
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 19 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volume Analysis Spring,3/28/2019 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 nR是n http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html 1日
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 19 Spring, 3/28/2019 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volume Analysis http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html
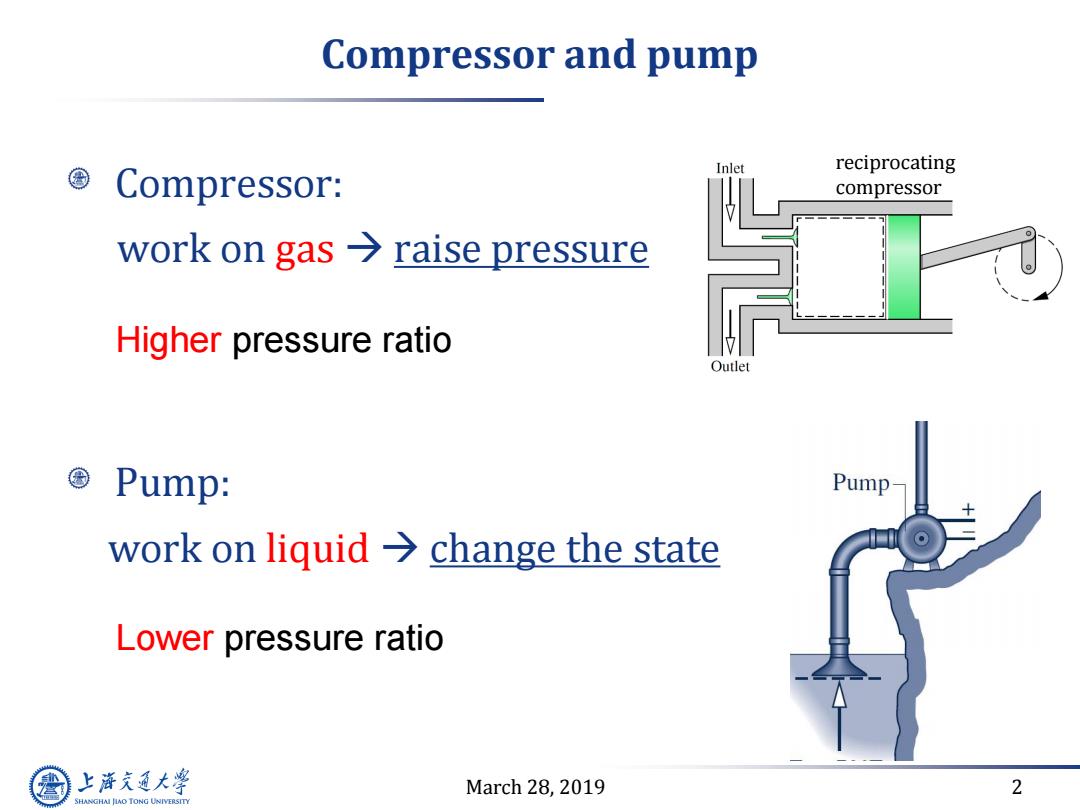
Compressor and pump Inlet reciprocating Compressor: compressor work on gas raise pressure Higher pressure ratio Outlet Pump: Pump work on liquid change the state Lower pressure ratio 上游充通大学 March 28,2019 2 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 28, 2019 2 Compressor and pump Compressor: work on gas raise pressure Pump: work on liquid change the state reciprocating compressor Higher pressure ratio Lower pressure ratio
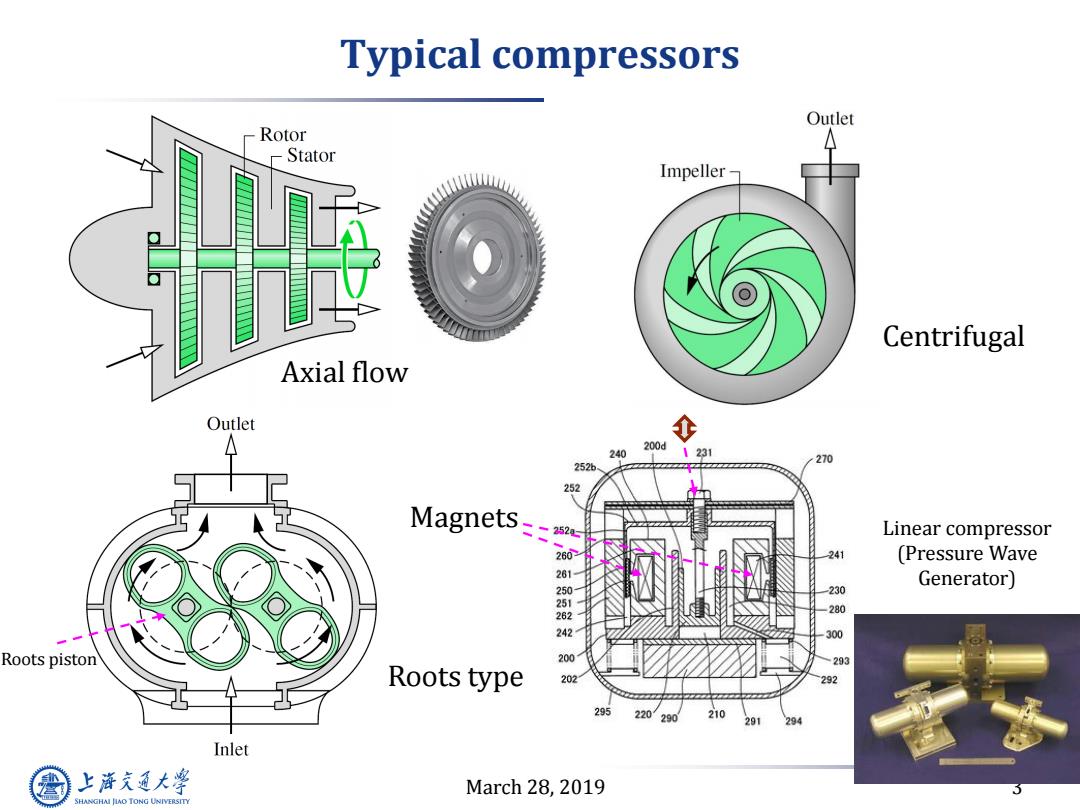
