
CHAPTER 6 THE HOSPITAL INDUSTRY
CHAPTER 6 THE HOSPITAL INDUSTRY

History of hospitals 1gth century hospitals could be fatal places to go to for medical care Higher mortality rates in the hospital than at home Late 18oos innovations helped lift hospital reputation Germ theory of disease Antiseptic techniques ▣Anesthesia X-ray technology Increased demand for hospital surgeries led to increased need for more hospital resources Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics History of hospitals 19th century hospitals could be fatal places to go to for medical care Higher mortality rates in the hospital than at home Late 1800s innovations helped lift hospital reputation Germ theory of disease Antiseptic techniques Anesthesia X-ray technology Increased demand for hospital surgeries led to increased need for more hospital resources

History of hospitals In 1946,the Hill-Burton Act increased the number of hospitals in the US Congress gave monies for building hospitals Any hospital receiving money had to provide free/low cost care to the poor Result:more hospitals and more hospital beds Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics History of hospitals In 1946, the Hill-Burton Act increased the number of hospitals in the US Congress gave monies for building hospitals Any hospital receiving money had to provide free/low cost care to the poor Result: more hospitals and more hospital beds
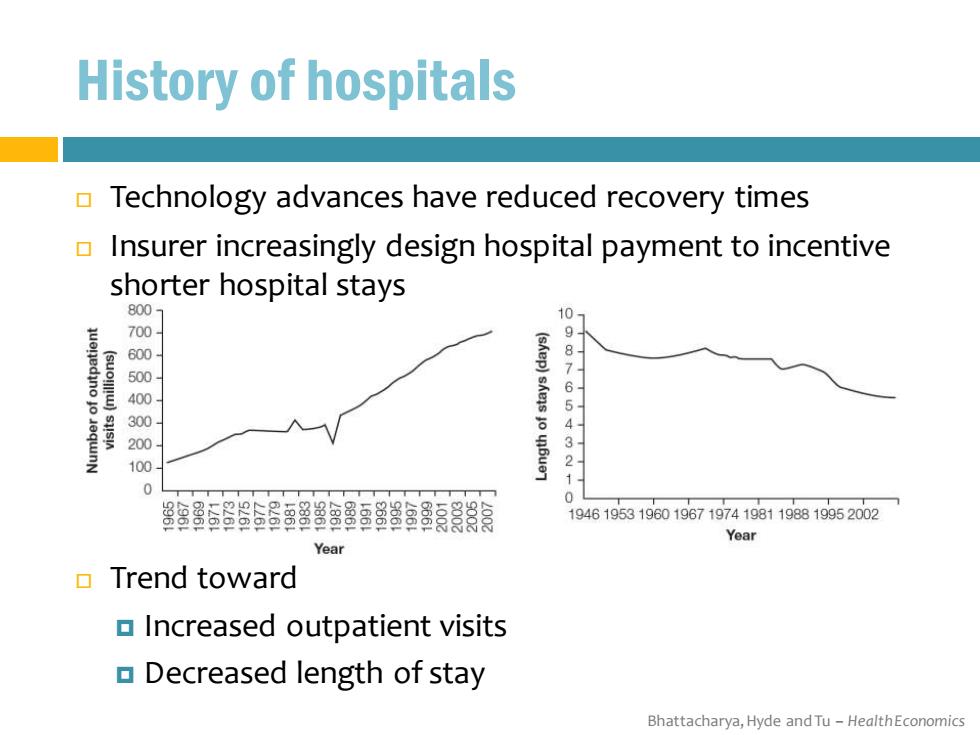
History of hospitals Technology advances have reduced recovery times Insurer increasingly design hospital payment to incentive shorter hospital stays 800 10 700 600 9 500 400 61 300 200 3 100 0 容5SS6S留B8BB餐33 194619531960196719741981198819952002 Year Year Trend toward Increased outpatient visits Decreased length of stay Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics History of hospitals Technology advances have reduced recovery times Insurer increasingly design hospital payment to incentive shorter hospital stays Trend toward Increased outpatient visits Decreased length of stay

THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN HOSPITALS AND PHYSICIANS Ch 6:The Hospital Industry
Ch 6: The Hospital Industry THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN HOSPITALS AND PHYSICIANS
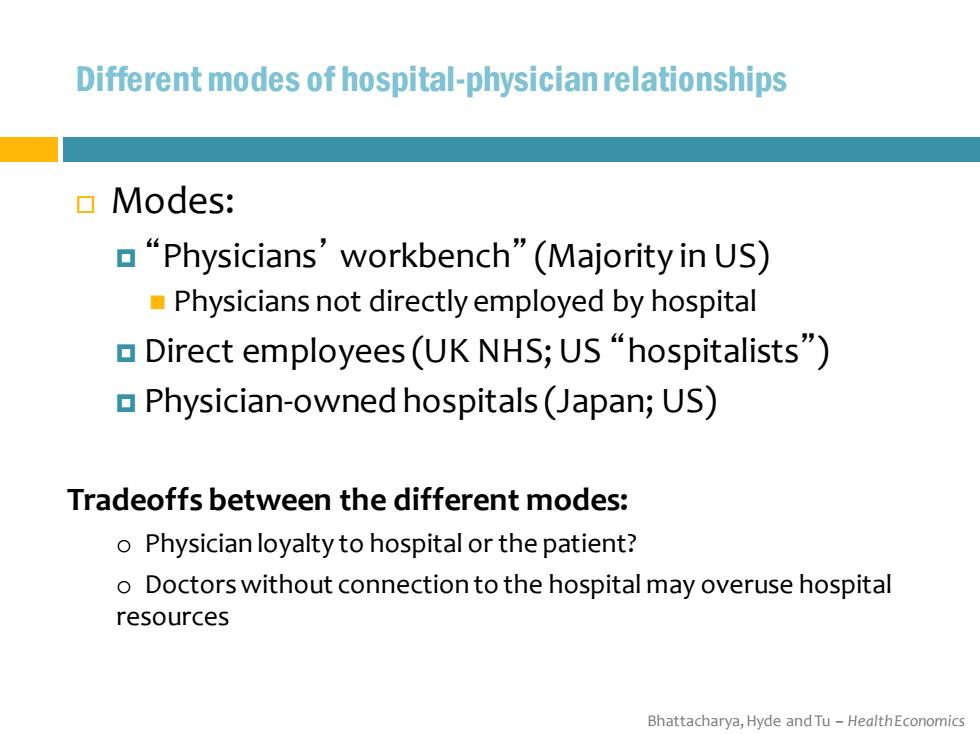
Different modes of hospital-physician relationships ▣Modes: a“Physicians'workbench”(Majority in US) Physicians not directly employed by hospital ▣Direct employees(UK NHS;US“hospitalists”) Physician-owned hospitals(Japan;US) Tradeoffs between the different modes: o Physician loyalty to hospital or the patient? o Doctors without connection to the hospital may overuse hospital resources Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Different modes of hospital-physician relationships Modes: “Physicians’workbench” (Majority in US) ◼ Physicians not directly employed by hospital Direct employees (UK NHS; US “hospitalists”) Physician-owned hospitals (Japan; US) Tradeoffs between the different modes: o Physician loyalty to hospital or the patient? o Doctors without connection to the hospital may overuse hospital resources
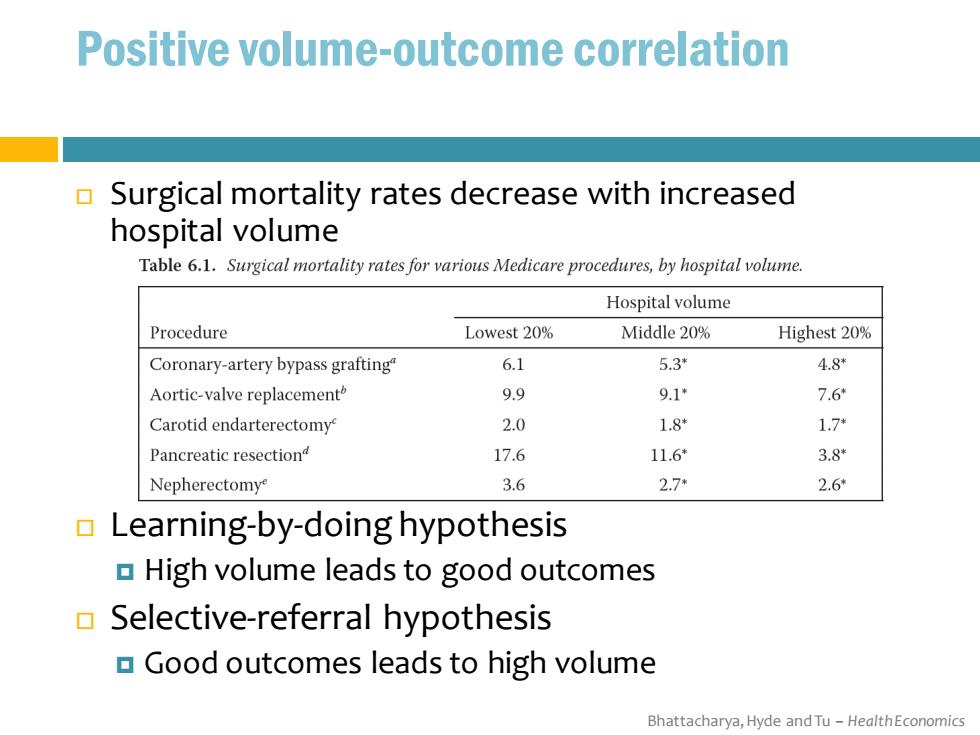
Positive volume-outcome correlation Surgical mortality rates decrease with increased hospital volume Table 6.1.Surgical mortality rates for various Medicare procedures,by hospital volume. Hospital volume Procedure Lowest 20% Middle 20% Highest 20% Coronary-artery bypass grafting" 6.1 5.3* 4.8 Aortic-valve replacement 9.9 9.1* 7.6 Carotid endarterectomy 2.0 1.8* 1.7* Pancreatic resectiond 17.6 11.6* 3.8* Nepherectomy 3.6 2.7* 2.6 Learning-by-doing hypothesis High volume leads to good outcomes Selective-referral hypothesis Good outcomes leads to high volume Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Surgical mortality rates decrease with increased hospital volume Learning-by-doing hypothesis High volume leads to good outcomes Selective-referral hypothesis Good outcomes leads to high volume Positive volume-outcome correlation

