
Organic Chemistry with BiologicalApplications,3rEdition John McMurry Chapter 09 Aromatic Compounds Aromatic rings are a common part of many biological structures and are particularty important in the chemistry of nucleic acids and several amino acids. How and why aromatic compounds are different from such apparently related compounds as alkenes
Chapter 09 Aromatic Compounds Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3 rd Edition John McMurry Aromatic rings are a common part of many biological structures and are particularly important in the chemistry of nucleic acids and several amino acids. How and why aromatic compounds are different from such apparently related compounds as alkenes

JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 9 Aromatic Compounds Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications Homework:P294:9.15:9.16P302:9.20 P307:9.24:P318e:9.56:P318i:9.74:9.81 Key Notes Aromaticity;Resonance Structure;Huckel rulej Electrophilic substitutions;Activating group;
Key Notes Aromaticity; Resonance Structure; Hückel rule; Electrophilic substitutions; Activating group; Homework: P294: 9.15; 9.16; P302: 9.20; P307:9.24; P318e:9.56; P318i: 9.74; 9.81;
Main Contents Structure Stability Aromaticity reactivity Preparation of Ar compounds Electrophilic substitutions Effects of substituents on E.S. Synthesis of mono-,di-and tri-substituted benzenes ■Other reactions Oxidation and reduction Nucleophilic Substitution
