
CHAPTER 2 DEMAND FOR HEALTH CARE
CHAPTER 2 DEMAND FOR HEALTH CARE

Standard economic demand curves are downward sloping As price(P)decreases,quantity (Q)demanded increases ▣Example: ■P=3,Q=4 lollipops ■P=$1,Q=8 lollipops P=50.50,Q=9 lollipops Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Standard economic demand curves are downward sloping As price (P) decreases, quantity (Q) demanded increases Example: ◼P=$3, Q=4 lollipops ◼P=$1, Q=8 lollipops ◼P=$0.50, Q=9 lollipops
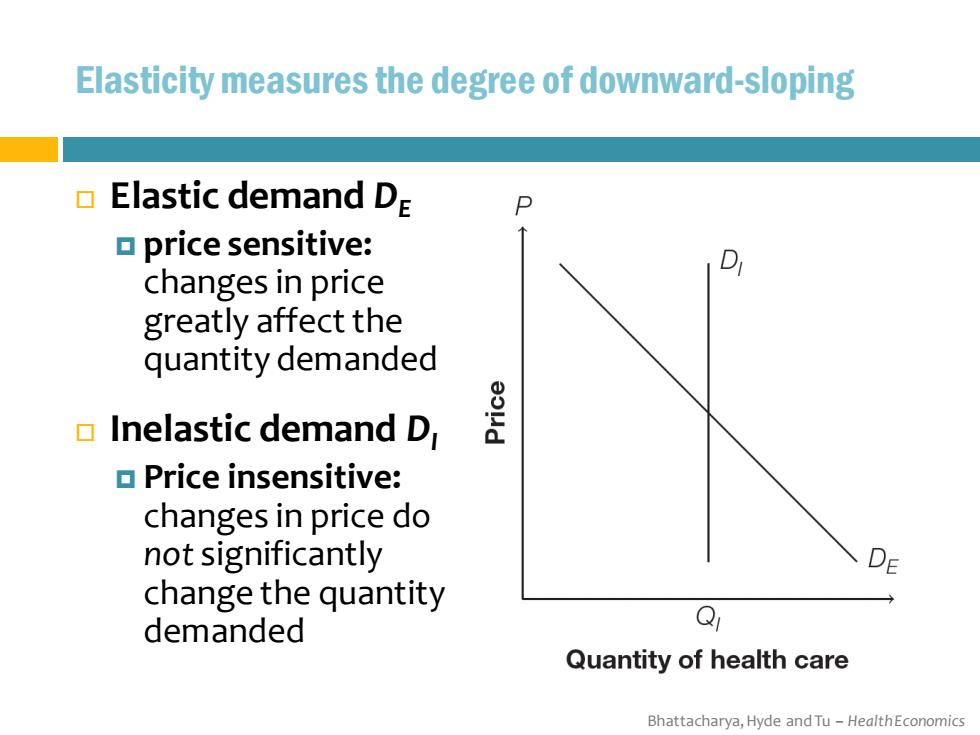
Elasticity measures the degree of downward-sloping Elastic demand DE a price sensitive: changes in price greatly affect the quantity demanded Inelastic demand D Price insensitive: changes in price do not significantly DE change the quantity demanded Q Quantity of health care Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Elasticity measures the degree of downward-sloping Elastic demand DE price sensitive: changes in price greatly affect the quantity demanded Inelastic demand DI Price insensitive: changes in price do not significantly change the quantity demanded

Does the demand curve for health care slope downward? Are people sensitive to the price of health care? Is demand for vaccines such that... ■P=5100,Q=1,000 ■P=51,Q=1,000 i.e.demand is inelastic? Is demand for band-aids such that... ■P=$100,Q=1 ■P=$1,Q=30 i.e.demand is elastic? If people always obey their doctors,then demand should be inelastic! Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Does the demand curve for health care slope downward? Are people sensitive to the price of health care? Is demand for vaccines such that… ◼ P = $100, Q=1,000 ◼ P = $1, Q=1,000 ◼ i.e. demand is inelastic? Is demand for band-aids such that… ◼ P = $100, Q = 1 ◼ P = $1, Q = 30 ◼ i.e. demand is elastic? If people always obey their doctors, then demand should be inelastic!

