
0 花华院 Organic Chemistry,6h Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 7 Alkyl Halides:Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com
By Junru Wang Email: wangjr07@163.com Chapter 7 Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Organic Chemistry, 6 h Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

0环+ Key Notes Nucleophilic Substitution ●SN1 ●SN2 ■Elimination(E1,E2) ■Nucleophilicity .The rate of the SN2 reaction increases with the nucleophilic strength of the incoming nucleophile. OThe rate of the SN1 reaction is unaffected by the nature of the nucleophile ■Leaving group
Key Notes Nucleophilic Substitution SN1 SN2 Elimination(E1,E2) Nucleophilicity The rate of the SN2 reaction increases with the nucleophilic strength of the incoming nucleophile. The rate of the SN1 reaction is unaffected by the nature of the nucleophile Leaving group

0 Content 发牌院。 Preparation and physical properties Nucleophilic substitution Factors affecting SN2 versus SN1 reactions ■Elimination Elimination versus substitution Reactions of alkyl halides Organometallic reactions
Content Preparation and physical properties Nucleophilic substitution Factors affecting SN2 versus SN1 reactions Elimination Elimination versus substitution Reactions of alkyl halides Organometallic reactions
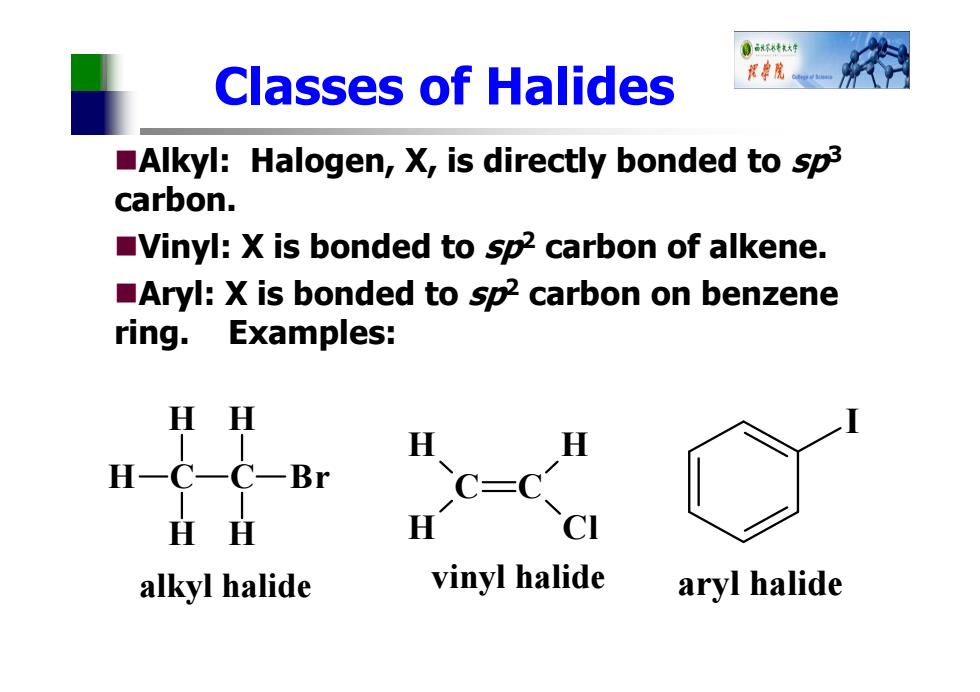
育不6特材车 Classes of Halides 花院 Alkyl:Halogen,X,is directly bonded to sp3 carbon. Vinyl:X is bonded to sp2 carbon of alkene. Aryl:X is bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring. Examples: HH H H一C一C一Br H H CI alkyl halide vinyl halide aryl halide
Classes of Halides Alkyl: Halogen, X, is directly bonded to sp3 carbon. Vinyl: X is bonded to sp2 carbon of alkene. Aryl: X is bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring. Examples: C H H H C H H Br alkyl halide C C H H H Cl vinyl halide I aryl halide

