
有机化学⊙RGAnIc cⅫEMISTRY 盖饼:王德儒8709282901 理学院寇化素理科,2层206 Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 08 09 AlRenes Key Notes Electrophile;Electrophilic additionj Carbocation stability;Conjugated dienes Homework.:8-238-298-349-30:9-31b)(c)(P274)
Chapter 08 & 09 Alkenes Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Key Notes Electrophile; Electrophilic addition; Carbocation stability; Conjugated dienes 有机化学ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 主讲:王俊儒 87092829(O) 理学院应化系理科楼2层C206 Homework:8-23; 8-29; 8-34; 9-30; 9-31(b), (c)(P274)

Content ☐Preparation ☐Reactions of alkenes -Electrophilic addition -Carbocation stabilization -Free-Radical Addition of HBr -Reduction and oxidation -Allylic halogenation ☐Conjugated dienes
Content ◼Preparation ◼Reactions of alkenes ◼Electrophilic addition ◼Carbocation stabilization ◼Free-Radical Addition of HBr ◼Reduction and oxidation ◼Allylic halogenation ◼Conjugated dienes
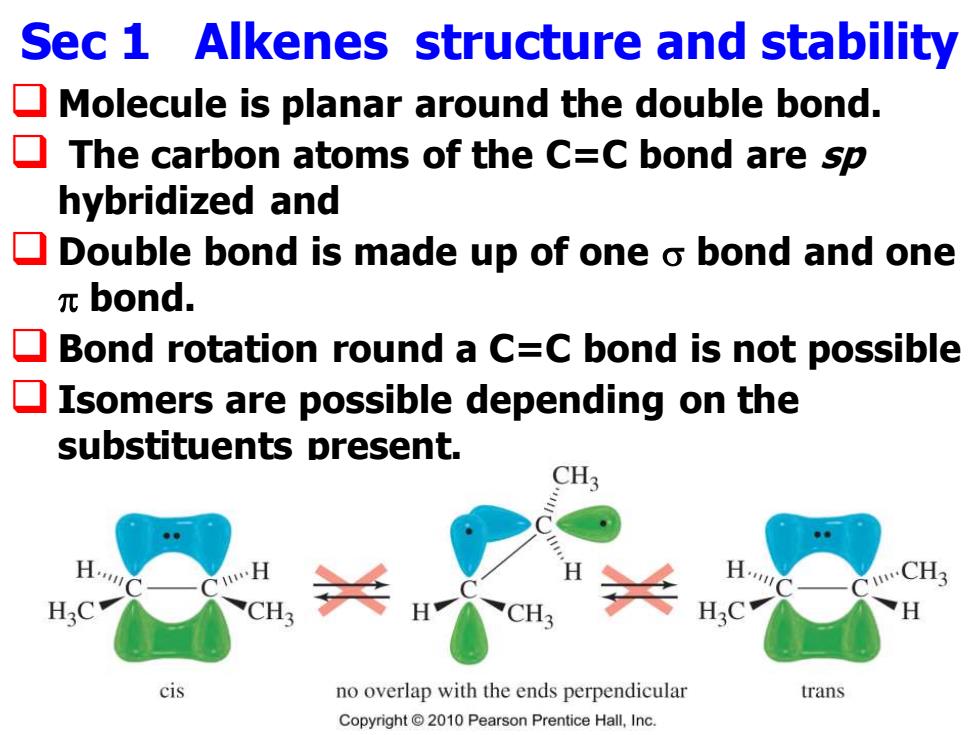
Sec 1 Alkenes structure and stability Molecule is planar around the double bond. The carbon atoms of the C=C bond are sp hybridized and Double bond is made up of one o bond and one πbond. Bond rotation round a C=C bond is not possible Isomers are possible depending on the substituents present. CH3 H. H. CH3 H3C cis no overlap with the ends perpendicular trans Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Sec 1 Alkenes structure and stability ❑ Molecule is planar around the double bond. ❑ The carbon atoms of the C=C bond are sp hybridized and ❑ Double bond is made up of one bond and one bond. ❑ Bond rotation round a C=C bond is not possible ❑ Isomers are possible depending on the substituents present
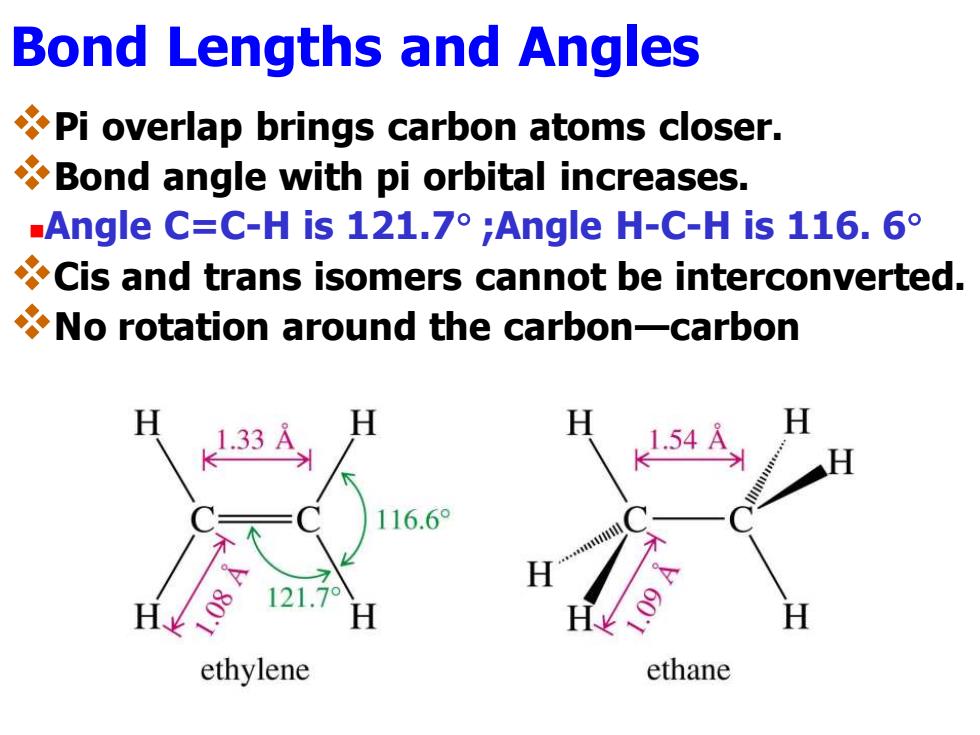
