
Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade.Jr. Chapter 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com

Content ■Introduction Classification of reactions Mechanisms:step-by-step pathway oIntermadiate?Transition state? ●Thermodynamics ●Kinetics

Key Notes ■Mechanism ■Homolytic cleavage Heterolytic cleavage ■Intermadiate ■Transition state

Introduction ■Reactants→Products:overall reaction. Mechanism:step-by-step pathway. To learn more about a reaction: ●Thermodynamics ●Kinetics

Reactions Bond formation Synthetic organic chemistry is about creating complex molecules from simple starting materials -a process which may involve many different reactions. Designing a synthesis is a bit like chess. a synthetic 'game strategy

Reactions Bond formation Basically,most reactions involve electron- rich molecules forming bonds to electron deficient molecules(i.e.nucleophiles forming bonds to electrophiles). The bond will be formed specifically between the nucleophilic center of the nucleophile and the electrophilic center of the electrophile

Sec 1 Classification Reactions can be classified as ■Acid/base reactions Functional group transformations; oone functional group can be converted into another. Normally these reactions are relatively straightforward and proceed in high yield carbon-carbon bond formations
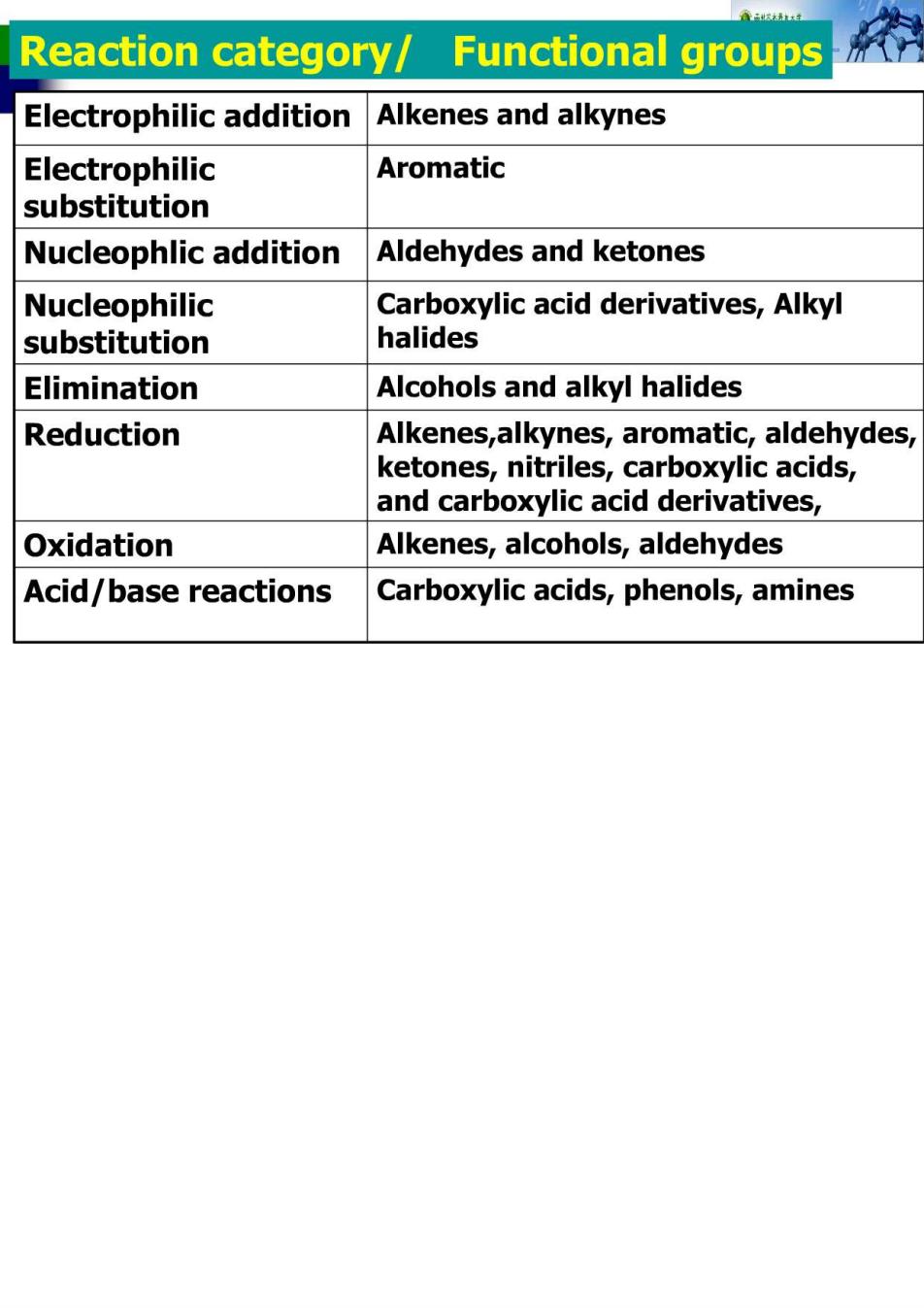
