
Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides
Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides
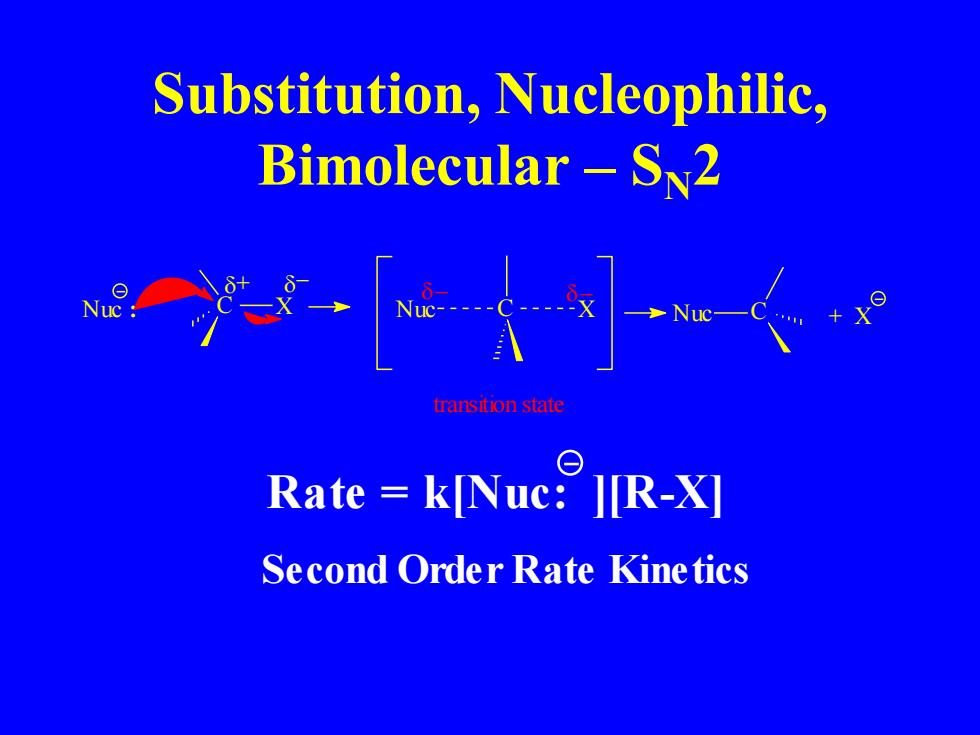
Substitution,Nucleophilic, Bimolecular-S2 一人]人 transition state Rate k[Nuc:][R-X] Second Order Rate Kinetics
Substitution, Nucleophilic, Bimolecular – SN2 C X + − Nuc : Nuc C X Nuc C + X transition state − − Rate = k[Nuc: ][R-X] Second Order Rate Kinetics
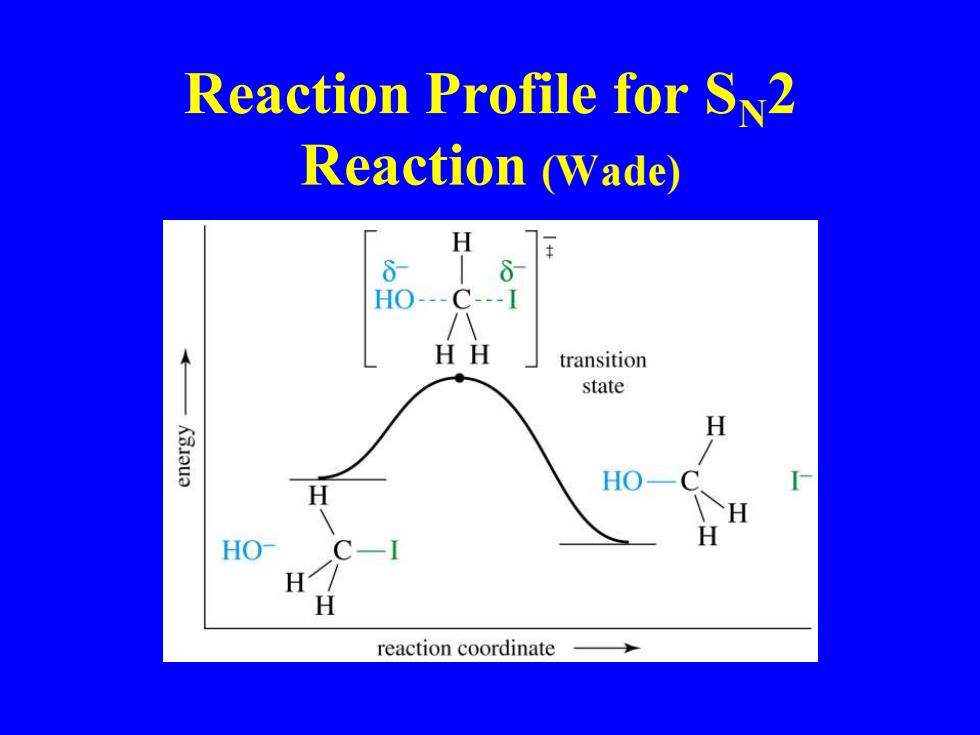
Reaction Profile for Sv2 Reaction (Wade) H 8 HO---C---I HH transition state H K.oua HO H reaction coordinate
Reaction Profile for SN2 Reaction (Wade)
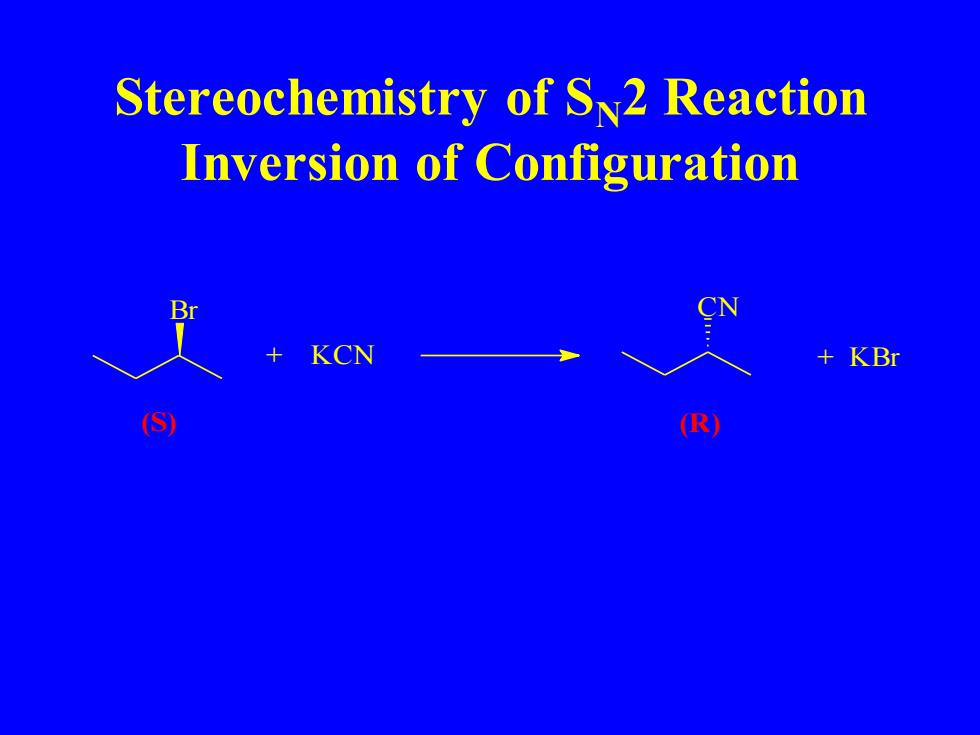