Typical compressors Outlet Rotor Stator Impeller- Centrifugal Axial flow Outlet 200d 240 231 270 2526. 252 Magnets- 252a Linear compressor 260 241 (Pressure Wave 261 Generator) 9 230 282 280 242 300 Roots piston 200 293 Roots type 202 292 295 220 290 210 291 294 Inlet 上降文通大学 March 28,2019 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 28, 2019 3 Typical compressors Axial flow Centrifugal Roots type Linear compressor (Pressure Wave Generator) Roots piston Magnets
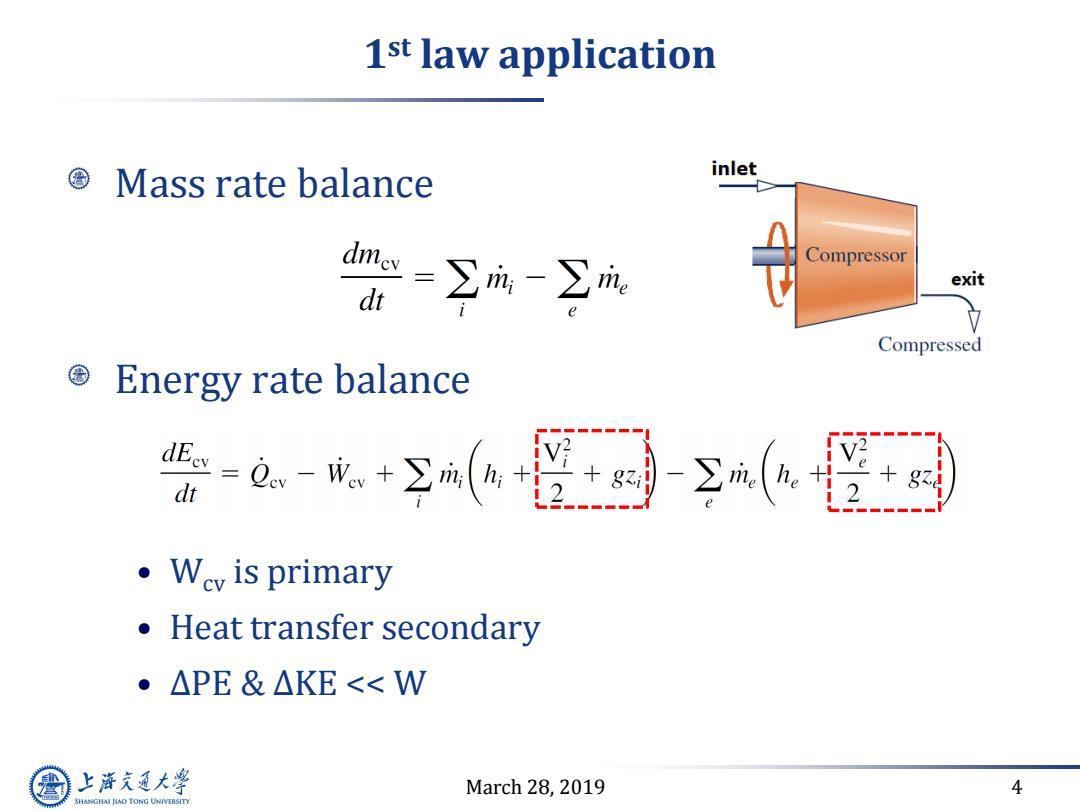
1st law application Mass rate balance inlet =∑成-∑m: Compressor exit di 立 Compressed Energy rate balance 长-0-成+区(产 dt ·Wcv is primary Heat transfer secondary ·△PE&△KE<<W 上游通大学 March 28,2019 4 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 28, 2019 4 1 st law application Mass rate balance Energy rate balance • Wcv is primary • Heat transfer secondary • ∆PE & ∆KE << W
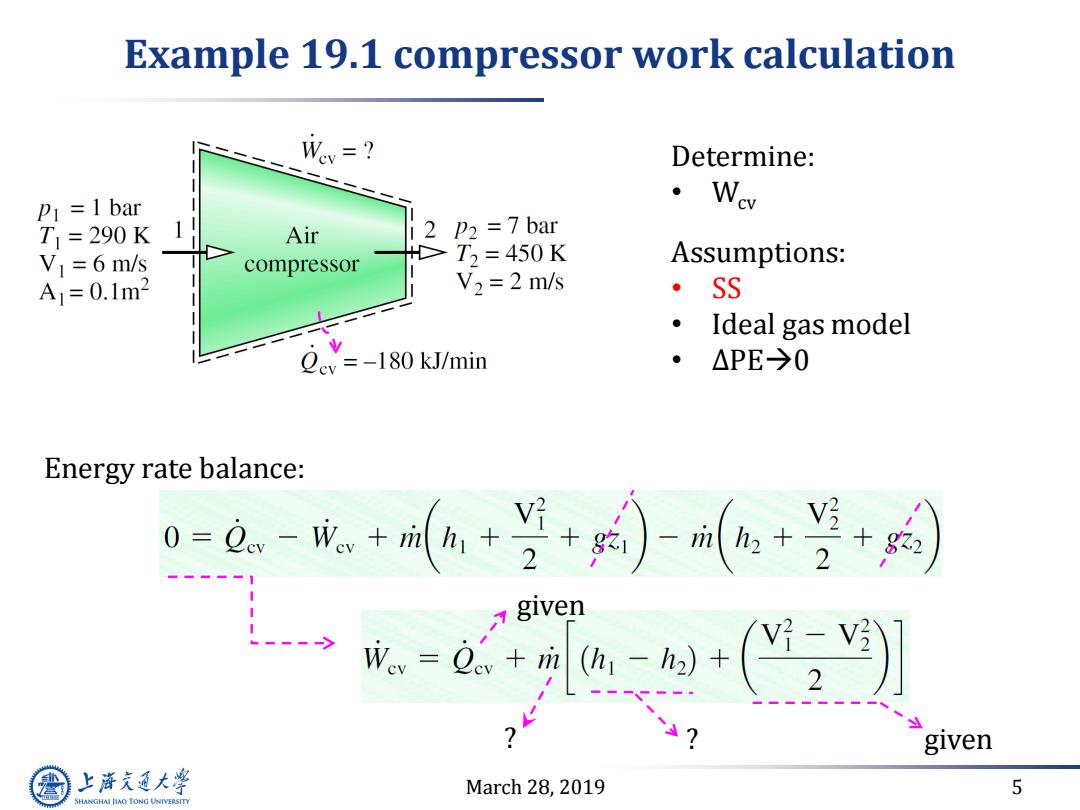
