
上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 48 Class Review and Final Exam. Spring,5/15/2018 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 M http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html SHANG 1日 ERSITY
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 48 Spring, 5/15/2018 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG Class Review and Final Exam. http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html

Chap.1 System,boundary,surrounding. Closed system/open system/adiabatic system/ isolated system 国 What is property?Distinguish property from non- property.Characteristics of property. 国 Extensive and intensive properties Units for pressure,temperature,specific volume 上游充通大粤 May15,2018 2 HANGHAI HAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 2 Chap. 1 System, boundary, surrounding. Closed system/open system/adiabatic system/ isolated system What is property? Distinguish property from non‐ property. Characteristics of property. Extensive and intensive properties Units for pressure, temperature, specific volume
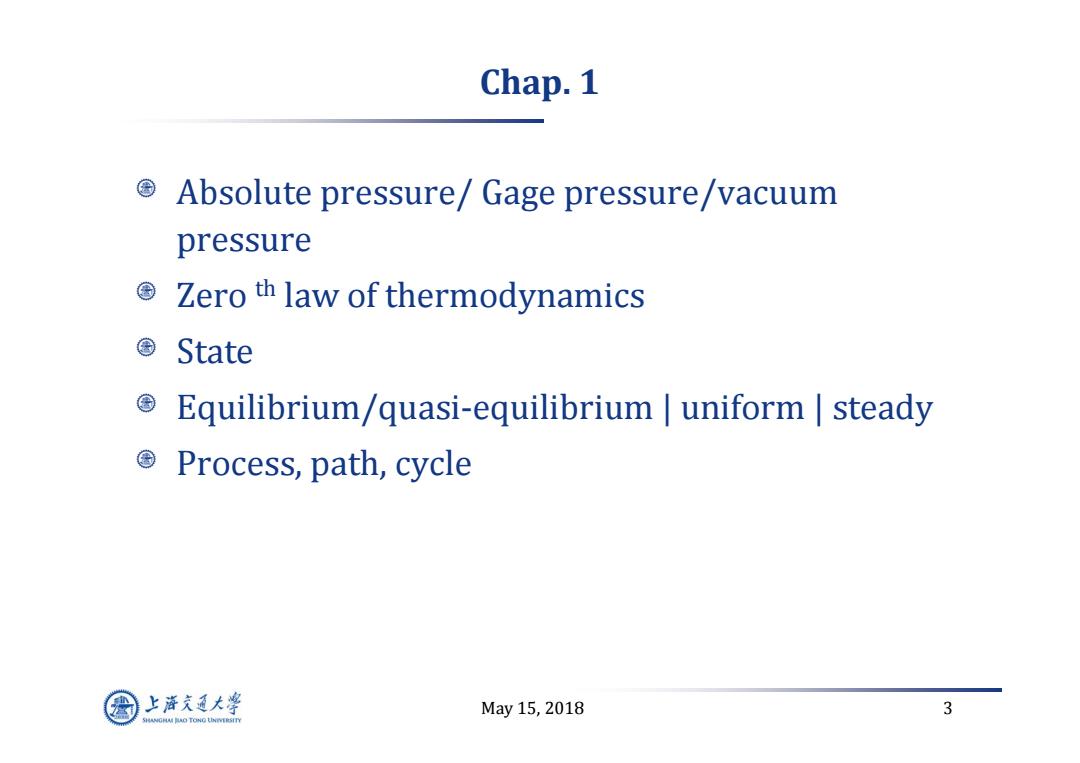
Chap.1 Absolute pressure/Gage pressure/vacuum pressure 国 Zero th law of thermodynamics State Equilibrium/quasi-equilibrium uniform steady 国 Process,path,cycle 上游充通大粤 May15,2018 3 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 15, 2018 3 Chap. 1 Absolute pressure/ Gage pressure/vacuum pressure Zero th law of thermodynamics State Equilibrium/quasi‐equilibrium | uniform | steady Process, path, cycle

