
上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY a Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 43-44 Cengel_Chapter 11 Refrigeration Cycles Spring,5/11/2018 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 是 唱目e http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html SHANG ERSITY
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 43‐44 Spring, 5/11/2018 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG Cengel_ Chapter 11 Refrigeration Cycles http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html
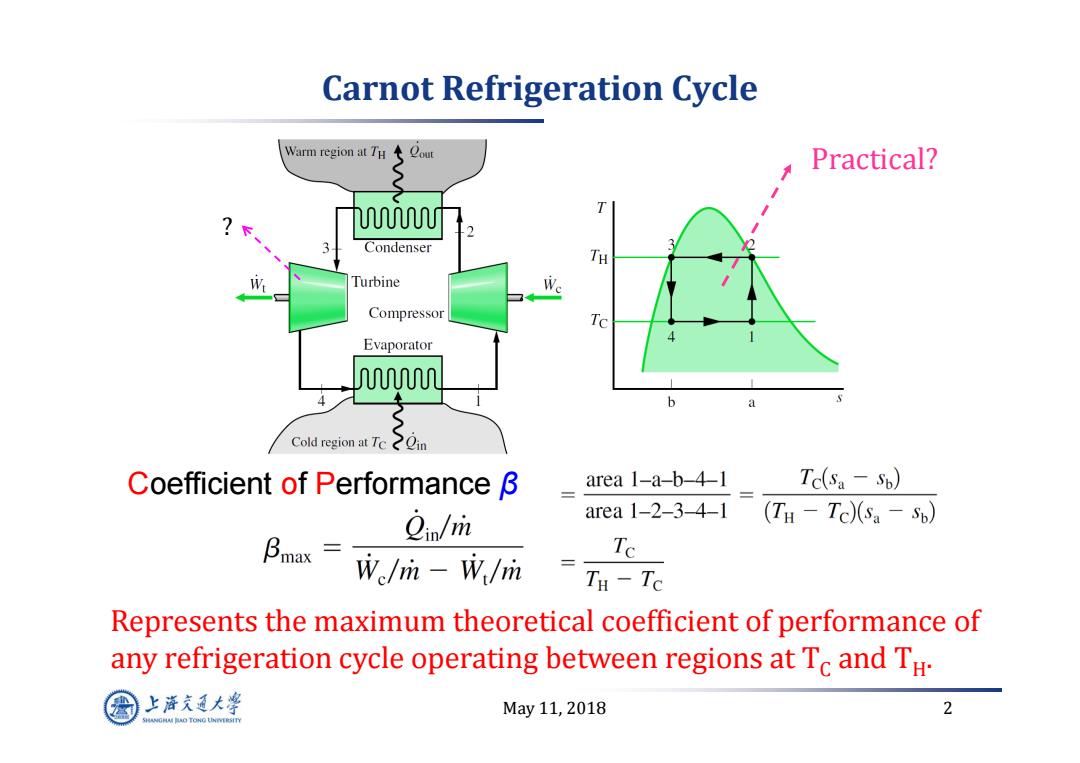
Carnot Refrigeration Cycle Warm region at TH Qout Practical? UUUT 3 Condenser TH Turbine Compressor Tc Evaporator mm b Cold region atTc之gin Coefficient of Performance B area 1-a-b-4-1 Tc(sa-Sp) 2in/m area 1-2-3-4-1 (TH -Tc)(Sa -Sp) Bmax Te We/m-W/mn TH-Tc Represents the maximum theoretical coefficient of performance of any refrigeration cycle operating between regions at Tc and TH. 上游充通大¥ May11,2018 2 HANGHAI HAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 11, 2018 2 Carnot Refrigeration Cycle Practical? Coefficient of Performance β Represents the maximum theoretical coefficient of performance of any refrigeration cycle operating between regions at T C and T H. ?