Example 19.1 compressor work calculation Wey=? Determine: =1 bar Wev T =290K Air 2 P2 =7bar > V=6 m/s compressor T2=450K Assumptions: A=0.1m2 V2 =2 m/s ·SS Ideal gas model Qev =-180 kJ/min ·△PE→0 Energy rate balance: 0=.-成-++-++ given =-( given 上游充通大学 March 28,2019 5 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 28, 2019 5 Example 19.1 compressor work calculation Determine: • Wcv Assumptions: • SS • Ideal gas model • ∆PE0 Energy rate balance: given given ? ?

Solution Wev=? P1=1 bar T1=290K Air 2 P2=7bar Mass flow rate VI=6 m/s compressor T,=450K A1=0.1m2 V2 =2 m/s AVI m Ideal gas EoS Qcy=-180 kJ/min 1(0.1m2)6m/s)(105N/m (R/M)T 2897gR)290 8314Nm 2=0.72kgs Given temperature,Table A-17 (ideal gas air )>h,h2 T1=290K,h1=290.16k/kg.T2=450K,h2=451.8k/kg. -e.+a--(] -(-1)l+02e016-451 kJ +(,ergdisoal -119.4kW 上游充通大学 negative March 28,2019 6 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 28, 2019 6 Solution Mass flow rate Ideal gas EoS Given temperature, Table A-17 (ideal gas air ) h1 , h2 T1 = 290 K, h1 = 290.16 kJ/kg. T2 = 450 K, h2 = 451.8 kJ/kg. negative
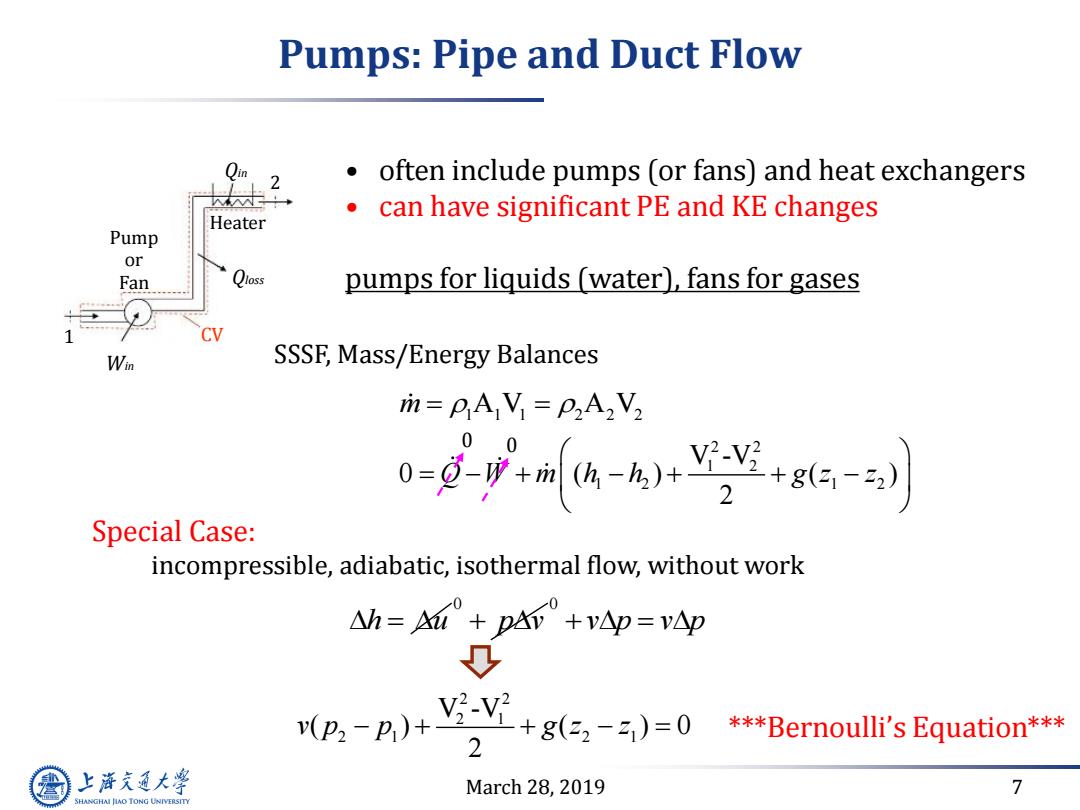
