
Chapter 6 Production Chapter Outline >The Technology of Production >[soquants(等产量线) >Production with one Variable Input >Production with Two Variable Inputs >Returns to Scale(规模报酬)
Chapter 6 Production Chapter Outline ➢ The Technology of Production ➢ Isoquants (等产量线) ➢ Production with one Variable Input ➢ Production with Two Variable Inputs ➢ Returns to Scale (规模报酬)

6.1 The Technology of Production Theory of the firm-Explanation of how a firm makes cost-minimizing production decisions and how its cost varies with its output. Factors of production-Inputs into the production process (e.g.,labor,capital,and materials). A production function describes the maximum output a firm can produce for each specified combination of inputs. Q=FK,L)
6.1 The Technology of Production ❑ Theory of the firm-Explanation of how a firm makes cost-minimizing production decisions and how its cost varies with its output. ❑ Factors of production-Inputs into the production process (e.g., labor, capital, and materials). ❑ A production function describes the maximum output a firm can produce for each specified combination of inputs. Q = F(K, L)

6.2Is0 quant(等产量线) An isoquant is a curve that shows all combinations of inputs that yield a given level of output. ▣Isoquant map-Graph(曲线图)combining several isoquants, used to describe a production function. A firm's production function can be represented by a series of isoquants associated with different levels of output
❑ An isoquant is a curve that shows all combinations of inputs that yield a given level of output. ❑ Isoquant map—Graph(曲线图)combining several isoquants, used to describe a production function. A firm’s production function can be represented (描述)by a series of isoquants associated with different levels of output. 6.2 Isoquant (等产量线)
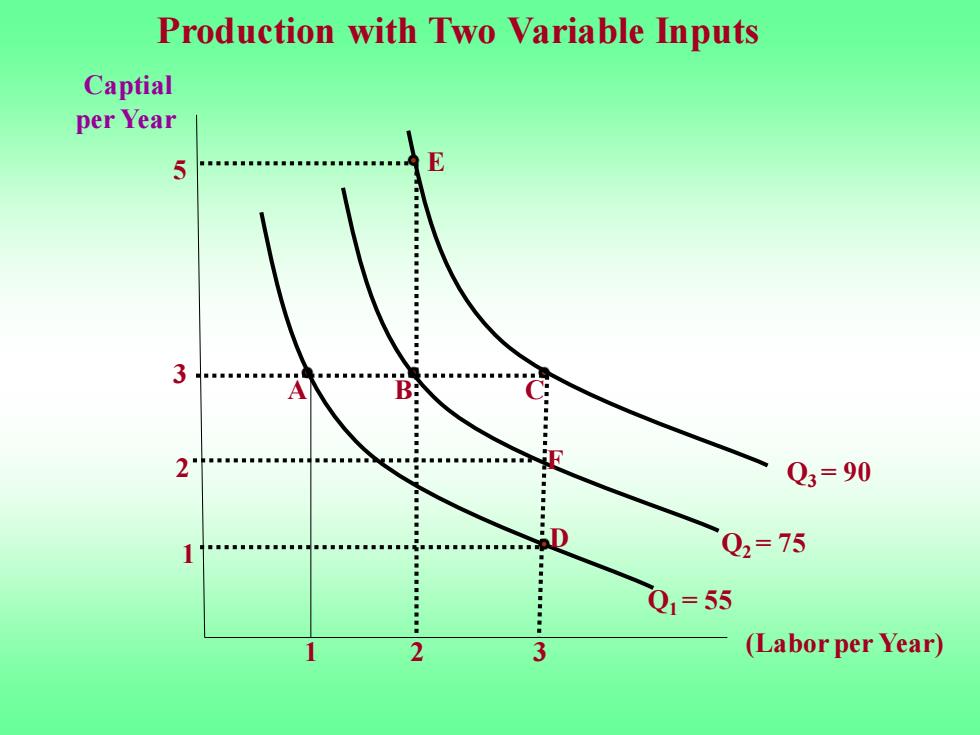
Production with Two Variable Inputs Captial per Year 5 3 DCC0 ■■■■■■■■■■ A B: 2。 Q3=90 ■■■■■■■■ Q2=75 Q1=55 3 (Labor per Year)
Production with Two Variable Inputs A B C Q1 = 55 Q2 = 75 Q3 = 90 (Labor per Year) Captial per Year 1 2 3 1 3 5 D E 2 F

