
CHAPTER 14 HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT
CHAPTER 14 HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT

Intro Health technology assessment(HTA)is comprised of two parts: Cost effectiveness analysis(the science of comparing the costs and benefits of different medical treatments) Cost-benefit analysis(the process of choosing an optimal treatment by creating a tradeoff between money and health) HTA may sound dry and technical but it generates enormous controversy because it involves placing an explicit value on human life. Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Intro Health technology assessment (HTA) is comprised of two parts: Cost effectiveness analysis (the science of comparing the costs and benefits of different medical treatments) Cost-benefit analysis (the process of choosing an optimal treatment by creating a tradeoff between money and health) HTA may sound dry and technical but it generates enormous controversy because it involves placing an explicit value on human life

COST EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS Ch 14 Health technology assessment
Ch 14 | Health technology assessment COST EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS
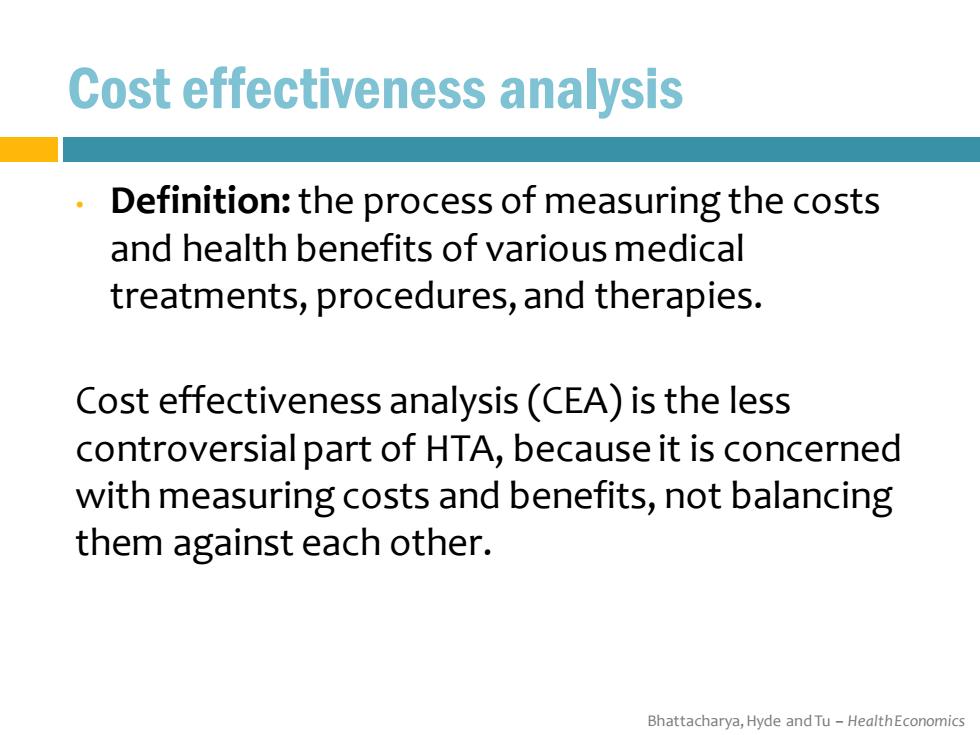
Cost effectiveness analysis Definition:the process of measuring the costs and health benefits of various medical treatments,procedures,and therapies. Cost effectiveness analysis(CEA)is the less controversial part of HTA,because it is concerned with measuring costs and benefits,not balancing them against each other. Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Cost effectiveness analysis • Definition: the process of measuring the costs and health benefits of various medical treatments, procedures, and therapies. Cost effectiveness analysis (CEA) is the less controversial part of HTA, because it is concerned with measuring costs and benefits, not balancing them against each other

Cost effectiveness analysis Often multiple treatments,with varying costs, can be used to treat a given disease. ·In such cases How do insurance companies decide which treatments,if any,to provide coverage for? How do patients decide between an expensive and highly effective treatment and a low-cost treatment that is less effective? Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Cost effectiveness analysis • Often multiple treatments, with varying costs, can be used to treat a given disease. • In such cases • How do insurance companies decide which treatments, if any, to provide coverage for? • How do patients decide between an expensive and highly effective treatment and a low-cost treatment that is less effective?