Need randomized experiments Randomized experiments: Definition:a study that assigns treatments randomly to different groups of study participants Includes: A control group(no treatment) ■Placebo group Helps generate experimental groups that are statistically similar to each other Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Need randomized experiments Randomized experiments: Definition: a study that assigns treatments randomly to different groups of study participants Includes: ◼A control group (no treatment) ◼Placebo group Helps generate experimental groups that are statistically similar to each other
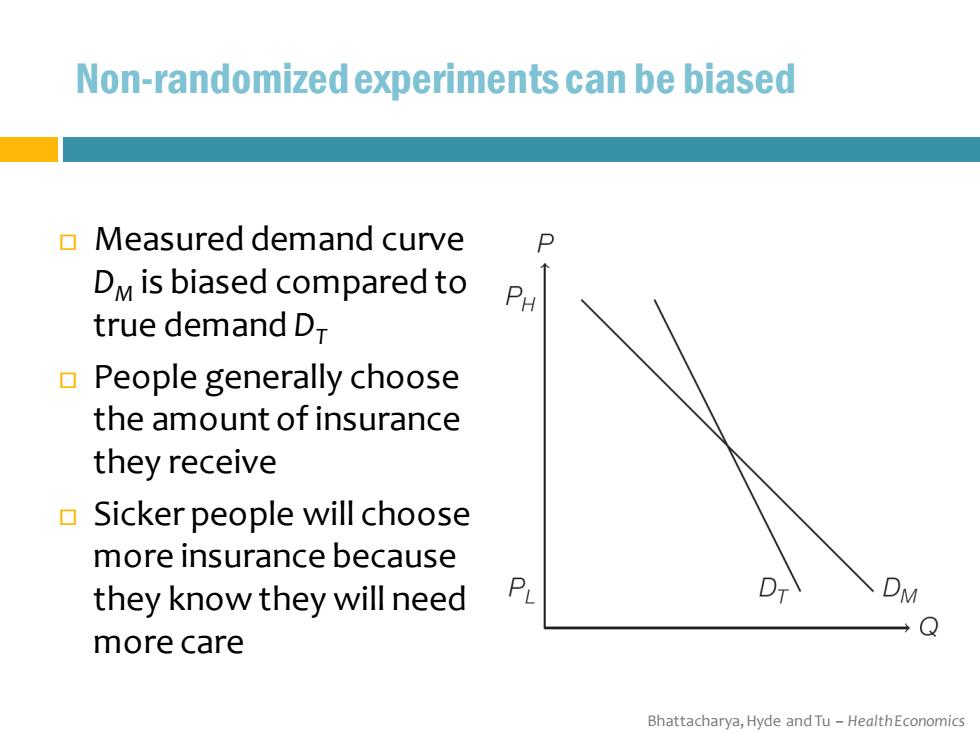
Non-randomized experiments can be biased Measured demand curve P DM is biased compared to PH true demand D People generally choose the amount of insurance they receive Sicker people will choose more insurance because they know they will need PL DM Q more care Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Non-randomized experiments can be biased Measured demand curve DM is biased compared to true demand DT People generally choose the amount of insurance they receive Sicker people will choose more insurance because they know they will need more care

Evidence from Randomized Experiments
Evidence from Randomized Experiments

Two Randomized Experiments RAND Health Insurance Experiment (HIE) Oregon Medicaid Experiment Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Two Randomized Experiments RAND Health Insurance Experiment (HIE) Oregon Medicaid Experiment
RAND HIE Randomly assigned 2,o00 families from six US cities to different insurance coverage plans Copayments groups: ■Free,25%,50%,and95% Tracked utilization of health care (Q)in each copayment plan(P) Copayment acts as the marginal cost that each family faces when buying care Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics RAND HIE Randomly assigned 2,000 families from six US cities to different insurance coverage plans Copayments groups: ◼Free, 25%, 50%, and 95% Tracked utilization of health care (Q) in each copayment plan (P) Copayment acts as the marginal cost that each family faces when buying care
Oregon Medicaid Experiment Compared two groups of low-income adults Medicaid lottery winners vs.lottery losers Lottery winners got to apply for public health insurance through Medicaid So they faced lower out-of-pocket prices for care Lottery losers could not get Medicaid (but might have purchased outside insurance) Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Oregon Medicaid Experiment Compared two groups of low-income adults Medicaid lottery winners vs. lottery losers Lottery winners got to apply for public health insurance through Medicaid So they faced lower out-of-pocket prices for care Lottery losers could not get Medicaid (but might have purchased outside insurance)