
Chapter 9 The Analysis of Competitive Markets Chapter Outline Evaluating the Gains and Losses from Government Policies -Consumer and Producer Surplus The Efficiency of a Competitive Market ·Minimum Prices Price Supports and Production Quotas Import Quotas and Tariffs The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy
Chapter 9 The Analysis of Competitive Markets Chapter Outline • Evaluating the Gains and Losses from Government Policies —Consumer and Producer Surplus • The Efficiency of a Competitive Market • Minimum Prices • Price Supports and Production Quotas • Import Quotas and Tariffs • The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy
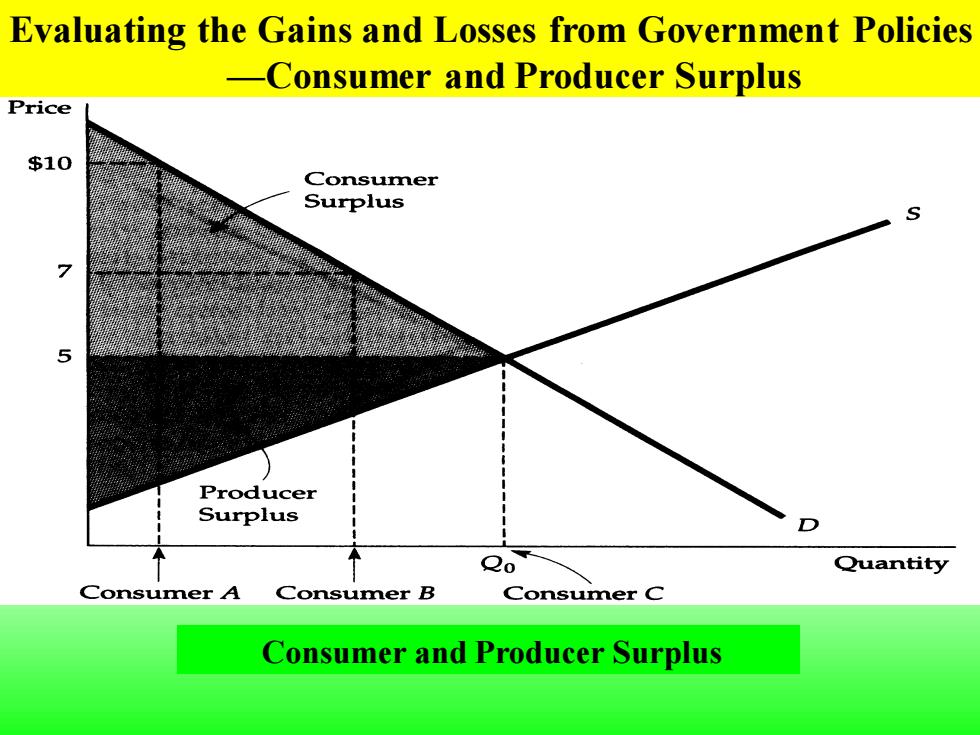
Evaluating the Gains and Losses from Government Policies -Consumer and Producer Surplus Price $10 Consumer Surplus 5 Producer Surplus o Quantity Consumer A Consumer B Consumer C Consumer and Producer Surplus
Evaluating the Gains and Losses from Government Policies —Consumer and Producer Surplus Consumer and Producer Surplus

Consumer A would pay $10 for a good whose market price is $5 and therefore enjoys a benefit of $5.Consumer B enjoys a benefit of $2,and Consumer C,who values the good at exactly the market price,enjoys no benefit.Consumer surplus,which measures the total benefit to all consumers,is the shaded area between the demand curve and the market price
Consumer A would pay $10 for a good whose market price is $5 and therefore enjoys a benefit of $5. Consumer B enjoys a benefit of $2, and Consumer C, who values the good at exactly the market price, enjoys no benefit. Consumer surplus, which measures the total benefit to all consumers, is the shaded area between the demand curve and the market price

