
Chapter 18 Externalities and Public Goods Chapter Outline ▣Externalities Ways of Correcting Market Failure Externalities and Property Rights Common Property Resources ▣Public Goods Private Preferences for Public Goods
Chapter 18 Externalities and Public Goods Chapter Outline ❑ Externalities ❑ Ways of Correcting Market Failure ❑ Externalities and Property Rights ❑ Common Property Resources ❑ Public Goods ❑ Private Preferences for Public Goods

18.1 Externality Externality-Action taken by either a producer or a consumer which affects other producers or consumers but is not accounted for by the market price. Externalities can arise between producers,between customers, or between consumers and producers. They can be negative-when the action of one party imposes costs -or positive-when the action of one party benefits another party
18.1 Externality Externality-Action taken by either a producer or a consumer which affects other producers or consumers but is not accounted for by the market price. Externalities can arise between producers, between customers, or between consumers and producers. They can be negative- when the action of one party imposes costs —or positive– when the action of one party benefits another party

A negative externality occurs,for example,when a steel plant dumps its waste in a river that fishermen downstream depend on for their daily catch.The more waste the steel plant dumps in the river,the fewer fish will be supported
A negative externality occurs, for example, when a steel plant dumps its waste in a river that fishermen downstream depend on for their daily catch. The more waste the steel plant dumps in the river, the fewer fish will be supported

The firm,however,has no incentive to account for() the external costs that it imposes on fishermen when making its production decision. Furthermore,there is no market in which these external costs can be transmitted into the price of steel
The firm, however, has no incentive to account for(考虑) the external costs that it imposes on fishermen when making its production decision. Furthermore, there is no market in which these external costs can be transmitted into the price of steel

A positive externality occurs when a home owner repaints her house and plants (an attractive garden. ▣All the neighbors benefit from(受益于)this activity,yet the home owner's decision to repaint and landscape(从事自然美化工作) probably did not take these benefits into account,because his neighbors would not pay for the benefit ()
A positive externality occurs when a home owner repaints her house and plants (建立) an attractive garden. All the neighbors benefit from (受益于) this activity, yet the home owner’s decision to repaint and landscape(从事自然美化工作) probably did not take these benefits into account, because his neighbors would not pay for the benefit (好处)

Marginal external cost Increase in cost imposed externally as one or more firms increase output by one unit. ▣Marginal social cost Sum of the marginal cost of production and the marginal external cost
Marginal external cost Increase in cost imposed externally as one or more firms increase output by one unit. Marginal social cost Sum of the marginal cost of production and the marginal external cost
Price MSC Price MC MSCI S=MCI MECI MEC q*91 Firm Output 2*Qi Industry Output External Cost
Industry Output External Cost