Bond Lengths and Angles Pi overlap brings carbon atoms closer. Bond angle with pi orbital increases. .Angle C:=C-His121.7°;Angle H-C-His116.6° Cis and trans isomers cannot be interconverted. No rotation around the carbon-carbon 1.33 16.6° ethylene ethane
Bond Lengths and Angles ❖Pi overlap brings carbon atoms closer. ❖Bond angle with pi orbital increases. ◼Angle C=C-H is 121.7 ;Angle H-C-H is 116. 6 ❖Cis and trans isomers cannot be interconverted. ❖No rotation around the carbon—carbon
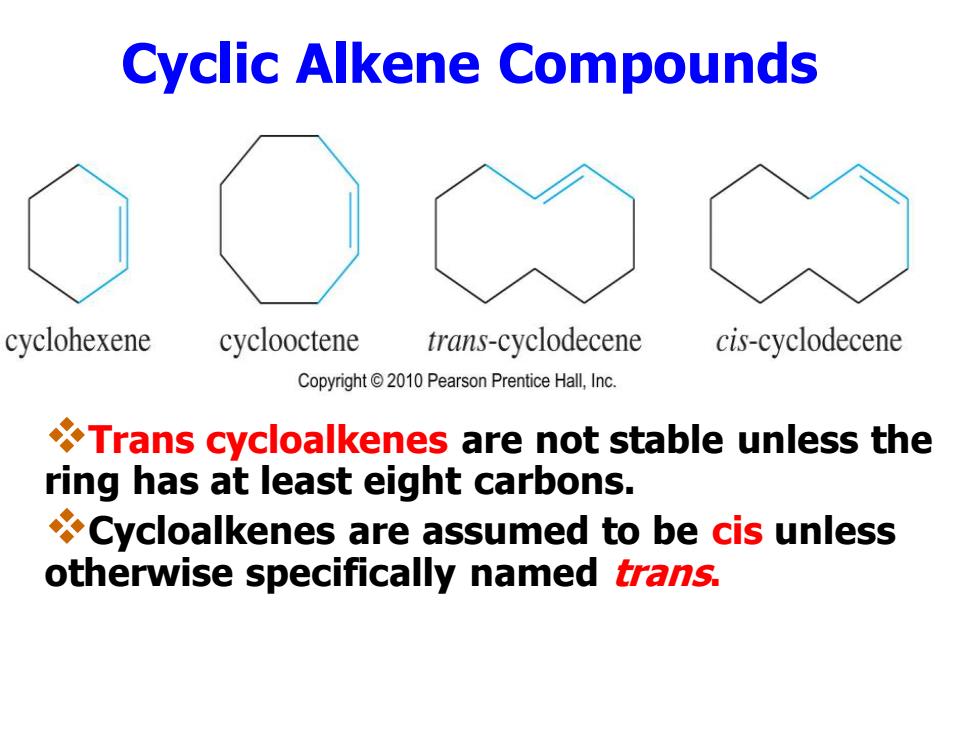
Cyclic Alkene Compounds cyclohexene cyclooctene trans-cyclodecene cis-cyclodecene Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Trans cycloalkenes are not stable unless the ring has at least eight carbons. Cycloalkenes are assumed to be cis unless otherwise specifically named trans
