Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 19 Aldehydes and Ketones http://www.study-organic-chemistry.com/
Chapter 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. http://www.study-organic-chemistry.com/

自秋转大好 Content Carbonyl Structure Properties Preparation >Functional group transformations >Carbon-carbon bond formation >C-C Bond cleavage Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones ●C=O ●o-H,a-C
Content ◼Carbonyl Structure & Properties ◼Preparation ➢Functional group transformations ➢Carbon-carbon bond formation ➢C-C Bond cleavage ◼Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones ⚫C=O ⚫-H, - C
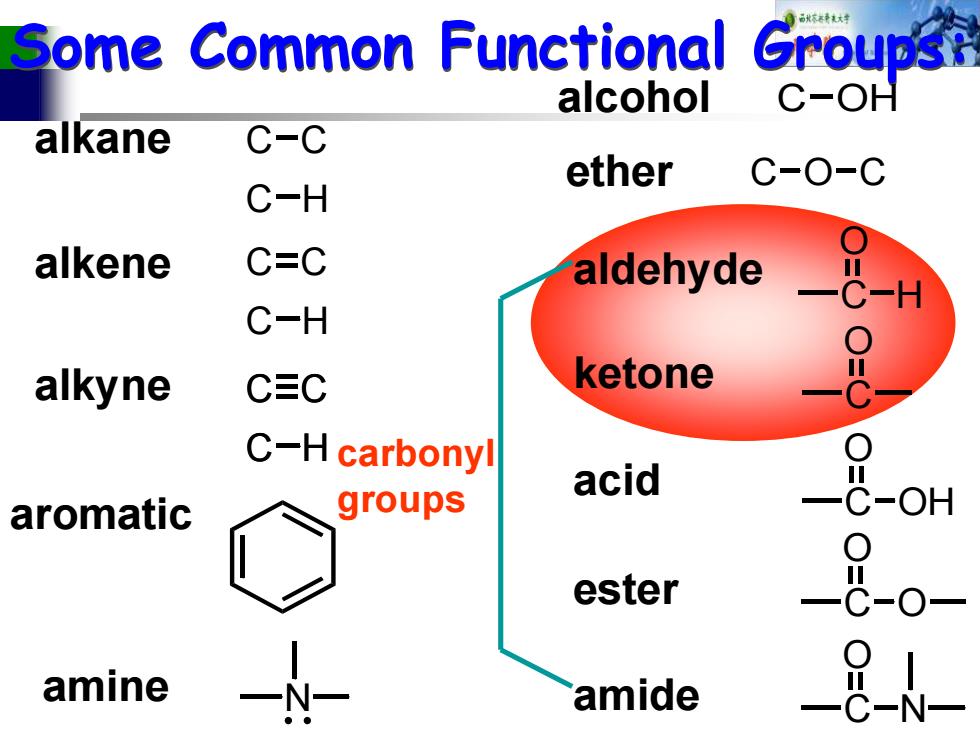
Some Common Functional Groupsi alcohol C-OH alkane C-C ether C-O-C C-H alkene C=C aldehyde C-H alkyne C三C ketone C-H carbonyl acid aromatic groups OH ester amine amide N
Some Common Functional Groups: C C C H alkane alkene C C C H alkyne C C C H C C C H aromatic alcohol C OH ether C O C C O H aldehyde C O ketone C O OH acid C O ester O C O N amide N amine carbonyl groups