Stereochemistry of S2 Reaction Inversion of Configuration KCN KBr S R
Stereochemistry of SN2 Reaction Inversion of Configuration Br + KCN CN + KBr (S) (R)
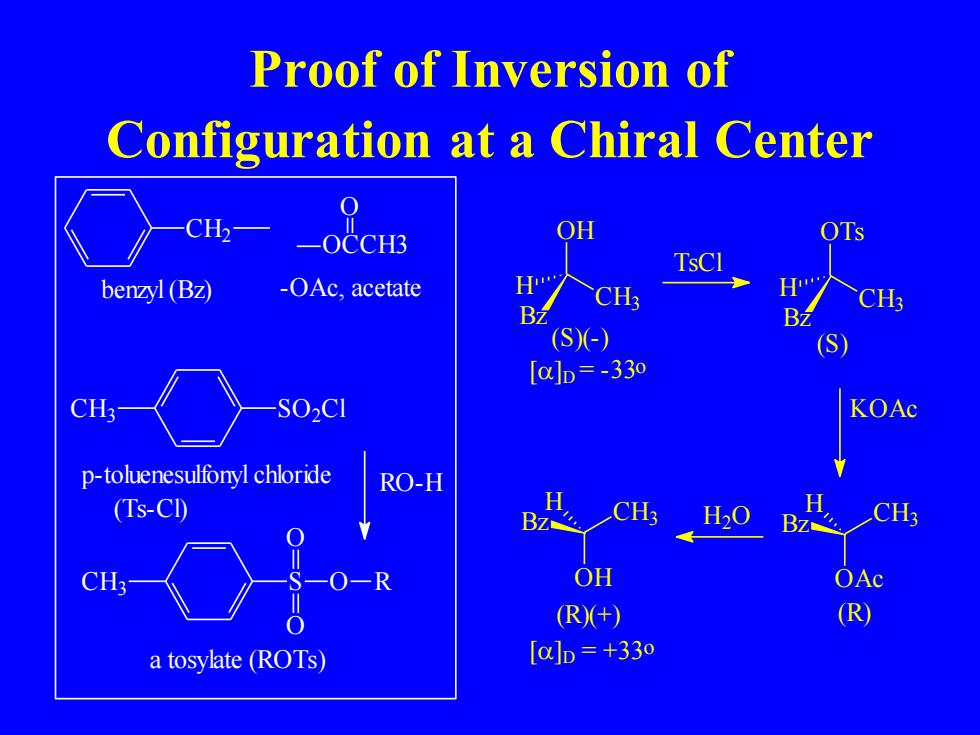
Proof of Inversion of Configuration at a Chiral Center CH2一 _OCCH3 TsCl benzyl (BZ) -OAc,acetate 6m.. CH CH; BZ (S(-) (S [a]D=-33o CH3- S02C1 KOAc p-toluenesulfonyl chloride RO-H (Ts-CI) BZ CH H20 CH3- -R OH OAc (R(+) R) a tosylate (ROTs) [a]D=+33o
Proof of Inversion of Configuration at a Chiral Center CH2 benzyl (Bz) CH SO2Cl 3 p-toluenesulfonyl chloride (Ts-Cl) CH3 S O O O R RO-H a tosylate (ROTs) OH CH3 Bz H []D = -33o (S)(-) TsCl OTs CH3 Bz H (S) KOAc OCCH3 O -OAc, acetate OAc Bz CH3 H (R) OH Bz CH3 H []D = +33o (R)(+) H2O
