
音说不末精天手 Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 4 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com

CONTENT Classification of Hydrocarbons ■Physical properties Reactions Mechanisms of Alkanes Structure Conformation of Alkanes Conformation of Cycloalkanes

Key Notes ■Mechanisms ■Conformation ■Ring strain ■Conformers ■Cis-trans isomers
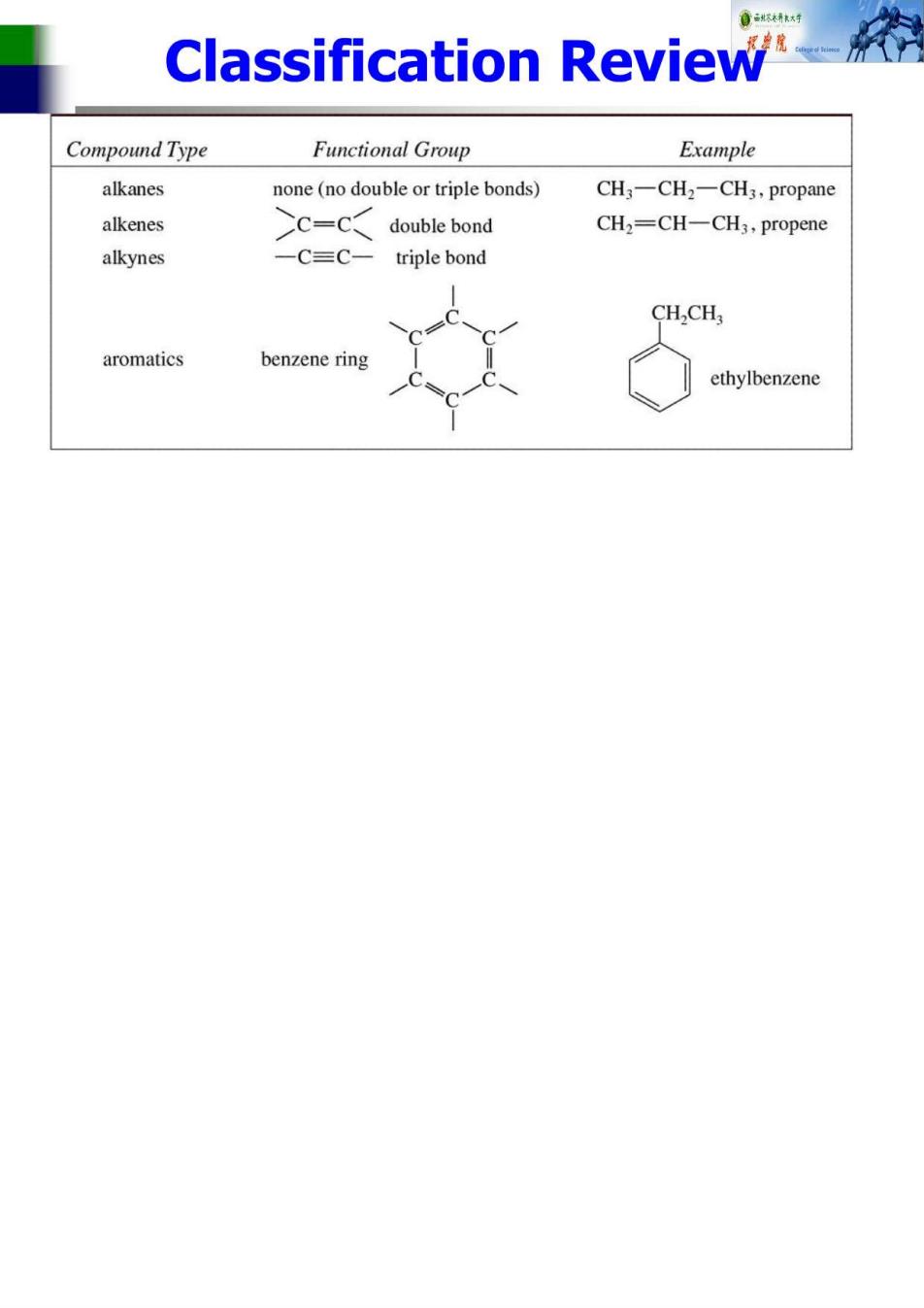
