Conformational Analysis Newman Projections Ring Strain Cyclohexane Conformations
Conformational Analysis Newman Projections Ring Strain Cyclohexane Conformations
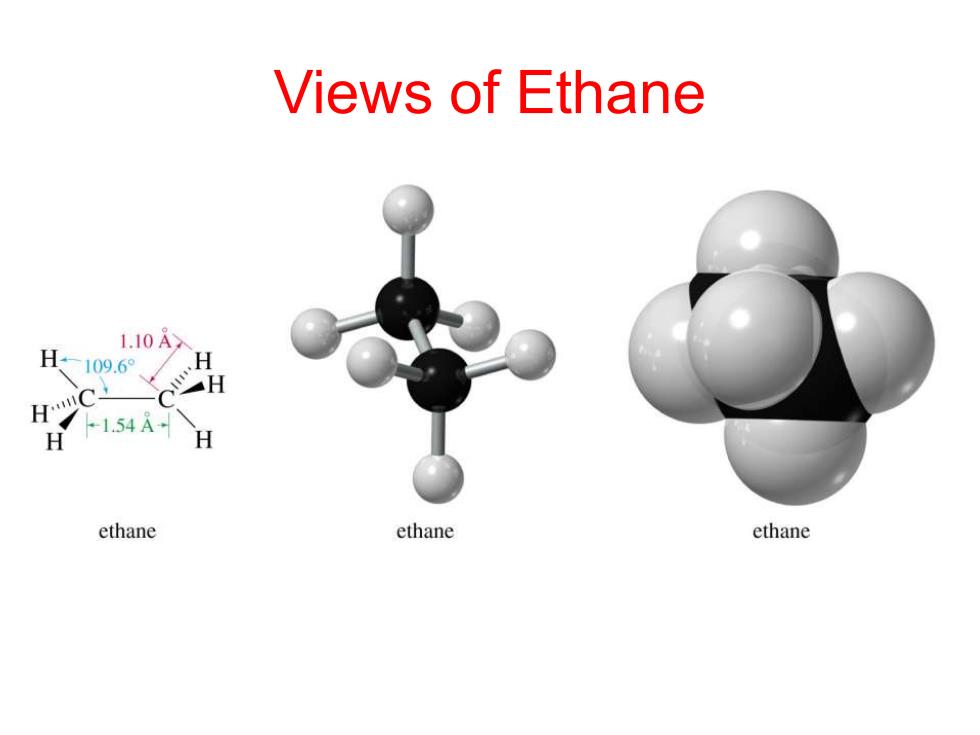
Views of Ethane 1.10A H-109.6°、/ H 1C H 154A H H ethane ethane ethane
Views of Ethane
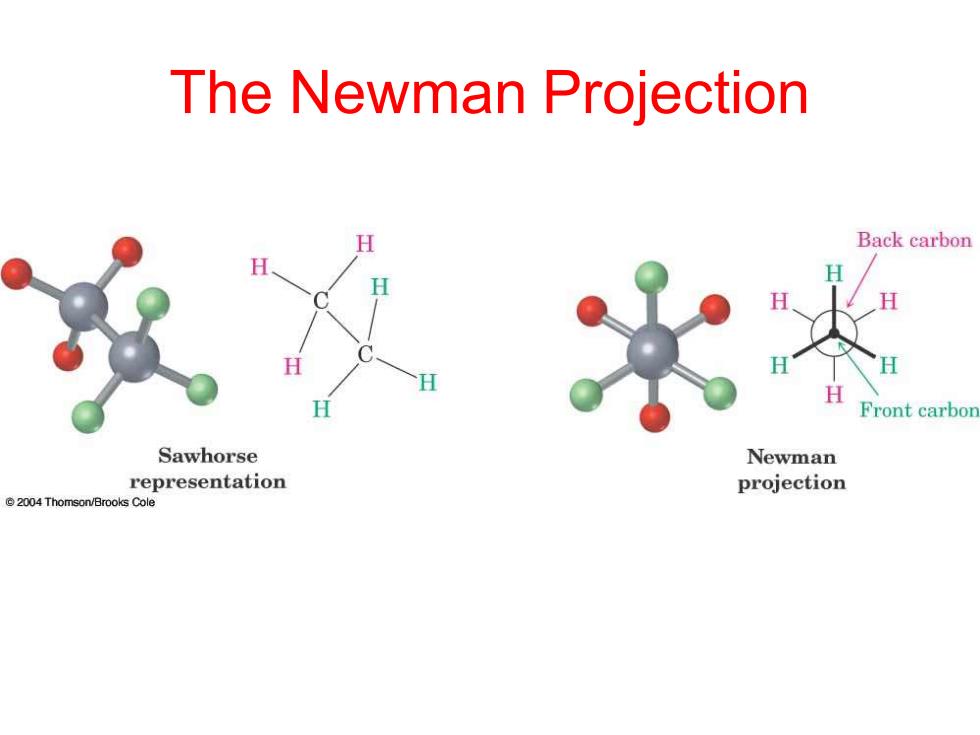
The Newman Projection H Back carbon Front carbon Sawhorse Newman representation projection 2004 Thomson/Brooks Cole
The Newman Projection
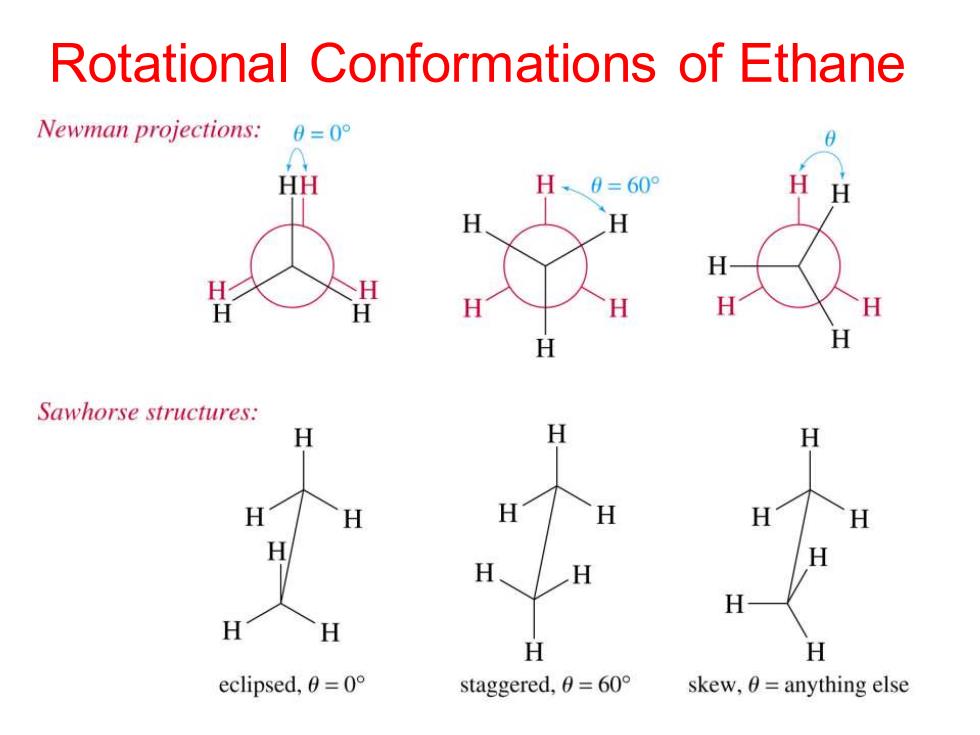
Rotational Conformations of Ethane Newman projections: 0=0° HH H、0=60 H H H H H H H H H Sawhorse structures: H H H H H H H H H H eclipsed,0=0° staggered,0=60° skew,0=anything else
Rotational Conformations of Ethane
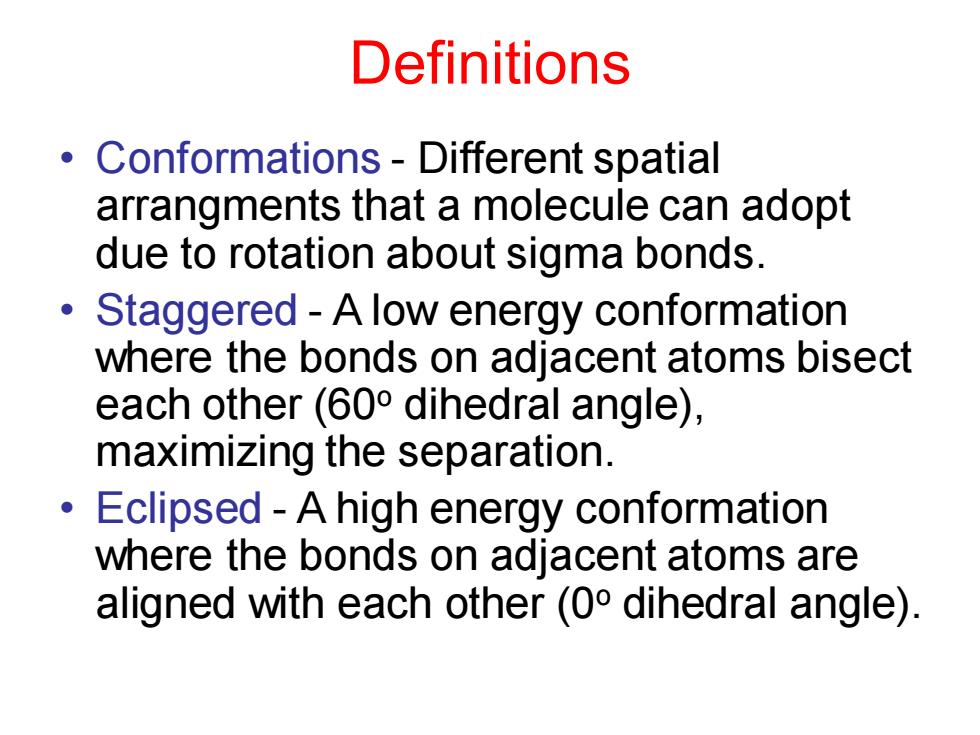