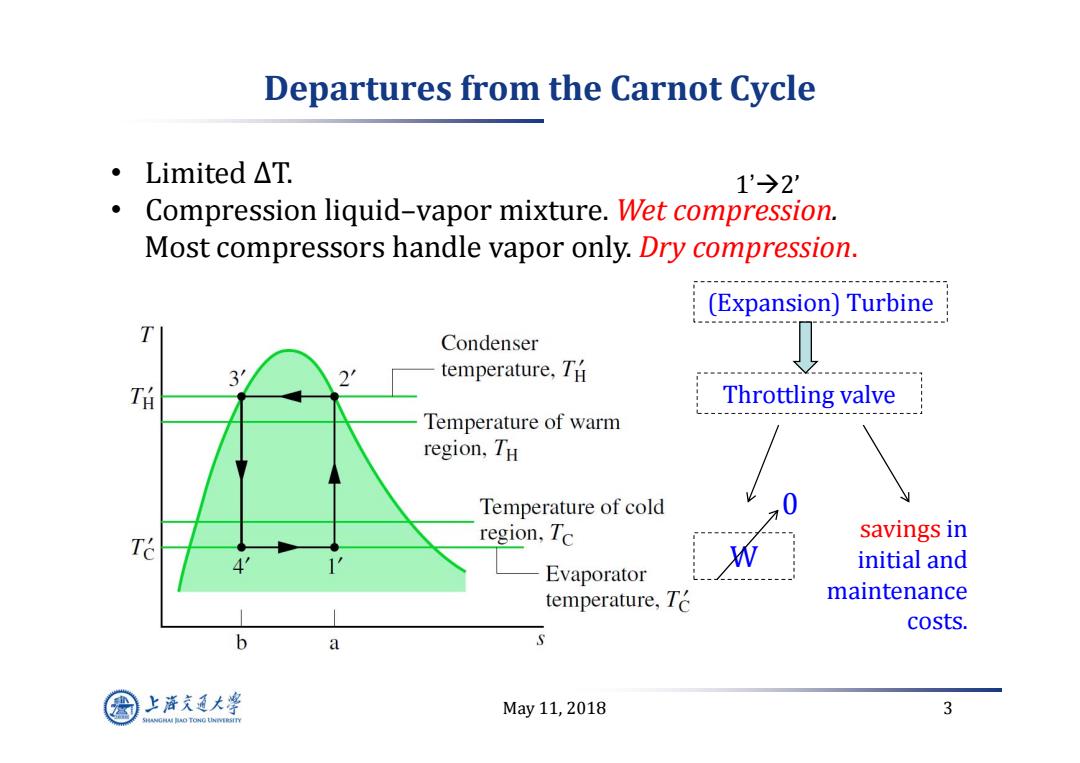
Departures from the Carnot Cycle ·Limited△T. 1'→2' Compression liquid-vapor mixture.Wet compression. Most compressors handle vapor only.Dry compression. (Expansion)Turbine T Condenser 2' temperature,TH TH Throttling valve Temperature of warm region,TH Temperature of cold 0 T region,Tc savings in W initial and Evaporator temperature,Te maintenance costs. b a 上游充通大¥ May11,2018 3 SHANGHA BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 11, 2018 3 Departures from the Carnot Cycle • Limited ∆T. • Compression liquid–vapor mixture. Wet compression. Most compressors handle vapor only. Dry compression. savings in initial and maintenance costs. (Expansion) Turbine Throttling valve W 0 1’2’

Vapor-compression refrigeration cycle ●Evaporator: Ci=hha m Qin-refrigeration capacity.(kW). Alternative unit:ton of refrigeration,211 kJ/min. i We Compressor =h2-hi m------小 unuut Condenser ●Condenser VExpansion Compressor =h2-h3! valve i_m Evaporator m ●Throttling process Saturated or superheated vapor 2m 上海文①大学 May11,2018 4 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 11, 2018 4 Vapor ‐compression refrigeration cycle

