
第5卷第4期 智能系统学报 Vol.5 No.4 2010年8月 CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems Aug.2010 doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4785.2010.04.000 A new illumination preprocessing method for face recognition GAN Sheng College of Information Science and Technology,Nankai University,Tianjin 300071,China) Abstract:Differences in illumination of the same face can defeat simple face recognition systems,yet most methods that compensate are too difficult to implement.Local quotient image (LQI)is an efficient illumination preprocessing method for face recognition systems.An illumination model and a face model were developed,and their use in the new method was analyzed in detail.Analysis of the methods computational complexity showed it to be efficient.Experimental results on Yale Face Database B showed that the method can effectively eliminate the effects of differences in illumination and provides considerable improvement in recognition rates. Keywords:face recognition;illumination preprocessing;local quotient image;illumination model CLC Number:TP391.41 Document code:A Article ID:1673-4785(2009)06-0549-12 Face recognition has become one of the most suc- conests] symmetric shape-from-shading,quotient cessful applications of image analysis and understand- image,gamma intensity correctionsf quotient ing as a result of significant rescarch work in the last image,eigenphases,histogram equalization and decade2.However,variations in the quality of ima- logarithm tranforGood results have been repor ges heavily affect the performance of current face rec- ted by all these methods.However,some of these ognition systems.Experiments done on the Facial Rec- methods require other images of the same person under ognition Technology (FERET)database and the Face different illumination conditions and some have a com- Recognition Vendor Test 2000 (FRVT2000)tests paratively high computational complexity which makes showed that variations in illumination are among the them impractical.For example,Shape-From-Shading, bottlenecks for a practical face recognition system Quotient Image,Illumination Cones all require more Face appearance can change dramatically due to illu- than one image of the same person,while Self Quotient mination changes,and "the variations between the im- Image and Eigenphases have comparatively high com- ages of the same face due to illumination are almost al- putational complexity.Histogram equalization and log- ways larger than image variations due to change in face arithm transforms are easy to implement and don t re- identity"[41.Fig.1 shows the same person under dif- quire other images,but their performance is not good ferent illumination conditions in Yale Face Database enough. Blsj A novel illumination preprocessing method for hu- man face recognition was proposed and is discussed in this paper.Two major advantages of the method are that it has a low computational complexity and requires Fig.1 The same person under different illumination condi- no other images. tions in Yale Face Database B The remainder of this paper is organized as fol- Many methods have been proposed to deal with lows.Section 1 introduces the human face model and the illumination problem,including illumination illumination model adopted in this paper.Section 2 de- Received Date: scribes the proposed method in detail.Sections 3 and 4 Corresponding Author: show the experimental results and conclusions

