
CHAPTER 3 DEMAND FOR HEALTH: THE GROSSMAN MODEL
CHAPTER 3 DEMAND FOR HEALTH: THE GROSSMAN MODEL

Intro Previously... Demand for health care is downward sloping People choose amount of health care they receive based on price People choose their health care,but do they choose their own health? Is health somethingthat happens to us?Or do we choose it? We use the Grossman model to explore this question Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Intro Previously… Demand for health care is downward sloping People choose amount of health care they receive based on price People choose their health care, but do they choose their own health? Is health something that happens to us? Or do we choose it? We use the Grossman model to explore this question

The 3 Roles of Health (H) Health plays three roles in the Grossman model: 1.A consumption good 2.An input into production 3.A form of stock/capital (an investment) Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics The 3 Roles of Health (H) Health plays three roles in the Grossman model: 1. A consumption good 2. An input into production 3. A form of stock/capital (an investment)

Health as a consumption good
Health as a consumption good

Health as a direct input into utility Health as a consumption good enters directly into utility 口 Single-period Utility at time t U=U(Hy Z) H level of health ▣Zt=“home good” Everything non-health that contributes to utility E.g.video games,time with friends,movie tickets **Note:health health care Health care is not explicitly in the utility function i.e.Getting vaccines does not provide utility but staying healthy does Health as a consumption good Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Health as a direct input into utility Health as a consumption good enters directly into utility Single-period Utility at time t Ut= U(Ht , Zt ) Ht = level of health Zt= “home good” ◼ Everything non-health that contributes to utility ◼ E.g. video games, time with friends, movie tickets **Note: health ≠ health care Health care is not explicitly in the utility function ◼ i.e. Getting vaccines does not provide utility but staying healthy does Health as a consumption good
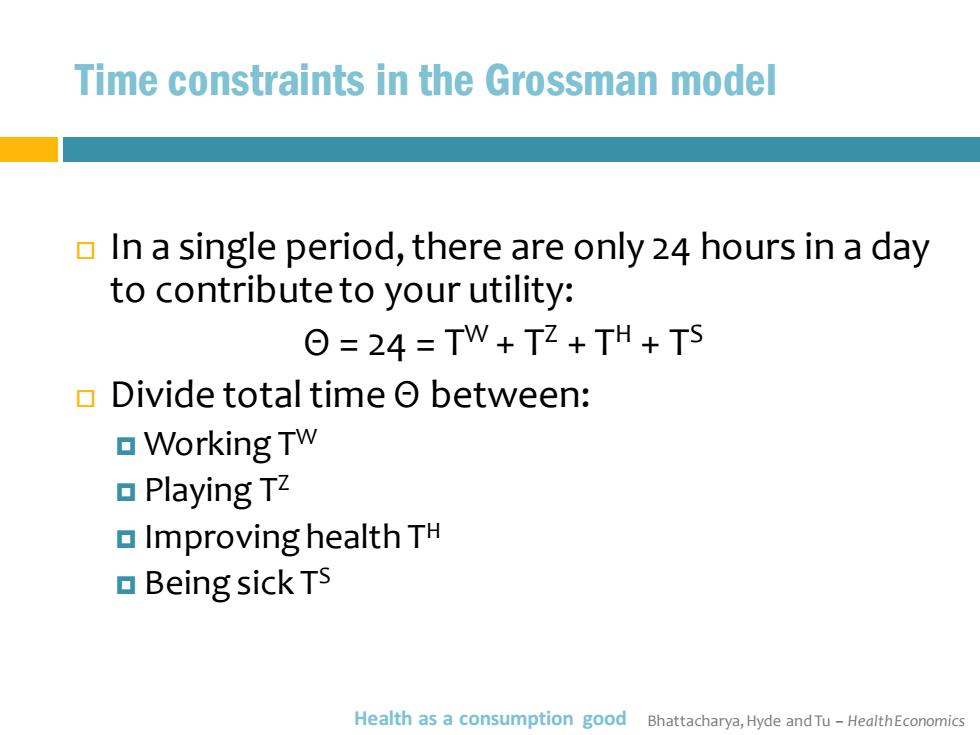
Time constraints in the Grossman model In a single period,there are only 24 hours in a day to contribute to your utility: Θ=24=TW+TZ+TH+TS Divide total time between: Working Tw Playing TZ Improving health TH Being sick TS Health as a consumption good Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Time constraints in the Grossman model In a single period, there are only 24 hours in a day to contribute to your utility: Θ = 24 = TW + TZ + TH + TS Divide total time Θ between: Working TW Playing TZ Improving health TH Being sick TS Health as a consumption good