Cost effectiveness analysis If one treatment is both cheaper and more effective than a second treatment,then the second treatment is said to be dominated by the first. It is never optimal to use a dominated treatment, because there is always a more effective and cheaper alternative available. Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Cost effectiveness analysis • If one treatment is both cheaper and more effective than a second treatment, then the second treatment is said to be dominated by the first. • It is never optimal to use a dominated treatment, because there is always a more effective and cheaper alternative available
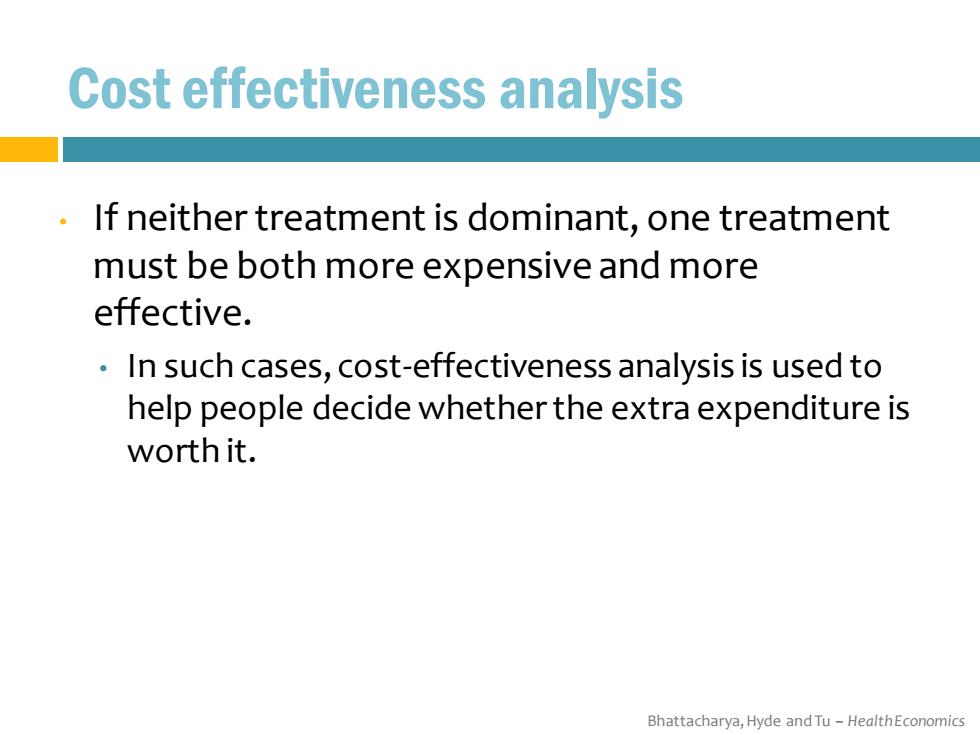
Cost effectiveness analysis If neither treatment is dominant,one treatment must be both more expensive and more effective. In such cases,cost-effectiveness analysis is used to help people decide whether the extra expenditure is worth it. Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Cost effectiveness analysis • If neither treatment is dominant, one treatment must be both more expensive and more effective. • In such cases, cost-effectiveness analysis is used to help people decide whether the extra expenditure is worth it
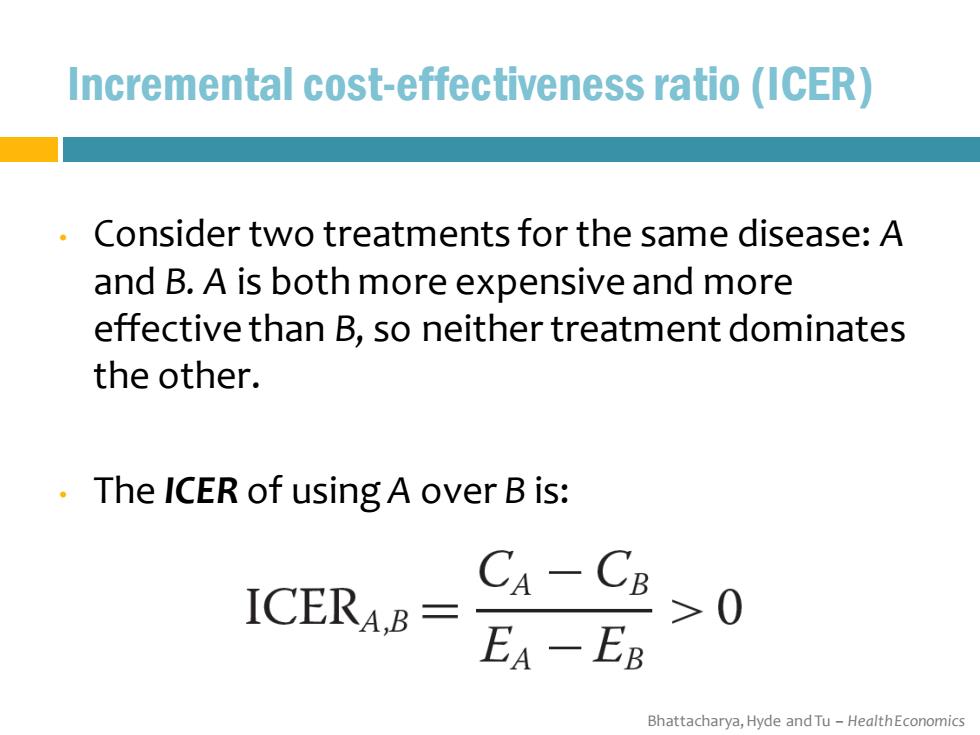
Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) Consider two treatments for the same disease:A and B.A is both more expensive and more effective than B,so neither treatment dominates the other. The ICER of using A over B is: ICERA,B= CA-CB >0 EA-EB Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) • Consider two treatments for the same disease: A and B. A is both more expensive and more effective than B, so neither treatment dominates the other. • The ICER of using A over B is:

Lead poisoning example Which treatment strategy is superior? Table 14.2.Comparison oftwo lead poisoning treatments. Treatment strategy Cost of treatment Prob.of reading disability Conservative treatment $786 35.3% Aggressive treatment $1,778 21.6% Source:Data from Table 1 in Glotzer et al.(1995). Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Lead poisoning example Which treatment strategy is superior?

Lead poisoning example $1,778-$786 ICER Agg,Cons= =$7,241/reading disability 0.353-0.216 This ICER provides a price for avoiding a reading disability. In some sense,people can avoid a reading disability for an average price of $7,241. Note that the ICER does not make a determination about whether this is worth it or not,it is just an empirical fact about costs. Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Lead poisoning example This ICER provides a price for avoiding a reading disability. In some sense, people can avoid a reading disability for an average price of $7,241. Note that the ICER does not make a determination about whether this is worth it or not, it is just an empirical fact about costs