2 智能系统学报 第5卷 We then computed the illumination variations 1 Human face model and illumination within a small facet W on each face image.The results model are shown in Fig.3.The images in the last row of Fig. 3 are almost all black,which means that illumination In this paper,we adopted the human face model difference within a small facet W is almost zero.We and illumination model proposed by Xie and Lam can see that the illumination conditions almost remain constant within a small facet.See Ref.16]for de- Faces can be regarded as Lambertian surfaces,and the tails. face image can be described by the product of the albe- do and the cosine angle between a point light source and the surface normal: (a)illumination environments I(x,y)=p(x,y)·n(x,y)·s.(1) where I(,y)is the intensity value of the pixel at (x, y)in the image..O≤p(x,y)≤1 is the corresponding (b)face images under different illumination environments albedo,n(x,y)is the surface normal direction,and s is the light source direction (point light source)and whose magnitude is the light source intensity (c)illumination variations within each facet A face model widely used in computer graphics Fig 3 (a)illumination environments (b)face images applications was adopted for this paper.We treated a under different illumination environments (c)il- human face as a combination of a sequence of small, lumination variations within each facet flat facets -4.Fig.2 shows a human face overlaid 2 Local quotient image method with this corresponding CANDIDE-3 models,a com- bination of a sequence of triangular facets. Our method applies a filter to each pixel of the face image,and obtains a new image which is insensi- tive to illumination. In our method,a small and flat facet W is repre- sented by a filter of size n x n.The filter W(x,y)is centered on the pixel x,y.We define Fig.2 CANDIDE-3 model of a human face In this paper,we addressed the illumination prob- 1'(,y))=I(xy) 既u,0)' (2) lem for face recognition under the following assump- where I(,y)is the intensity value of the original face tions:The area of each facet W is small enough to be image,and I'(,y)is the intensity value after process- considered a planar patch and for each point(,y)E ing. W,the surface normal direction n(x,y)is considered Based on the assumption made in the prior sec- to be a constant.In addition,the light source is as- tion,the surface normal direction within W is a con- sumed to be directional;the light source direction s is stant,that is,n(x,y)=n(u,)and the light source also almost constant within W. direction s is almost constant within W(x,y).And we The appropriateness of this assumption has been get: proven by DU BO.In that work,9 different illumi- '(x,y)=I(xy) nation environments (including several environments 既1(u,)) (s,)eW(,y) illuminated by spotlights from Debevec http:/ p(,y)·n(x,y)·S=p(,y) p(u,)·n(u,v)·sp(u,t) (3) www.debevec.org/Probes)were used on face models Obviously,I'(x,y)is irrelevant to illumination to generate face images under different illumination and reveals the nature of the face image.This means conditions
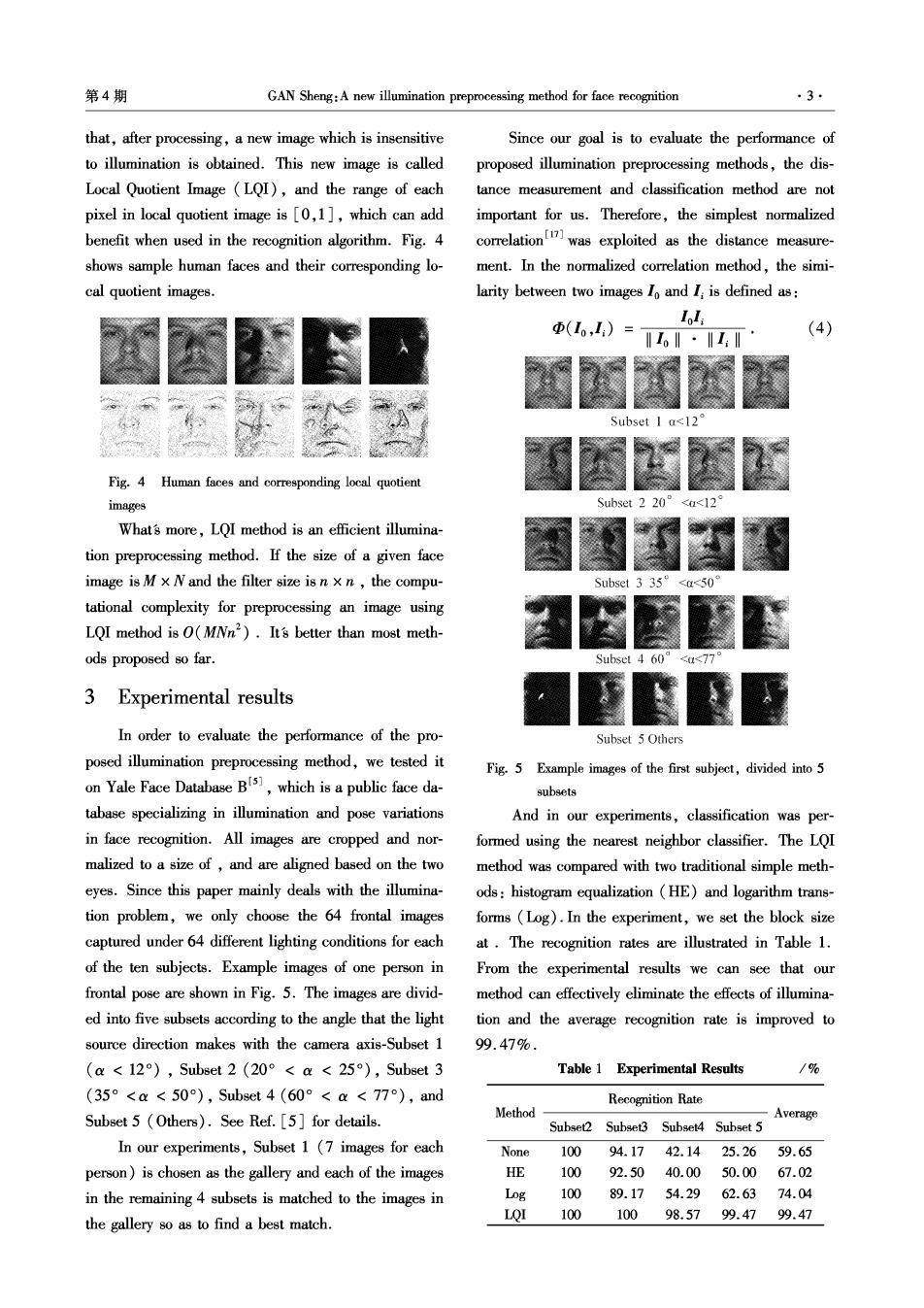