Producer surplus is the shaded area between the supply curve and the market price.Together consumer and producer surplus measure the welfare benefit of a competitive market. >Welfare effects-Gains and losses caused by government intervention in the market
Producer surplus is the shaded area between the supply curve and the market price. Together consumer and producer surplus measure the welfare benefit of a competitive market. ➢ Welfare effects-Gains and losses caused by government intervention in the market
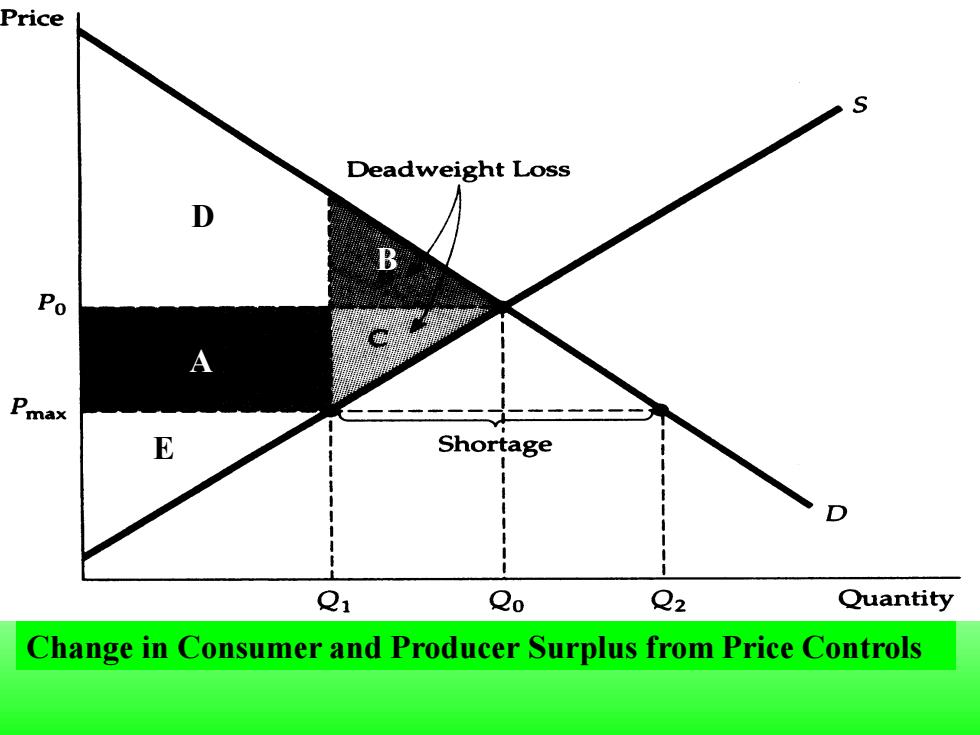
Price S Deadweight Loss D Po Pma以 E Shortage Q1 Qo Q2 Quantity Change in Consumer and Producer Surplus from Price Controls
Change in Consumer and Producer Surplus from Price Controls B A D E

●Deadweight loss(无谓损失)-Net loss of total(consumer plus producer)surplus. The price of a good has been regulated to be no higher than Pmax,Which is below the market-clearing price Po. The gain to consumers is the difference between rectangle A and triangle B(A-B). The loss to producers is the sum of rectangle A and triangle C (A+C).Triangles B and C together measure the deadweight loss from price controls(B+C)
⚫ Deadweight loss (无谓损失) - Net loss of total (consumer plus producer)surplus. ◆The price of a good has been regulated to be no higher than Pmax, which is below the market-clearing price P0 . The gain to consumers is the difference between rectangle A and triangle B (A-B). The loss to producers is the sum of rectangle A and triangle C (A+C). Triangles B and C together measure the deadweight loss from price controls (B+C)
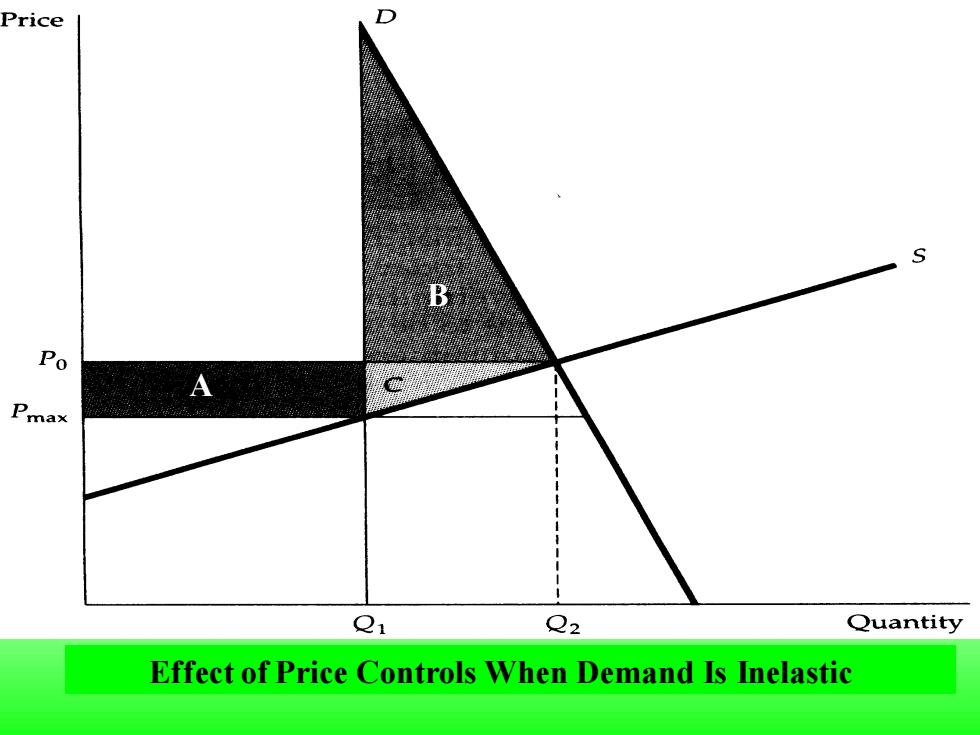
Price D S Po Pmax Q1 Q2 Quantity Effect of Price Controls When Demand Is Inelastic
Effect of Price Controls When Demand Is Inelastic B A

