
Chapter 15 Investment,Time, and Capital Markets Chapter Outline >Stocks versus Flows >Present Discounted Value >The value of a Bond >The Net Present Value Criterion for Capital Investment Decisions >Adjustments for Risk >Investment Decisions by Consumers >Intertemporal Production Decisions- Depletable Resources >How Are Interest Rates Determined?
Chapter 15 Investment, Time, and Capital Markets Chapter Outline ➢ Stocks versus Flows ➢ Present Discounted Value ➢ The value of a Bond ➢ The Net Present Value Criterion for Capital Investment Decisions ➢ Adjustments for Risk ➢ Investment Decisions by Consumers ➢ Intertemporal Production Decisions— Depletable Resources ➢ How Are Interest Rates Determined?
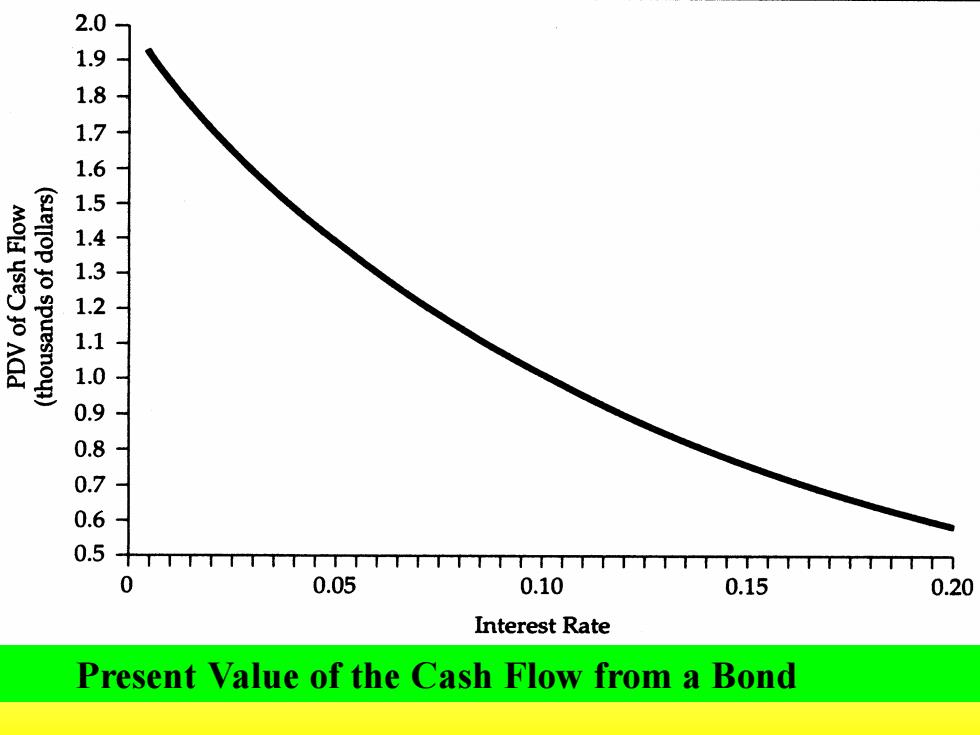
2 1.9 12 MOId ySe Jo ACd 54321096 0.6 0.5 0 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 Interest Rate Present Value of the Cash Flow from a Bond
Present Value of the Cash Flow from a Bond