第4期 GAN Sheng:A new illumination preprocessing method for face recognition ·3· that,after processing,a new image which is insensitive Since our goal is to evaluate the performance of to illumination is obtained.This new image is called proposed illumination preprocessing methods,the dis- Local Quotient Image (LQI),and the range of each tance measurement and classification method are not pixel in local quotient image is [0,1],which can add important for us.Therefore,the simplest normalized benefit when used in the recognition algorithm.Fig.4 correlation was exploited as the distance measure- shows sample human faces and their corresponding lo- ment.In the normalized correlation method,the simi- cal quotient images. larity between two images To and I:is defined as: Iol; (L,I)= (4) Subset I a<12 Fig.4 Human faces and corresponding local quotient images Subset 2 20 <a<12 Whats more,LQI method is an efficient illumina- tion preprocessing method.If the size of a given face image is M x N and the filter size is n x n,the compu- Subset 3359 <50 tational complexity for preprocessing an image using LQI method is (MAn2).Its better than most meth- ods proposed so far. 4609 <77 3 Experimental results In order to evaluate the performance of the pro- Subset 5 Others posed illumination preprocessing method,we tested it Fig.5 Example images of the first subject,divided into 5 on Yale Face Database B,which is a public face da- subsets tabase specializing in illumination and pose variations And in our experiments,classification was per- in face recognition.All images are cropped and nor- formed using the nearest neighbor classifier.The LQI malized to a size of,and are aligned based on the two method was compared with two traditional simple meth- eyes.Since this paper mainly deals with the illumina- ods:histogram equalization (HE)and logarithm trans- tion problem,we only choose the 64 frontal images forms(Log).In the experiment,we set the block size captured under 64 different lighting conditions for each at.The recognition rates are illustrated in Table 1. of the ten subjects.Example images of one person in From the experimental results we can see that our frontal pose are shown in Fig.5.The images are divid- method can effectively eliminate the effects of illumina- ed into five subsets according to the angle that the light tion and the average recognition rate is improved to source direction makes with the camera axis-Subset 1 99.47%. (a<12),Subset2(20°<a<25°),Subset3 Table 1 Experimental Results /% (35°<a<50),Subset4(60°<a<77),and Recognition Rate Method Subset 5 (Others).See Ref.[5]for details. -Average Subset2 Subset3 Subset4 Subset 5 In our experiments,Subset 1 (7 images for each None 100 94.1742.14 25.2659.65 person)is chosen as the gallery and each of the images HE 100 92.5040.00 50.0067.02 in the remaining 4 subsets is matched to the images in Log 100 89.1754.29 62.6374.04 LOI 100 100 98.5799.4799.47 the gallery so as to find a best match

4 智能系统学报 第5卷 4 Conclusions robust face recognition against varying lighting conditions [C]//IEEE International Workshop on Analysis and Model- An efficient illumination preprocessing method for ing of Faces and Gestures.Nice,France,2003:157-164. face recognition under varying lighting conditions was [9]WANG H,LI S,WANG Y.Face recognition under various proposed.The method regards the faces as Lambertian lighting conditions using self quotient image[C]//Proceed- surfaces,and treats faces as a combination of a se- ings of Interational Conference on Automatic Face and Ges- quence of small and flat facets.This system