上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 47 Chapter 9 Gas Power Systems (section 9.10) Spring,5/9/2019 强 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG VMLLMMAAD 目e http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html 1日G
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 47 Spring, 5/9/2019 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG Chapter 9 Gas Power Systems (section 9.10) http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html
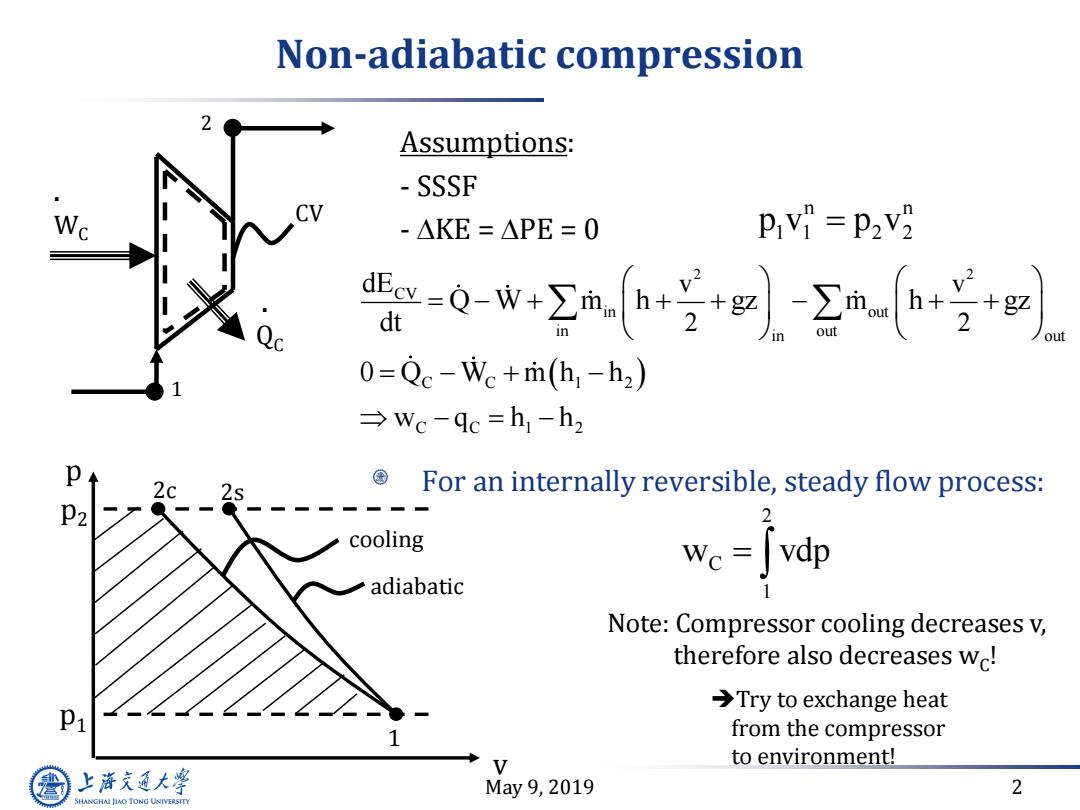
Non-adiabatic compression Assumptions: SSSF W -△KE=△PE=0 -0+2a宁l-2++ out 0=Qc-Wc+m(h-h2) →wc-qc=h1-h2 国 For an internally reversible,steady flow process: P2 2 cooling we Jvdp adiabatic 1 Note:Compressor cooling decreases v, therefore also decreases wc! >Try to exchange heat P1 from the compressor to environment! 上游充通大 May9,2019 2 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 2 Non-adiabatic compression 2 2 CV in out in out in out C C 1 2 C C 1 2 v v 2 2 dE Q W m h gz m h gz dt 0 Q W m h h w q h h Assumptions: - SSSF - KE = PE = 0 1 2 . WC . QC CV v 1 2s p p2 p1 2c cooling adiabatic