Because most of the bond's payments occur in the future,the present Discounted value declines as the interest rare increases. For example,when the interest rate is 5 percent,the PDV of a 10-year bond paying $100 per year on a principal of $1000 is $1386
Because most of the bond's payments occur in the future, the present Discounted va1ue declines as the interest rare increases. For example, when the interest rate is 5 percent, the PDV of a 10-year bond paying $100 per year on a principal of $1000 is $l386
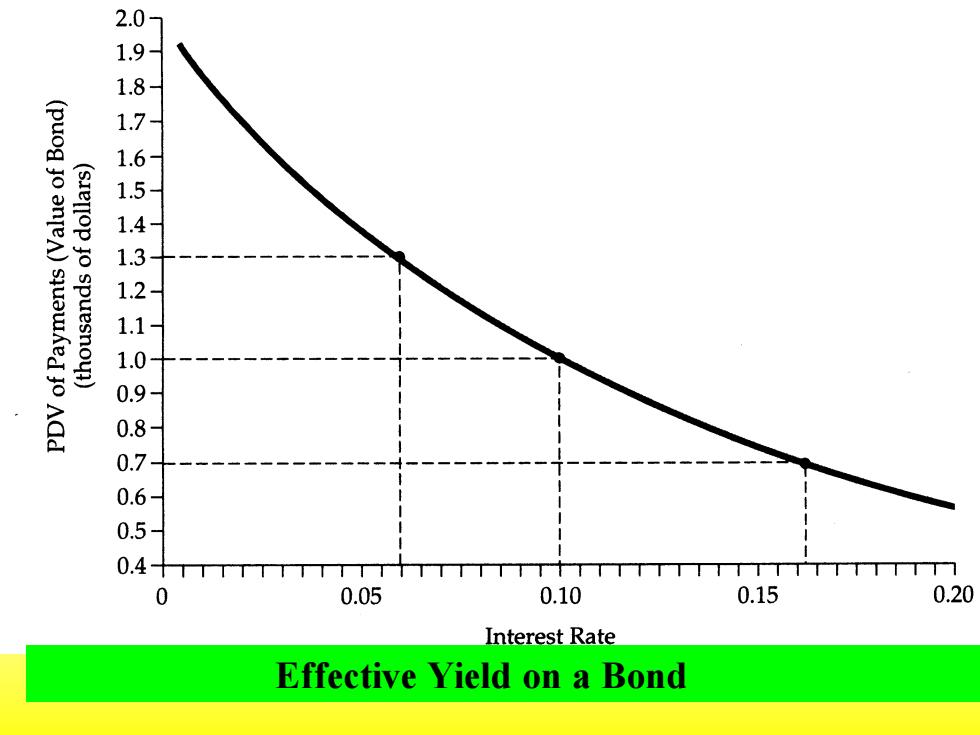
2.0 1.9 1.8 1.7 (puog jo anten)squawAed Jo ACd (sIellop jo spuesnoyl) 06 0 0.4十n t 0 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 Interest Rate Effective Yield on a Bond
Effective Yield on a Bond

The effective yield is the interest rate that equates the present value of the bond's payment stream with the bond's market price. The figure shows the present value of the payment stream as a function of the interest rate.The effective yield can thus be found by drawing a horizontal line at the level of the bond's price
The effective yield is the interest rate that equates the present value of the bond's payment stream with the bond's market price. The figure shows the present value of the payment stream as a function of the interest rate. The effective yield can thus be found by drawing a horizontal line at the level of the bond's price

For example,if the price of this bond were $1000,its effective yield would be about 10 percent.If the price were $1300,the effective yield would be about 6 percent;if the price were $700, it would be 16.2 percent
For example, if the price of this bond were $1000, its effective yield would be about 10 percent. If the price were $1300, the effective yield would be about 6 percent; if the price were $700, it would be 16.2 percent
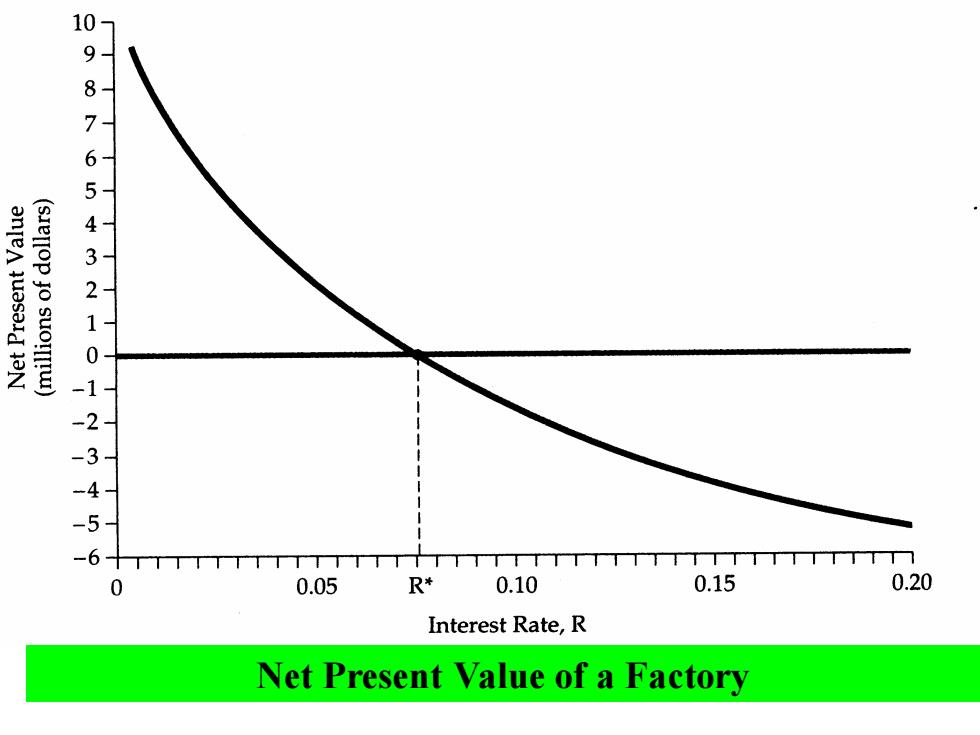
(sIellop jo suo!ll!u) 198765492101234 -5 6十TTTT 0 0.05 R* 0.10 0.15 0.20 Interest Rate,R Net Present Value of a Factory
Net Present Value of a Factory