Classification Review Compound Type Functional Group Example alkanes none(no double or triple bonds) CH3-CH2-CH3,propane alkenes C=C double bond CH2=CH-CH3,propene alkynes -C=C-triple bond CH2CH aromatics benzene ring ethylbenzene

Sec 1 Physical Properties Solubility:hydrophobic Density:less than 1 g/mL Boiling points increase with increasing carbons (little less for branched chains). Melting points increase with increasing carbons(less for odd-number of carbons)
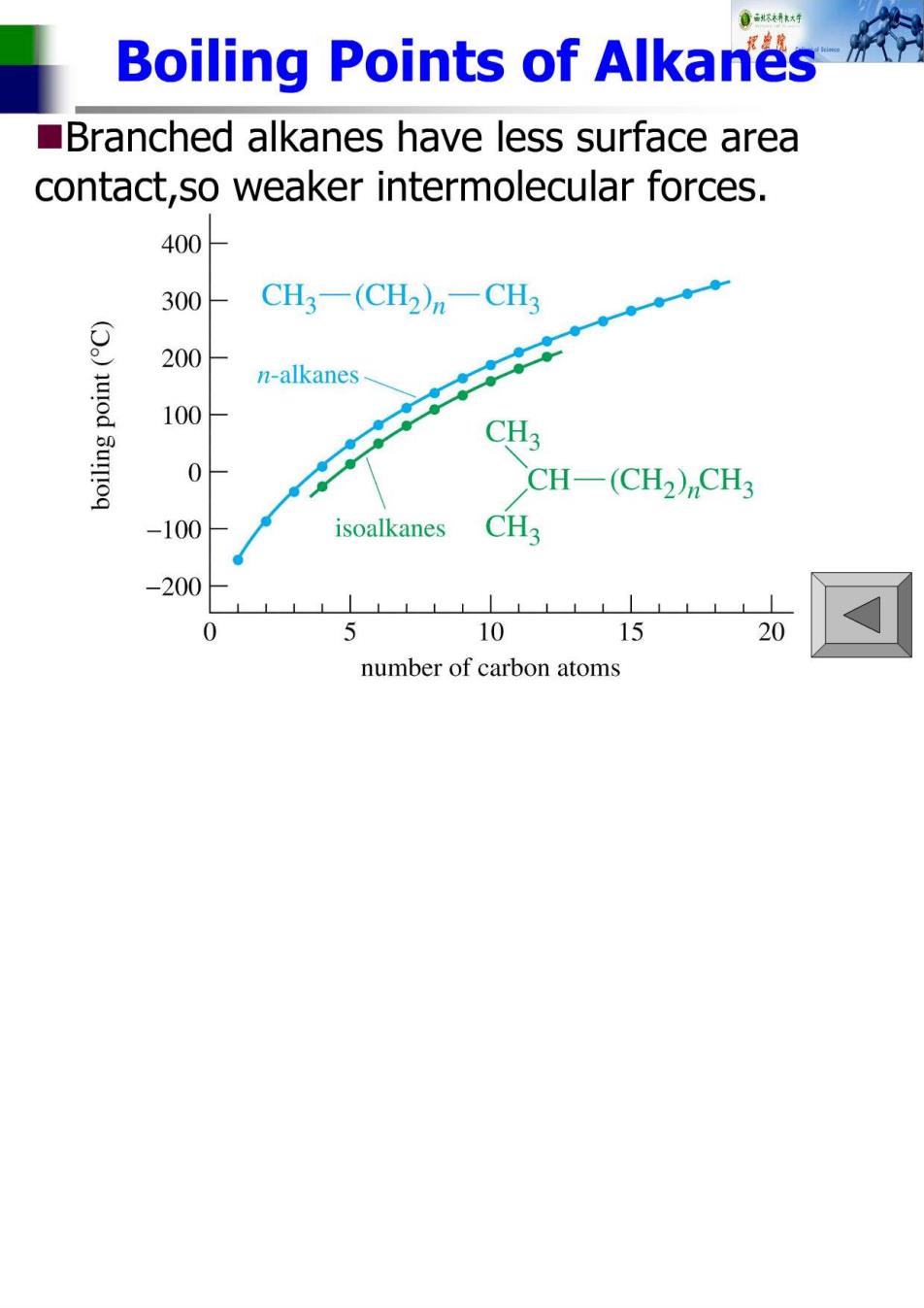
Boiling Points of Alkanes Branched alkanes have less surface area contact,so weaker intermolecular forces. 400 300- CH3一(CH2)n一CH3 ● 200- n-alkanes.、 100 CH3 0 CCH-(CH2),CH3 -100 isoalkanes CH3 -200 0 10 15 20 number of carbon atoms
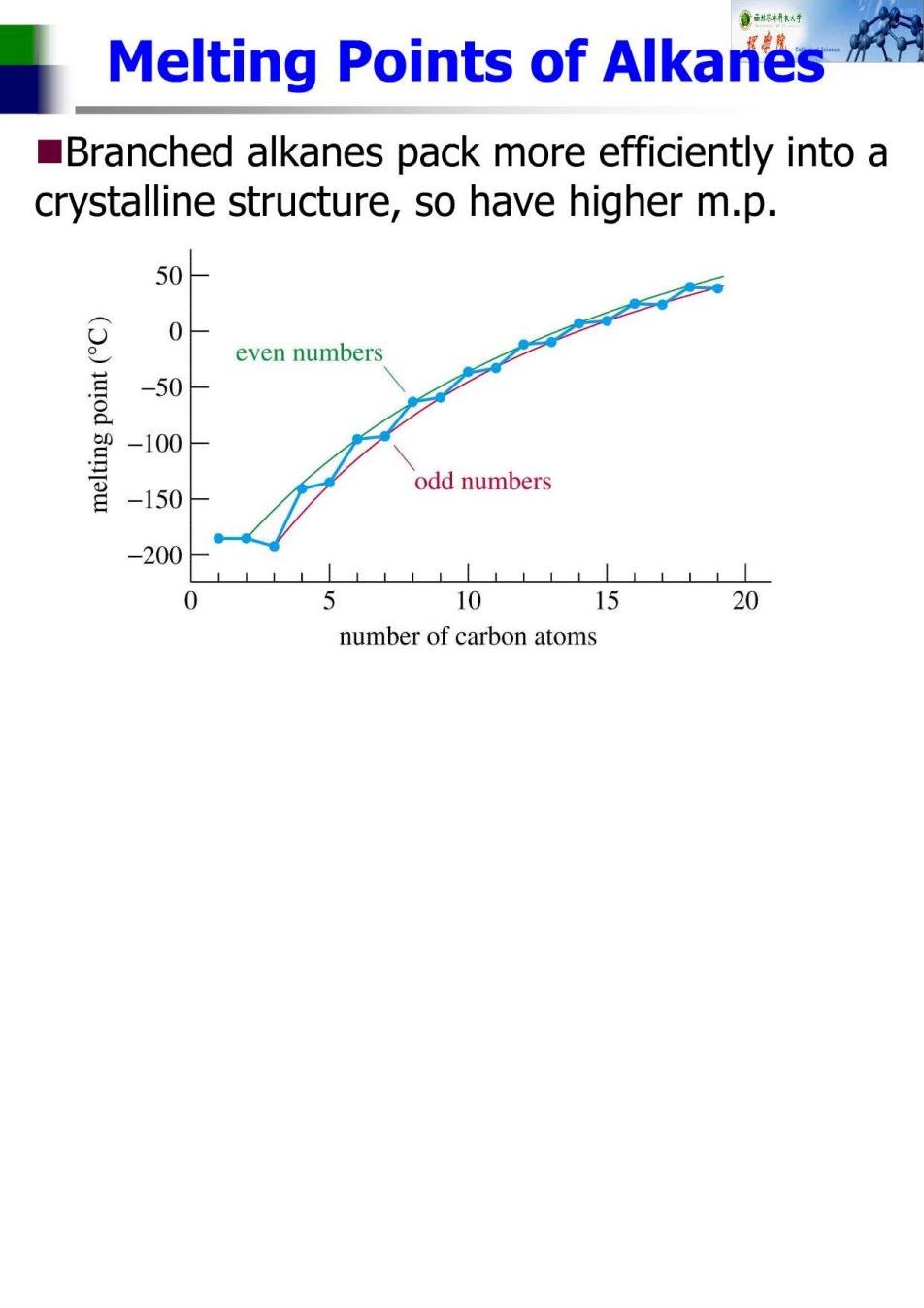