For an internally reversible, steady flow process: 2 C 1 w vdp Note: Compressor cooling decreases v, therefore also decreases wC ! Try to exchange heat from the compressor to environment! n n 1 1 2 2 p v p v
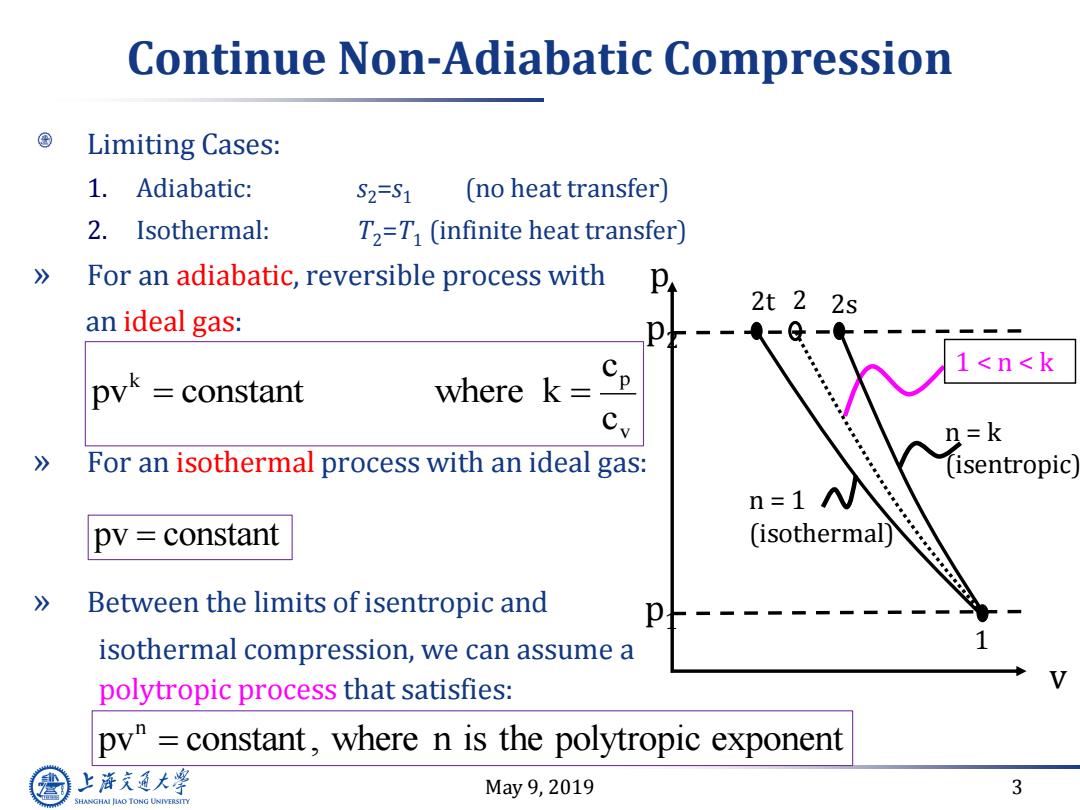
Continue Non-Adiabatic Compression Limiting Cases: 1.Adiabatic: S2=S1 (no heat transfer) 2.Isothermal: T2=T (infinite heat transfer) 》 For an adiabatic,reversible process with 2t22s an ideal gas: a-@ 1<n<k pyk =constant where k= 2=k 》 For an isothermal process with an ideal gas: (isentropic n=1 N pv constant (isothermal) 》 Between the limits of isentropic and isothermal compression,we can assume a polytropic process that satisfies: py"constant,where n is the polytropic exponent 上游究通大粤 May9,2019 3 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 3 Continue Non-Adiabatic Compression Limiting Cases: 1. Adiabatic: s2=s1 (no heat transfer) 2. Isothermal: T2=T1 (infinite heat transfer) » For an adiabatic, reversible process with an ideal gas: » For an isothermal process with an ideal gas: » Between the limits of isentropic and isothermal compression, we can assume