Main Contents ◼Structure & Stability ◼Aromaticity & reactivity ◼Preparation of Ar compounds ◼Electrophilic substitutions ◼Effects of substituents on E.S. ✓Synthesis of mono-, di- and tri-substituted benzenes ◼Other reactions ✓Oxidation and reduction ✓Nucleophilic Substitution
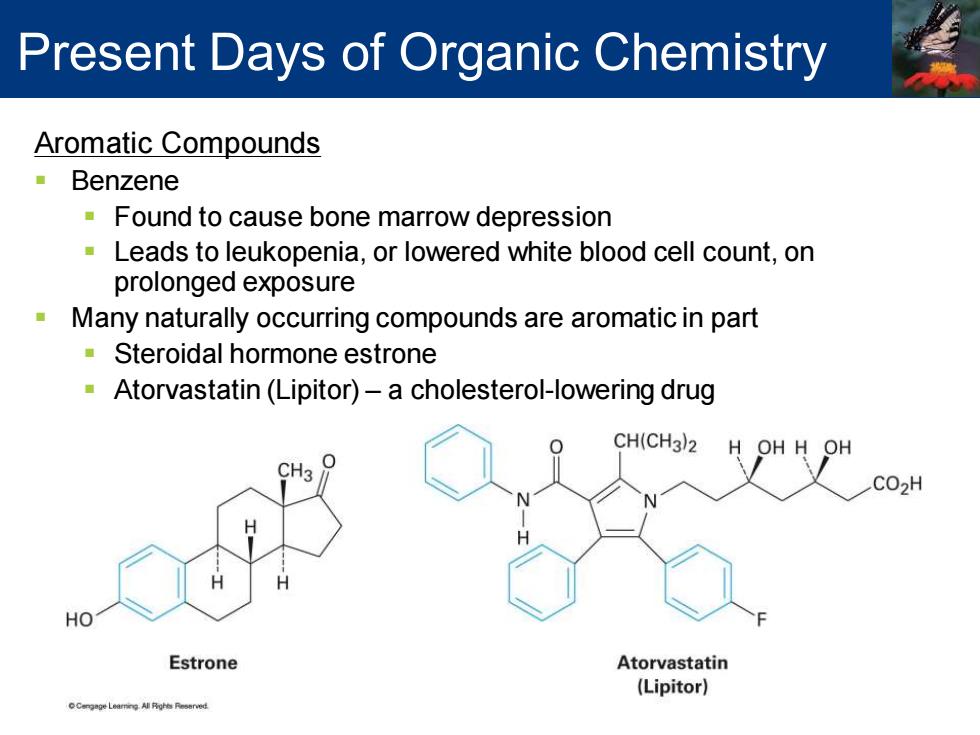
Present Days of Organic Chemistry Aromatic Compounds Benzene Found to cause bone marrow depression Leads to leukopenia,or lowered white blood cell count,on prolonged exposure Many naturally occurring compounds are aromatic in part Steroidal hormone estrone Atorvastatin (Lipitor)-a cholesterol-lowering drug CH(CH3)2 H OH H OH CH3 CO2H HO Estrone Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
Aromatic Compounds ▪ Benzene ▪ Found to cause bone marrow depression ▪ Leads to leukopenia, or lowered white blood cell count, on prolonged exposure ▪ Many naturally occurring compounds are aromatic in part ▪ Steroidal hormone estrone ▪ Atorvastatin (Lipitor) – a cholesterol-lowering drug Present Days of Organic Chemistry
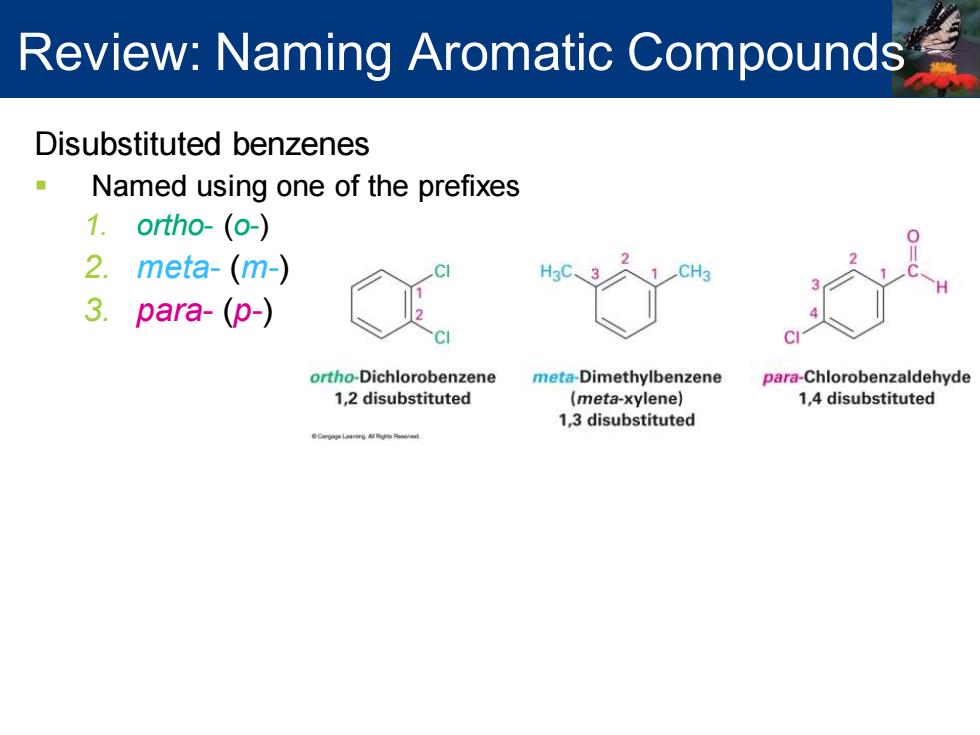
Review:Naming Aromatic Compounds Disubstituted benzenes Named using one of the prefixes 1.ortho-(o-) 2.meta-(m-) CH3 3.para-(p-) ortho-Dichlorobenzene meta-Dimethylbenzene para-Chlorobenzaldehyde 1,2 disubstituted (meta-xylene) 1,4 disubstituted 1,3 disubstituted
Disubstituted benzenes ▪ Named using one of the prefixes 1. ortho- (o-) 2. meta- (m-) 3. para- (p-) Review: Naming Aromatic Compounds
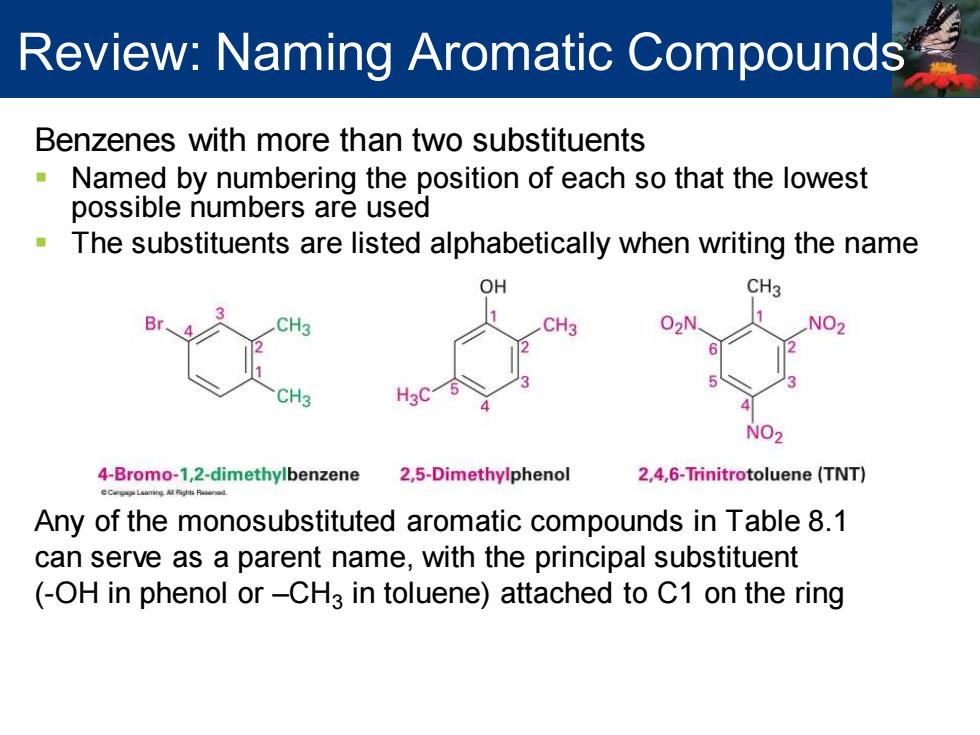