Carbonyl Compounds TABLE 18-1 Some Common Classes of Carbonyl Compounds Class General Formula Class General Formula ketones R-C-R aldehydes carboxylic acids OH acid chlorides esters R -O-R amides Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Carbonyl Compounds
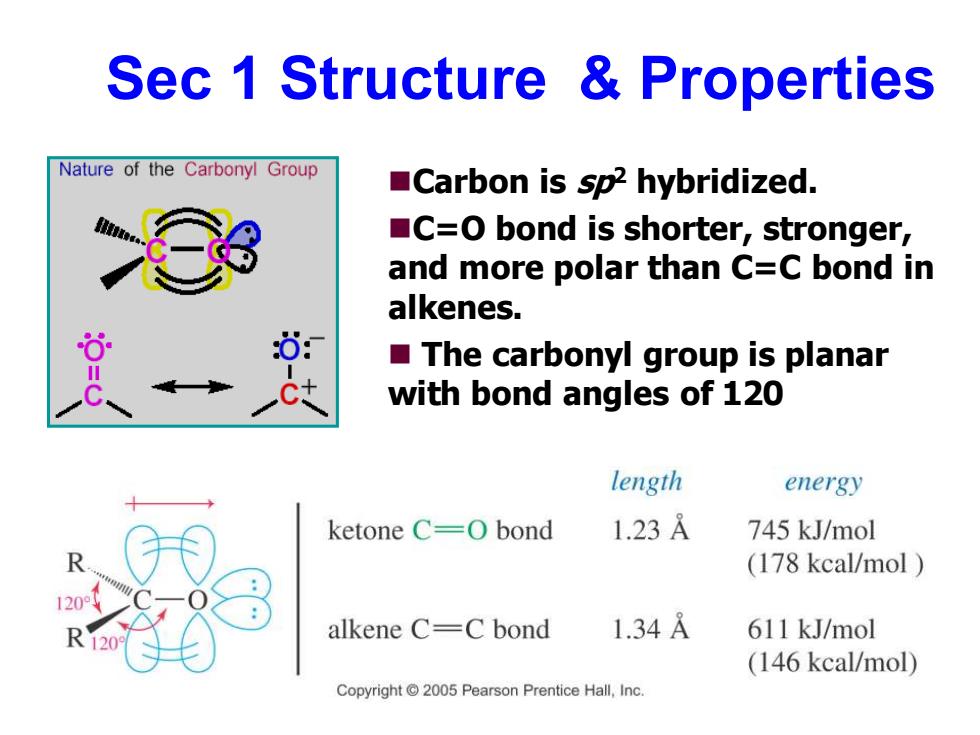
Sec 1 Structure Properties Nature of the Carbonyl Group Carbon is sp2 hybridized. C=O bond is shorter,stronger, and more polar than C=C bond in alkenes. The carbonyl group is planar with bond angles of 120 length energy ketone C=O bond 1.23A 745 kJ/mol (178 kcal/mol alkene C=C bond 1.34A 611 kJ/mol (146 kcal/mol) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Sec 1 Structure & Properties ◼Carbon is sp2 hybridized. ◼C=O bond is shorter, stronger, and more polar than C=C bond in alkenes. ◼ The carbonyl group is planar with bond angles of 120
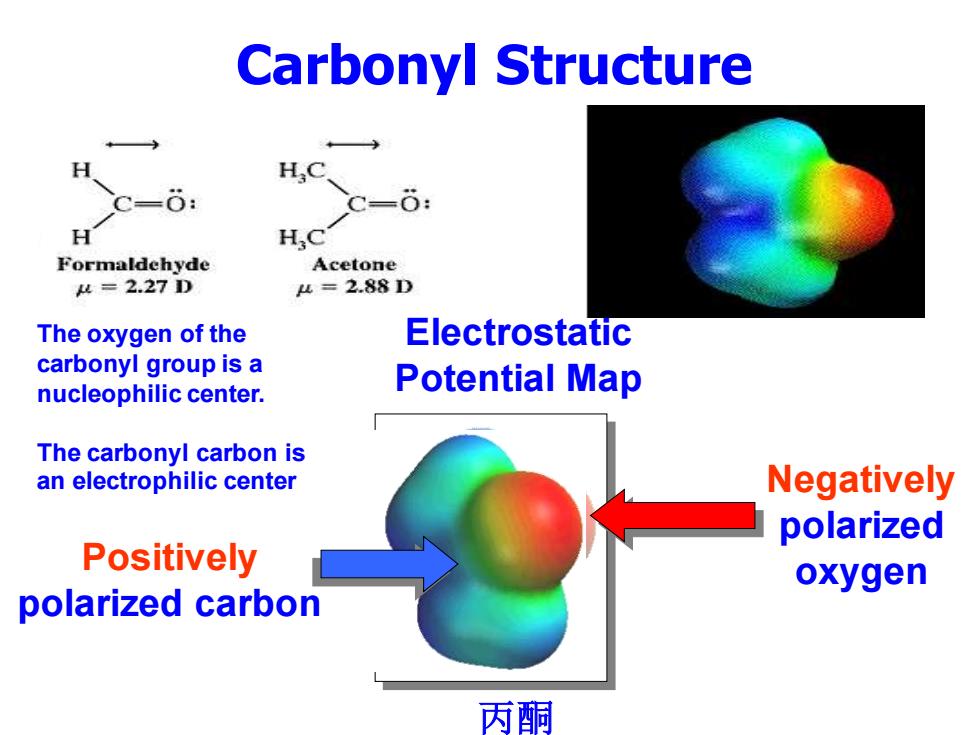
Carbonyl Structure H,C c=6: H Formaldehyde Acetone 4=2.27D 4=2.88D The oxygen of the Electrostatic carbonyl group is a nucleophilic center. Potential Map The carbonyl carbon is an electrophilic center Negatively polarized Positively oxygen polarized carbon 丙酮