a polytropic process that satisfies: k p v c pv constant where k c pv constant n pv constant , where n is the polytropic exponen t v 1 2s p p2 p1 1 < n < k 2t 2 n = k (isentropic) n = 1 (isothermal)
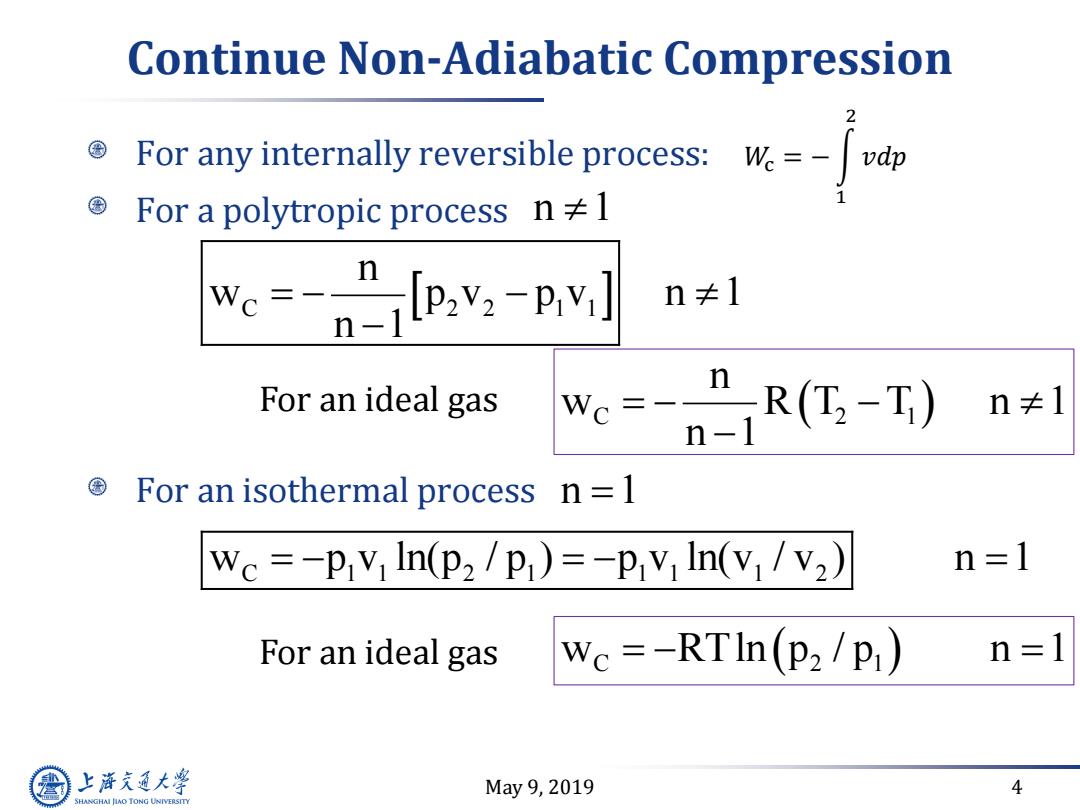
Continue Non-Adiabatic Compression For any internally reversible process:W-dp For a polytropic process n1 w--ntpv.-pv] n≠1 we--n-R(G-T) n For an ideal gas n≠1 For an isothermal process n =1 We =-P:V In(p2 /p)=-P:V In(Vi V2) n=1 For an ideal gas We=-RTIn(P2/P) n=1 上游充通大学 May9,2019 4 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 4 Continue Non-Adiabatic Compression For any internally reversible process: For a polytropic process For an isothermal process 𝑊c = − න 1 2 𝑣𝑑𝑝 C 2 2 1 1 n w p v p v n 1 n 1 For an ideal gas C 2 1 n w R T T n 1 n 1 n 1 w p v ln(p / p ) p v ln(v / v ) n 1 C 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 For an ideal gas w RTln p / p n 1 C 2 1 n 1

Two-stage Compression with Intercooling 2 Intercooler T P2 P2 2s 2s Px 2 P1 2 T 1 Ti 2t S S 图 上游充通大学 May9,2019 5 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 5 Two-stage Compression with Intercooling s T 1 x t=y 2 2s x x s 2t T1 p2 px p1 qI air x Intercooler wc 2 y 1 1 1 2 . WC . QC CV s T 1 2 2s T1 p2 p1