Review:Naming Aromatic Compounds Benzenes with more than two substituents Named by numbering the position of each so that the lowest possible numbers are used The substituents are listed alphabetically when writing the name OH CH3 CH3 02N CH H3C NO2 4-Bromo-1,2-dimethylbenzene 2,5-Dimethylphenol 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene(TNT) Any of the monosubstituted aromatic compounds in Table 8.1 can serve as a parent name,with the principal substituent (-OH in phenol or-CH3 in toluene)attached to C1 on the ring
Benzenes with more than two substituents ▪ Named by numbering the position of each so that the lowest possible numbers are used ▪ The substituents are listed alphabetically when writing the name Any of the monosubstituted aromatic compounds in Table 8.1 can serve as a parent name, with the principal substituent (-OH in phenol or –CH3 in toluene) attached to C1 on the ring Review: Naming Aromatic Compounds

Early Days of Organic Chemistry Aromatic Compounds Formerly used to describe fragrant substances such as benzaldehyde (from cherries,peaches,and almonds), toluene (from Tolu balsam),and benzene (from coal distillate) CH3 Benzene Benzaldehyde Toluene Now used to refer to the class of compounds that contain six-membered benzene-like rings with three double bonds
Aromatic Compounds ▪ Formerly used to describe fragrant substances such as benzaldehyde (from cherries, peaches, and almonds), toluene (from Tolu balsam), and benzene (from coal distillate) ▪ Now used to refer to the class of compounds that contain six-membered benzene-like rings with three double bonds Early Days of Organic Chemistry

