
版像 NJUAT 南京大学 人工智能学院 SCHODL OF ARTIFICIAL INTELUGENCE,NANJING UNIVERSITY Lecture 4.Gradient Descent Method Il Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Peng Zhao zhaop@lamda.nju.edu.cn Nanjing University
Lecture 4. Gradient Descent Method II Peng Zhao zhaop@lamda.nju.edu.cn Nanjing University Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023)

Outline GD for Smooth Optimization Smooth and Convex Functions Smooth and Strongly Convex Functions Nesterov's Accelerated GD Extension to Composite Optimization Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 4.Gradient Descent Method II 2
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 4. Gradient Descent Method II 2 Outline • GD for Smooth Optimization • Smooth and Convex Functions • Smooth and Strongly Convex Functions • Nesterov’s Accelerated GD • Extension to Composite Optimization
Part 1.GD for Smooth Optimization ·Smooth and Convex Smooth and Strongly Convex Extension to Constrained Case Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 4.Gradient Descent Method II 3
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 4. Gradient Descent Method II 3 Part 1. GD for Smooth Optimization • Smooth and Convex • Smooth and Strongly Convex • Extension to Constrained Case
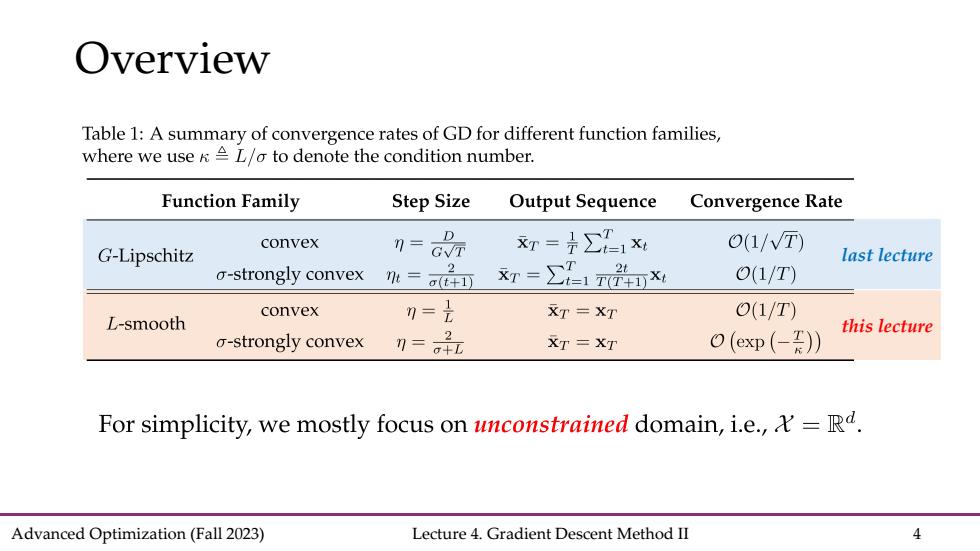
Overview Table 1:A summary of convergence rates of GD for different function families, where we use KL/o to denote the condition number. Function Family Step Size Output Sequence Convergence Rate convex 刀 xr=∑1x 0(1/T) G-Lipschitz last lecture a-strongly convex 2 m=a(t+1) xr=∑1nX O(1/T) convex 0=是 XT =XT O(1/T) L-smooth this lecture o-strongly convex 刀=品 XT =XT O(exp(-I)) For simplicity,we mostly focus on unconstrained domain,i.e.,=Rd. Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 4.Gradient Descent Method II 4
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 4. Gradient Descent Method II 4 Overview last lecture this lecture