Reaction category/ Functional groups Electrophilic addition Alkenes and alkynes Electrophilic Aromatic substitution Nucleophlic addition Aldehydes and ketones Nucleophilic Carboxylic acid derivatives,Alkyl substitution halides Elimination Alcohols and alkyl halides Reduction Alkenes,alkynes,aromatic,aldehydes, ketones,nitriles,carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives, Oxidation Alkenes,alcohols,aldehydes Acid/base reactions Carboxylic acids,phenols,amines
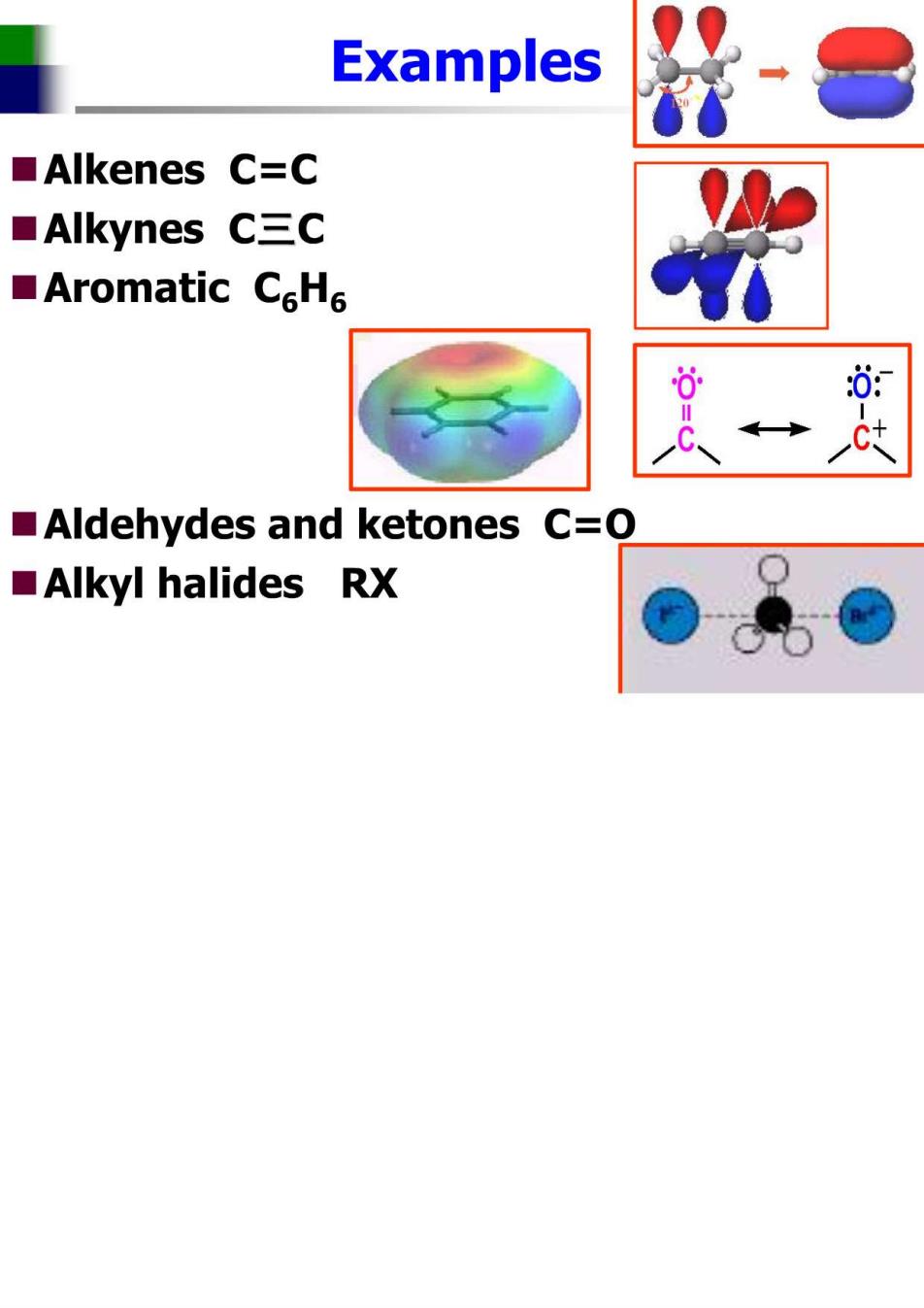
Examples ■Alkenes C=C ■Alkynes C三C ■Aromatic CeH6 0: Aldehydes and ketones C=O ■Alkyl halides RX
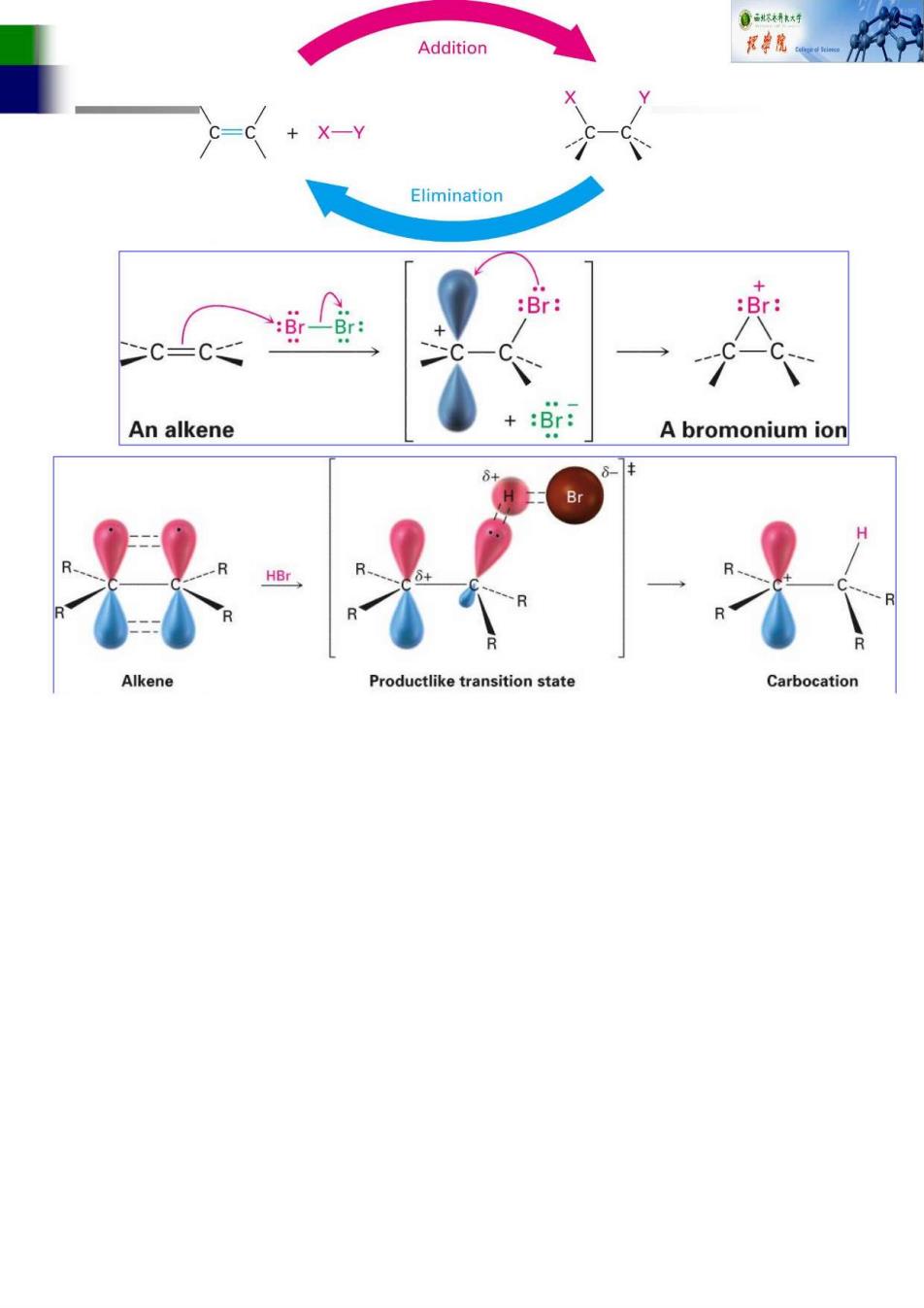
Addition Elimination Br An alkene A bromonium ion 保1