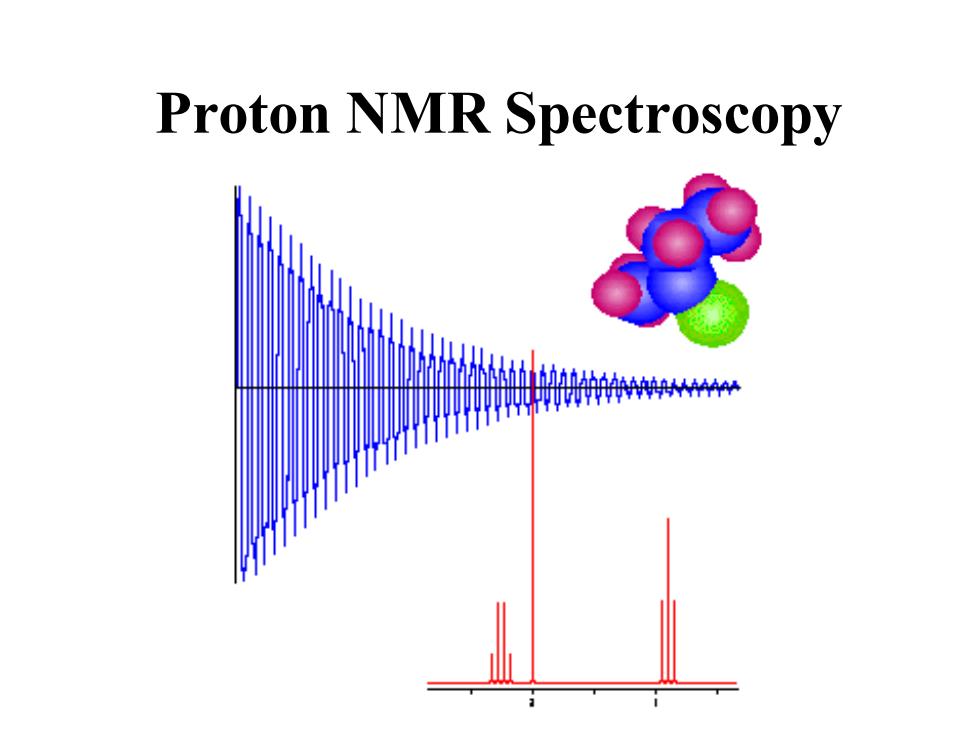
Proton NMR Spectroscopy
Proton NMR Spectroscopy
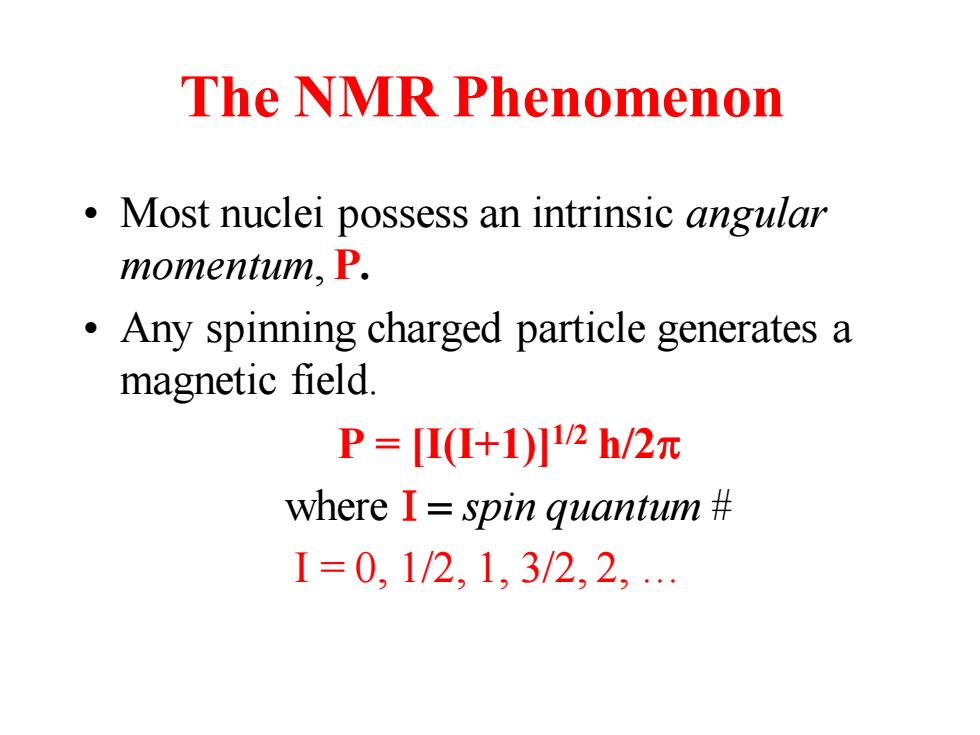
The NMR Phenomenon Most nuclei possess an intrinsic angular momentum,P. Any spinning charged particle generates a magnetic field. P=Π(+1)2h/2元 where I spin quantum I=0,1/2,1,3/2,2
The NMR Phenomenon • Most nuclei possess an intrinsic angular momentum, P. • Any spinning charged particle generates a magnetic field. P = [I(I+1)]1/2 h/2p where I = spin quantum # I = 0, 1/2, 1, 3/2, 2, …

Which nuclei have a "spin"? If mass and atomic are both even,I =0 and the nucleus has no spin. e.g.Carbon-12,Oxygen-16 For each nucleus with a spin,the of allowed spin states can be quantized: For a nucleus with I,there are 21+1 allowed spin states. H,13C,19F,31P all have I 1/2 △E=yh/2π)Bo
Which nuclei have a “spin”? • If mass # and atomic # are both even, I = 0 and the nucleus has no spin. e.g. Carbon-12, Oxygen-16 • For each nucleus with a spin, the # of allowed spin states can be quantized: • For a nucleus with I, there are 2I + 1 allowed spin states. 1H, 13C, 19F, 31P all have I = 1/2 DE = g(h/2p)Bo
