
Chapter 9 Microbial Ecology
Chapter 9 Microbial Ecology

Microbiological Ecology: Microbial ecology is the study of the behavior and activities of microorganisms in their natural environments
Microbiological Ecology: Microbial ecology is the study of the behavior and activities of microorganisms in their natural environments

9.1 Microorganisms in Nature Ecosystem 9.1.1 Microorganisms in Aquatic Environment 1.Freshwater microorganism (1)Oligotrophic hydromicroorganism (2)Copiotrophic hydromicroorganism 2.Marine microorganism
9.1 Microorganisms in Nature Ecosystem 9.1.1 Microorganisms in Aquatic Environment 1. Freshwater microorganism (1)Oligotrophic hydromicroorganism (2)Copiotrophic hydromicroorganism 2. Marine microorganism

0.1mm Figure 9-1 Thiomargarita namibiensis the World's Known the Largest Bacterium.[From Lansing M.Prescott et al Microbiology (fifth edition)]
Figure 9-1 Thiomargarita namibiensis ,the World`s Known the Largest Bacterium.[From Lansing M. Prescott et al Microbiology (fifth edition)]

9.1.2 Microorganisms in atmosphere Table 9-1 Bacterium quantity in 1M3 air in different environments Environment Numbers barn 1-2×106 dorm 20000 city street 5000 Town park 200 Air up the ocean 1-2 north pole (north 0 latitude80°) (From ZhouDeqin,,Edition One,Page284)
9.1.2 Microorganisms in atmosphere Table 9-1 Bacterium quantity in 1M3 air in different environments Environment Numbers barn 1-2×106 dorm 20000 city street 5000 Town park 200 Air up the ocean 1-2 north pole(north latitude80°) 0 (From ZhouDeqin, ,Edition One,Page284)

9.1.3 Microorganisms in Soil Environment Bacterium quantities have a general decuple degression law per gram soil bacteria 108)>actinomyces (~107)>mildew (~106)>microzyne (~105)>algae (~104)>protozoan (~103)
9.1.3 Microorganisms in Soil Environment Bacterium quantities have a general decuple degression law per gram soil :bacteria(~ 108)>actinomyces(~107)>mildew (~106)>microzyne(~105)>algae (~104)>protozoan(~103)

9.1.4 Microorganism Grown inside and outside Organisms 1,Normal Microbiota of the Humans Body and Animals. 2,The Microbiota of the Plants (1)Rhizosphere Microorganisms (2)adnascent Microorganisms (3)endogenesis Microorganisms
9.1.4 Microorganism Grown inside and outside Organisms 1、Normal Microbiota of the Humans Body and Animals. 2、The Microbiota of the Plants (1) Rhizosphere Microorganisms (2)adnascent Microorganisms (3)endogenesis Microorganisms

