
Chapter 7 The Cost of Production Chapter Outline >Measuring Cost:Which Cost Matters? Cost in the Short Run >Long-Run Versus Short-Run Cost Curves >Production with Two Outputs-Economies of Scope Copyright by Caidonghong
Copyright by Caidonghong Chapter 7 The Cost of Production Chapter Outline ➢ Measuring Cost: Which Cost Matters? ➢ Cost in the Short Run ➢ Long-Run Versus Short-Run Cost Curves ➢ Production with Two Outputs—Economies of Scope

7.1 Measuring Cost:Which Cost Matters? >Accounting cost-Actual expenses plus depreciation charges 折旧费)for capital equipment. >Economic cost-Cost to a firm of utilizing economic resources in production,including opportunity cost. >Opportunity cost-Cost()associated with opportunities that are forgone()when a firm's resources are not put to their highest-value use. Copyright by Caidonghong
Copyright by Caidonghong 7.1 Measuring Cost: Which Cost Matters? ➢ Accounting cost-Actual expenses plus depreciation charges (折旧费) for capita1 equipment. ➢ Economic cost-Cost to a firm of utilizing economic resources in production, including opportunity cost. ➢ Opportunity cost—Cost(代价) associated with opportunities that are forgone(放弃) when a firm’s resources are not put to their highest-value use

▣A sunk cost(沉设成本)is an expenditure that has been made and cannot be recovered(挽▣). After it has been incurred(蒙受),it should be ignored when making future economic decisions. Copyright by Caidonghong
Copyright by Caidonghong ❑ A sunk cost (沉没成本) is an expenditure that has been made and cannot be recovered (挽回). After it has been incurred (蒙受), it should be ignored when making future economic decisions