Pumps:Pipe and Duct Flow 2 often include pumps (or fans)and heat exchangers can have significant PE and KE changes Heater Pump or Fan Qloss pumps for liquids (water),fans for gases SSSF,Mass/Energy Balances i=pA V=P2A2V2 0=i9r6-6++g-司 Special Case: incompressible,adiabatic,isothermal flow,without work △h=A+pM+vp=vp ,-P+,Y+g5-=0 ***Bernoulli's Equation*** 2 上游充通大学 March 28,2019 7 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 28, 2019 7 Pumps: Pipe and Duct Flow 2 Qin • often include pumps (or fans) and heat exchangers • can have significant PE and KE changes pumps for liquids (water), fans for gases Pump or Fan 1 Heater Qloss CV Win SSSF, Mass/Energy Balances Special Case: incompressible, adiabatic, isothermal flow, without work 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 V -V ( ) ( ) 0 2 v p p g z z m 1 1 1 A V A V 2 2 2 h u 0 p v 0 v p v p 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 V -V 0 ( ) ( ) 2 Q W m h h g z z ***Bernoulli’s Equation*** 0 0
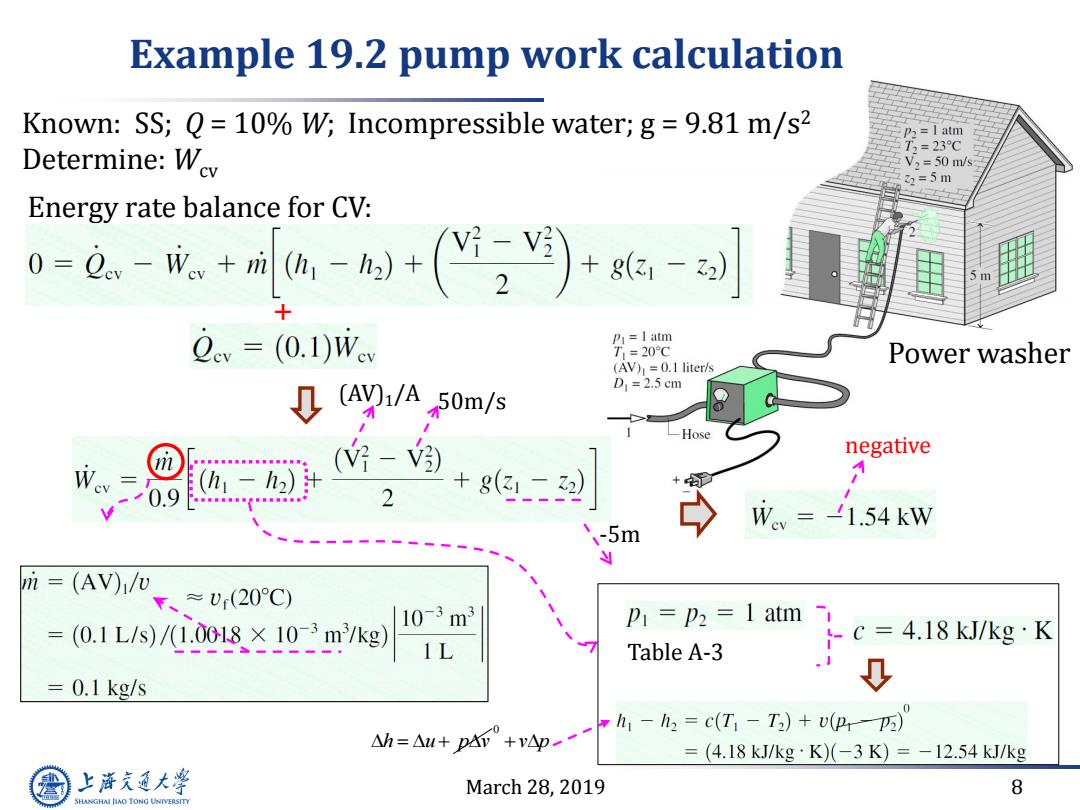