0礼不水牛大号 Classes of Alkyl Halides Methyl halides:only one C,CH2X Primary:C to which X is bonded has only one C-C bond. Secondary:C to which X is bonded has two C-C bonds. Tertiary:C to which X is bonded has three C-C bonds
Classes of Alkyl Halides Methyl halides: only one C, CH 3 X Primary: C to which X is bonded has only one C-C bond. Secondary: C to which X is bonded has two C-C bonds. Tertiary: C to which X is bonded has three C-C bonds

清我不8米大 Polarity and Reactivity Halogens are more electronegative than C. Carbon-halogen bond is polar,so carbon has partial positive charge. Carbon can be attacked by a nucleophile. Halogen can leave with the electron pair. H+ 6+6- HC一C】 H chloromethane EPM of chloromethane Copyright2005 Pearson Prentce Hall,Inc
Polarity and Reactivity Halogens are more electronegative than C. Carbon-halogen bond is polar, so carbon has partial positive charge. Carbon can be attacked by a nucleophile. Halogen can leave with the electron pair

0环行 Uses of Alkyl Halides" Solvents-degreasers and dry cleaning fluid Reagents for synthesis of other compounds Anesthetic:Halothane is CFCHCIBr ●CHCl3 used originally(toxic and carcinogenic)麻醉剂 >In 1847,the Edinburgh obstetrician James Young Simpson first used chloroform for general anesthesia during childbirth Freons,chlorofluorocarbons or CFC's Freon 12,CF2Cl2,now replaced with Freon 22, CF,CHCI,not as harmful to ozone layer. Pesticides -DDT banned in U.S. extremely toxic to insects but not as toxic to mammals
Uses of Alkyl Halides Solvents - degreasers and dry cleaning fluid Reagents for synthesis of other compounds Anesthetic: Halothane is CF 3CHClBr CHCl 3 used originally (toxic and carcinogenic)麻醉剂 In 1847, the Edinburgh obstetrician James Young Simpson first used chloroform for general anesthesia during childbirth Freons, chlorofluorocarbons or CFC’s Freon 12, CF 2Cl 2, now replaced with Freon 22, CF 2CHCl, not as harmful to ozone layer. Pesticides - DDT banned in U.S. extremely toxic to insects but not as toxic to mammals

0环4+大 Uses of Alkyl Halides" 杀虫剂、杀灭蚊子(疟疾) DDT1939年后广泛使用(残留高) Srilanka ●1934-1935150万(8万died) ●1963:仅15例 ●1968-1969第二季度60万例 1972:环境保护组织(EPA) 废除 ■冷却液和喷气燃料推进剂
Uses of Alkyl Halides 杀虫剂、杀灭蚊子(疟疾) DDT 1939年后广泛使用(残留高) Srilanka : 1934-1935 150万( 8 万 died ) 1963: 仅15 例 1968-1969第二季度60万例 1972:环境保护组织(EPA)废除 冷却液和喷气燃料推进剂

0环行 B.P Densities 院。 Greater intermolecular forces,higher b.p. .Dipole-dipole attractions not significantly different for different halides London forces greater for larger atoms Greater mass,higher b.p. Spherical shape decreases b.p. (CH3)3CBr CH3(CH2)3Br 73C 102°C ■Densities .Alkyl fluorides and chlorides less dense than water. .Alkyl dichlorides,bromides,and iodides more dense than water
B.P & Densities Greater intermolecular forces, higher b.p. Dipole-dipole attractions not significantly different for different halides London forces greater for larger atoms Greater mass, higher b.p. Spherical shape decreases b.p. (CH 3 ) 3CBr CH 3(CH 2 ) 3Br 73 C 102 C Densities •Alkyl fluorides and chlorides less dense than water. •Alkyl dichlorides, bromides, and iodides more dense than water

Sec 1 PREPARATION AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ■PREPARATION .Halogenation(Allylic Halogenation) ●Vith HX ●From alcohol ●Diazonium coupling(for aryl halide only) ■Use
Sec 1 PREPARATION AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES PREPARATION Halogenation(Allylic Halogenation) With HX From alcohol Diazonium coupling (for aryl halide only) Use