Working substance:p-h diagram 4000 3000 2000 R134a Tcond:A0-55C ressure 198 ratio 600 500 2.0-3.0 LLL100LOC00bo06066600 300 200 0900 Enthalpy [kJ/kg] x=0.10 00 030 040 050 060 0,70 0.80 40 =0.20 040 0.50 50 2--100 120 140 160T 130 200220 300 150-250W △h≈120~150k/kg 20020 T△h≈2535k/kg 三im,△h WFm,△h/ comp,e/ ←≈65% 3.5-6.0kg/hr no.is 50-80W 上游充通大率 3.0-5.0 compe May11,2018 5 SHANGHA BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 11, 2018 5 comp,e evap,r COP W Q MSRS 150‐250 W Enthalpy [kJ/kg] Pressure ratio 2.0 ‐3.0 h 120~150 kJ/kg Qevap ,r m r h Tevap: 10 ‐25 C Tcond: 40 ‐55 C h 25~35 kJ/kg r comp,e o,is m h W 65% 3.5‐6.0 kg/hr 50 ‐80 W 3.0 ‐5.0 R134a Working substance: p‐h diagram
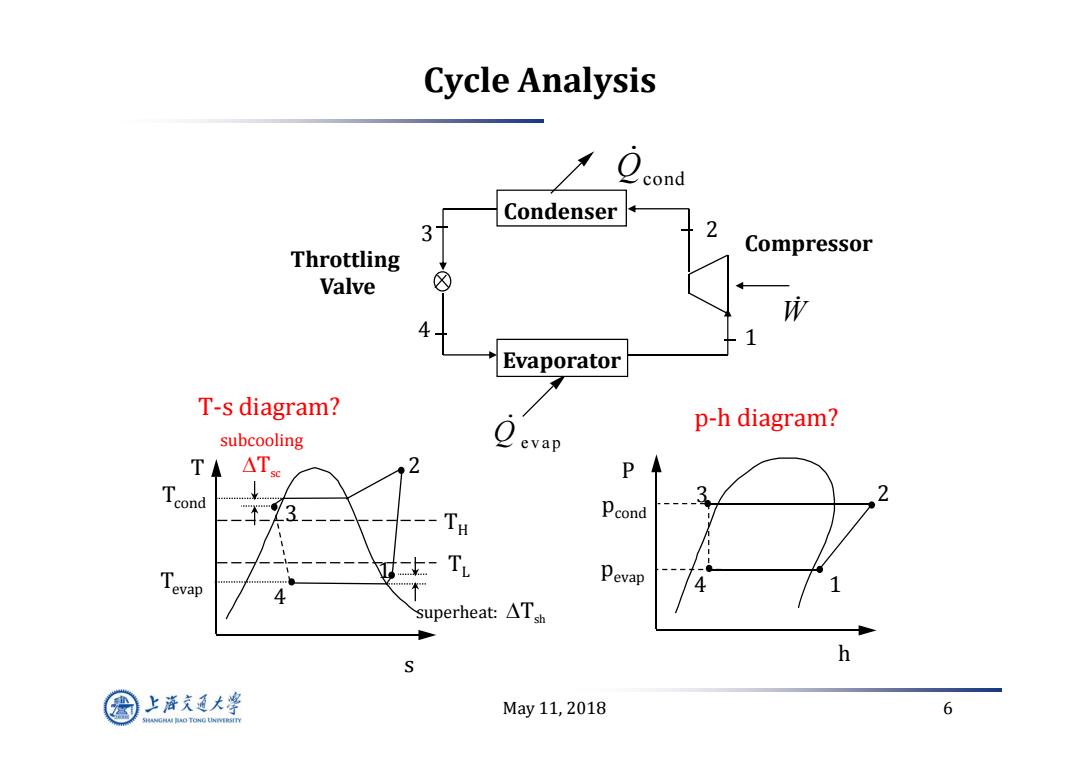
Cycle Analysis Condenser 3 2 Compressor Throttling Valve 成 4 1 Evaporator T-s diagram? subcooling Q p-h diagram? evap TA △Tc 2 P Tcond 3 Pcond 女T Pevap 4 superheat:△Th h 上游充通大率 May11,2018 6 SHANGHA BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 11, 2018 6 Cycle Analysis P h 3 2 4 1 pcond pevap s T 2 1 3 4 Tcond Tevap T H T L subcooling Tsc superheat: Tsh Compressor Throttling Valve Condenser 1 3 2 4 Evaporator W Qcond Q evap T‐s diagram? p‐h diagram?