Chap.2 Energy potential energy (PE)kinetic energy (KE) 国 Change of energy pv Work/boundary work/shaft work/flow work... External force,non-quasi-equilibrium problem Sign (+/-definition of heat transfer and work 国 Internal energy... 上游充通大粤 May15,2018 4 HANGHAI HAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 4 Chap. 2 Energy | potential energy (PE) |kinetic energy (KE) Change of energy Work/boundary work/ shaft work/ flow work… External force, non‐quasi‐equilibrium problem Sign (+/ ‐ ) definition of heat transfer and work Internal energy… pv
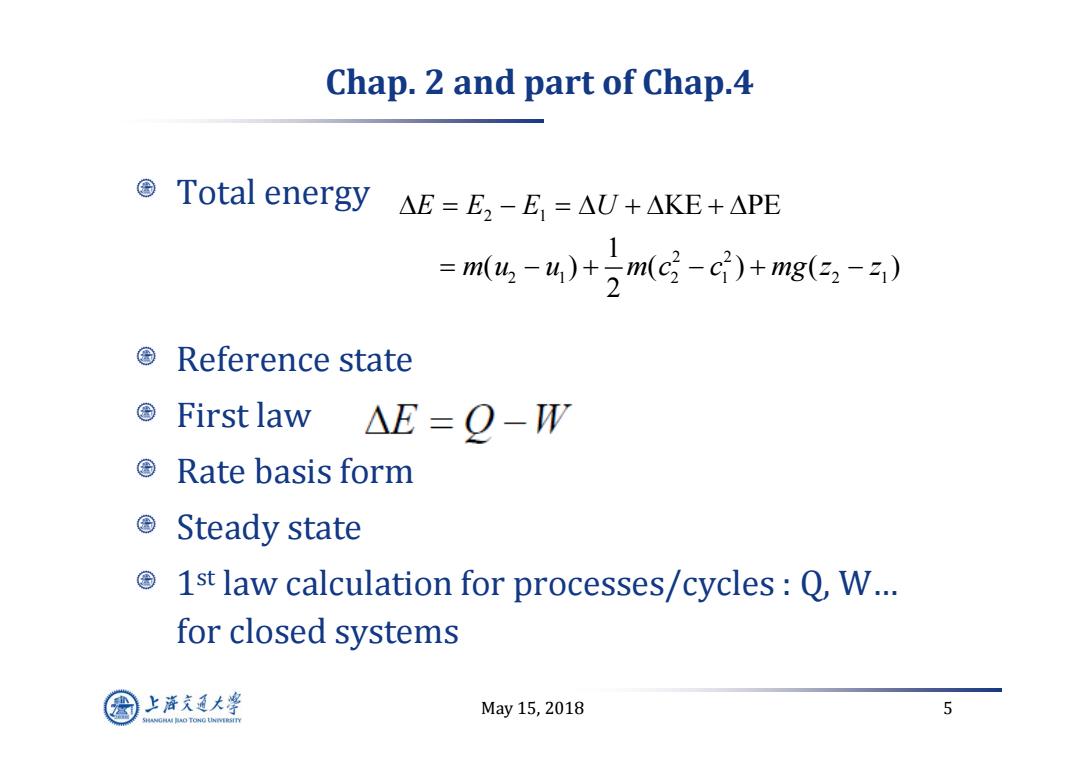
Chap.2 and part of Chap.4 ©Total energy△E=E,-E,=AU+AKE+APE =m,-4)+)m(c-c)+mg(32-2) Reference state First law △E=Q-W ©Rate basis form Steady state 国 1st law calculation for processes/cycles:Q,W... for closed systems 上游充通大¥ May15,2018 5 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 15, 2018 5 Chap. 2 and part of Chap.4 Total energy Reference state First law Rate basis form Steady state 1st law calculation for processes/cycles : Q, W… for closed systems 2 1 2 2 21 21 21 KE PE 1 ( ) ( )( ) 2 EE E U mu u mc c m g z z
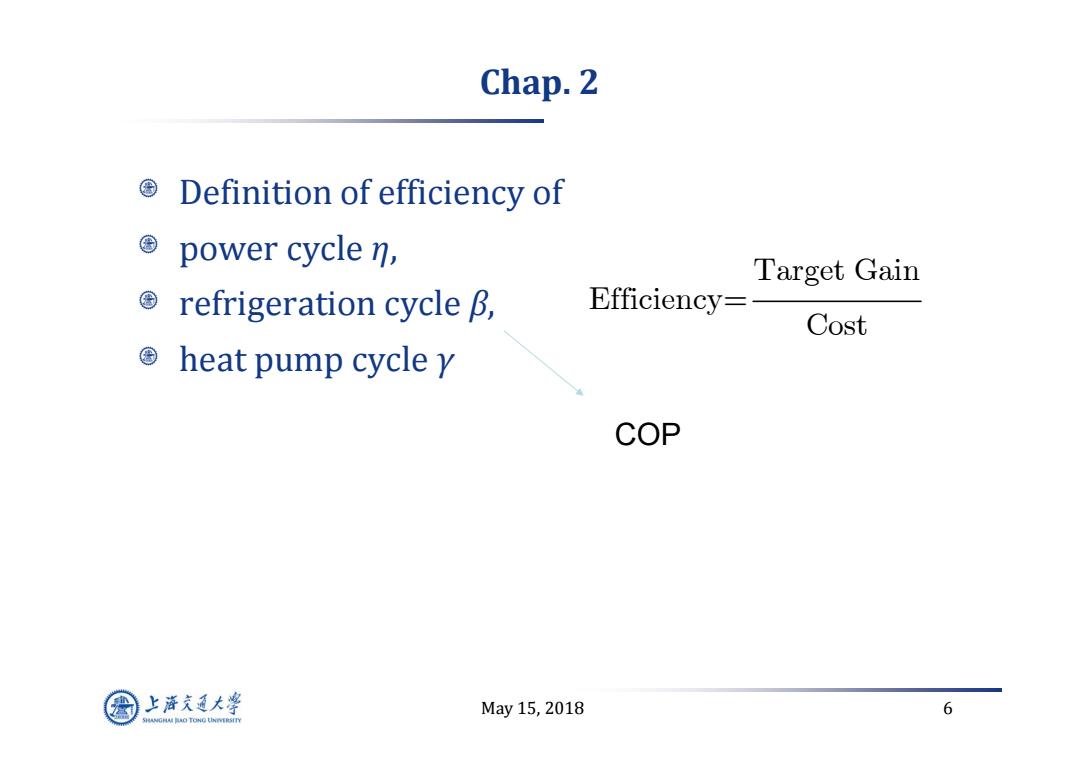
