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY Software Testing 15/6/82
Software Testing Outline • Test organization • Test planning and estimation • Test progress monitoring and control • Configuration management • Risk and testing • Incident management 15/6/8 2

Test Organization Understand the importance of independent testing Explain the benefits and drawbacks of independent testing Recognize different team members to be considered for the organization of a test team Realize tasks of typical test leader and tester 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SoftwareTesting 15/5/18 3
Software Testing 15/5/18 3 • Understand the importance of independent testing • Explain the benefits and drawbacks of independent testing • Recognize different team members to be considered for the organization of a test team • Realize tasks of typical test leader and tester Test Organization

Independent Testing Spectrum of independence: -No independent testers,developers test their own code -Independent testers within the development teams -Independent test team or group within the organization, reporting to project management or executive management -Independent testers from the business organization or user community -Independent test specialists for specific test targets such as usability testers,security testers or certification testers -Independent testers outsources or external to the organization 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY Software Testing 15/6/84
Software Testing Independent Testing 15/6/8 4 Spectrum of independence: – No independent testers, developers test their own code – Independent testers within the development teams – Independent test team or group within the organization, reporting to project management or executive management – Independent testers from the business organization or user community – Independent test specialists for specific test targets such as usability testers, security testers or certification testers – Independent testers outsources or external to the organization

Why independence? For a complex or safety critical projects: -Multiple levels of testing -Some or all of the levels done by independent testers Development staff may -Participate in testing,especially at lower levels -Limit their effectiveness since lack of objectivity Independent tester should have clear direction -Have the authority to require and define test processes and rules -Take on such process-related roles 同濟大学 SoftwareTesting 15/6/8 5 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Software Testing Why independence? 15/6/8 5 For a complex or safety critical projects: – Multiple levels of testing – Some or all of the levels done by independent testers Development staff may – Participate in testing, especially at lower levels – Limit their effectiveness since lack of objectivity Independent tester should have clear direction – Have the authority to require and define test processes and rules – Take on such process-related roles
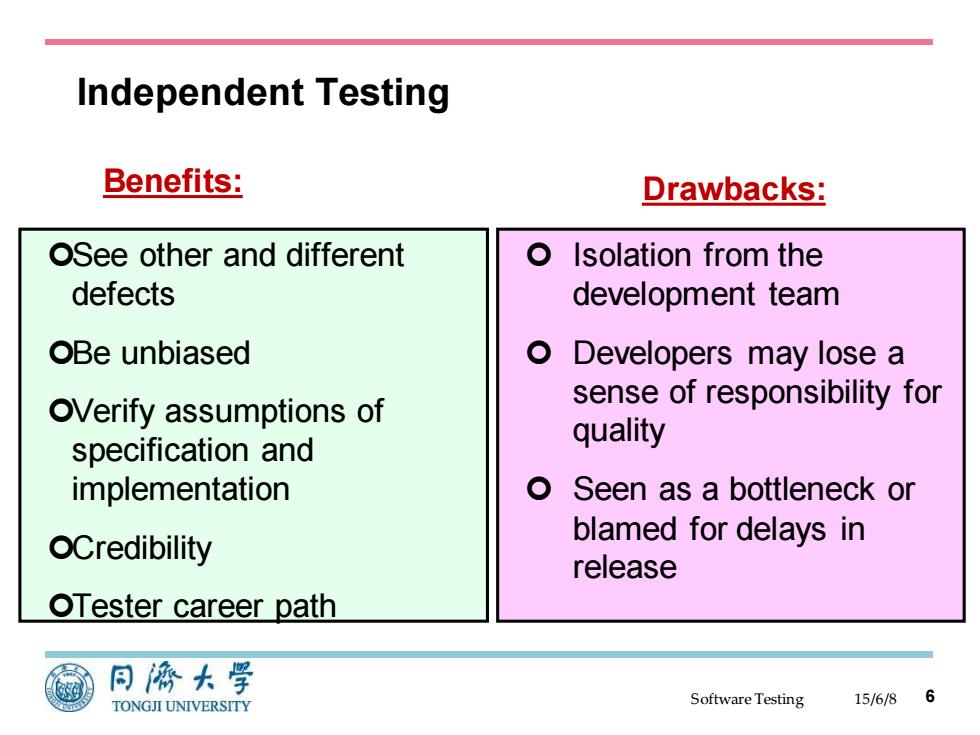
Independent Testing Benefits: Drawbacks: OSee other and different Isolation from the defects development team OBe unbiased Developers may lose a OVerify assumptions of sense of responsibility for specification and quality implementation o Seen as a bottleneck or OCredibility blamed for delays in release OTester career path 同海大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SoftwareTesting 15/6/86
Software Testing Independent Testing 15/6/8 6 Benefits: See other and different defects Be unbiased Verify assumptions of specification and implementation Credibility Tester career path Isolation from the development team Developers may lose a sense of responsibility for quality Seen as a bottleneck or blamed for delays in release Drawbacks:
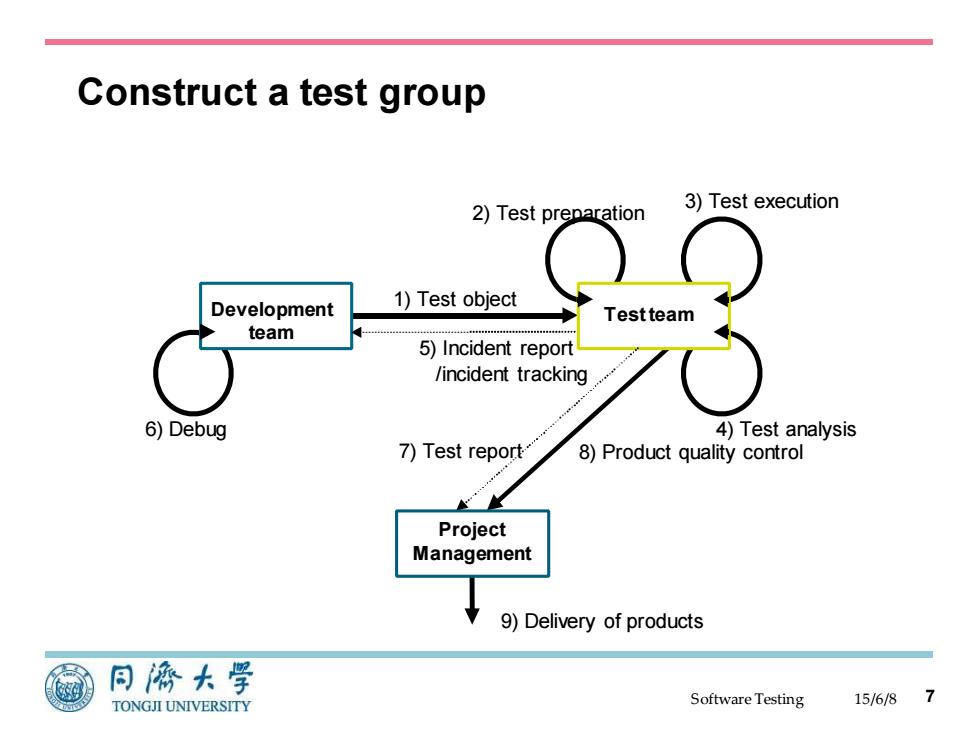
Construct a test group 2)Test preparation 3)Test execution Development 1)Test object Testteam team 5)Incident report /incident tracking 6)Debug 4)Test analysis 7)Test report' 8)Product quality control Project Management 9)Delivery of products 同源大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SoftwareTesting 15/6/8
Software Testing Construct a test group 15/6/8 7 Development team Test team Project Management 1) Test object 2) Test preparation 3) Test execution 8) Product quality control 9) Delivery of products 6) Debug 5) Incident report /incident tracking 7) Test report 4) Test analysis