Total cost (TC)-Total economic cost of production,consisting of fixed and variable costs,which can be divided into fixed cost and variable cost. In the short run,one or more of the firm's inputs are fixed. Fixed cost(FC)-Cost that does not vary with the level of output. Variable cost (VC)-Cost that varies as output varies. Copyright by Caidonghong
Copyright by Caidonghong ❑ Total cost (TC) - Total economic cost of production, consisting of fixed and variable costs, which can be divided into fixed cost and variable cost. In the short run, one or more of the firm'sinputs are fixed. ❑ Fixed cost(FC)-Cost that does not vary with the level of output. ❑ Variable cost (VC)-Cost that varies as output varies
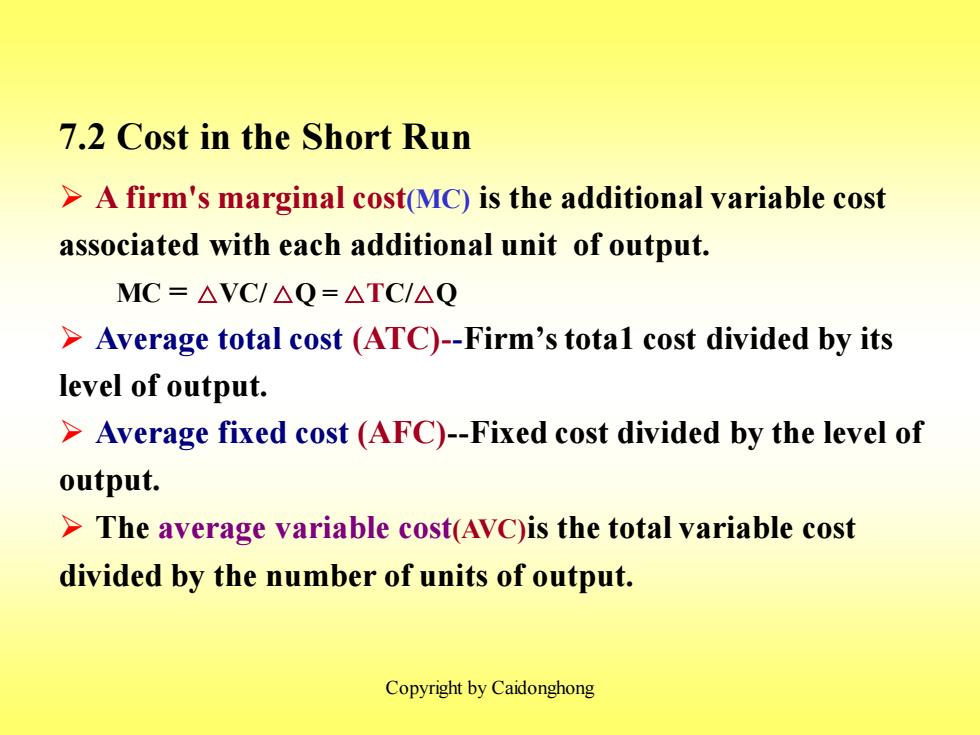
7.2 Cost in the Short Run >A firm's marginal cost(MC)is the additional variable cost associated with each additional unit of output. MC=△VC/△Q=△TC/△Q >Average total cost (ATC)-Firm's total cost divided by its level of output. >Average fixed cost (AFC)-Fixed cost divided by the level of output. >The average variable cost(AVC)is the total variable cost divided by the number of units of output. Copyright by Caidonghong
Copyright by Caidonghong 7.2 Cost in the Short Run ➢ A firm's marginal cost(MC) is the additional variable cost associated with each additional unit of output. MC = △VC/ △Q = △TC/△Q ➢ Average total cost (ATC)-Firm’stota1 cost divided by its level of output. ➢ Average fixed cost (AFC)-Fixed cost divided by the level of output. ➢ The average variable cost(AVC)is the total variable cost divided by the number of units of output
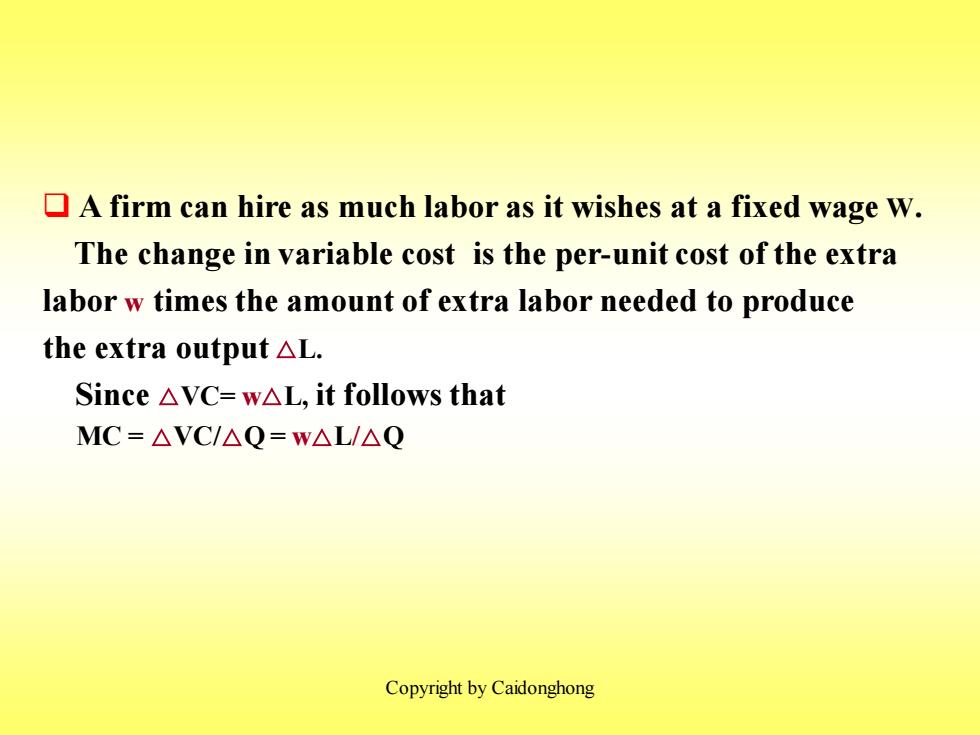
A firm can hire as much labor as it wishes at a fixed wage W. The change in variable cost is the per-unit cost of the extra labor w times the amount of extra labor needed to produce the extra output△L. Since△VC=w△L,it follows that MC=△VC/△Q=w△L/△Q Copyright by Caidonghong
Copyright by Caidonghong ❑ A firm can hire as much labor as it wishes at a fixed wage W. The change in variable cost is the per-unit cost of the extra labor w times the amount of extra labor needed to produce the extra output △L. Since △VC= w△L, it follows that MC = △VC/△Q = w△L/△Q