Cyclic Alkene Compounds ❖Trans cycloalkenes are not stable unless the ring has at least eight carbons. ❖Cycloalkenes are assumed to be cis unless otherwise specifically named trans
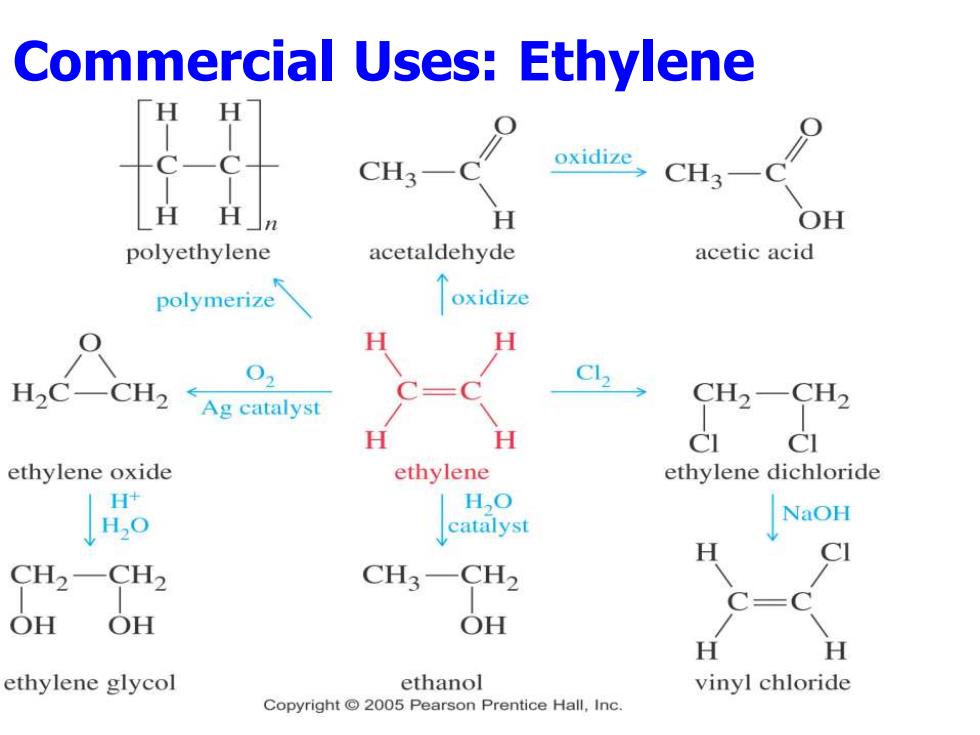
Commercial Uses:Ethylene H H CH3- oxidize CH3- H H」n OH polyethylene acetaldehyde acetic acid polymerize oxidize H H H2CCH2←Ag catalyst C12 CH2-CH2 H H CI ethylene oxide ethylene ethylene dichloride H+ H,O HO NaOH catalyst CI CH2-CH2 CH3-CH2 OH OH OH H ethylene glycol ethanol vinyl chloride Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Commercial Uses: Ethylene
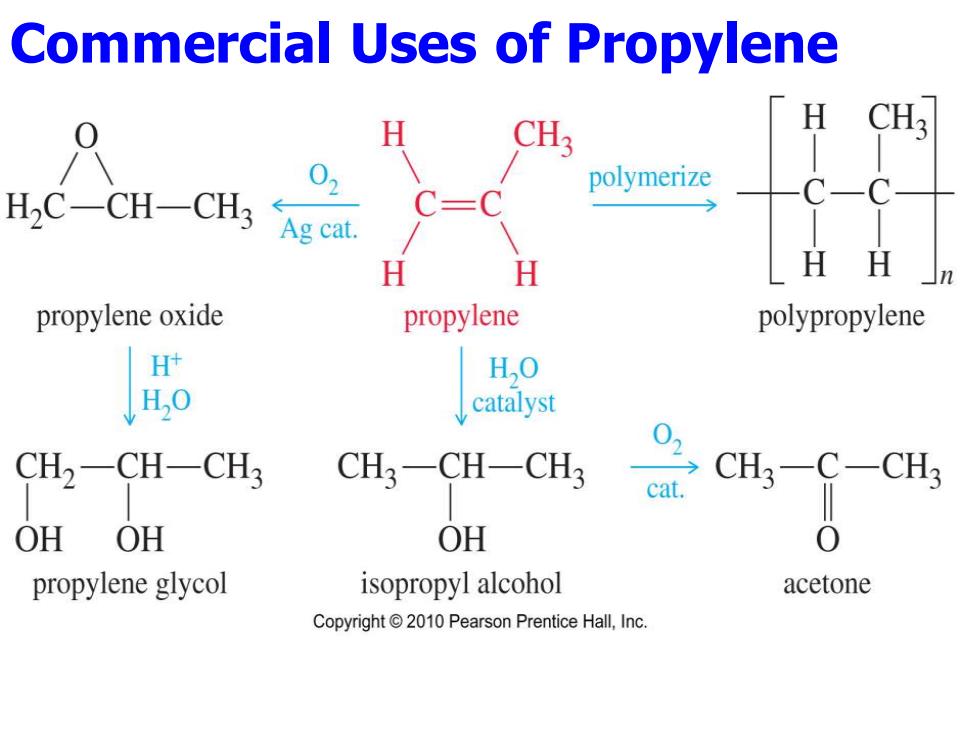
Commercial Uses of Propylene H 02 HC-CH-CH3 Ag cat polymerize H H HH propylene oxide propylene polypropylene H H,O H,0 catalyst CH2-CH-CH3 CH3一CH-CH cat. CH3-C-CH3 OH OH OH 0 propylene glycol isopropyl alcohol acetone Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Commercial Uses of Propylene