Structure of test groups Executive Management Software System Test Hardware Group Group Group Integration Software Test Group Developers Development Performance Scalability Automation Sustaining Test Group Test Group Test Group Test Group Test Group 同海大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SoftwareTesting 15/6/88
Software Testing Structure of test groups 15/6/8 8

Test leader/manager/coordinator Typical tasks: -Devise test strategies,plans -Ensure configuration management of -Write or review test policy testware -Consult on testing for other project activities-Ensure traceability -Test estimation Measure test progress,evaluate the -Test resource acquisition quality of the testing and the product -Lead specification -Plan any test automation -Preparation -Select tools and organize any tester -Implementation and execution of tests training -Monitor and control the test execution -Ensure implementation of the test -Adapt the test plan based on test results environment -Schedule tests -Write test summary reports 同源大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SoftwareTesting 15/6/89
Software Testing Test leader/manager/coordinator 15/6/8 9 Typical tasks: – Devise test strategies, plans – Write or review test policy – Consult on testing for other project activities – Test estimation – Test resource acquisition – Lead specification – Preparation – Implementation and execution of tests – Monitor and control the test execution – Adapt the test plan based on test results – Ensure configuration management of testware – Ensure traceability – Measure test progress, evaluate the quality of the testing and the product – Plan any test automation – Select tools and organize any tester training – Ensure implementation of the test environment – Schedule tests – Write test summary reports

Testers Typical tasks: -Review and contribute to test plans -Analyze,review and assess user requirements,specifications -Create test suites,cases,data and procedures -Set up the test environment -Implement tests on all test levels -Execute and log the tests -Evaluate results and document problems found -Monitor testing using the appropriate tools -Automate tests -Measure performance of components and systems -Review each others'tests 同海大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY Software Testing 15/6/810
Software Testing Testers 15/6/8 10 Typical tasks: – Review and contribute to test plans – Analyze, review and assess user requirements, specifications – Create test suites, cases, data and procedures – Set up the test environment – Implement tests on all test levels – Execute and log the tests – Evaluate results and document problems found – Monitor testing using the appropriate tools – Automate tests – Measure performance of components and systems – Review each others’ tests