Chap.2 Definition of efficiency of ©power cycle n, Target Gain refrigeration cycle B, Efficiency= Cost heat pump cycle y COP 上游充通大 May15,2018 6 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 15, 2018 6 Chap. 2 Definition of efficiency of power cycle η, refrigeration cycle β, heat pump cycle γ Target Gain Efficiency= Cost COP
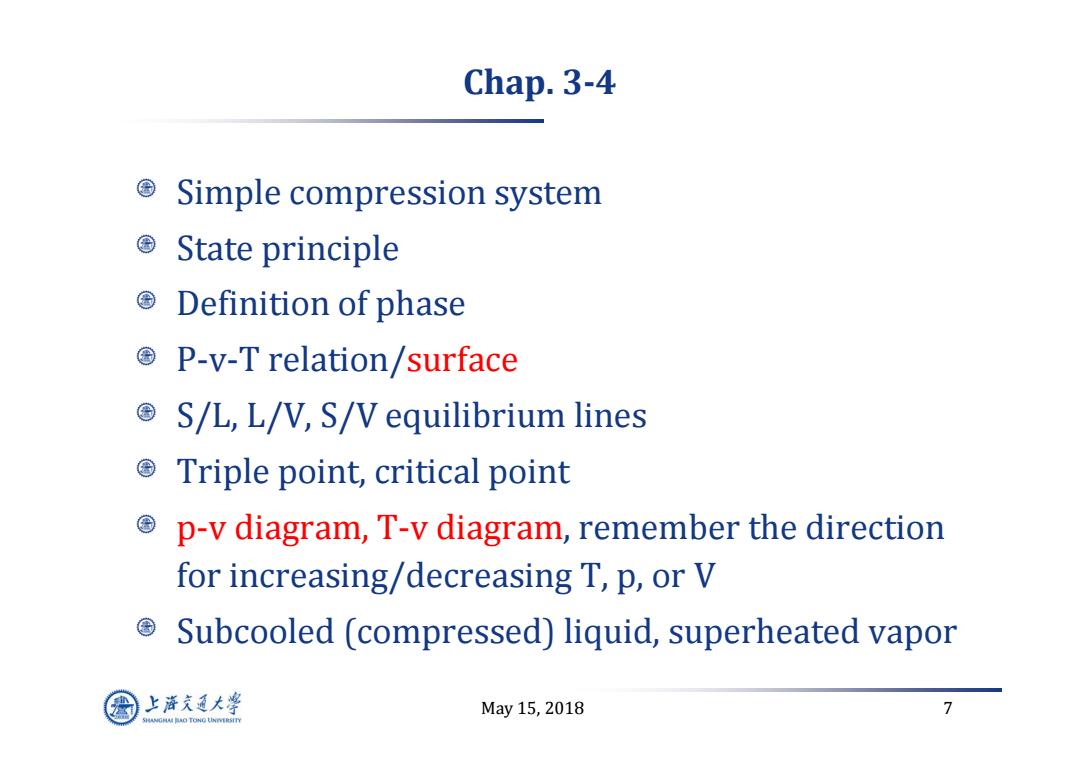
Chap.3-4 Simple compression system ©State principle ©Definition of phase P-v-T relation/surface S/L,L/V,S/V equilibrium lines Triple point,critical point p-v diagram,T-v diagram,remember the direction for increasing/decreasing T,p,or V 国 Subcooled (compressed)liquid,superheated vapor 上游充通大¥ May15,2018 7 HANGHAI HAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 7 Chap. 3 ‐ 4 Simple compression system State principle Definition of phase P‐v‐T relation/surface S/L, L/V, S/V equilibrium lines Triple point, critical point p‐v diagram, T‐v diagram, remember the direction for increasing/decreasing T, p, or V Subcooled (compressed) liquid, superheated vapor
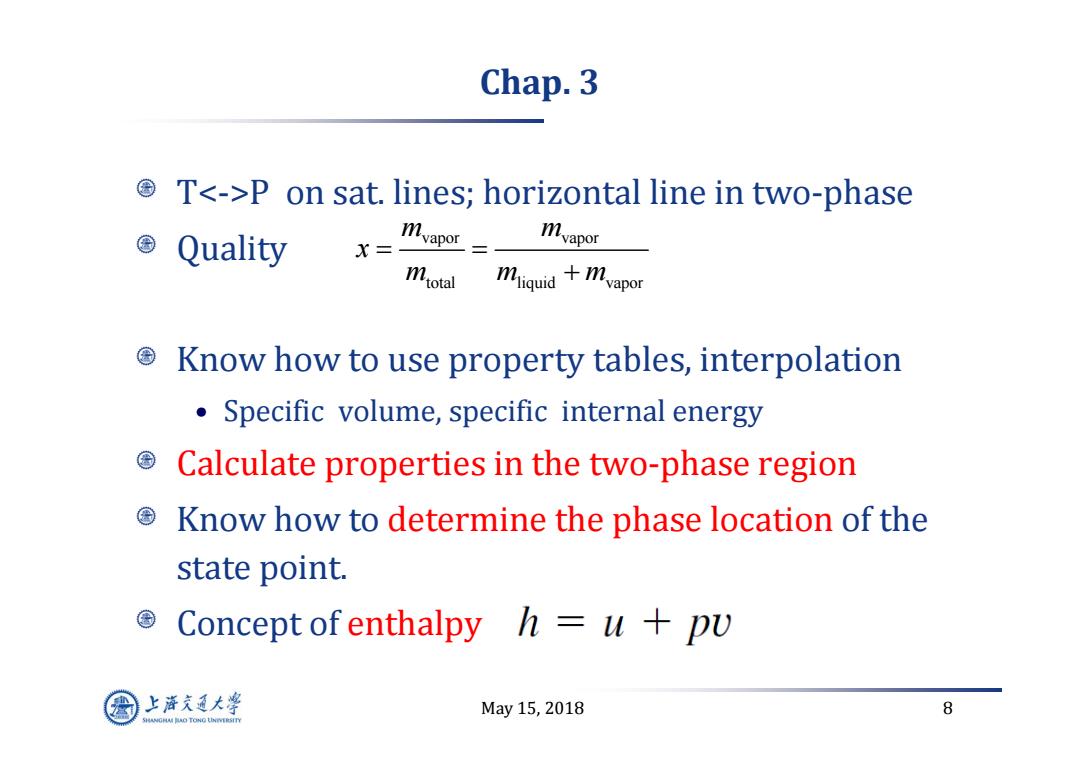
Chap.3 TP on sat.lines;horizontal line in two-phase Quality X=- vapor二- mvapor mrotal miguid+mvapor © Know how to use property tables,interpolation Specific volume,specific internal energy © Calculate properties in the two-phase region Know how to determine the phase location of the state point. Concept of enthalpy h=u+pu 上游充通大率 May15,2018 8 HANGHAI HAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 8 Chap. 3 TP on sat. lines; horizontal line in two‐phase Quality Know how to