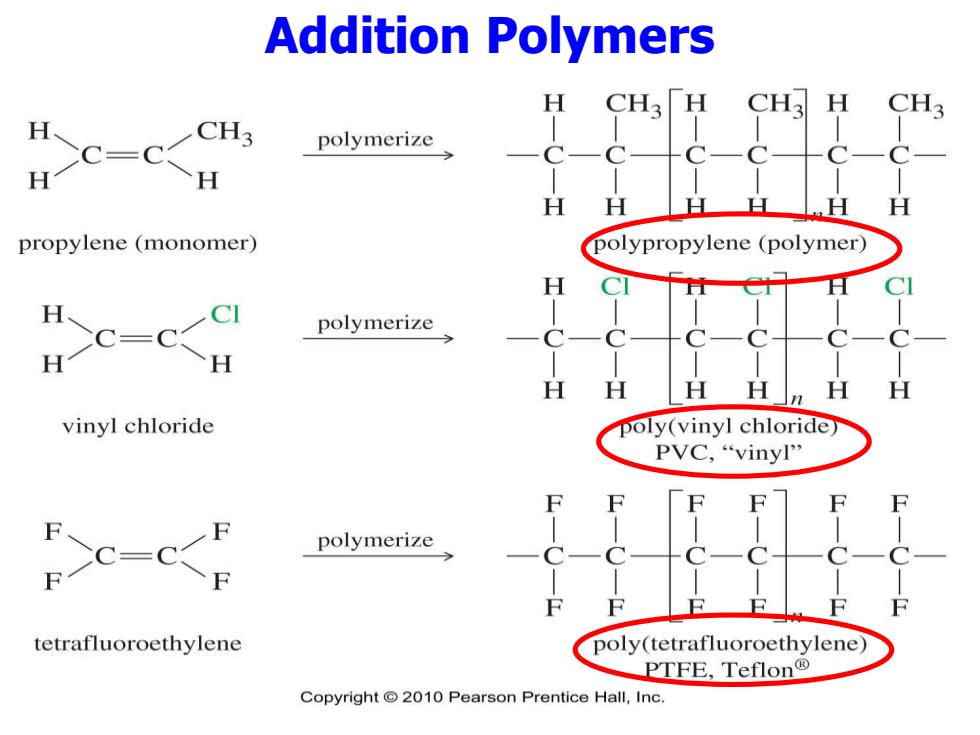
Addition Polymers H CH3「H CH3 H CH3 CH3 H CC-CCH polymerize H H propylene(monomer) polypropylene (polymer) H C=C polymerize H H H n vinyl chloride poly(vinyl chloride PVC,“vinyl'' polymerize tetrafluoroethylene poly(tetrafluoroethylene) PTFE,Teflon® Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Addition Polymers
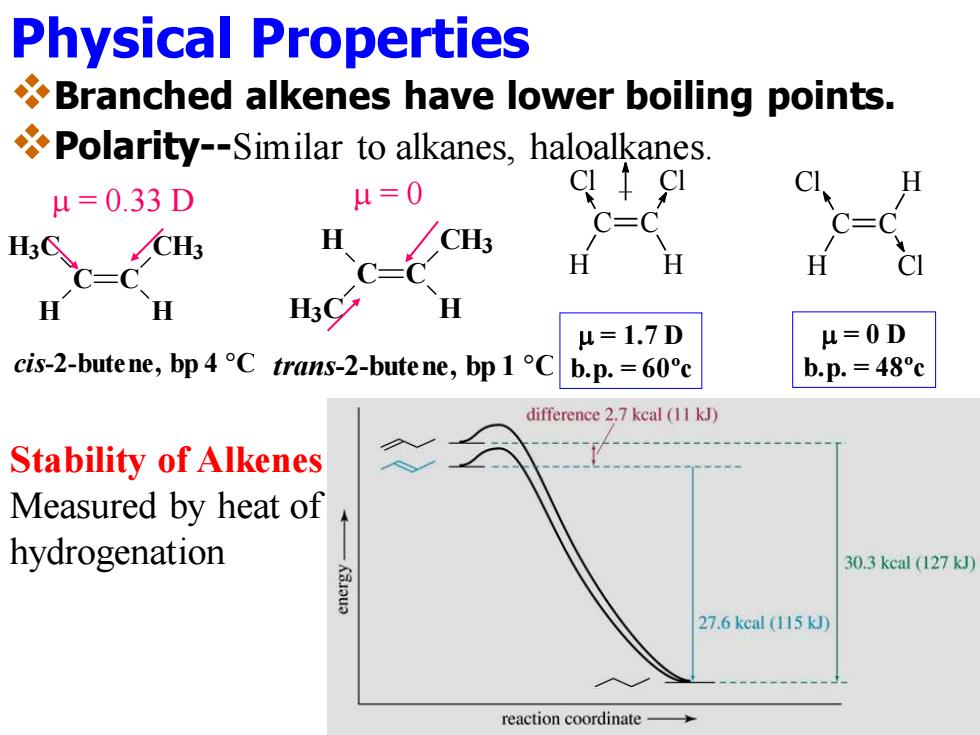
Physical Properties Branched alkenes have lower boiling points. Polarity--Similar to alkanes,haloalkanes. u=0 H u=0.33D C=C H CH3 C=C H H 人交 H H u=1.7D H=0D cis-2-butene,bp 4 C trans-2-butene,bp 1 Cb.p.=60c b.p.=48c difference 2.7 kcal (11 kJ) Stability of Alkenes Measured by heat of hydrogenation 30.3 kcal (127 kJ) 27.6kcal(115kJ) reaction coordinate
