
CHAPTER FOUR Money and Inflation macroeconomics N.Gregory Mankiw College of Management,HUST
macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw macro College of Management, HUST CHAPTER FOUR Money and Inflation

In this chapter you will learn -The classical theory of inflation causes effects social costs "Classical"-assumes prices are flexible markets clear. Applies to the long run. CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 1
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 1 In this chapter you will learn ▪ The classical theory of inflation – causes – effects – social costs ▪ “Classical” - assumes prices are flexible & markets clear. ▪ Applies to the long run

Content 1.Money and money supply 2.The quantity theory of money 3.The Fisher effect 4.The money demand function 5.The social costs of inflation 6.Hyperinflation 7.The Classical Dichotomy 8.Chapter summary CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 2
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 2 Content 1. Money and money supply 2. The quantity theory of money 3. The Fisher effect 4. The money demand function 5. The social costs of inflation 6. Hyperinflation 7. The Classical Dichotomy 8. Chapter summary

1 Money:definition Money is the stock of assets that can be @ AL11695679A readily used to make transactions. CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 3
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 3 Money: definition Money is the stock of assets that can be readily used to make transactions. 1
Money:functions 1. medium of exchange we use it to buy stuff 2.store of value transfers purchasing power from the present to the future 3.unit of account the common unit by which everyone measures prices and values CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 4
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 4 Money: functions 1. medium of exchange we use it to buy stuff 2. store of value transfers purchasing power from the present to the future 3. unit of account the common unit by which everyone measures prices and values 1
1 Money:types 1.fiat money has no intrinsic value example:the paper currency we use 2.commodity money ·has intrinsic value ·examples.gold coins, cigarettes in P.O.W.camps CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 5
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 5 Money: types 1. fiat money • has no intrinsic value • example: the paper currency we use 2. commodity money • has intrinsic value • examples: gold coins, cigarettes in P.O.W. camps 1

1 Discussion Question Which of these are money? a.Currency b.Checks c.Deposits in checking accounts (called demand deposits) d.( Credit cards e. Certificates of deposit (called time deposits) CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 6
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 6 Discussion Question Which of these are money? a. Currency b. Checks c. Deposits in checking accounts (called demand deposits) d. Credit cards e. Certificates of deposit (called time deposits) 1

The money supply monetary policy -The money supply is the quantity of money available in the economy. -Monetary policy is the control over the money supply. CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 7
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 7 The money supply & monetary policy ▪ The money supply is the quantity of money available in the economy. ▪ Monetary policy is the control over the money supply. 1
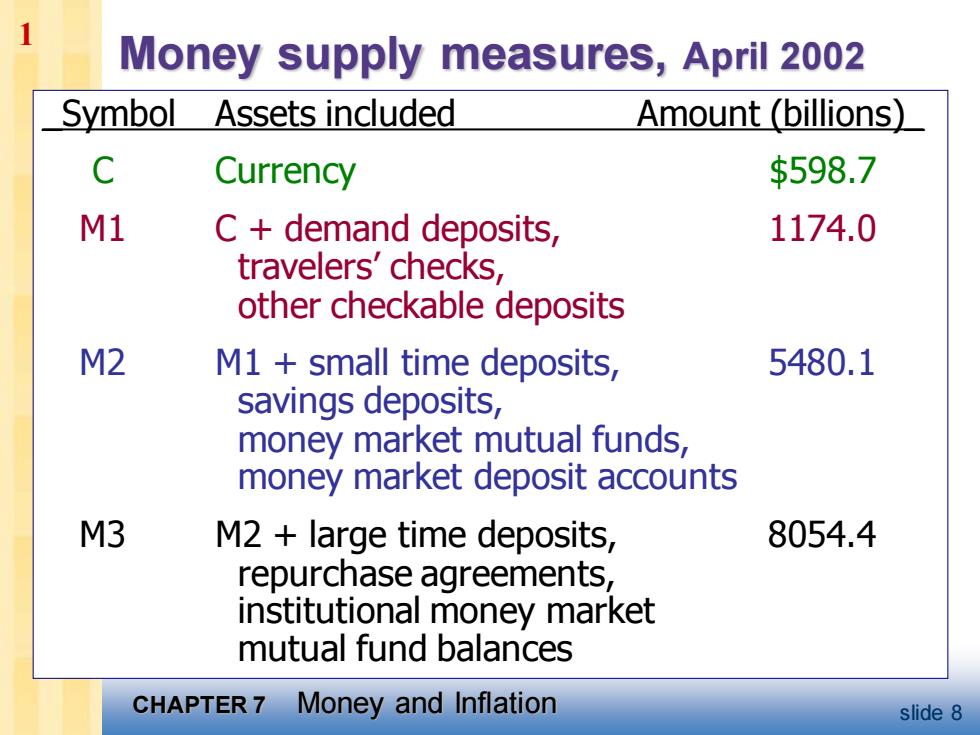
Money supply measures,April 2002 Symbol Assets included Amount (billions) C Currency $598.7 M1 C demand deposits, 1174.0 travelers'checks, other checkable deposits M2 M1 small time deposits, 5480.1 savings deposits, money market mutual funds, money market deposit accounts M3 M2 large time deposits, 8054.4 repurchase agreements, institutional money market mutual fund balances CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 8
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 8 Money supply measures, April 2002 _Symbol Assets included Amount (billions)_ C Currency $598.7 M1 C + demand deposits, 1174.0 travelers’ checks, other checkable deposits M2 M1 + small time deposits, 5480.1 savings deposits, money market mutual funds, money market deposit accounts M3 M2 + large time deposits, 8054.4 repurchase agreements, institutional money market mutual fund balances 1

1 The central bank Monetary policy is conducted by a country's central bank. In the U.S., the central bank is called the Federal Reserve ("the Fed"). The Federal Reserve Building Washington,DC Return CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 9
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 9 The central bank ▪ Monetary policy is conducted by a country’s central bank. ▪ In the U.S., the central bank is called the Federal Reserve (“the Fed”). The Federal Reserve Building Washington, DC Return 1