Definitions Conformations-Different spatial arrangments that a molecule can adopt due to rotation about sigma bonds. ● Staggered-A low energy conformation where the bonds on adjacent atoms bisect each other(600 dihedral angle), maximizing the separation. Eclipsed-A high energy conformation ● where the bonds on adjacent atoms are aligned with each other(0 dihedral angle)
Definitions • Conformations - Different spatial arrangments that a molecule can adopt due to rotation about sigma bonds. • Staggered - A low energy conformation where the bonds on adjacent atoms bisect each other (60o dihedral angle), maximizing the separation. • Eclipsed - A high energy conformation where the bonds on adjacent atoms are aligned with each other (0o dihedral angle)
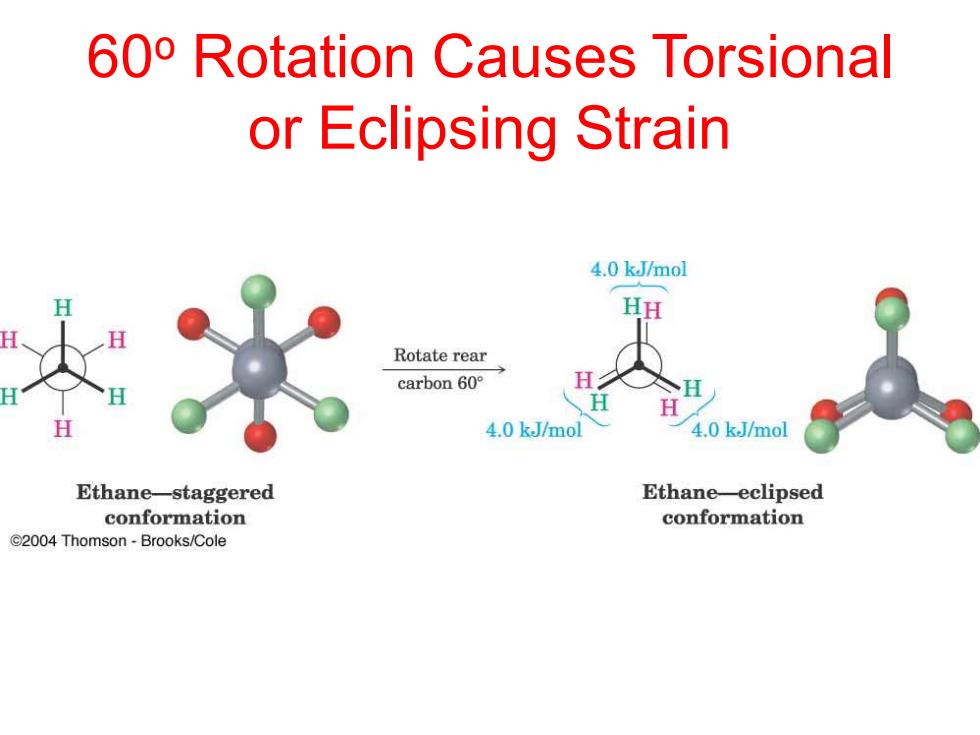