The marginal product of labor MPL is the change in output resulting from a 1-unit change in labor input,or AQ/AL. As a result, MC=△VC/△Q=w△L/△Q=wMPL Copyright by Caidonghong
Copyright by Caidonghong The marginal product of labor MPL is the change in output resulting from a 1-unit change in labor input, or △Q/△L. As a result, MC = △VC/△Q = w△L/△Q = w/MPL
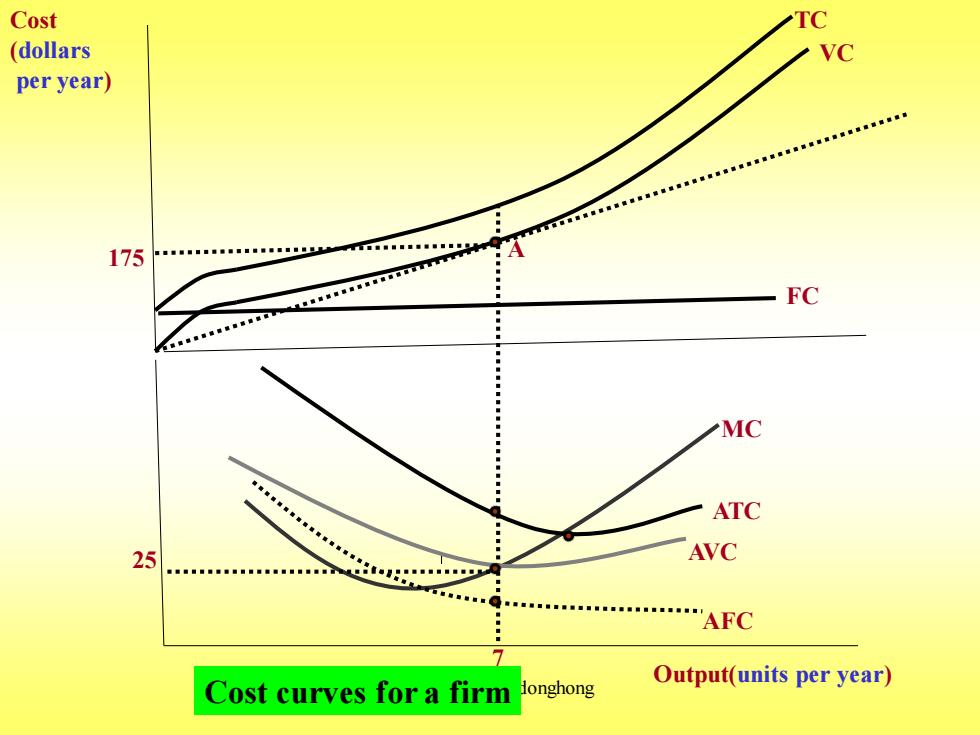
Cost (dollars per year) 175 FC MC ATC 25 AVC .AFC Output(units per year) Cost curves for a firm donghong
Copyright by Caidonghong 7 25 AFC AVC ATC MC VC TC 175 Output(units per year) Cost (dollars per year) Cost curves for a firm FC A

In (a)total cost TC is the vertical sum of fixed cost FC and variable cost VC. In (b)average total cost ATC is the sum of average variable cost AVC and average fixed cost AFC. Marginal cost MC crosses the average variable cost and average total cost curves at their minimum points. Note:Recall that AC=TC/Q.It follows that, △AC/△Q=IQ(△TC/△Q)-TC]/Q2=(MC-AC)/Q Clearly,when AC is increasing and MC >AC,AAC/AQ is positive. Correspondingly,when AC is decreasing and MC<AC,AAC/AQ is negative. Copyright by Caidonghong
Copyright by Caidonghong In (a) total cost TC is the vertical sum of fixed cost FC and variable cost VC. In (b) average total cost ATC is the sum of average variable cost AVC and average fixed cost AFC. Marginal cost MC crosses the average variab1e cost and average total cost curves at their minimum points. Note: Recall that AC = TC/Q. It follows that, △AC/△Q = [Q(△TC/△Q) – TC]/Q2 = (MC-AC)/Q Clearly, when AC is increasing and MC >AC, △AC/△Q is positive. Correspondingly, when AC is decreasing and MC<AC, △AC/△Q is negative

7.3 Cost in the Long Run >User cost(使用成本)of capital-Sum of the annual cost of owning and using a capital asset,equal to economic depreciation plus forgone interest. >Rental rate-Cost per year of rent ing one unit of capital. Isocost line -Graph showing all possible combinations of labor and capital that can be purchased for a given total cost. Copyright by Caidonghong
Copyright by Caidonghong 7.3 Cost in the Long Run ➢ User cost(使用成本)of capital-Sum of the annual cost of owning and using a capital asset, equal to economic depreciation plus forgone interest. ➢ Rental rate - Cost per year of rent ing one unit of capital. ➢ Isocost line - Graph showing all possible combinations of labor and capital that can be purchased for a given total cost