Convex and Smooth Theorem 1.Suppose the function f:Ra>R is convex and differentiable,and also L-smooth.GD updates by x=xt-mVf(xt)with step size n=1,and then GD enjoys the following convergence guarantee: -s2-x-。 T-1 T Note:we are working on unconstrained setting and using a fixed step size tuning. Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 4.Gradient Descent Method II 5
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 4. Gradient Descent Method II 5 Convex and Smooth Note: we are working on unconstrained setting and using a fixed step size tuning
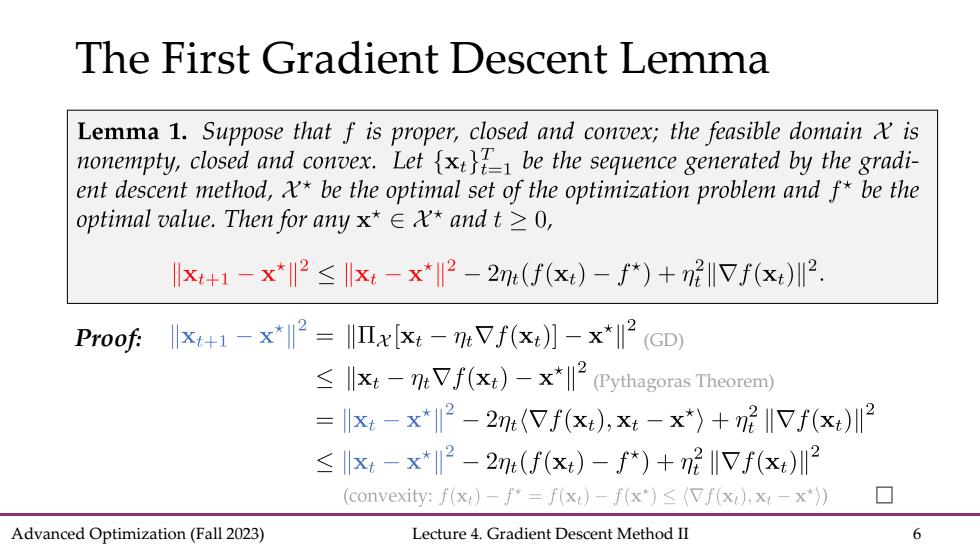
The First Gradient Descent Lemma Lemma 1.Suppose that f is proper,closed and convex;the feasible domain is nonempty,closed and convex.Letxbe the sequence generated by the gradi- ent descent method,x*be the optimal set of the optimization problem and f*be the optimal value.Then for any x*∈X*andt≥0, Ix+1-x*2≤x-x*2-2n(f(x)-f*)+m2IVf(x)川2. Proof:+x2=x[-mVf(x)-*(GD) llxt-nVf(xt)-x*2 (Pythagoras Theorem) llx:-x*ll2-2m(Vf(x:),x:-x*)+nVf(x)12 ≤川xt-x*2-2n(f(x)-f*)+m2IVf(x)川2 (convexity:f(x:)-f*=f(x)-f(x*)(Vf(x),x:-x*)) Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 4.Gradient Descent Method II 6
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 4. Gradient Descent Method II 6 The First Gradient Descent Lemma Proof: (Pythagoras Theorem) (GD)
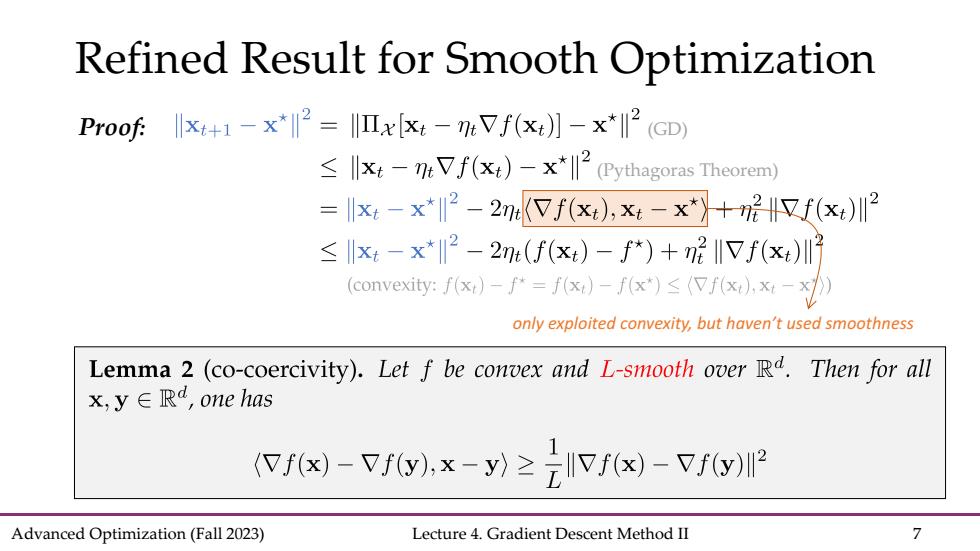
Refined Result for Smooth Optimization Proof x1-x2=Ixx:-nVf(x)]-x*l2 (GD) ≤小x4-0eVf(xt)-x*l2(Pythagoras Theorem) =xt-x*2-2eVf(x),xt-x*+呢H又f(x)2 ≤x-x*2-2m(f(x)-f*)+m2IVf(x)川7 (convexity:fx)-f=fxt)-fx*)≤(7f(xt,x-x》 only exploited convexity,but haven't used smoothness Lemma 2 (co-coercivity).Let f be convex and L-smooth over Rd.Then for all x,y∈Rd,one has (Vf(x)-Vf(y),x-y)2f(x)-Vf(y) Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 4.Gradient Descent Method II 7
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 4. Gradient Descent Method II 7 Refined Result for Smooth Optimization Proof: (Pythagoras Theorem) (GD) only exploited convexity, but haven’t used smoothness