60o Rotation Causes Torsional or Eclipsing Strain 4.0 kJ/mol HH Rotate rear carbon60° 4.0 kJ/mol 4.0 k.J/mol Ethane-staggered Ethane-eclipsed conformation conformation C2004 Thomson-Brooks/Cole
60o Rotation Causes Torsional or Eclipsing Strain

Types of Strain Steric -Destabilization due to the repulsion between the electron clouds of atoms or groups. Groups try to occupy some common space. Torsional Destabilization due to the repulsion between pairs of bonds caused by the electrostatic repulsion of the electrons in the bonds.Groups are eclipsed. Angle Destabilisation due to distortion of a bond angle from it's optimum value caused by the electrostatic repulsion of the electrons in the bonds.e.g.cyclopropane
Types of Strain • Steric - Destabilization due to the repulsion between the electron clouds of atoms or groups. Groups try to occupy some common space. • Torsional - Destabilization due to the repulsion between pairs of bonds caused by the electrostatic repulsion of the electrons in the bonds. Groups are eclipsed. • Angle - Destabilisation due to distortion of a bond angle from it's optimum value caused by the electrostatic repulsion of the electrons in the bonds. e.g. cyclopropane

Definitions Anti Description given to two substitutents attached to adjacent atoms when their bonds are at 180 with respect to each other. Syn Description given to two substitutents attached to adjacent atoms when their bonds are at 0o with respect to each other. Gauche -Description given to two substitutents attached to adjacent atoms when their bonds are at 600 with respect to each other