Melting Points of Alkanes Branched alkanes pack more efficiently into a crystalline structure,so have higher m.p 50H 0- even numbers od 3unw -50 -100 odd numbers -150 -200 0 10 15 20 number of carbon atoms
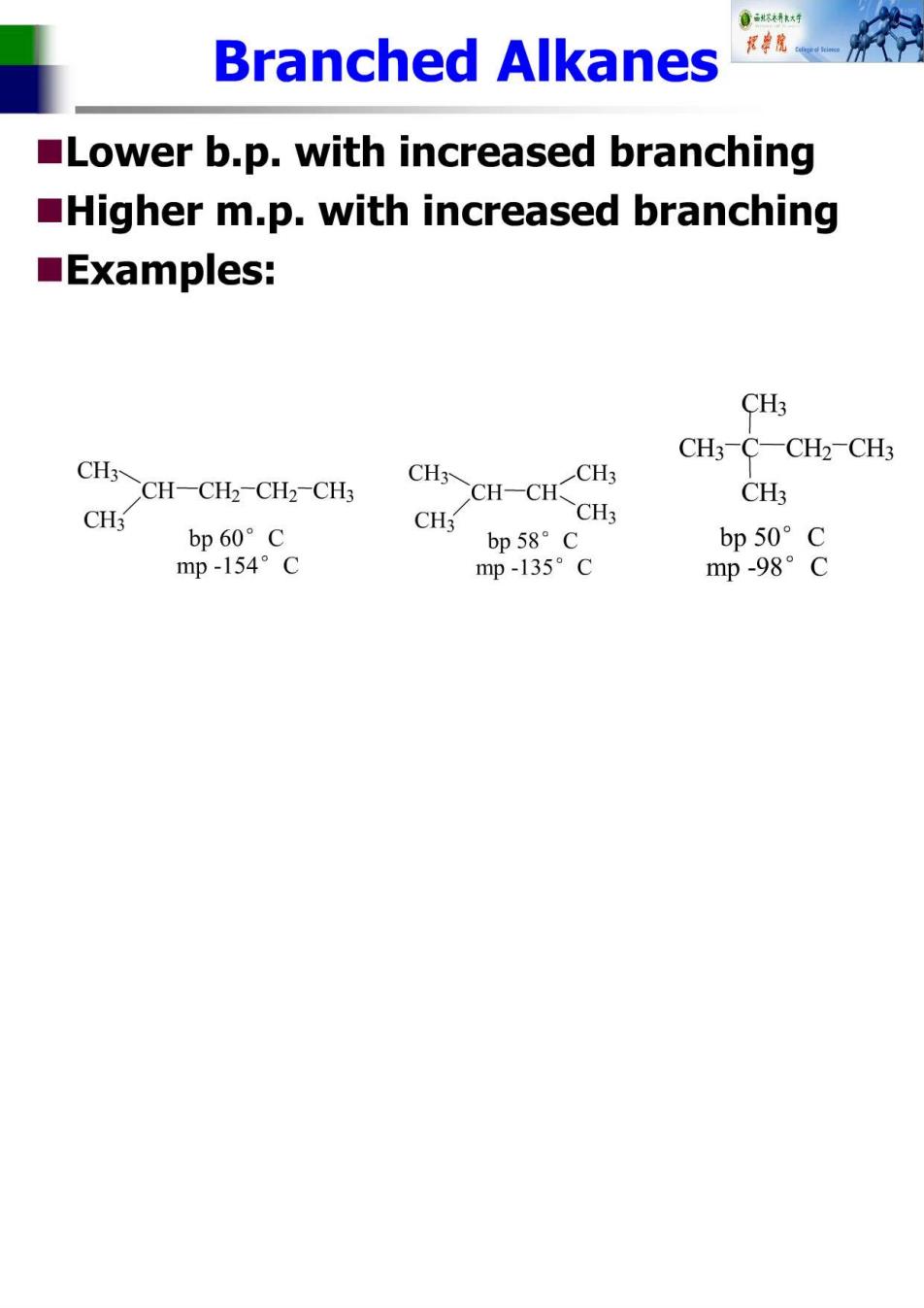
Branched Alkanes Lower b.p.with increased branching Higher m.p.with increased branching ■Examples: CH3 CH3-C-CH2-CH3 CH3 