Example 19.2 pump work calculation Known:SS;Q=10%W;Incompressible water;g=9.81 m/s2 p2=I atm Determine:Wev T2=23℃ V2=50m/s 2=5m Energy rate balance for CV: 0=0。-成+刻+()+的-对 v=(0.1)Wev P=I atm T1=20C Power washer (Av)=0.1 liter/s ↓(ayi/A50m/s D1=2.5cm negative 1-h2) -+g + 0.9 2 Wev =-1.54 kW -5m m (AV)/v ≈U(20C) (0.1L/s)/1.0018×10-3m/kg) 10-3m3 P=p2=1 atm C= 4.18 kJ/kg K Table A-3 1 0.1 kg/s h=△u+p4+y-一 h1-h2=c(T-T2)+vP-) = (4.18kJ/kg·K)(-3K)=-12.54kJ/kg 上降文通大学 March 28,2019 8 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 28, 2019 8 Energy rate balance for CV: Example 19.2 pump work calculation + -5m 50m/s (AV)1/A Table A-3 negative Power washer Known: SS; Q = 10% W; Incompressible water; g = 9.81 m/s2 Determine: Wcv h u p v 0 v p

Other examples for interests Compressor Example Water Pumping Example Given:Hydrogen compressor, Given:D1=10 cm,D2=15 cm; Inlet:T1=320K,P1=0.2MPa,=100m/s,D1=0.1m T2=T1=Tatm=20C Outlet:T2=520 K,P2=1.2 MPa,D2=0.1 m P2=P1=Patm=101.3 Pa V2=15 L/s 2 Negligible heat loss ÷V=15L/s System Wsh 