Continue Two-stage Compression with Intercooling Savings in work 2t 2 2s P2 - Isentropic compression pvk const Px _Isothermal compression Polytropic pv const compression pvn const P1 1 Limits:px=p2>savings=0 →An optimum exits! Px=p1→savings=0 上游京通大学 May9,2019 6 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 6 Continue Two-stage Compression with Intercooling Limits: px = p2 savings = 0 px = p1 savings = 0 An optimum exits! v p p2 2t Isothermal compression pv = const p1 px 2 2s Polytropic compression pvn = const 1 y x Isentropic compression pvk = const Savings in work
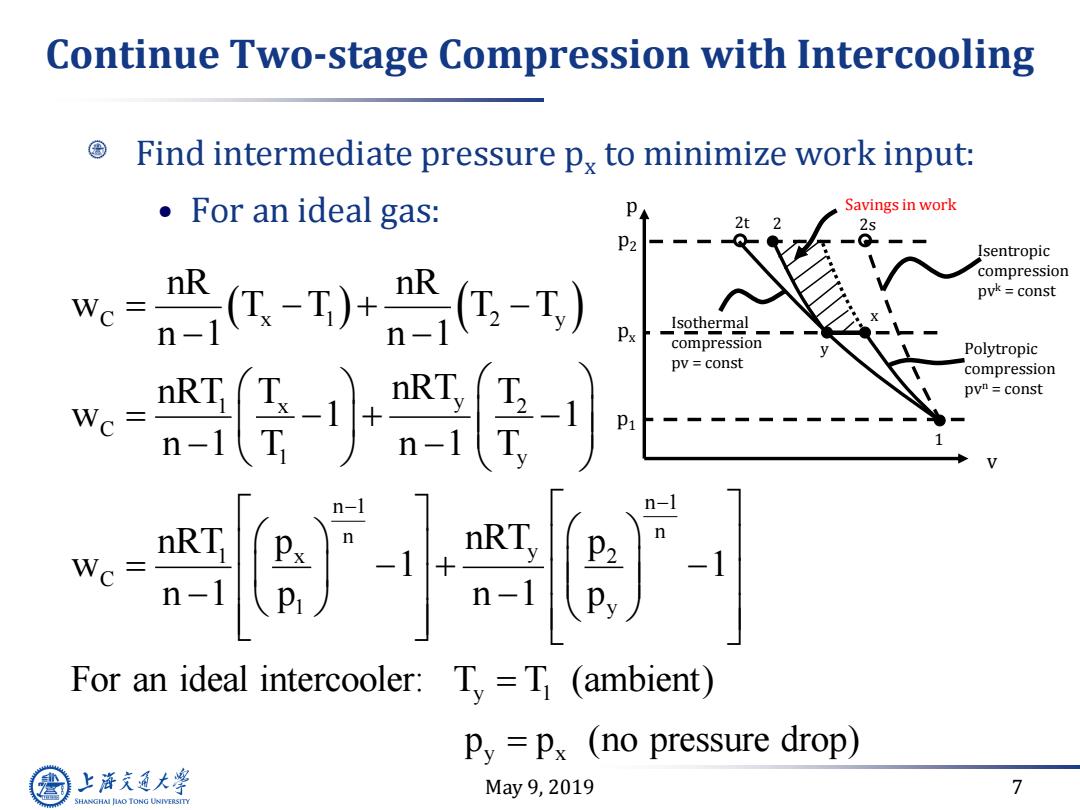
Continue Two-stage Compression with Intercooling Find intermediate pressure px to minimize work input: 。For an ideal gas: Savings in work 2t2 2s p2-- Isentropic compression -)+-T) nR pvk=const Wc= Px Isothermal compression Polytropic pv const compression pvh=const -1 P1 n- Q- For an ideal intercooler:T=T (ambient) Py =px (no pressure drop) 上游通大学 May9,2019 7 