Sec 1 Structure and Stability -Discovery of Benzene -Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. -Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to be CeHe. -Other related compounds with low C:H ratios had a pleasant smell,so they were classified as aromatic
Sec 1 Structure and Stability ▪Discovery of Benzene ▪ Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. ▪ Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to be C6H6 . ▪ Other related compounds with low C:H ratios had a pleasant smell, so they were classified as aromatic

AdGif-UNREGIST Kekule Structure -Proposed in 1866 by Friedrich Kekule, shortly after multiple bonds were suggested. -Failed to explain existence of only one isomer of 1.2-dichlorobenzene. all C-C bond double bond lengths 1.397A 1.34A single bond 1.48A resonance representation bond order=l片 butadiene combined representation Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
KekuléStructure ▪Proposed in 1866 by Friedrich Kekulé, shortly after multiple bonds were suggested. ▪Failed to explain existence of only one isomer of 1,2-dichlorobenzene
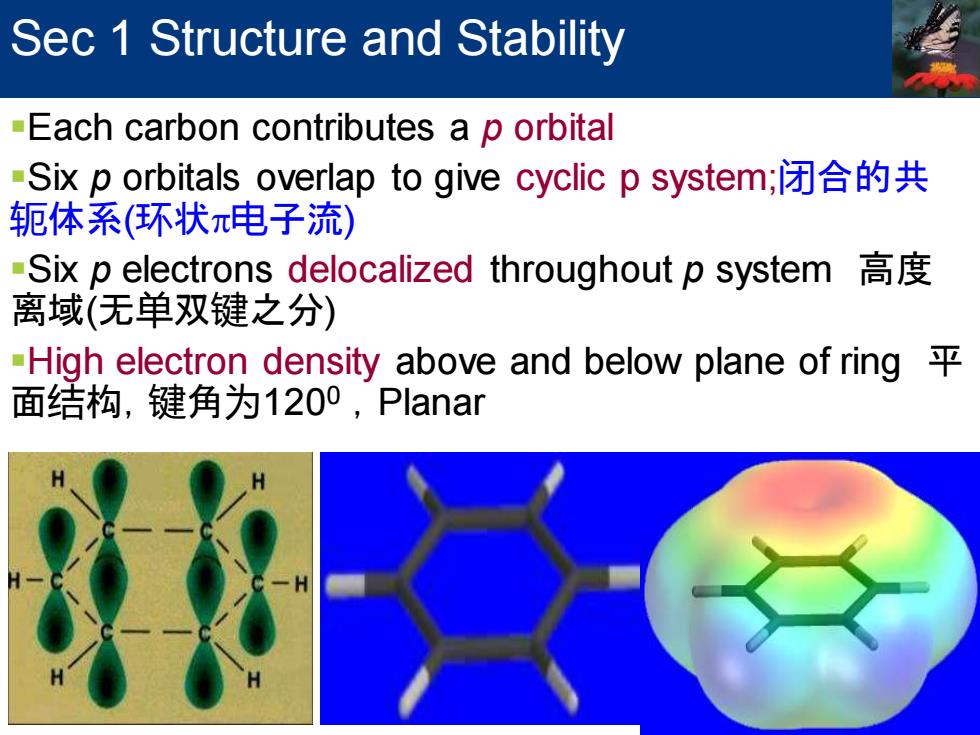
Sec 1 Structure and Stability -Each carbon contributes a p orbital Six p orbitals overlap to give cyclic p system;闭合的共 轭体系(环状π电子流) -Six p electrons delocalized throughout p system 离域(无单双键之分) -High electron density above and below plane of ring 面结构,键角为1200,Planar
Sec 1 Structure and Stability ▪Each carbon contributes a p orbital ▪Six p orbitals overlap to give cyclic p system;闭合的共 轭体系(环状电子流) ▪Six p electrons delocalized throughout p system 高度 离域(无单双键之分) ▪High electron density above and below plane of ring 平 面结构,键角为1200 ,Planar