65m Pump Water 1 Find:(1)mass flow rate in kg/min,(2)shaft power Find:pump power required Assumptions:(1)SSSF,(2)Ape =0,(3)adiabatic, Assumptions:1)SSSF,2)adiabatic,3)water (4)Hz is ideal gas is incompressible 上游充通大 March 28,2019 9 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 28, 2019 9 Other examples for interests Compressor Example Given: Hydrogen compressor, Inlet: T1 = 320 K, P1 =0.2 MPa, V1=100 m/s, D1 = 0.1 m Outlet: T2 = 520 K, P2 =1.2 MPa, D2 = 0.1 m Negligible heat loss 2 System : Wsh 1 Find: (1) mass flow rate in kg/min, (2) shaft power Assumptions: (1) SSSF, (2) ∆pe =0, (3) adiabatic, (4) H2 is ideal gas Water Pumping Example 2 CV 65 m Pump V 15 L/s 1 Water Find: pump power required Assumptions: 1) SSSF, 2) adiabatic, 3) water is incompressible Given: D1 = 10 cm, D2 = 15 cm; T2 = T1 = Tatm = 20oC P2 = P1 = Patm = 101.3 Pa V2 = 15 L/s

Homework: Problems:M4.60,M4.67 上游充通大学 March 28,2019 10 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 28, 2019 10 Homework: Problems: M4.60, M4.67