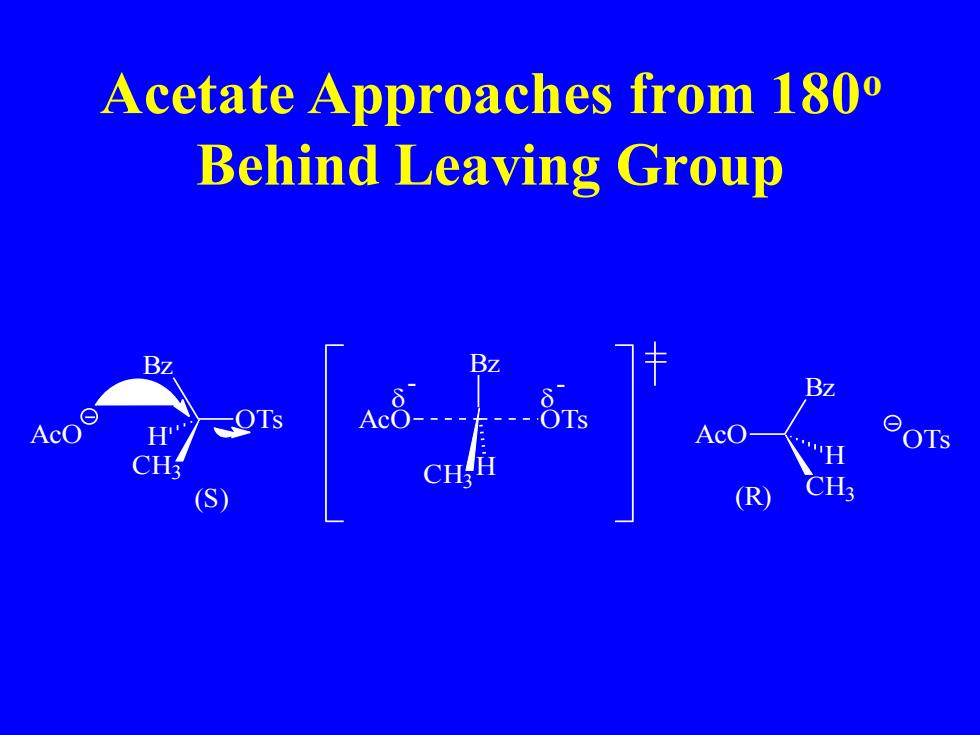
Acetate Approaches from 180 Behind Leaving Group AcO " OTs S (R
Acetate Approaches from 180o Behind Leaving Group OTs Bz CH3 AcO H Bz CH3 H AcO OTs - - AcO Bz CH3 H (S) (R) OTs
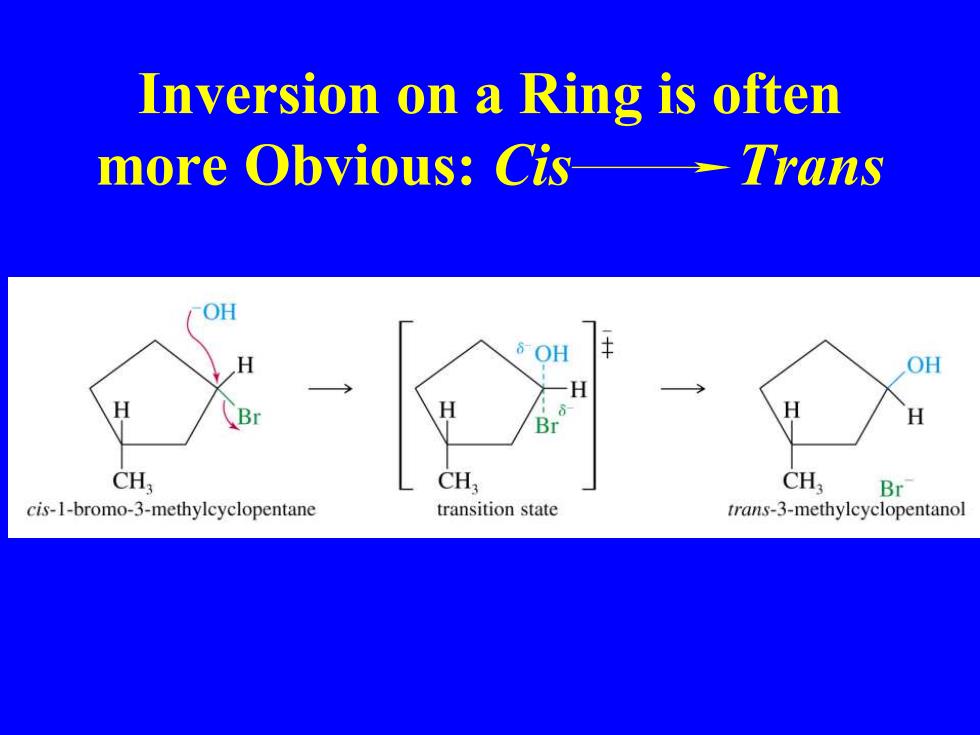
Inversion on a Ring is often more Obvious:Cis--Trans OH OH OH H H CH CH CH, Br cis-1-bromo-3-methylcyclopentane transition state trans-3-methylcyclopentanol
Inversion on a Ring is often more Obvious: Cis Trans
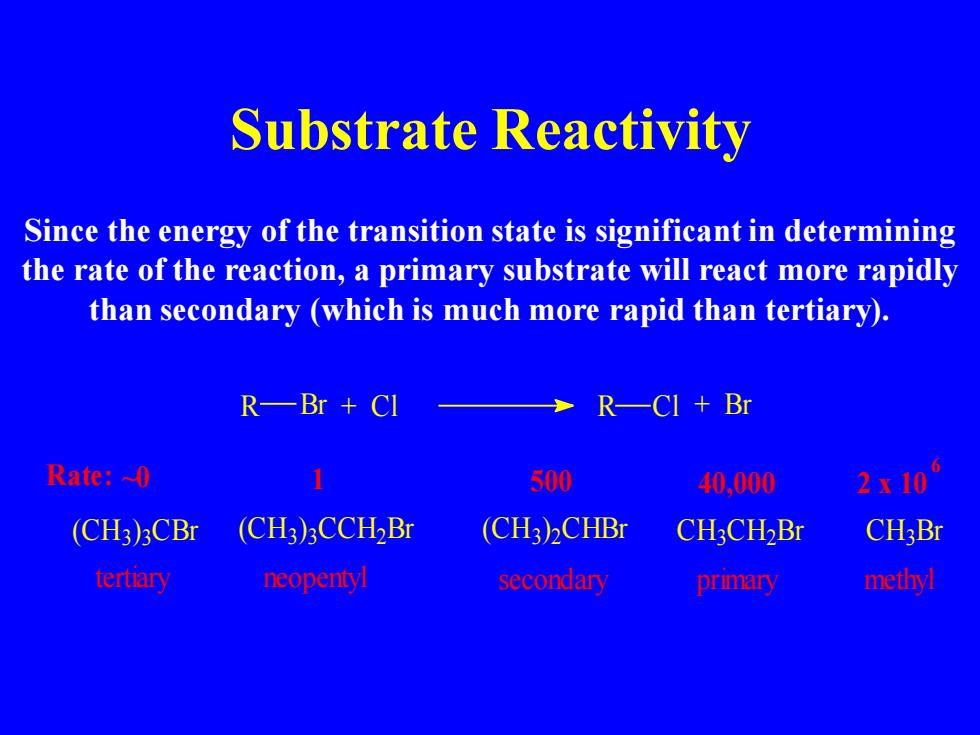
Substrate Reactivity Since the energy of the transition state is significant in determining the rate of the reaction,a primary