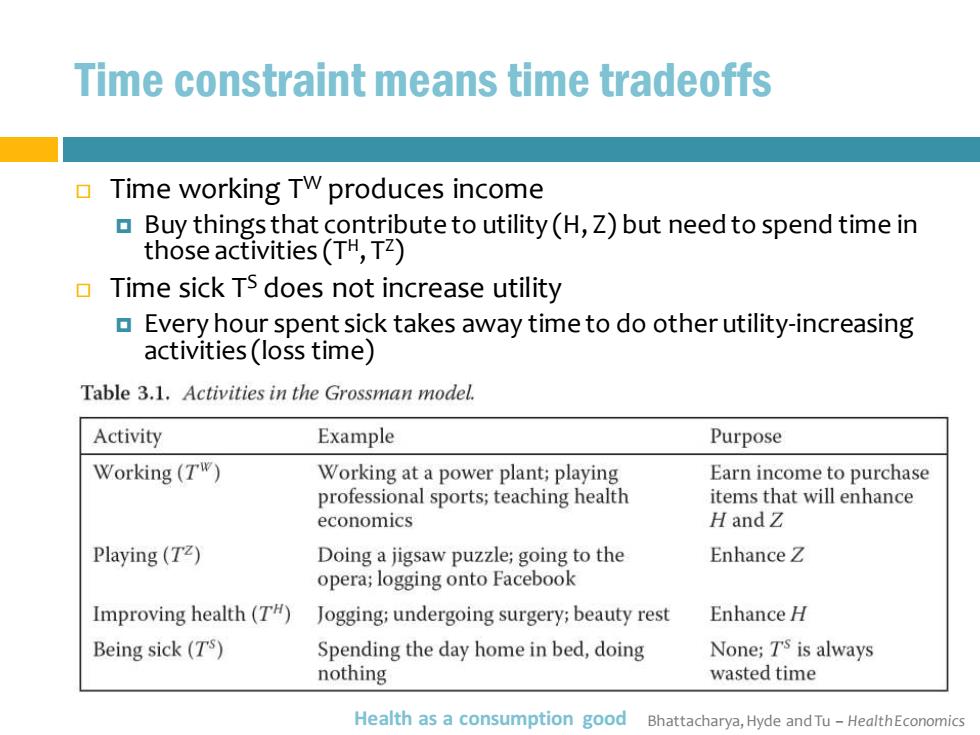
Time constraint means time tradeoffs 口 Time working TW produces income Buy things that contribute to utility(H,Z)but need to spend time in those activities(TH,TZ) Time sick TS does not increase utility Every hour spent sick takes away time to do other utility-increasing activities(loss time) Table 3.1.Activities in the Grossman model. Activity Example Purpose Working(TW) Working at a power plant;playing Earn income to purchase professional sports;teaching health items that will enhance economics H and Z Playing(TZ) Doing a jigsaw puzzle;going to the Enhance Z opera;logging onto Facebook Improving health(T#) Jogging;undergoing surgery;beauty rest Enhance H Being sick(TS) Spending the day home in bed,doing None;T's is always nothing wasted time Health as a consumption good Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Time constraint means time tradeoffs Time working TW produces income Buy things that contribute to utility (H, Z) but need to spend time in those activities (TH, TZ ) Time sick TS does not increase utility Every hour spent sick takes away time to do other utility-increasing activities (loss time) Health as a consumption good
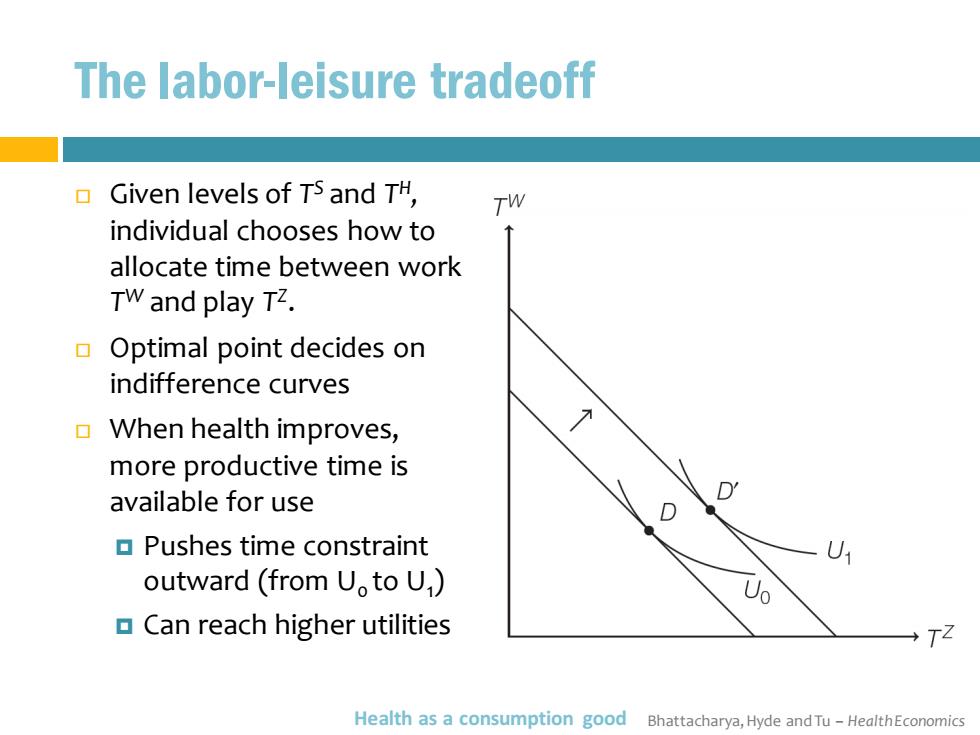
The labor-leisure tradeoff Given levels of TS and TH, Tw individual chooses how to allocate time between work TW and play TZ. Optimal point decides on indifference curves When health improves, more productive time is D available for use D Pushes time constraint U outward (from U.to U) Uo Can reach higher utilities TZ Health as a consumption good Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics The labor-leisure tradeoff Given levels of T S and T H , individual chooses how to allocate time between work T W and play T Z . Optimal point decides on indifference curves When health improves, more productive time is available for use Pushes time constraint outward (from U0 to U1 ) Can reach higher utilities Health as a consumption good
Health as an input into production
Health as an input into production

The three roles of health (H) Health plays three roles in the Grossman model: A consumption good 2.An input into production Of health(H) Of productive time(TP) 3.A form of stock/capital (an investment) Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics The three roles of health (H) Health plays three roles in the Grossman model: 1. A consumption good 2. An input into production Of health (H) Of productive time (TP ) 3. A form of stock/capital (an investment)