Carbonyl Structure 丙酮 Electrostatic Potential Map Positively polarized carbon Negatively polarized oxygen The oxygen of the carbonyl group is a nucleophilic center. The carbonyl carbon is an electrophilic center
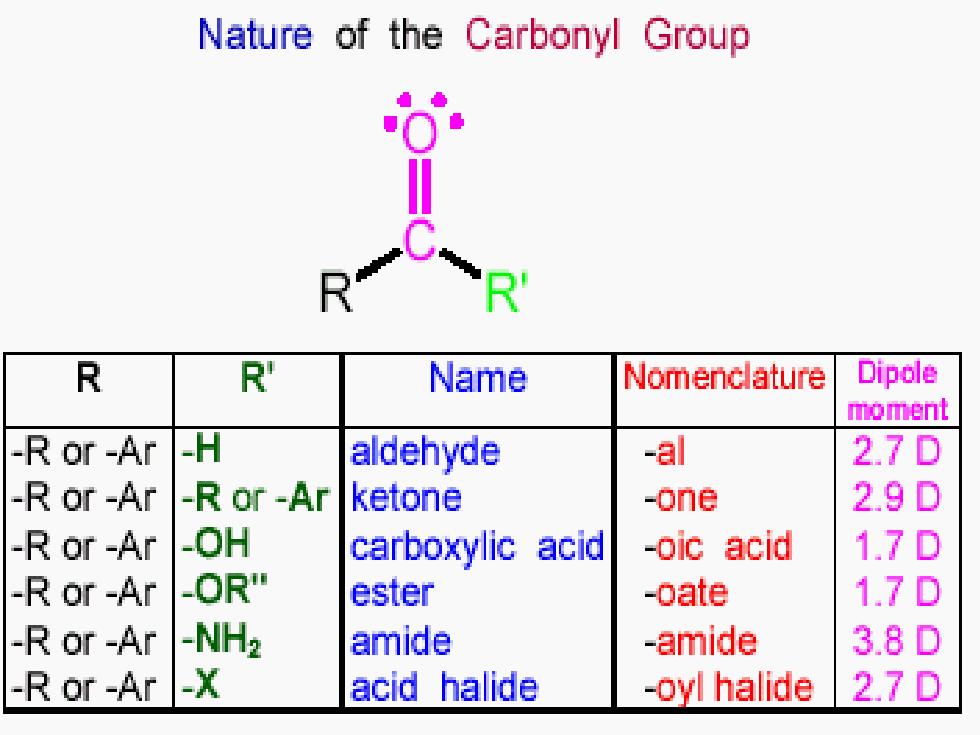
Nature of the Carbonyl Group R R Name Nomenclature Dipole moment -R or -Ar H aldehyde -al 2.7D -R or -Ar -R or-Ar ketone -one 2.9D -R or-Ar OH carboxylic acid -oic acid 1.7D -R or-Ar -OR" ester -oate 1.7D -R or-Ar -NH2 amide -amide 3.8D -R or-Ar -X acid halide -oyl halide 2.7D
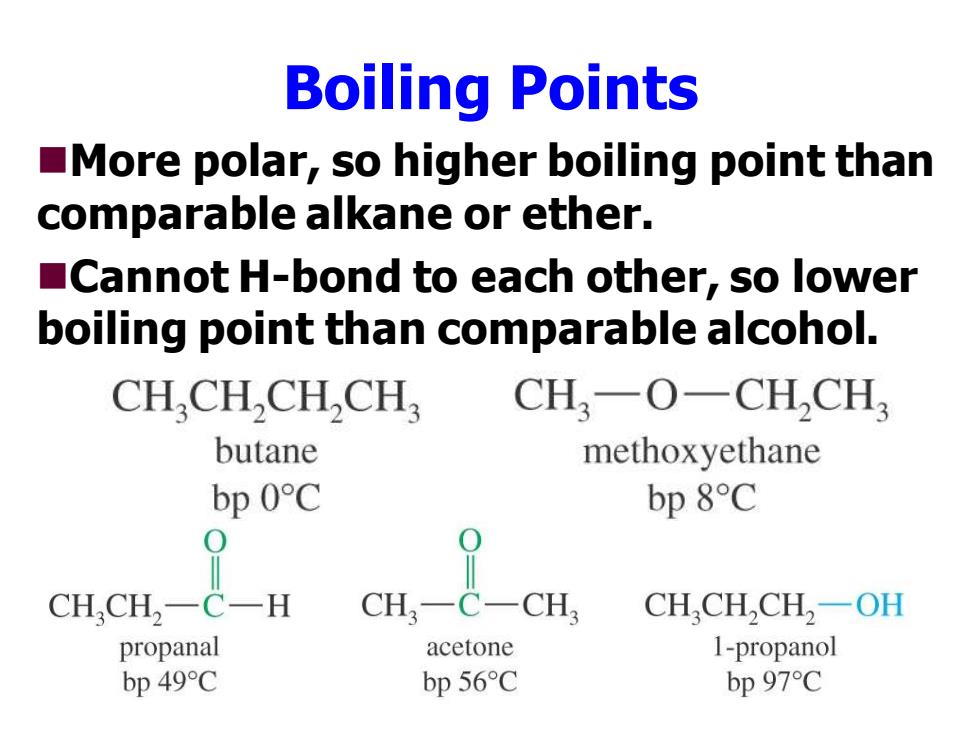
Boiling Points More polar,so higher boiling point than comparable alkane or ether. Cannot H-bond to each other,so lower boiling point than comparable alcohol. CH.CH,CH,CH CH,一O-CHCH3 butane methox yethane bp 0C bp 8C 0 CHCH2一C一H CH,一 C-CH CH,CH,CH,一OH propanal acetone 1-propanol bp 49C bp 56 C bp 97C
Boiling Points ◼More polar, so higher boiling point than comparable alkane or ether. ◼Cannot H-bond to each other, so lower boiling point than comparable alcohol