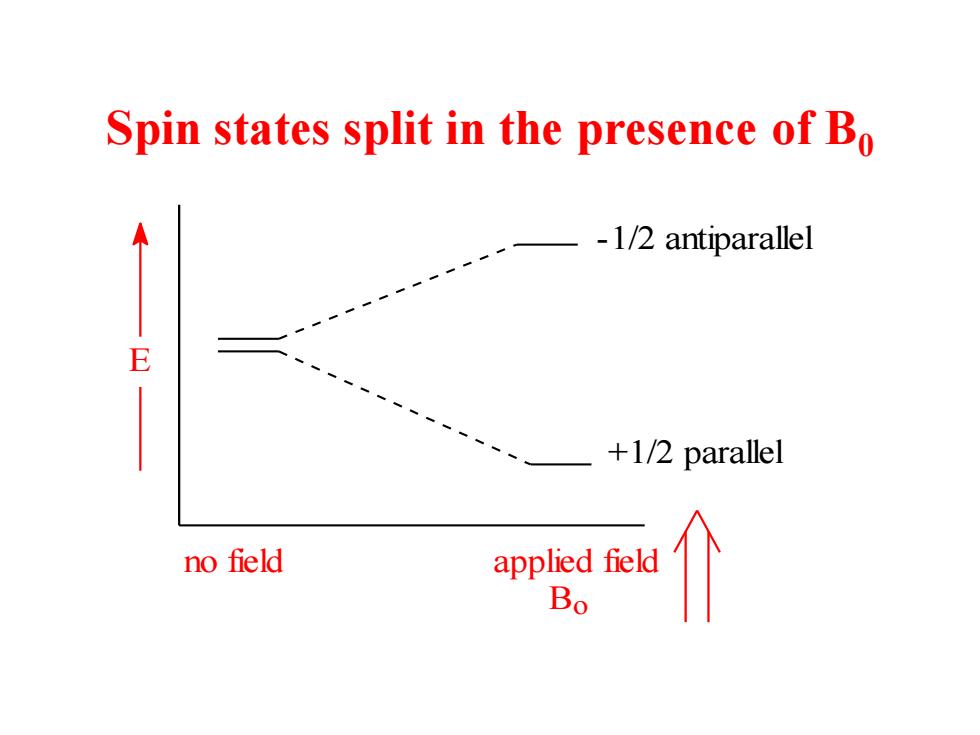
Spin states split in the presence of Bo -1/2 antiparallel E +1/2 parallel no field applied field Bo
Spin states split in the presence of B0 no field applied field E +1/2 parallel -1/2 antiparallel Bo
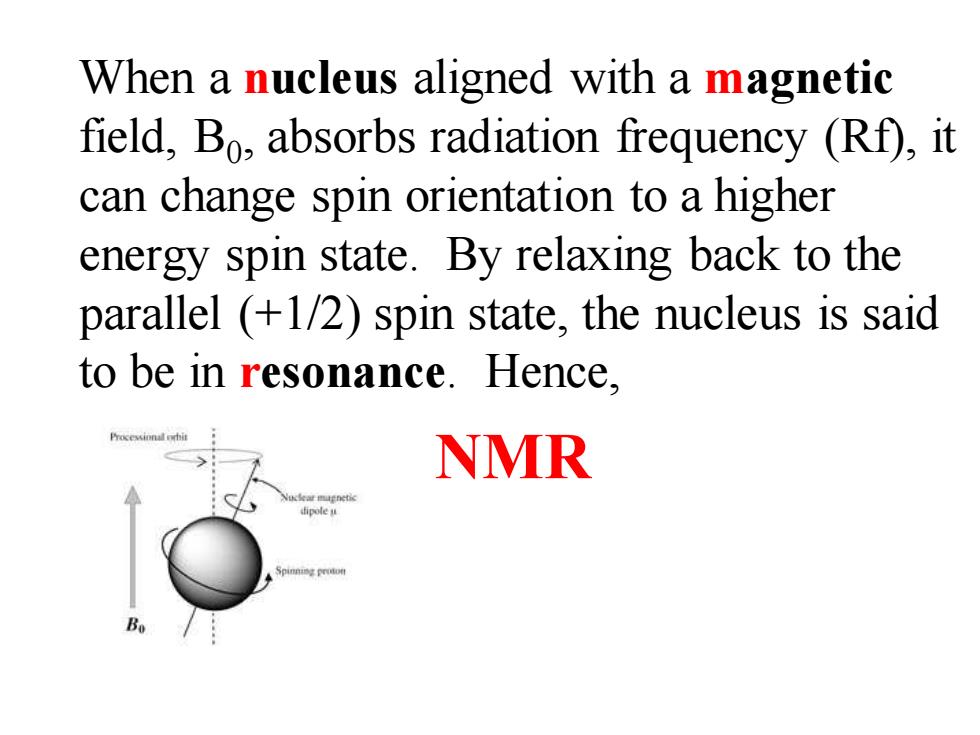
When a nucleus aligned with a magnetic field,Bo,absorbs radiation frequency (Rf),it can change spin orientation to a higher energy spin state.By relaxing back to the parallel (+1/2)spin state,the nucleus is said to be in resonance.Hence, NMR B
When a nucleus aligned with a magnetic field, B0 , absorbs radiation frequency (Rf), it can change spin orientation to a higher energy spin state. By relaxing back to the parallel (+1/2) spin state, the nucleus is said to be in resonance. Hence, NMR

Presence of Magnetic Field No field With field