CH-CH-CH2-CH CH CH-CHCH CH3 CH3 CH3 bp60°c bp58°C bp50°C mp-154°C mp-135°C mp-98°C

Major Uses of Alkanes C1-C2:gases(natural gas) C3-C4:liquified petroleum (LPG) ■Cs-Cg:gasoline C-C16:diesel,kerosene,jet fuel C17-up:lubricating oils,heating oil Origin:petroleum refining
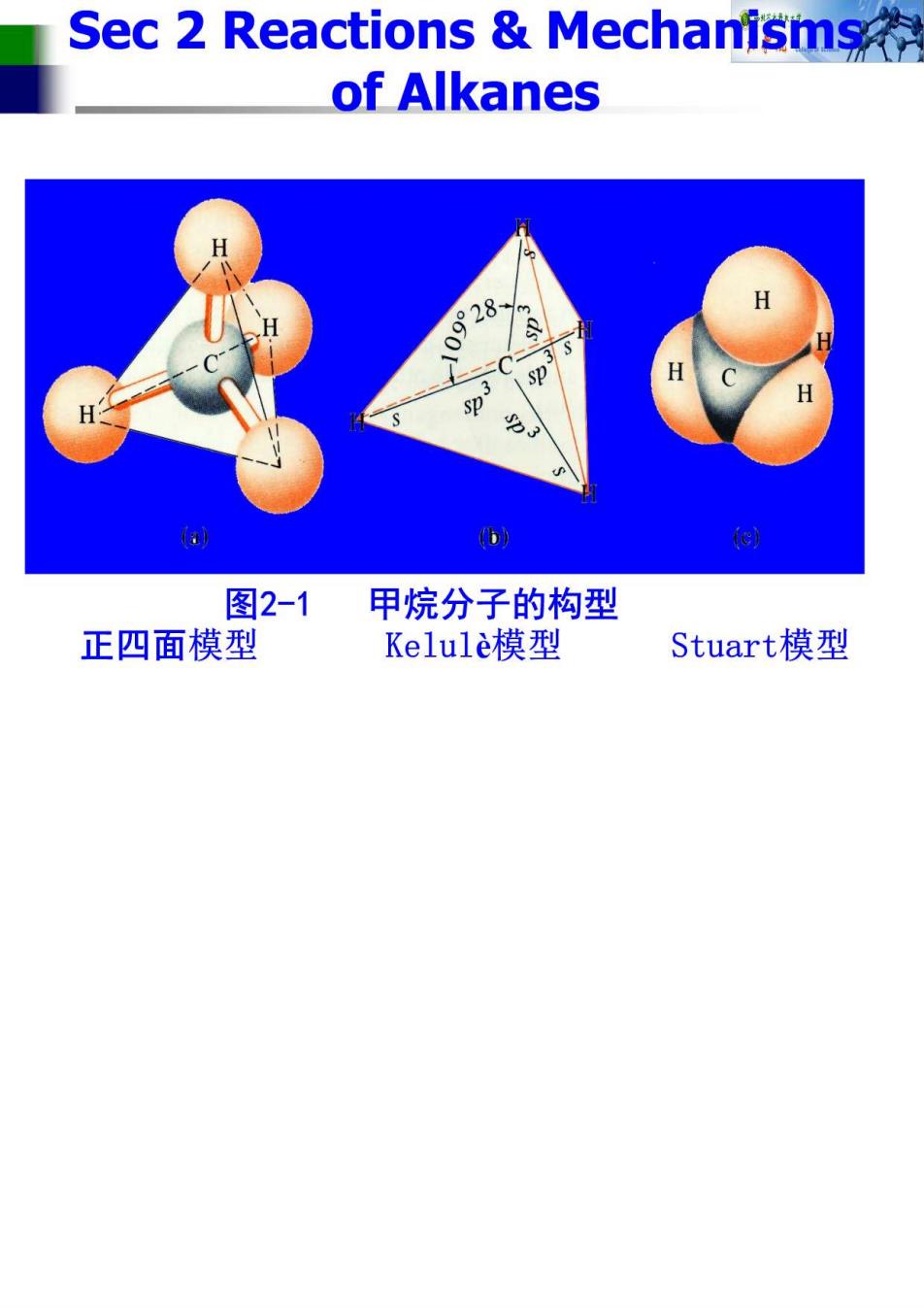
Sec 2 Reactions Mechanisms of Alkanes sp (a) b 图2-1甲烷分子的构型 正四面模型 Kelule模型 Stuart模型