
CHAPTER FIVE The Open Economy macroeconomics N.Gregory Mankiw College of Management,HUST
macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw macro College of Management, HUST CHAPTER FIVE The Open Economy

Chapter objectives Accounting identities(会计恒等式)for the open economy ■ Small open economy model ·what makes it“small'” how the trade balance and exchange rate are determined how policies affect trade balance exchange rate CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 1
CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 1 Chapter objectives ▪ Accounting identities(会计恒等式) for the open economy ▪ Small open economy model ▪ what makes it “small” ▪ how the trade balance and exchange rate are determined ▪ how policies affect trade balance & exchange rate

Content 1. Trade balance and net capital outflow 2. Saving and investment in a small open economy 2.1 The model 2.2 How policy influence the trade balance 3. Exchange rate 3.1 nominal and real exchange rate 3.2 The determinants of real exchange rate 3.3 How policy influence the real exchange rate 3.4 The determinants of nominal exchange rate 3.5 The purchasing-power parity(购买力平价) 4. Chapter summary CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 2
CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 2 Content 1. Trade balance and net capital outflow 2. Saving and investment in a small open economy 2.1 The model 2.2 How policy influence the trade balance 3. Exchange rate 3.1 nominal and real exchange rate 3.2 The determinants of real exchange rate 3.3 How policy influence the real exchange rate 3.4 The determinants of nominal exchange rate 3.5 The purchasing-power parity (购买力平价) 4. Chapter summary
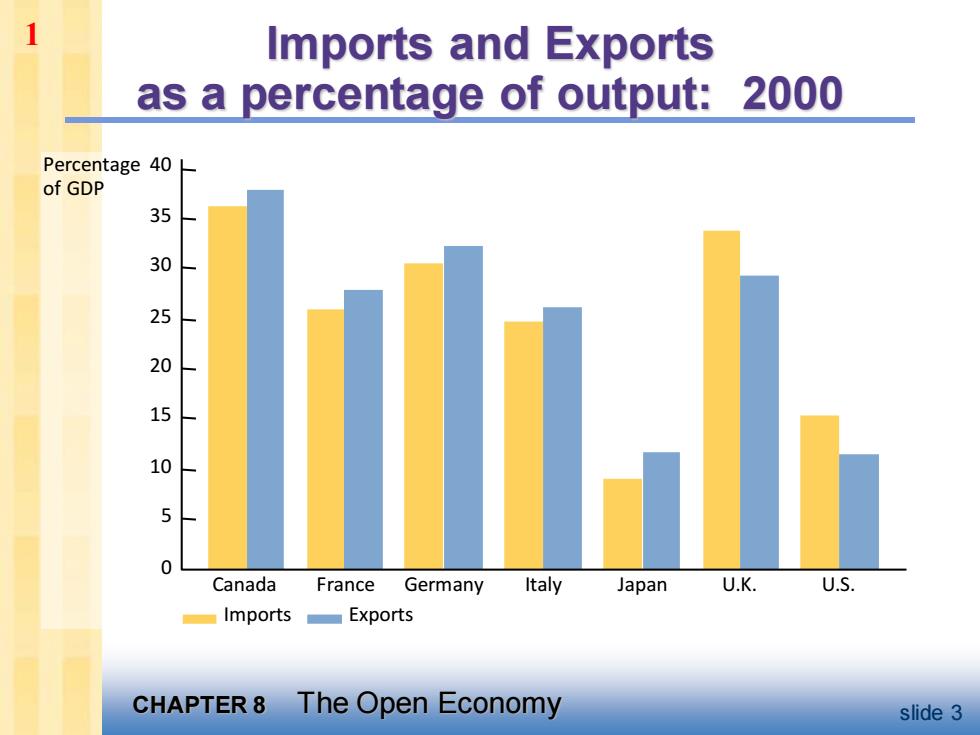
1 Imports and Exports as a percentage of output: 2000 Percentage 40 of GDP 35 30 25 20 10 5 0 Canada France Germany Italy Japan U.K. U.S. Imports Exports CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 3
CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 3 Percentage of GDP 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Canada France Germany Italy Japan U.K. U.S. Imports Exports Imports and Exports as a percentage of output: 2000 1

Net export and trade balance NX=net exports[(a.ka(仅)the“trade balance'” (贸易收支)]=EX-IM ■IfNX>0, country has a trade surplust(贸易顺差) equal to NX ■fNX<0, country has a trade deficit(贸易逆差) equal to-NX CHAPTER8 The Open Economy slide 5
CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 5 NX = net exports[ (a.k.a.(又名) the “trade balance” (贸易收支)]= EX – IM ▪ If NX > 0, country has a trade surplus(贸易顺差) equal to NX ▪ If NX < 0, country has a trade deficit (贸易逆差) equal to – NX Net export and trade balance 1