is widely ture Recognition.Seoul,Korea,2004:819-824. [10]SAVVIDES M,KUMAR B V,KHOSLA P.Eigenphases used in computer graphics applications.A local quo- vs.eigenfaces C]//Proceedings of 17th International tient image method was applied to the face image pixel Conference on Patter Recognition.Cambridge,UK, by pixel.The images obtained after preprocessing were 2004:810-813 supposed to be invariant to illumination variations.The [11]SAVVIDES M,KUMAR V.Illumination normalization u- experimental results demonstrated the effectiveness of sing logarithm transforms for face authentication[C]//Pro- our method. ceedings of the 4th international conference on Audio-and References: video-based biometric person authentication.Guildford, UK,2003:549556. [1]SAMAL A,IYENGAR P.Automatic recognition and analy- [12]XIE X,LAM K M.An efficient illumination normalization sis of human faces and facial expressions:a survey[J]. Pattern Recognition,1992,25(1):65-77. method for face recognition[J].Pattern Recognition Let- [2]CHELLAPPA R,WILSON C L,SIROHEY S.Human and ters,2006,27(6):609617. [13]FENG G C,YUEN P C.Recognition of head-and-shoulder machine recognition of faces:a survey[J].Proceedings of the IEEE,1995,83(5):705-740. face image using virtual frontal-view image [J].IEEE [3]PHILLIPS P J,MOON H,RIZVI S A.The FERET evalua- Transactions on Systems Man Cybemnet,2000,30(6): 871-882. tion methodology for face-recognition algorithms[J].IEEE [14]HWANG W,LEE S W.Reconstruction of partially dam- Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000,22(10):1090-1104. aged face images based on a morphable face model[J]. [4]ADINI Y,MOSES Y,ULLMAN S.Face recognition:the IEEE Transactions on Patter Analysis and Machine Intel- ligence,2003,25(3):365-372. problem of compensating for changes in illumination direc- [15]AHLBERG J.CANDIDE-3-un updated parameterised face tion[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Ma- chine Intelligence,1997,19(7):721-732. [R].LiTH-ISY-R-2326,2001. 5]GEORGHIADES S,BELHUMEUR P N,KRIEGMAN D J. [16]DU Bo.Research on illumination preprocessing approaches From few to many:illumination cone models for face recog- in face recognition[D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Sci- ence,2005. nition under variable lighting and pose[J].IEEE Transac- tions on Pattem Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2001, [17]BARON R J.Mechanisms of human facial recogntion[J]. 23(6):643660. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies,1981,15 (2):137-178 [6]ZHAO W,CHELLAPPA R.Illumination-insensitive face Biographies: recognition using symmetric shape-from-shading[C]//Pro- ceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision Sheng Gan obtained his bachelor's degree in Computer Science in 2006 from and Pattern Recognition.Hilton Head Island,USA,2001: 286-293. Beijing Normal University.At the same [7]SHASHUA A,RAVIV T R.The quotient image:class- time he also obtained another bachelor's based re-rendering and recognition with varying illumina- degree in English Literature.He won the tions[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Ma- first prize in Mathematics Contest for Bei- chine Intelligence,2001,23(2):129-139. jing College Students in 2004.He ranks among the top 5%in [8]SHAN S,GAO W,CAO B.Illumination normalization for his department.His field of interest is Computer vision and Pat- ter recognition