use property tables, interpolation • Specific volume, specific internal energy Calculate properties in the two‐phase region Know how to determine the phase location of the state point. Concept of enthalpy vapor vapor total liquid vapor m m x mmm
Chap.3 ④ Evaluate h,v,u,q,w or changes for processes (single phase,or two-phase) Specific heat(const.v,const.p),specific heat ratio Approximate values for v,u,and h at liquid states (incompressible)can be obtained using saturated liquid data (based on Temperature) 上游充通大粤 May15,2018 9 HANGHAI HAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 9 Chap. 3 Evaluate h, v, u, q, w or changes for processes (single phase, or two‐phase) Specific heat (const. v, const. p), specific heat ratio Approximate values for v, u, and h at liquid states (incompressible) can be obtained using saturated liquid data (based on Temperature)
Chap.3 Ideal gas model Universal gas constant,gas constant,their relations Pay attention to the units. Ideal gas equation of state u,h,cpc:temperature dependent only(not for s) c-u;cp-h relations I cp c for ideal gas; 上游充通大粤 May15,2018 10 HANGHAI HAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 10 Chap. 3 Ideal gas model Universal gas constant, gas constant, their relations Pay attention to the units. Ideal gas equation of state u, h, c p, c v: temperature dependent only (not for s) c v‐ u; c p –h relations | c p, c v for ideal gas;