H Solubility H-bond H3C CH3 Good sovent foracoh(Fig.2.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding of a ketone with water. Lone pair of electrons on oxygen of carbonyl can accept a hydrogen bond from O-H or N-H. Low molecular weight aldehydes and ketones (e.g.formaldehyde and acetone)are soluble in water. large molecular weight aldehydes and ketones are insoluble in water. Aromatic ketones and aldehydes are insoluble in water due to the hydrophobic aromatic ring. Acetone and acetaldehyde are miscible in water
Solubility ◼Good solvent for alcohols. ◼Lone pair of electrons on oxygen of carbonyl can accept a hydrogen bond from O-H or N-H. ◼Low molecular weight aldehydes and ketones (e.g. formaldehyde and acetone) are soluble in water. ◼large molecular weight aldehydes and ketones are insoluble in water. ◼Aromatic ketones and aldehydes are insoluble in water due to the hydrophobic aromatic ring. ◼Acetone and acetaldehyde are miscible in water

Formaldehyde Gas at room temperature. Formalin is a 40%aqueous solution. H H h、H-8HE HO _H 0→ OH H-C >H formaldehyde, b.p.-21C formalin trioxane,m.p.62C
Formaldehyde ◼Gas at room temperature. ◼Formalin is a 40% aqueous solution. O C O C O C H H H H H H heat H C O H H2O H C H OH HO trioxane, m.p. 62C formaldehyde, b.p. -21C formalin