Presence of Magnetic Field
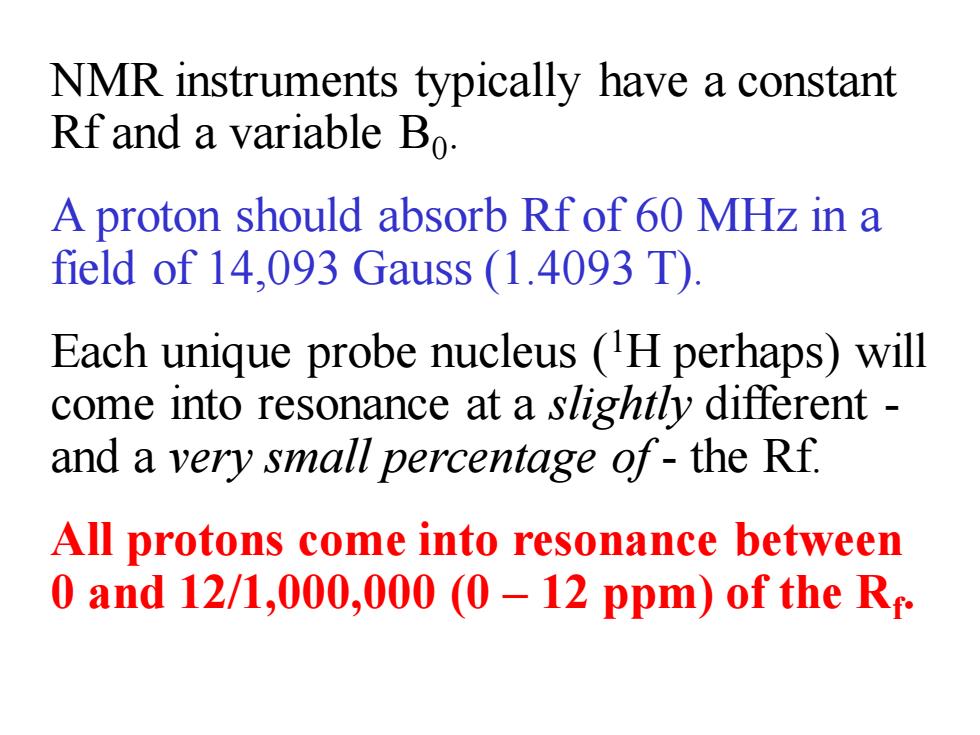
NMR instruments typically have a constant Rf and a variable Bo. A proton should absorb Rf of 60 MHz in a field of 14,093 Gauss (1.4093 T) Each unique probe nucleus (H perhaps)will come into resonance at a slightly different and a very small percentage of-the Rf. All protons come into resonance between 0 and 12/1,000,000(0-12 ppm)of the R
NMR instruments typically have a constant Rf and a variable B0 . A proton should absorb Rf of 60 MHz in a field of 14,093 Gauss (1.4093 T). Each unique probe nucleus (1H perhaps) will come into resonance at a slightly different - and a very small percentage of - the Rf. All protons come into resonance between 0 and 12/1,000,000 (0 – 12 ppm) of the Rf

Energy Difference (AE)Between Two Different Spin States of a Nucleus With I=1/2 -1/2 antiparallel E 100 MHZ 200 MHz 300 MHz 400 MHz parallel +1/2 23,500 47,000 70,500 104,000 inc.magnetic field strength,Gauss Bo