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 7 Continue Two-stage Compression with Intercooling Find intermediate pressure px to minimize work input: • For an ideal gas: C x 1 2 y 1 x 2 y C 1 y n 1 n 1 n n 1 x 2 y C 1 y y 1 y x nR nR w T T T T n 1 n 1 nRT T T nRT w 1 1 n 1 T n 1 T nRT p p nRT w 1 1 n 1 p n 1 p For an ideal intercooler: T T (ambient) p p (no pressure drop) v p p2 2t Isothermal compression pv = const p1 px 2 2s Polytropic compression pvn = const 1 y x Isentropic compression pvk = const Savings in work
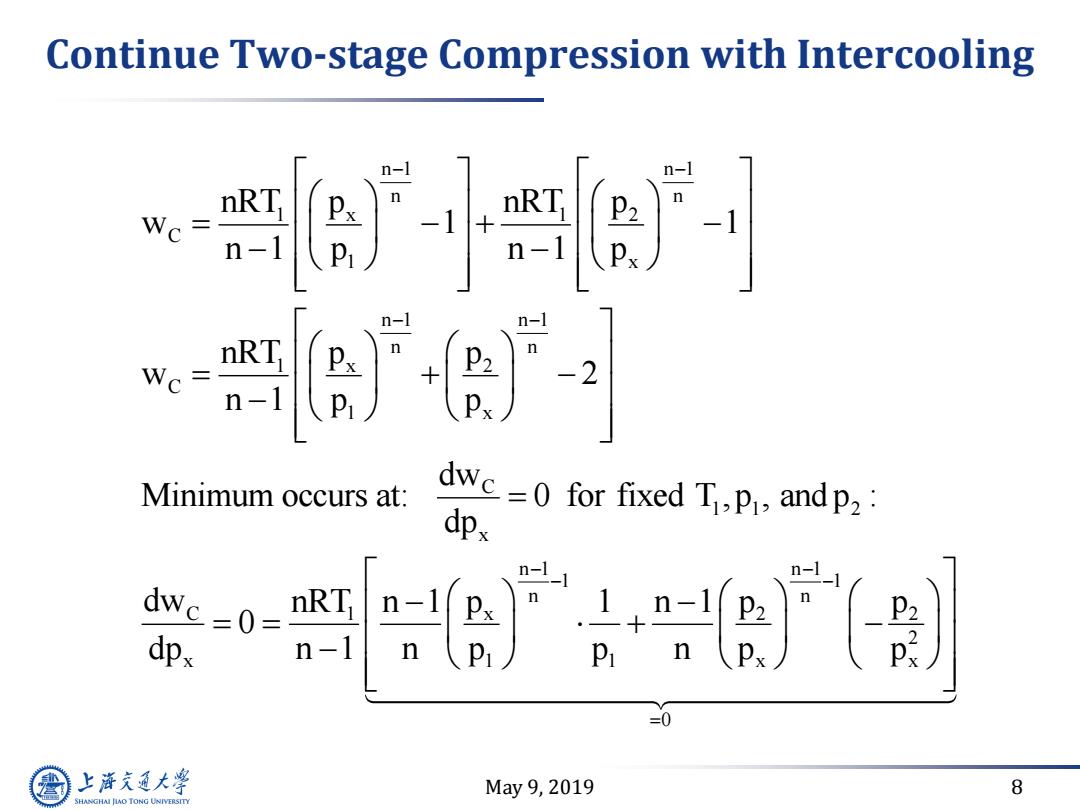
Continue Two-stage Compression with Intercooling nRT n-1 ] nRT Wc- 2 n-1 P Minimum occurs at: dwc=0for fixed T.P andp2 dpx R -1 dwc-0- RT dpx n-1 P =0 上游充通大 May9,2019 8 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 8 Continue Two-stage Compression with Intercooling n 1 n 1 n n 1 x 1 2 C 1 x n 1 n 1 n n 1 x 2 C 1 x C 1 1 2 x n 1 C 1 x x 1 nRT p nRT p w 1 1 n 1 p n 1 p nRT p p w 2 n 1 p p dw Minimum occurs at: 0 for fixed T ,p , and p : dp dw nRT p n 1 0 dp n 1 n p n 1 1 1 n n 2 2 2 1 x x 0 1 n 1 p p p n p p
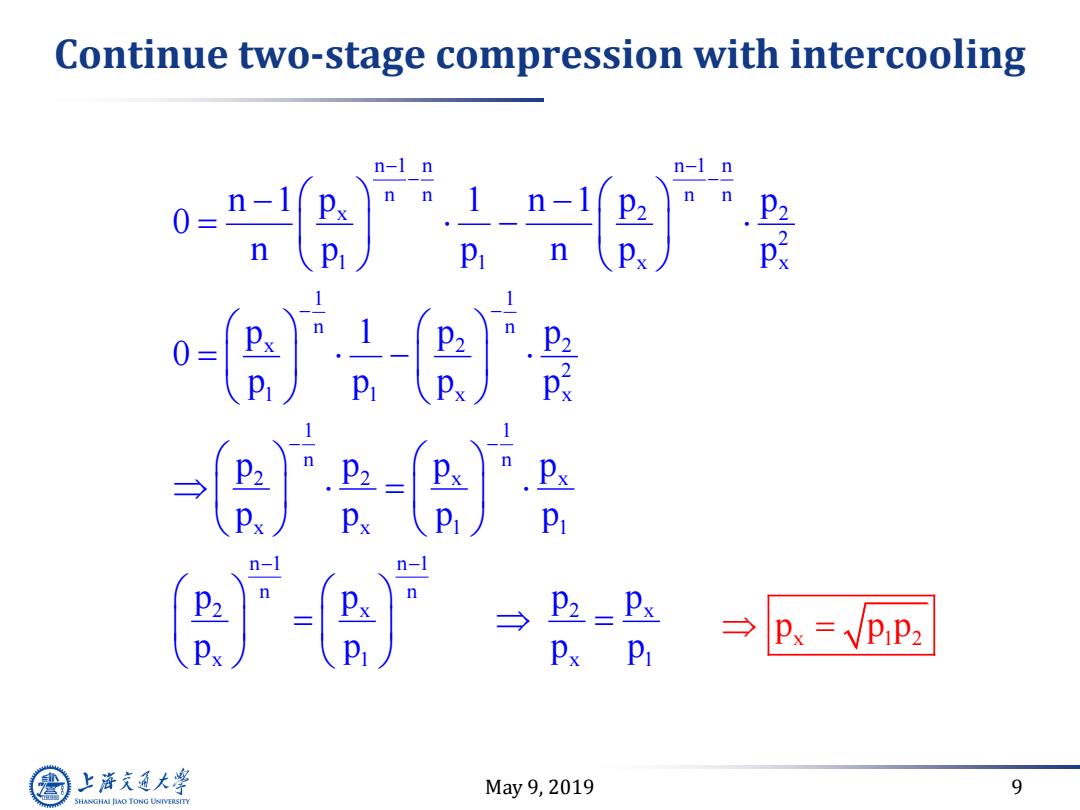
