0乐人号 Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 2 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com
By Junru Wang Email: wangjr07@163.com Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 2 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules

0 Key I Notes 状率院 ■Molecular Orbital oValence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory(VSEPR theory价层电子对互斥理论) ■Pi Bonding Hybrid Orbitals Sp3 Sp2 Sp ■Isomerism Bond and Molecular Dipole Moments Intermolecular Forces Boiling Points and Solubility
Key Notes Molecular Orbital zValence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR theory价层电子对互斥理论 ) Pi Bonding Hybrid Orbitals Sp3 , Sp2 , Sp1 Isomerism Bond and Molecular Dipole Moments Intermolecular Forces Boiling Points and Solubility

0标4g CONTENT 1.Bonding Molecular Orbital 2.Hybridization Molecular Shapes 3.3D Molecules Drawing 4.Isomerism 5.Polarity of Bonds Molecules 6.Intermolecular Forces their effects
CONTENT 1. Bonding & Molecular Orbital 2. Hybridization & Molecular Shapes 3. 3D Molecules Drawing 4. Isomerism 5. Polarity of Bonds & Molecules 6. Intermolecular Forces & their effects
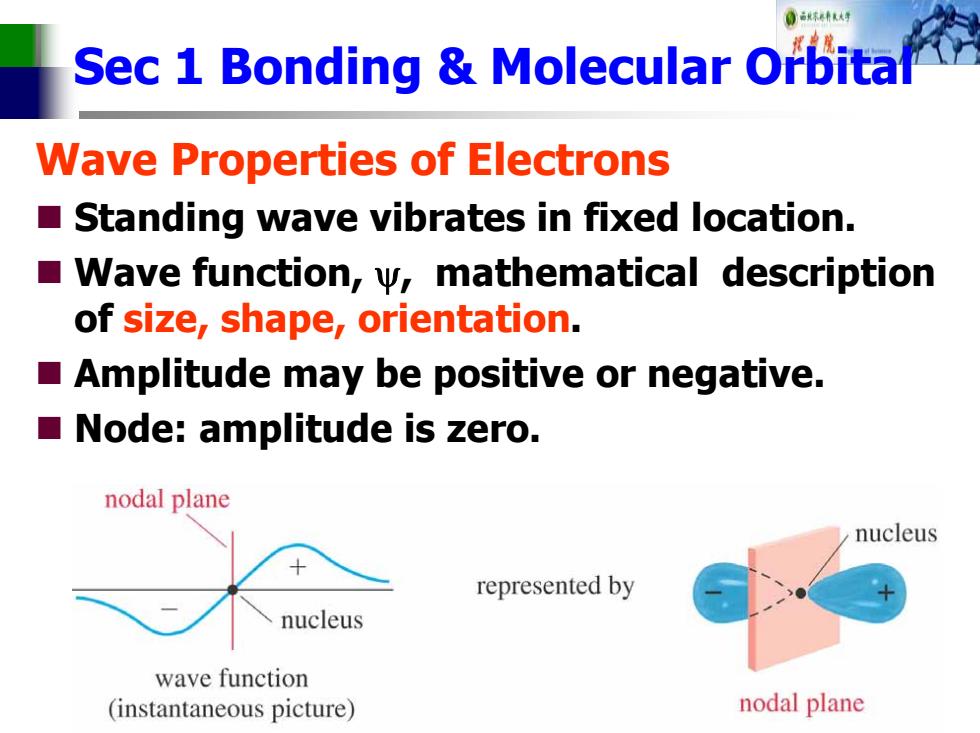
0 Sec 1 Bonding Molecular Orbital Wave Properties of Electrons Standing wave vibrates in fixed location. Wave function,w,mathematical description of size,shape,orientation. Amplitude may be positive or negative. Node:amplitude is zero. nodal plane nucleus represented by nucleus wave function (instantaneous picture) nodal plane
Sec 1 Bonding & Molecular Orbital Wave Properties of Electrons Standing wave vibrates in fixed location. Wave function, ψ, mathematical description of size, shape, orientation . Amplitude may be positive or negative. Node: amplitude is zero
04号 Wave Interactions 院 Linear combination of atomic orbitals oon different atoms produce molecular orbitals oon the same atom give hybrid orbitals. Conservation of orbitals. Waves that are in phase add together. Amplitude increases. Waves that are out of phase cancel out
Wave Interactions Linear combination of atomic orbitals zon different atoms produce molecular orbitals zon the same atom give hybrid orbitals. Conservation of orbitals. Waves that are in phase add together. Amplitude increases. Waves that are out of phase cancel out
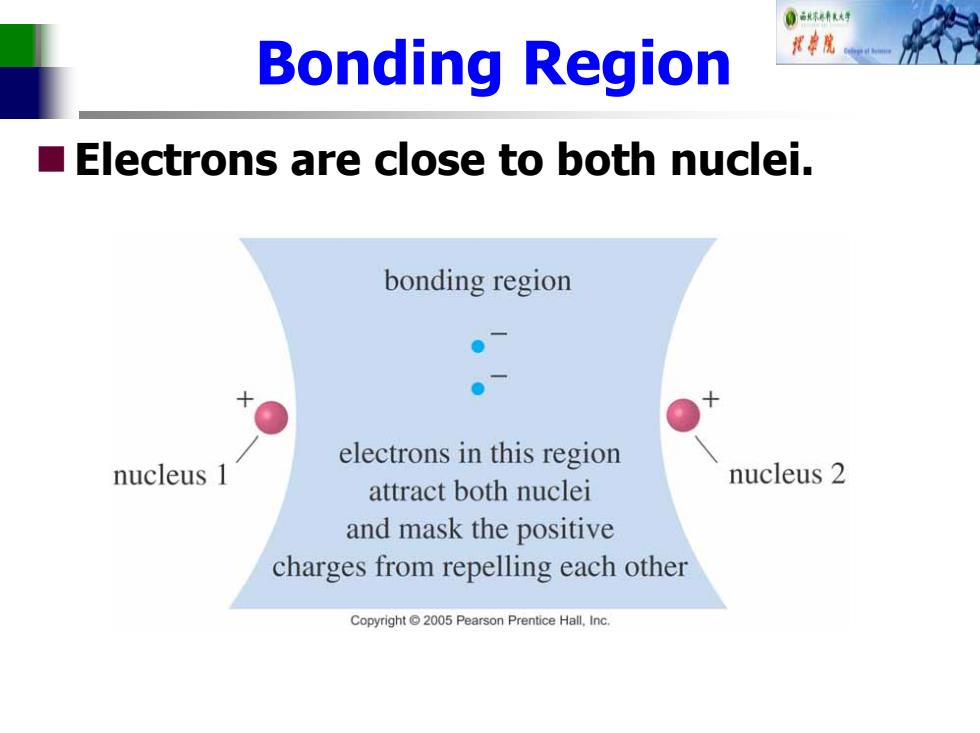
0林有 Bonding Region ■ Electrons are close to both nuclei. bonding region ●一 electrons in this region nucleus 1 nucleus 2 attract both nuclei and mask the positive charges from repelling each other Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Bonding Region Electrons are close to both nuclei