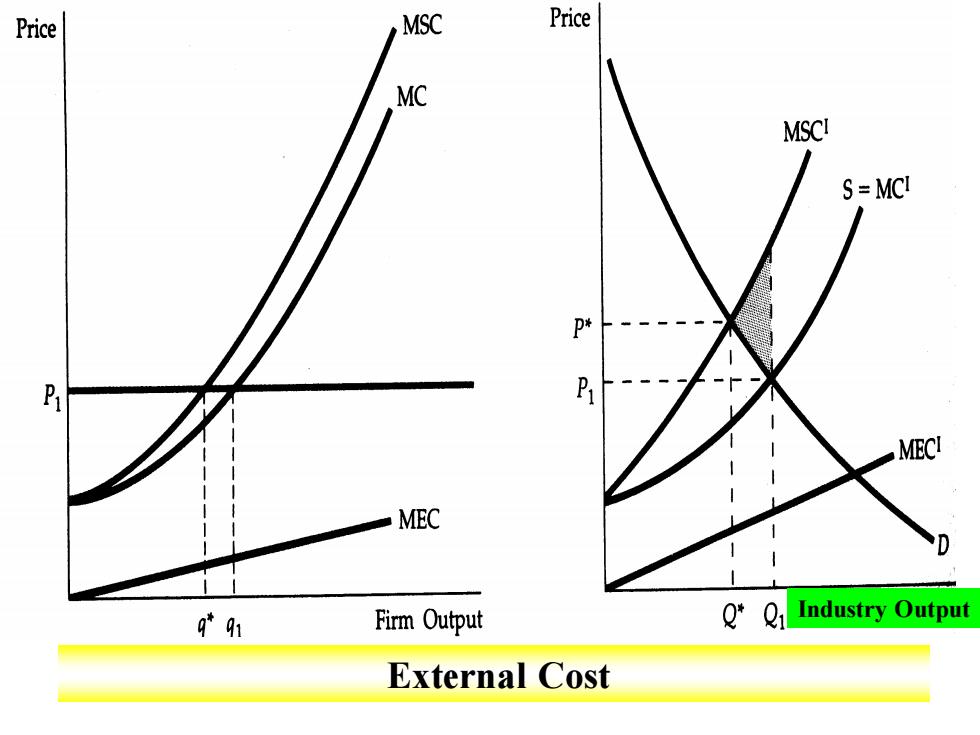
When there are negative externalities,the marginal social cost MSC is higher than the marginal cost MC.The difference is the marginal external cost MEC. In (a),a profit-maximizing firm produces at qu,where price is equal to MC.Because externalities are not reflected in market prices,they can be a source of economic inefficiency. The efficient output is q*,at which price equals MSC
When there are negative externalities, the marginal social cost MSC is higher than the marginal cost MC. The difference is the marginal external cost MEC. In (a), a profit-maximizing firm produces at q1 , where price is equal to MC. Because externalities are not reflected in market prices, they can be a source of economic inefficiency. The efficient output is q*, at which price equals MSC
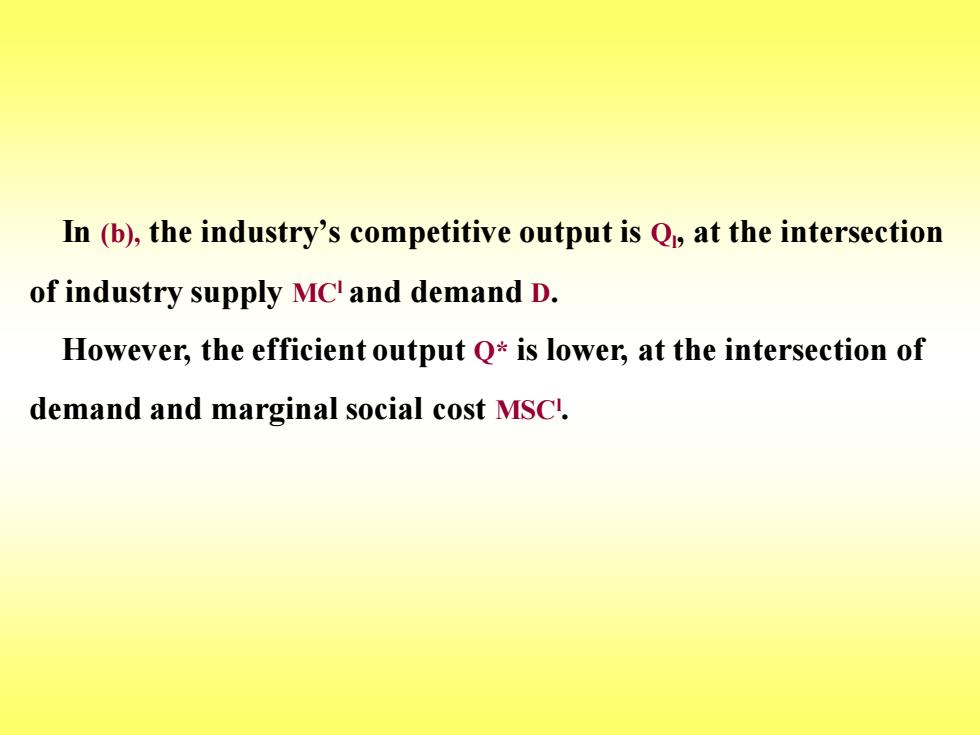
In(b),the industry's competitive output is Qp,at the intersection of industry supply MC and demand D. However,the efficient output Q*is lower,at the intersection of demand and marginal social cost MSC
In (b), the industry’s competitive output is Ql , at the intersection of industry supply MCl and demand D. However, the efficient output Q* is lower, at the intersection of demand and marginal social cost MSCl

Marginal external benefit-Increased benefit that accrues (自然增长)to other parties as a firm increases output by one unit. Marginal social benefit-Sum of the marginal private benefit plus the marginal external benefit
Marginal external benefit-Increased benefit that accrues (自然增长)to other parties as a firm increases output by one unit. Marginal social benefit -Sum of the marginal private benefit plus the marginal external benefit