Continue two-stage compression with intercooling n-1 n -2) n-I n n n P2 P2 p Px → →px=VpP2 Px Pi 上游充通大学 May9,2019 9 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 9 Continue two-stage compression with intercooling n 1 n n 1 n n n n n x 2 2 2 1 1 x x 1 1 n n x 2 2 2 1 1 x x 1 1 n n 2 2 x x x x 1 1 n 1 n 1 n n 2 x 2 x x 1 x 1 n 1 p 1 n 1 p p 0 n p p n p p p 1 p p 0 p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p x 1 2

Continue two-stage compression with intercooling n-l n- n For dwc=0(minimum work): Px dpx T n-l Pt Savings in work 2t 25 P2 Isentropic Also, P2 T T compression pvk=const T T Px _Isothermal__ compression Polytropic pv=const compression Thus,T2=Tx and Ty =T: pvh=const P1 w-)--)-2 nR >At optimal intermediate pressure,equal work in both stages! 上游通大学 May9,2019 10 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 10 Continue two-stage compression with intercooling n 1 n 1 n n C x x 2 x 1 1 x n 1 n 2 2 x x y 1 2 x y 1 C,1 x 1 2 y C,2 dw T p p For 0 (minimum work): dp T p p p T T Also, p T T Thus, T T and T T : nR nR w T T T T w n 1 n 1 At optimal intermediate pressure, equal work in both stages!