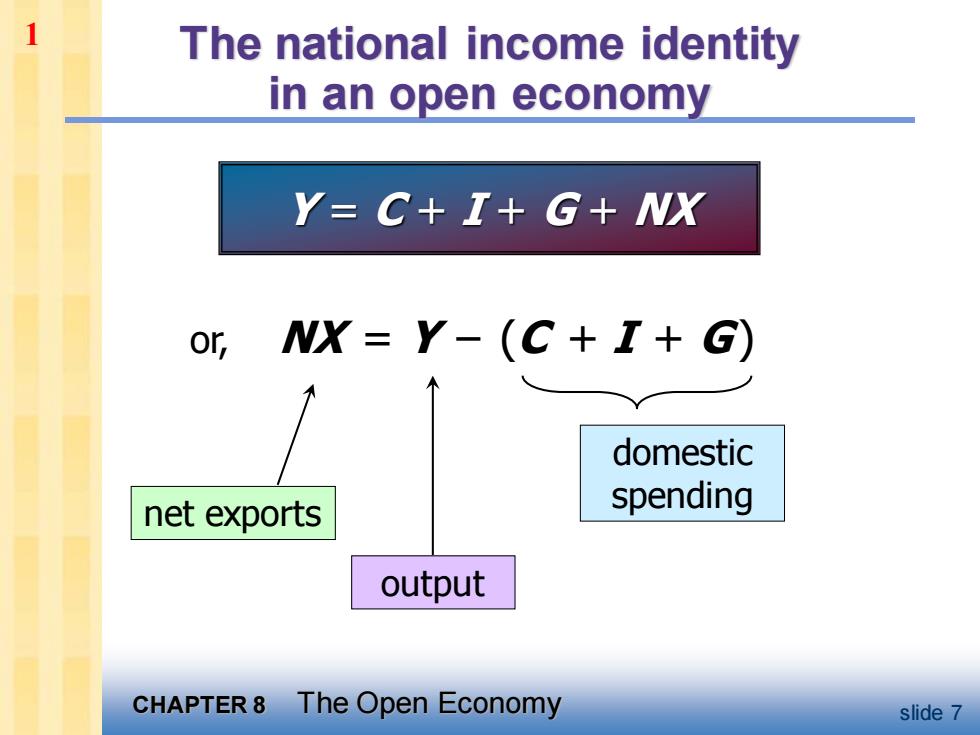
The national income identity in an open economy Y-C+I+G+NX or,NX=Y-(C+I+G) domestic net exports spending output CHAPTER8 The Open Economy slide 7
CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 7 The national income identity in an open economy Y = C + I + G + NX or, NX = Y – (C + I + G) net exports domestic spending output 1

1 International capital flows ■Net capital outflows S-I net outflow(资本净流出)of"loanable funds'”(可贷资金) net purchases of foreign assets the country's purchases of foreign assets minus foreign purchases of domestic assets When S >I,country is a net lender When S <I,country is a net borrower CHAPTER8 The Open Economy slide 8
CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 8 International capital flows ▪ Net capital outflows = S – I = net outflow(资本净流出)of “loanable funds”(可贷资金) = net purchases of foreign assets the country’s purchases of foreign assets minus foreign purchases of domestic assets ▪ When S > I, country is a net lender ▪ When S < I, country is a net borrower 1
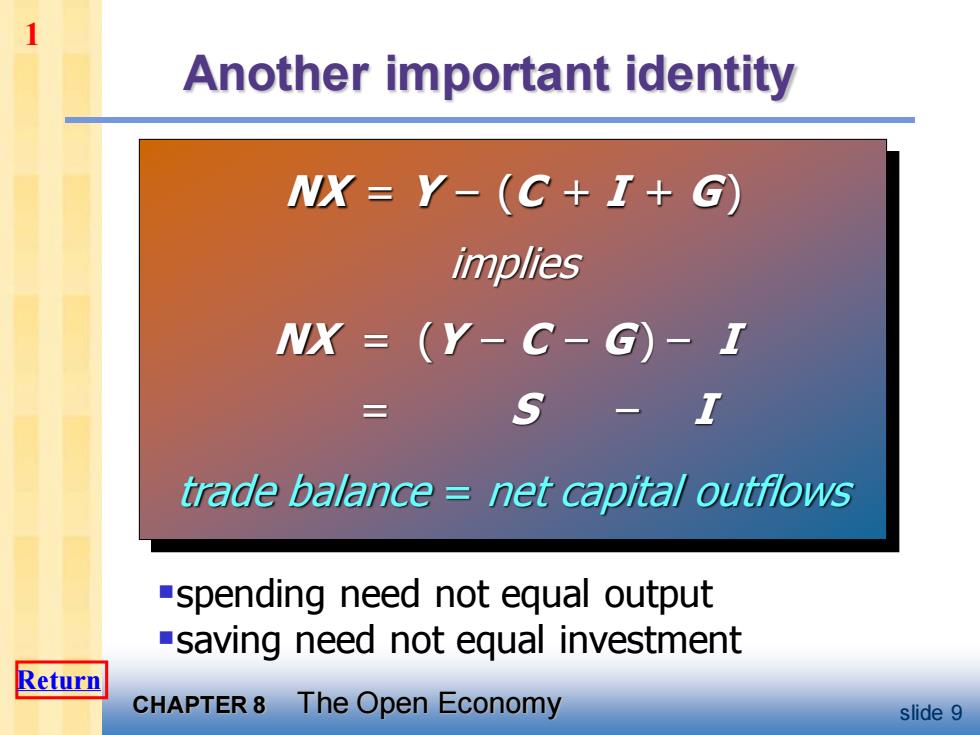
1 Another important identity NX=Y-(C+I+G) implies NX=(Y-C-G)-I 三 S trade balance net capital outflows -spending need not equal output -saving need not equal investment Return CHAPTER8 The Open Economy slide 9
CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 9 Another important identity NX = Y – (C + I + G ) implies NX = (Y – C – G ) – I = S – I trade balance = net capital outflows ▪spending need not equal output ▪saving need not equal investment 1 Return
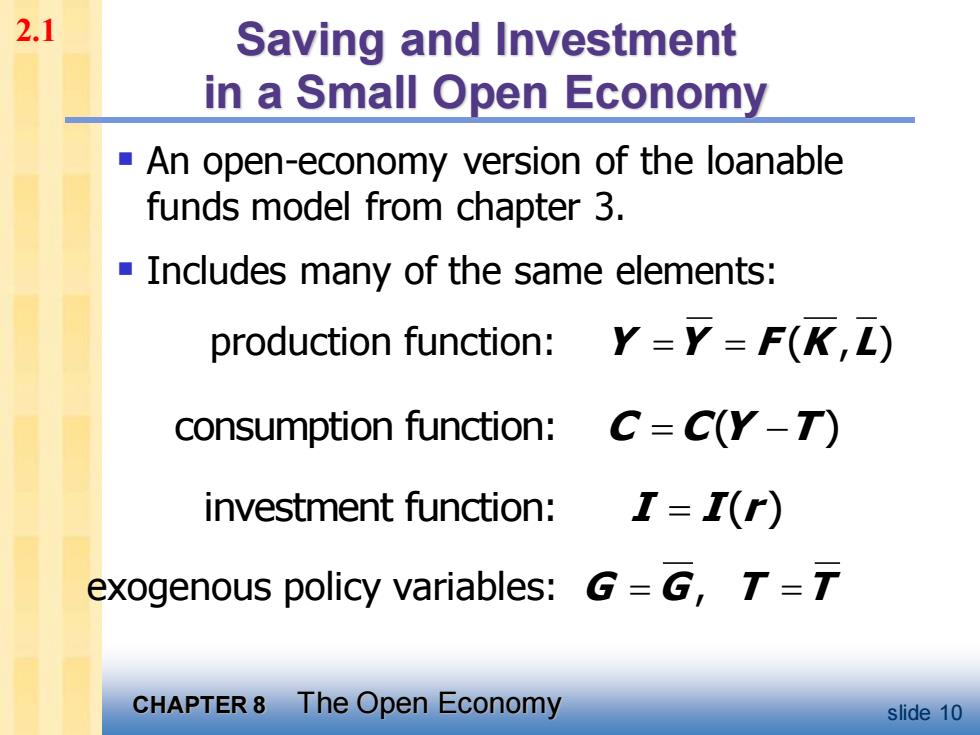
2.1 Saving and Investment in a Small Open Economy An open-economy version of the loanable funds model from chapter 3. -Includes many of the same elements: production function:Y=Y=F(K,L) consumption function:C=C(Y-T) investment function: I=I(r) exogenous policy variables:G=G,T=T CHAPTER8 The Open Economy slide 10
CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 10 Saving and Investment in a Small Open Economy ▪ An open-economy version of the loanable funds model from chapter 3. ▪ Includes many of the same elements: production function: ( , ) Y Y F K L = = consumption function: ( ) C C Y T = − investment function: ( ) I I r = exogenous policy variables: , G G T T = = 2.1
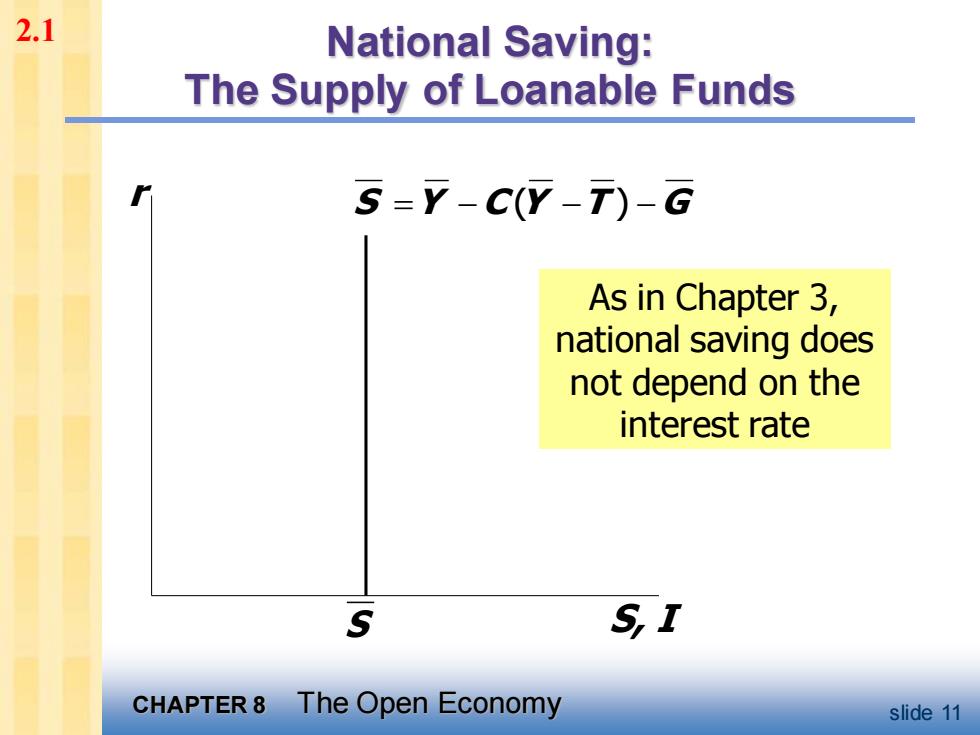
2.1 National Saving: The Supply of Loanable Funds 5=Y-CY-)-G As in Chapter 3, national saving does not depend on the interest rate S SI CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 11
CHAPTER 8 The Open Economy slide 11 National Saving: The Supply of Loanable Funds r S, I As in Chapter 3, national saving does not depend on the interest rate S Y C Y T G = − − − ( ) S 2.1