Co-coercive Operator Lemma 2 (co-coercivity).Let f be convex and L-smooth over Rd.Then for all x,y∈Rd,one has (Vf(x)-Vf(y).x-y)zlVf(x)-Vf(y) Definition 1(co-coercive operator).An operator C is called B-co-coercive(or B-inverse--strongly monotone,,forB>0,if for any x,y∈孔, (Cx-C,x-≥3Cx-CI2. The co-coercive condition is relatively standard in operator splitting literature and variational inequalities. Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 4.Gradient Descent Method II 8
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 4. Gradient Descent Method II 8 Co-coercive Operator The co-coercive condition is relatively standard in operator splitting literature and variational inequalities
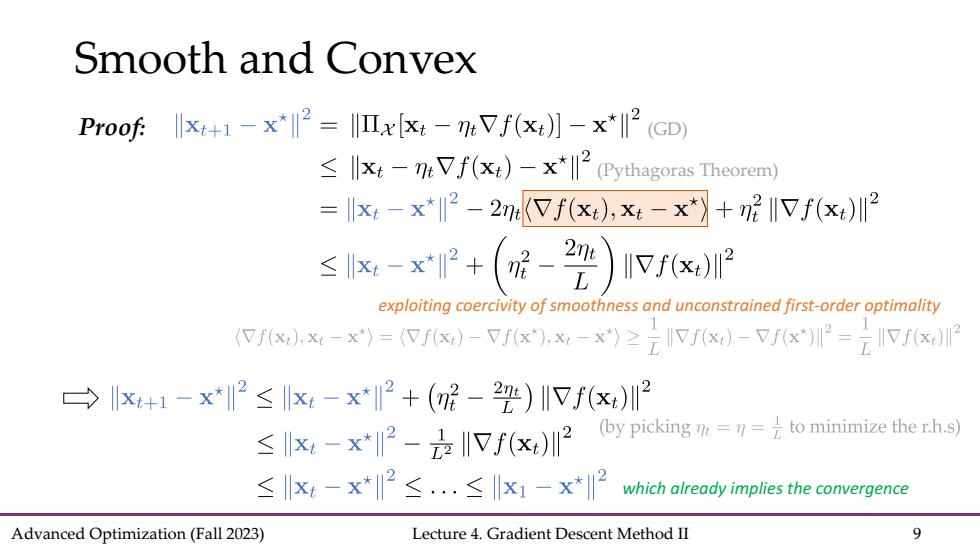
Smooth and Convex Proof:-x=Ix [:-mVf()]-x*2 (GD) llxt-nt Vf(xt)-x*(Pythagoras Theorem) =xt-x*2-2meVf(x),x-x*》+n呢I7f(x)I2 ≤x-xP+(-2) Vf(x)I2 exploiting coercivity of smoothness and unconstrained first-order optimality (fx,x4-x*)=(fx)-Vf(x),x-x)≥元IVf6x)-Vf6x*)川2=Vf(x)2 →x+1-x*2≤x-x*2+(2-22)I川Vf(x)2 ≤x-x*2-2IVf(x)2 (by picking=刀=是to minimize ther.h.s) ≤x4-x*2≤.≤x1-x*2 which already implies the convergence Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 4.Gradient Descent Method II 9
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 4. Gradient Descent Method II 9 Smooth and Convex Proof: (Pythagoras Theorem) (GD) exploiting coercivity of smoothness and unconstrained first-order optimality which already implies the convergence
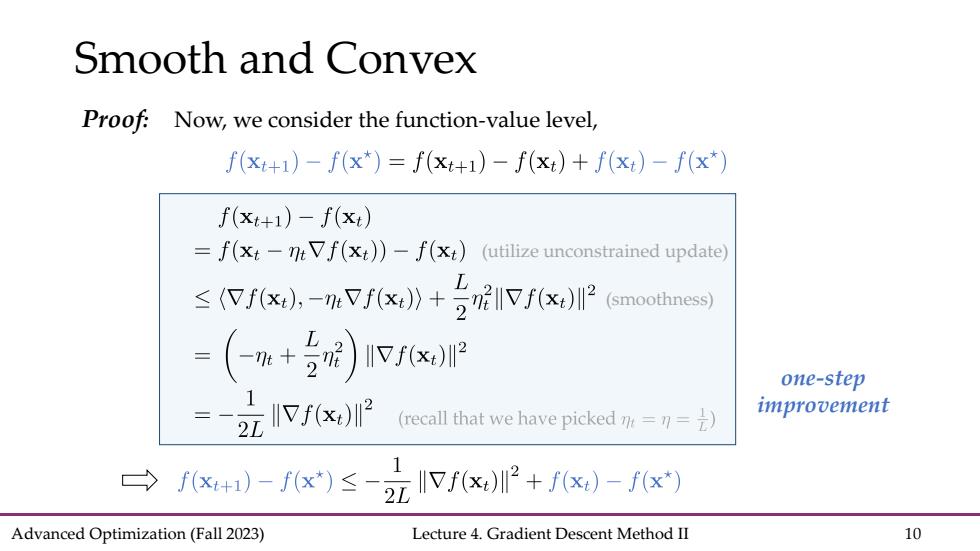
Smooth and Convex Proof:Now,we consider the function-value level, f(x+1)-f(x*)=f(xt+1)-f(xt)+f(x)-f(x*) f(x++1)-f(x) =f(xt-ntVf(xt))-f(xt)(utilize unconstrained update) ≤fx,-Vfx》+5呢IVf0x (smoothness) =(-e+)Ifx训e one-step 2元fx2 (recall that we have picked m=n=1) improvement f-fx≤克fP+)-fx Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 4.Gradient Descent Method II 10
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 4. Gradient Descent Method II 10 Smooth and Convex Proof: Now, we consider the function-value level, one-step improvement (smoothness) (utilize unconstrained update)