The NPV of a factory is the present discounted value of all the cash flows involved in building and operating it. Here it is the PDV of the flow of future profits less the current cost of construction.The NPV declines as the interest rate increases.At interest rate R*,the NPV is zero
The NPV of a factory is the present discounted value of all the cash flows involved in building and operating it. Here it is the PDV of the flow of future profits less the current cost of construction. The NPV declines as the interest rate increases. At interest rate R*, the NPV is zero

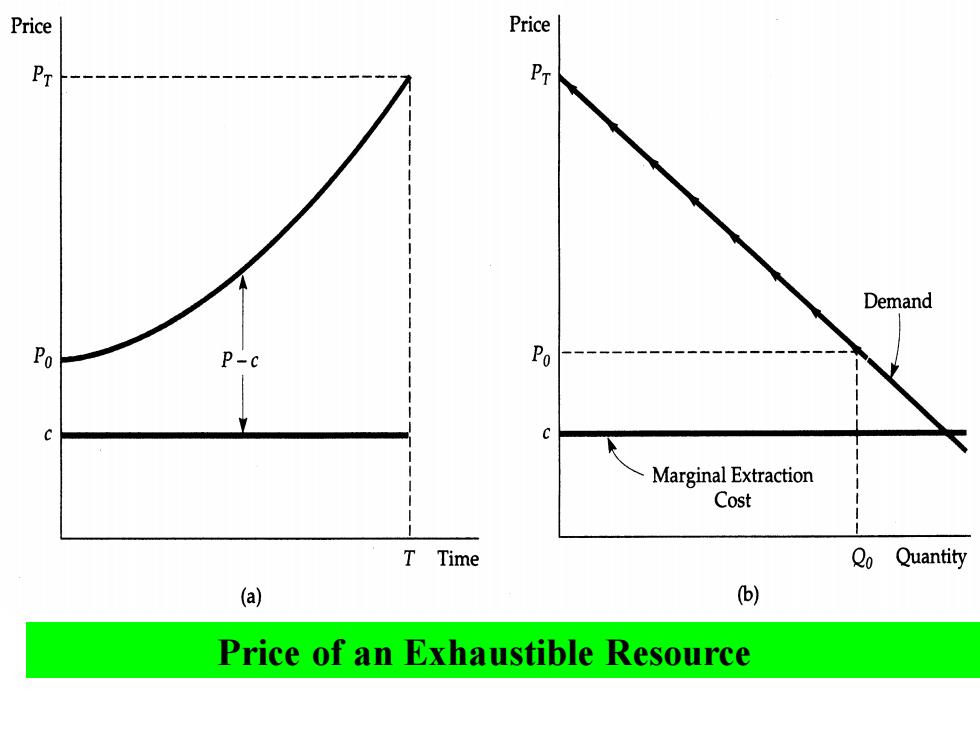
Price Price PT PT Demand Po Po Marginal Extraction Cost T Time Qo Quantity (a) (b) Price of an Exhaustible Resource
Price of an Exhaustible Resource