Does hospital experience or physician experience matter? Should you prefer having your surgery with an experienced physician or in an experienced hospital? McGrath et al.(2000)find Hospitals with more surgical experience have fewer complications than physicians with high experience Finding makes sense if teams of medical workers collaborate on surgeries,so individual physician experience less impactful Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Does hospital experience or physician experience matter? Should you prefer having your surgery with an experienced physician or in an experienced hospital? McGrath et al. (2000) find Hospitals with more surgical experience have fewer complications than physicians with high experience Finding makes sense if teams of medical workers collaborate on surgeries, so individual physician experience less impactful

THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN HOSPITALS AND HOSPITALS Ch 6:The hospital industry
Ch 6: The hospital industry THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN HOSPITALS AND HOSPITALS

Differentiated product oligopoly Hospital industry is a differentiated product oligopoly Strict barriers to entry Buildings,technology,staff,administration,etc. Few firms(oligopoly) Services provided by each firm are not perfect substitutes(differentiated products) Herfindahl-Hirschman Index 口HHI=∑s si=market share for a firm If HHI closer to 1 means few firms in the market (highly concentrated) If HHI closer to o means a large number of firms in the market Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Differentiated product oligopoly Hospital industry is a differentiated product oligopoly Strict barriers to entry Buildings, technology, staff, administration, etc. Few firms (oligopoly) Services provided by each firm are not perfect substitutes (differentiated products) Herfindahl-Hirschman Index HHI = ∑ si 2 si = market share for a firm If HHI closer to 1 means few firms in the market (highly concentrated) If HHI closer to 0 means a large number of firms in the market