Production isoquants show the various combinations of inputs necessary for the firm to produce a given output. A set of isoquants,or isoquant map,describes the firm's production function. Output increases as we move from isoquant Q(at which 55 units per year are produced at points such as A and D),to isoquant Q2 (75 units per year at points such as B and F)and to isoquant Q3 (90 units per year at points such as C and E)
Production isoquants show the various combinations of inputs necessary for the firm to produce a given output. A set of isoquants, or isoquant map, describes the firm’s production function. Output increases as we move from isoquant Q1 (at which 55 units per year are produced at points such as A and D), to isoquant Q2 (75 units per year at pointssuch as B and F) and to isoquant Q3 (90 units per year at pointssuch as C and E)

Short run-Period of time in which quantities of one or more production factors cannot be changed. Fixed input-Production factor that cannot be varied. Long run-Amount of time needed to make all production inputs variable
• Short run-Period of time in which quantities of one or more production factors cannot be changed. • Fixed input-Production factor that cannot be varied. • Long run-Amount of time needed to make all production inputs variable

6.3 Production with One Variable Input(labor) In the short run,one or more inputs to the production process are fixed.In the long run,all inputs are potentially variable. □Average product(平均产出)-Output per unit of a particular input. Average product of labor=output/labor input=Q/L ▣Marginal product边际产出)-Additional output produced as an input is increased by one unit. Marginal product of labor=change in output/change in labor input=AQ/AL
❑ In the short run, one or more inputs to the production process are fixed.In the long run, all inputs are potentially variable. ❑ Average product(平均产出)-Output per unit of a particular input. Average product of labor = output/labor input = Q/L ❑ Marginal product(边际产出)-Additional output produced as an input is increased by one unit. Marginal product of labor = change in output/change in labor input = △Q/△L 6.3 Production with One Variable Input(labor)