Cycle Analysis Typical Assumptions specified evaporating(Tevap)and condensing (Tcond) temperatures specified superheat entering the compressor specified subcooling leaving the condenser constant pressure throughout heat exchangers negligible kinetic and potential energy changes for all components adiabatic throttling valve specified isentropic efficiency for compressor adiabatic compressor 上游充通大率 May11,2018 7 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 11, 2018 7 Cycle Analysis Typical Assumptions • specified evaporating ( Tevap) and condensing ( Tcond) temperatures • specified superheat entering the compressor • specified subcooling leaving the condenser • constant pressure throughout heat exchangers • negligible kinetic and potential energy changes for all components • adiabatic throttling valve • specified isentropic efficiency for compressor • adiabatic compressor

Cycle Analysis Compressor Inlet State P1=Pevap h1=h (Tevap+ATsh,Pevap) Compressor Outlet State P2 =Pcond TA isentropic specific work Tcond h2 =h+(h2sh) isentropic efficiency S h2s=h(p2,S2=S1) 上游充通大率 May11,2018 8 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 11, 2018 8 Cycle Analysis Compressor Inlet State p 1 = pevap h 1 = h (Tevap + Tsh , pevap ) Compressor Outlet State p 2 = pcond h2s = h (p 2 , s 2 = s 1 ) isentropic specific work 2s 1 2 1 s isentropic efficiency (h h ) h h T s 2 Tcond Tevap p 2 1 2s

Cycle Analysis Condenser Outlet State P 3 P3=Pcond Pcond h3=h (Tcond+ATsc,Pcond) L negative Pevap Evaporator Inlet State p4 =Pevap h4=h3 上游充通大率 May11,2018 9 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 11, 2018 9 Cycle Analysis Condenser Outlet State p 3 = pcond h 3 = h (Tcond + Tsc , pcond ) Evaporator Inlet State p 4 = pevap h 4 = h 3 P h 3 4 Pcond negative Pevap
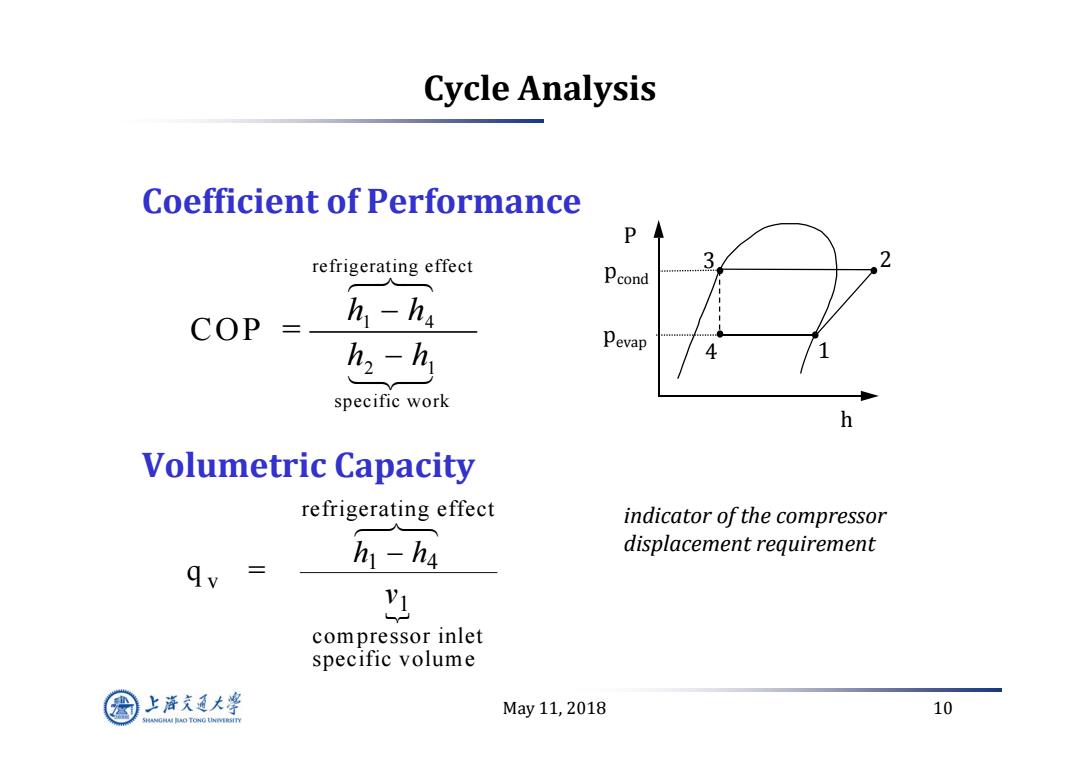
Cycle Analysis Coefficient of Performance P refrigerating effect 3 Pcond COP = h1-h4 五2-九 Pevap 4 specific work h Volumetric Capacity refrigerating effect indicator of the compressor h1-h4 displacement requirement compressor inlet specific volume 上游充通大率 May11,2018 10 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 11, 2018 10 Cycle Analysis Coefficient of Performance Volumetric Capacity P h 3 2 4 1 pcond pevap q = v refrigerating effect compressor inlet specific volume h h v 1 4 1 refrigerating effect 1 4 2 1 specific work COP = h h h h indicator of the compressor displacement requirement