If demand is sufficiently inelastic,triangle B can be larger than rectangle A.In this case,consumers suffer a net loss from price controls
If demand is sufficiently inelastic, triangle B can be larger than rectangle A. In this case, consumers suffer a net loss from price controls
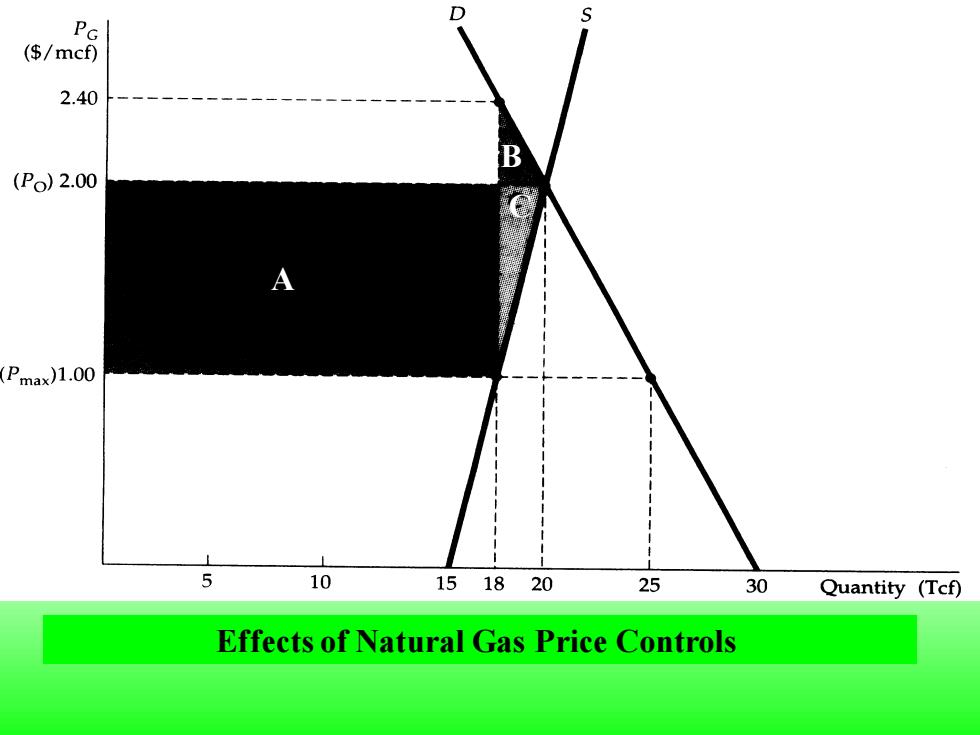
D PG ($/mcf) 2.40 B (Po)2.00 (Pmax)1.00 10 151820 25 30 Quantity (Tcf) Effects of Natural Gas Price Controls
Effects of Natural Gas Price Controls A A B C

The market-clearing price of natural gas is $2 per mef,and the maximum allowable price is $1.A shortage of 25-18=7 Tcf results.The gain to consumers is rectangle A minus triangle B, and the loss to producers is rectangle A plus triangle C
The market-clearing price of natural gas is $2 per mcf, and the maximum allowable price is $1. A shortage of 25-18 = 7 Tcf results. The gain to consumers is rectangle A minus triangle B, and the loss to producers is rectangle A plus triangle C