Energy Difference (DE) Between Two Different Spin States of a Nucleus With I=1/2 +1/2 -1/2 E 100 MHz 200 MHz 300 MHz 400 MHz 23,500 47,000 70,500 104,000 parallel antiparallel inc. magnetic field strength, Gauss B0

What Does an NMR Spectrum Tell You? .of chemically unique H's in the molecule of signals The types of H's that are present e.g. aromatic,vinyl,aldehyde .. chemical shift The number of each chemically unique H integration The H's proximity to eachother spin-spin splitting
What Does an NMR Spectrum Tell You? • # of chemically unique H’s in the molecule # of signals • The types of H’s that are present e.g. aromatic, vinyl, aldehyde … chemical shift • The number of each chemically unique H integration • The H’s proximity to eachother spin-spin splitting
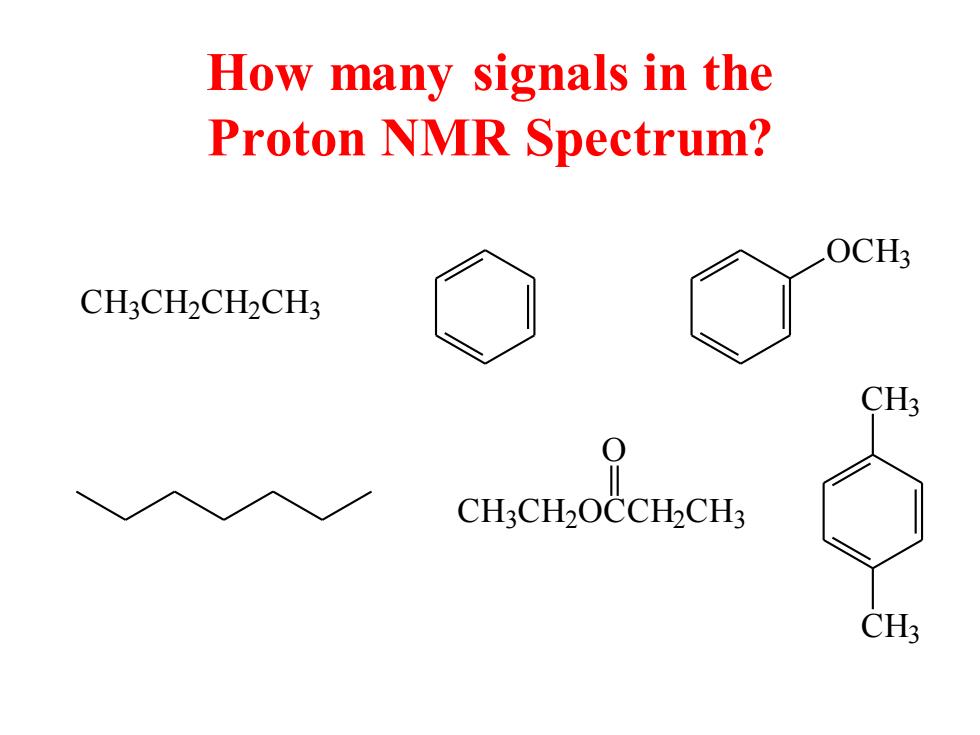
How many signals in the Proton NMR Spectrum? OCH3 CH3CH2CH2CH3 CH3 0 CH.CH2OCCHCH3 CH3
How many signals in the Proton NMR Spectrum? C H3 C H2 C H2 C H3 OCH3 C H3 C H2 OCCH2 C H3 O CH3 CH3