substrate will react more rapidly than secondary (which is much more rapid than tertiary). R—Br+CI R一CI+Br Rate:~0 500 40,000 2x10 (CH3)3CBr (CH3)3CCH2Br (CH3)2CHBr CH3CH2Br CH3Br tertiary neopenty secondary primary methyl
Substrate Reactivity Since the energy of the transition state is significant in determining the rate of the reaction, a primary substrate will react more rapidly than secondary (which is much more rapid than tertiary). 6 tertiary neopentyl secondary primary methyl Rate: ~0 (CH3 ) 3 CBr C H C H3 Br (CH3) 3CCH2Br (CH3) 2CHBr 3 C H2 Br R Br + Cl R Cl + Br 1 500 40,000 2 x 10
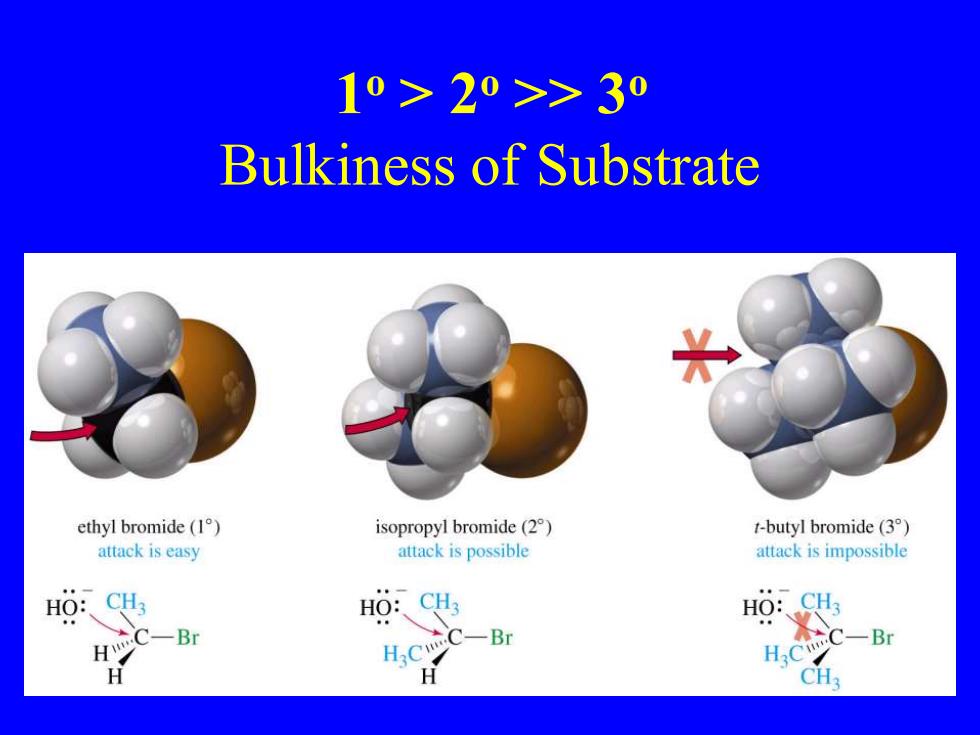
10>20>>30 Bulkiness of Substrate ethyl bromide(1) isopropyl bromide(2) t-butyl bromide(3) attack is easy attack is possible attack is impossible HO:、CH HO:、CH3 C一Br C-Br H H.C H.cC-Br H CH3
1 o > 2o >> 3o Bulkiness of Substrate

Polar,Aprotic Solvents Solvents should be able to "cage"the metal cation CH3SCH:CHCN HCN(CH3)CHCCH DMSO acetonitrile DMF acetone Polar,protic solvents lower energy of nucleophile HOCH3 by solvation CH3OH---Br---HOCH; CH3OH
Polar, Aprotic Solvents by solvation Polar, protic solvents lower energy of nucleophile C H3O H HOCH3 C H3O H Br HOCH3 acetone O C H3 C N C H3 CCH3 DMSO acetonitrile DMF O HCN(CH3 ) 2 O C H3 SCH3 Solvents should be able to "cage" the metal cation