0木有人写 Sigma(o)Bonding Electron density lies between the nuclei. A bond may be formed by s-s,p-p,s-p, or hybridized orbital overlaps. The bonding MO is lower in energy than the original atomic orbitals. The antibonding MO is higher in energy than the atomic orbitals
Sigma(σ) Bonding Electron density lies between the nuclei. A bond may be formed by s-s, p-p, s-p, or hybridized orbital overlaps. The bonding MO is lower in energy than the original atomic orbitals. The antibonding MO is higher in energy than the atomic orbitals

0林司 Bonding Molecular Orbital Two hydrogens,1s constructive overlap Constructive Interaction:The two 1s orbitals are in phase and have the same sign. add bonding molecular orbital represented by: o-bonding MO Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Bonding Molecular Orbital Two hydrogens, 1s constructive overlap

0林人号 Anti-Bonding Molecular Orbital Two hydrogens,destructive overlap. Destructive interaction:The two Is orbitals are out of phase. add antibonding molecular orbital represented by: node Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Anti-Bonding Molecular Orbital Two hydrogens, destructive overlap
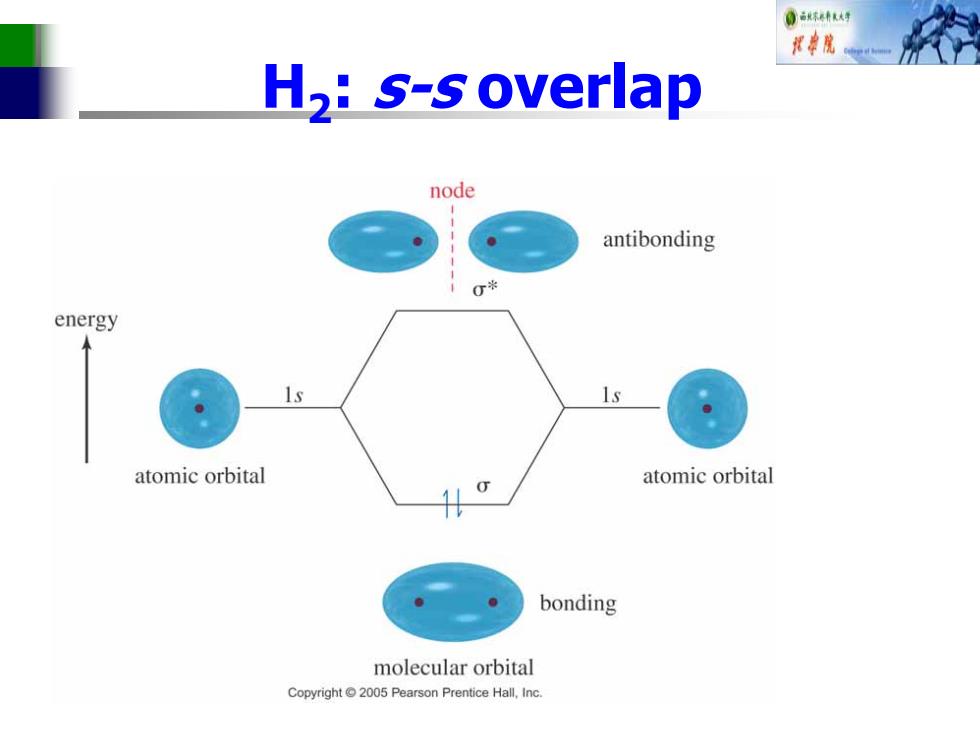
0 样串院 H,:s-s overlap node antibonding 0兴 energy atomic orbital atomic orbital bonding molecular orbital Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
H2: s-s overlap