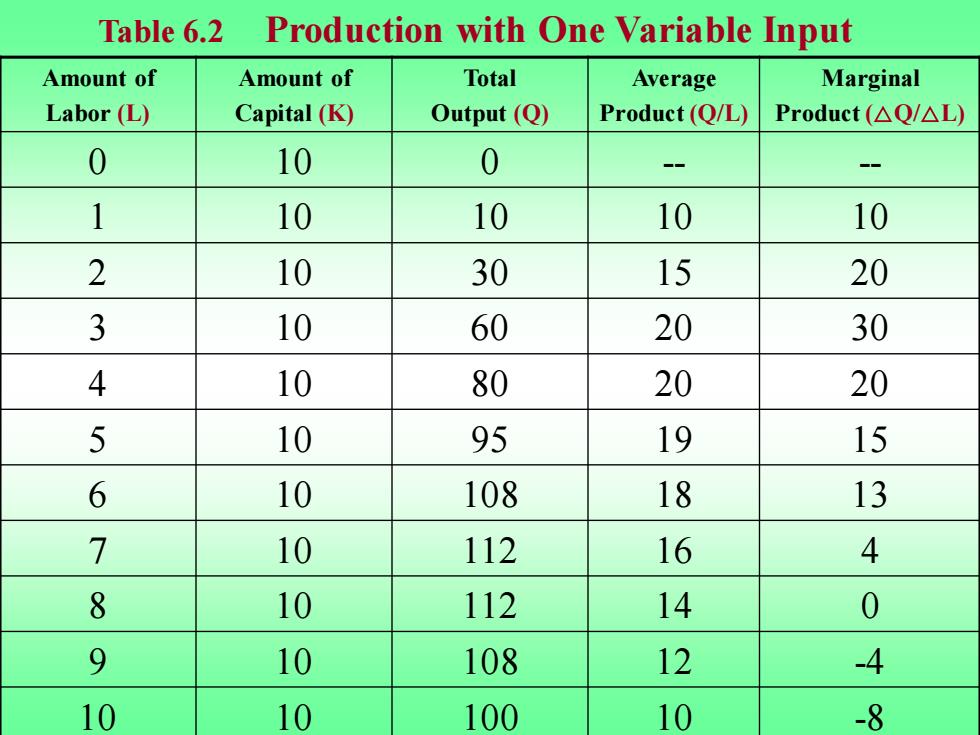
Table 6.2 Production with One Variable Input Amount of Amount of Total Average Marginal Labor (L) Capital(K) Output (Q) Product(Q/L) Product(△Q/△L 0 10 0 1 10 10 10 10 2 10 30 15 20 3 10 60 20 30 4 10 80 20 20 5 10 95 19 15 6 10 108 18 13 7 10 112 16 4 8 10 112 14 0 9 10 108 12 -4 10 10 100 10 -8
Amount of Labor (L) Amount of Capital (K) Total Output (Q) Average Product (Q/L) Marginal Product (△Q/△L) 0 10 0 - - 1 10 10 10 10 2 10 30 15 20 3 10 60 20 30 4 10 80 20 20 5 10 95 19 15 6 10 108 18 13 7 10 112 16 4 8 10 112 14 0 9 10 108 12 -4 10 10 100 10 -8 Table 6.2 Production with One Variable Input
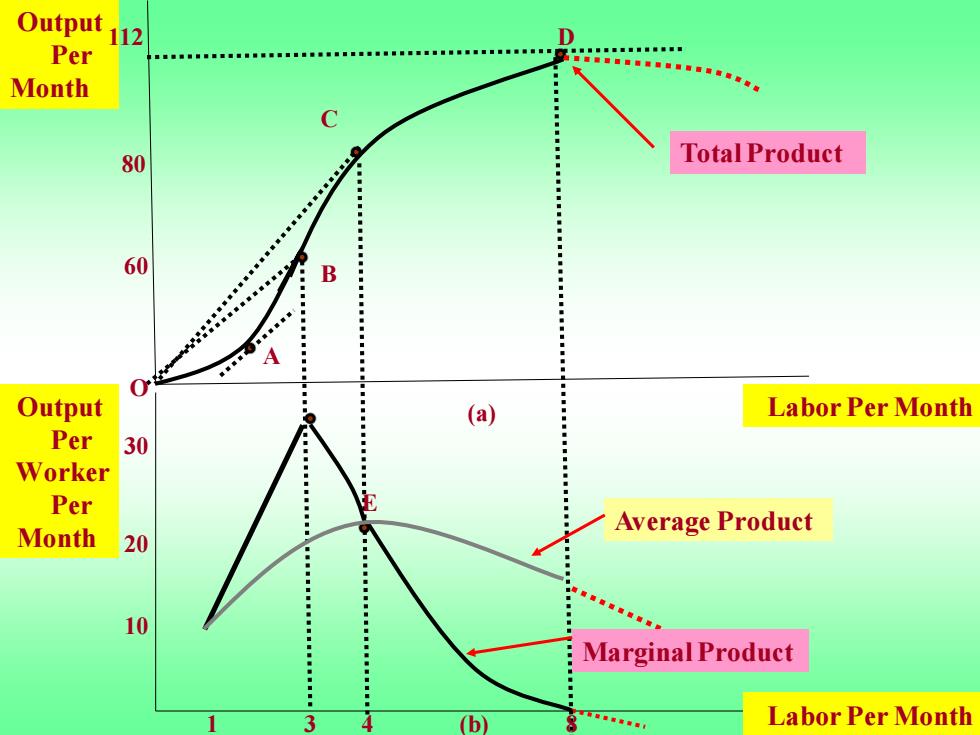
Output 112 D Per ■■■■■■■■ Month 80 Total Product 60 B A Output (a) Labor Per Month Per 30 Worker Per Month Average Product 20 10 Marginal Product b Labor Per Month
Output Per Month Labor Per Month Labor Per Month Marginal Product Average Product Total Product 1 3 4 8 10 20 30 60 112 E A B C D (a) (b) Output Per Worker Per Month 80 O

The total product curve in (a)shows the output produced for different amounts of labor input.The average and marginal products in (b)can be obtained(using the data in Table 6.2)from the total product curve. At point A,the marginal product is 20 because the tangent() to the total product curve has a slope of 20.At point B in (a)the average product of labor is 20,which is the slope of the line from the origin(原点,origin of coordinates)toB
The total product curve in (a) shows the output produced for different amounts of labor input. The average and marginal products in (b) can be obtained(using the data in Table 6.2)from the total product curve. At point A, the marginal product is 20 because the tangent(切线) to the total product curve has a slope of 20. At point B in (a) the average product of labor is 20, which is the slope of the line from the origin (原点, origin of coordinates) to B