Definitions • Anti - Description given to two substitutents attached to adjacent atoms when their bonds are at 180o with respect to each other. • Syn - Description given to two substitutents attached to adjacent atoms when their bonds are at 0o with respect to each other. • Gauche - Description given to two substitutents attached to adjacent atoms when their bonds are at 60o with respect to each other
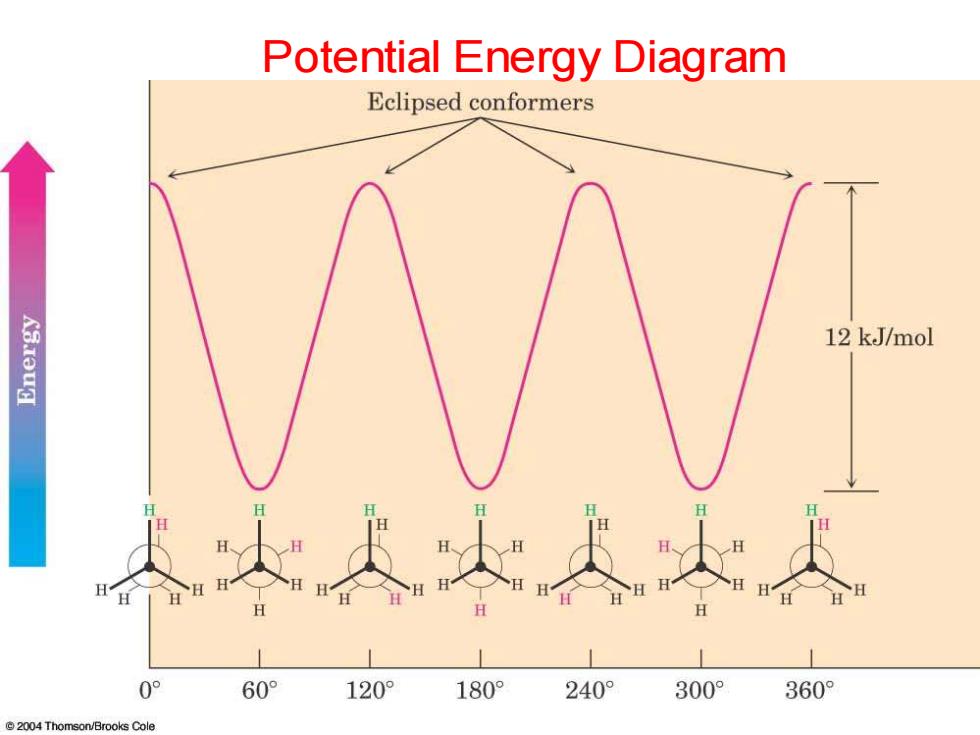
Potential Energy Diagram Eclipsed conformers siau出 12 kJ/mol 0° 60° 120° 180 240° 300° 360 2004 Thomson/Brooks Cole
Potential Energy Diagram
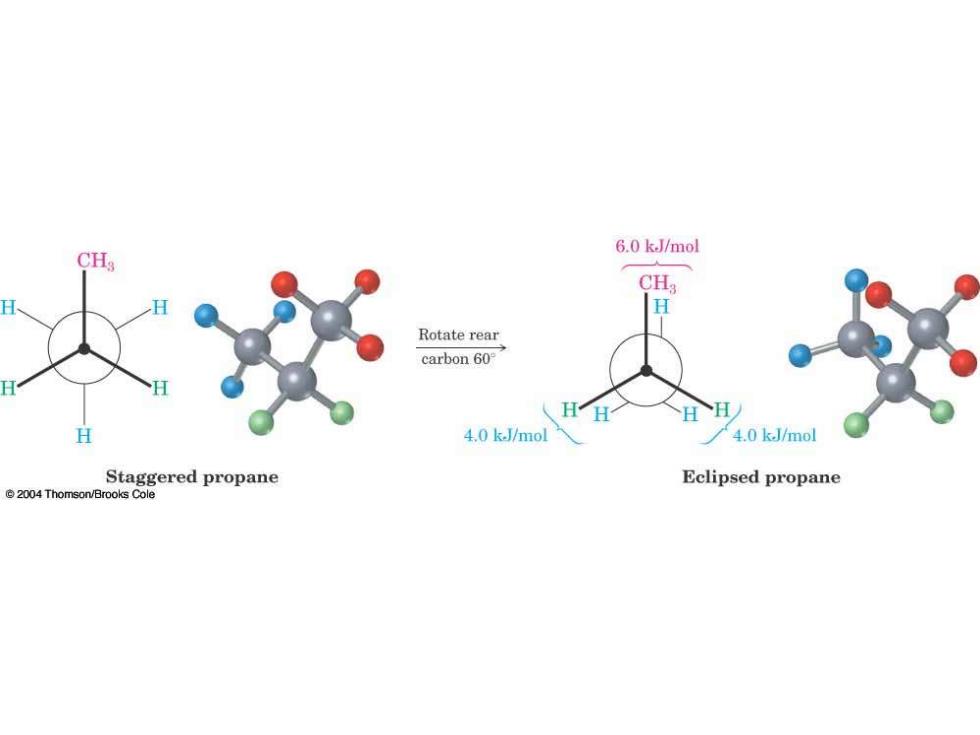
6.0 k.J/mol CHs CH H Rotate rear carbon 60 4.0 k.J/mol 4.0 k.J/mol Staggered propane Eclipsed propane 2004 Thomson/Brooks Cole