Physical Properties ❖Branched alkenes have lower boiling points. ❖Polarity--Similar to alkanes, haloalkanes. Cl C H C H Cl Cl C H C Cl H m = 1.7 D b.p. = 60ºc m = 0 D b.p. = 48ºc m = 0.33 D cis-2-butene, bp 4 °C C C H H3C H CH3 m = 0 trans-2-butene, bp 1 °C C C H H H3C CH3 Stability of Alkenes Measured by heat of hydrogenation
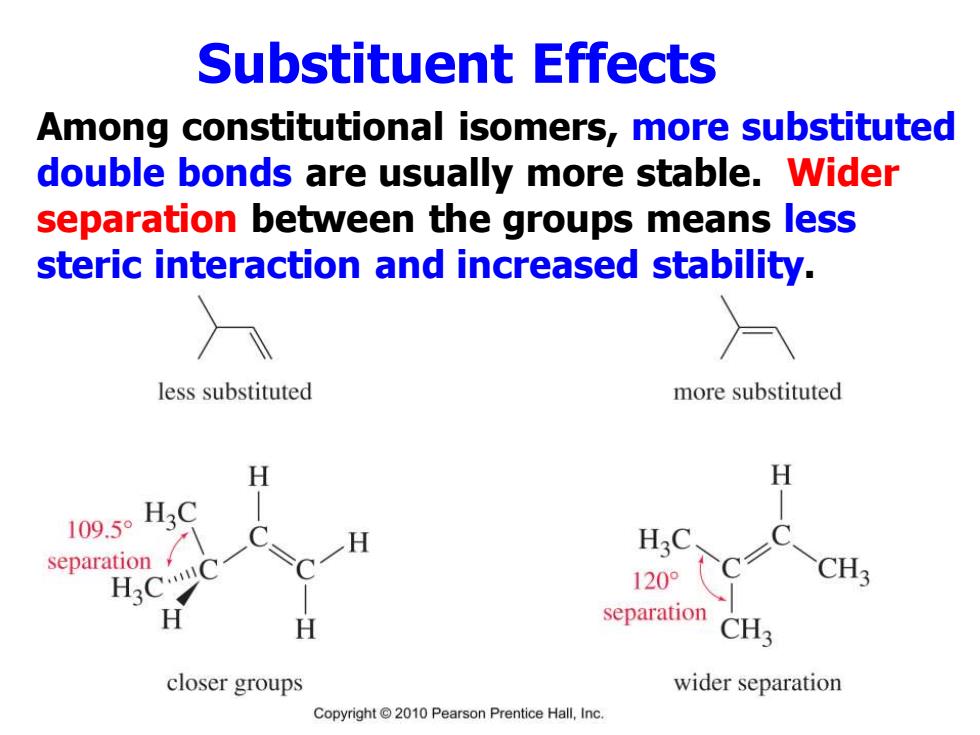
Substituent Effects Among constitutional isomers,more substituted double bonds are usually more stable.Wider separation between the groups means less steric interaction and increased stability. less substituted more substituted H H 109.50H3C separation 120° CH3 separation CH3 closer groups wider separation Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Substituent Effects Among constitutional isomers, more substituted double bonds are usually more stable. Wider separation between the groups means less steric interaction and increased stability