9.2 The Relationships of Microbials and also with other Organisms 1.Neutralism 2.Mutualism (1)Mutualism between microorganisms (2)Mutualism between propagation and microorganisms 3.Symbiosis (1)Symbiosis between microorganisms (2)Plant-microorganism symbiosis (3)Animal-microorganism symbiosis
9.2 The Relationships of Microbials and also with other Organisms 1. Neutralism 2. Mutualism (1) Mutualism between microorganisms (2) Mutualism between propagation and microorganisms 3. Symbiosis (1) Symbiosis between microorganisms (2) Plant-microorganism symbiosis (3) Animal-microorganism symbiosis
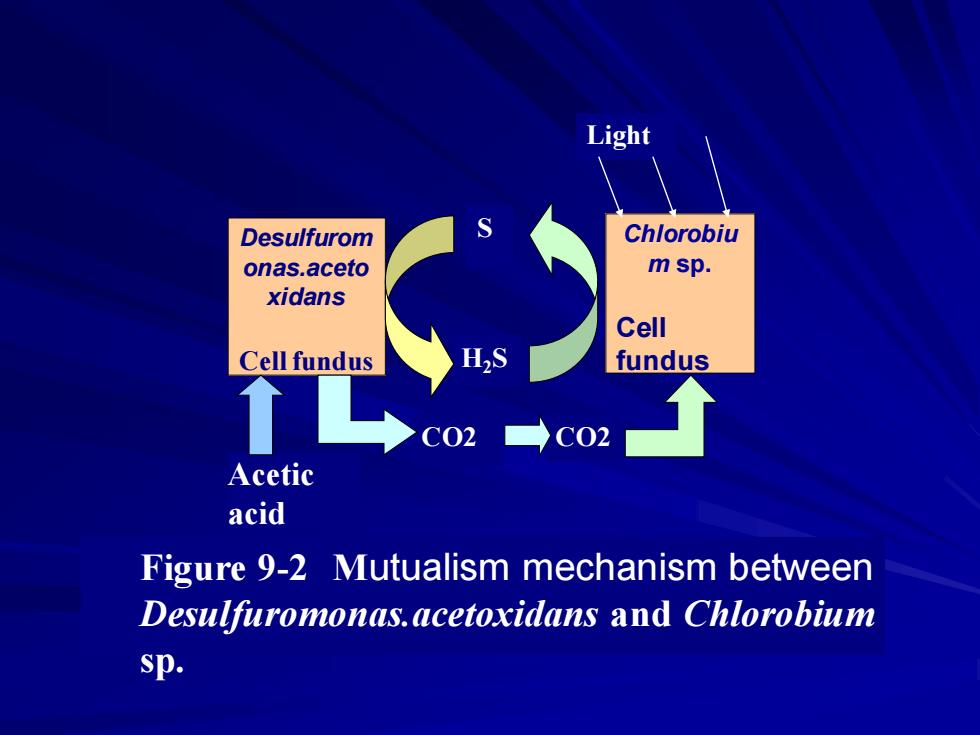
Light Desulfurom Chlorobiu onas.aceto m sp. xidans Cell Cell fundus fundus >c 2→c02 Acetic acid Figure 9-2 Mutualism mechanism between Desulfuromonas.acetoxidans and Chlorobium sp
Acetic acid Light Figure 9-2 Mutualism mechanism between Desulfuromonas.acetoxidans and Chlorobium sp. Desulfurom onas.aceto xidans Cell fundus Chlorobiu m sp. Cell fundus S H2S CO2 CO2
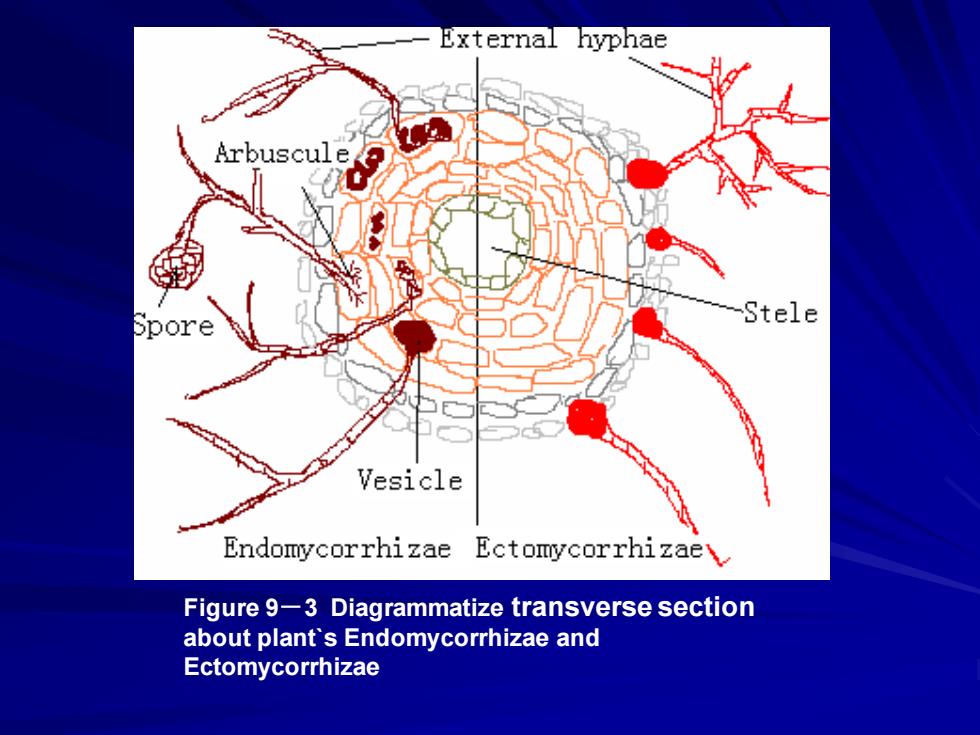
External hyphae Arbuscule Spore Stele Vesicle Endomycorrhizae Ectomycorrhizae\ Figure 9-3 Diagrammatize transverse section about plant's Endomycorrhizae and Ectomycorrhizae
Figure 9-3 Diagrammatize transverse section about plant`s Endomycorrhizae and Ectomycorrhizae