
Functional Groups
Functional Groups
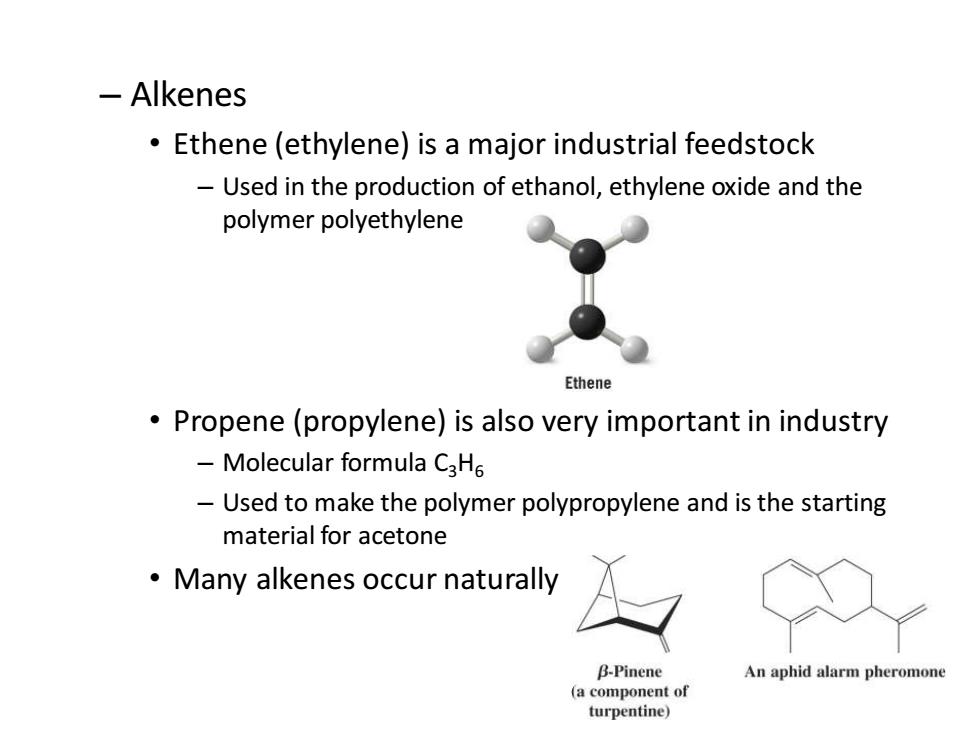
-Alkenes Ethene(ethylene)is a major industrial feedstock Used in the production of ethanol,ethylene oxide and the polymer polyethylene Ethene Propene(propylene)is also very important in industry Molecular formula C3H6 Used to make the polymer polypropylene and is the starting material for acetone Many alkenes occur naturally B-Pinene An aphid alarm pheromone (a component of turpentine)
2 – Alkenes • Ethene (ethylene) is a major industrial feedstock – Used in the production of ethanol, ethylene oxide and the polymer polyethylene • Propene (propylene) is also very important in industry – Molecular formula C3H6 – Used to make the polymer polypropylene and is the starting material for acetone • Many alkenes occur naturally
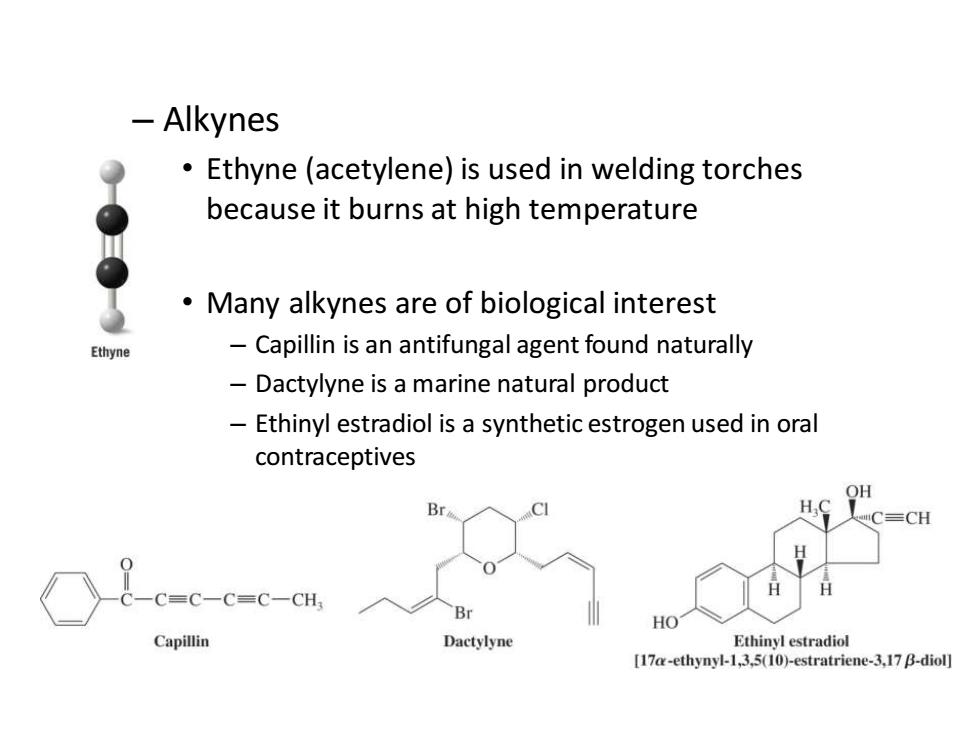
-Alkynes Ethyne(acetylene)is used in welding torches because it burns at high temperature Many alkynes are of biological interest Ethyne Capillin is an antifungal agent found naturally Dactylyne is a marine natural product Ethinyl estradiol is a synthetic estrogen used in oral contraceptives Br CH C=C-C=C-CH; Br HO Capillin Dactylyne Ethinyl estradiol [17a-ethynyl-1,3,5(10)-estratriene-3,17 B-diol]
– Alkynes • Ethyne (acetylene) is used in welding torches because it burns at high temperature • Many alkynes are of biological interest – Capillin is an antifungal agent found naturally – Dactylyne is a marine natural product – Ethinyl estradiol is a synthetic estrogen used in oral contraceptives
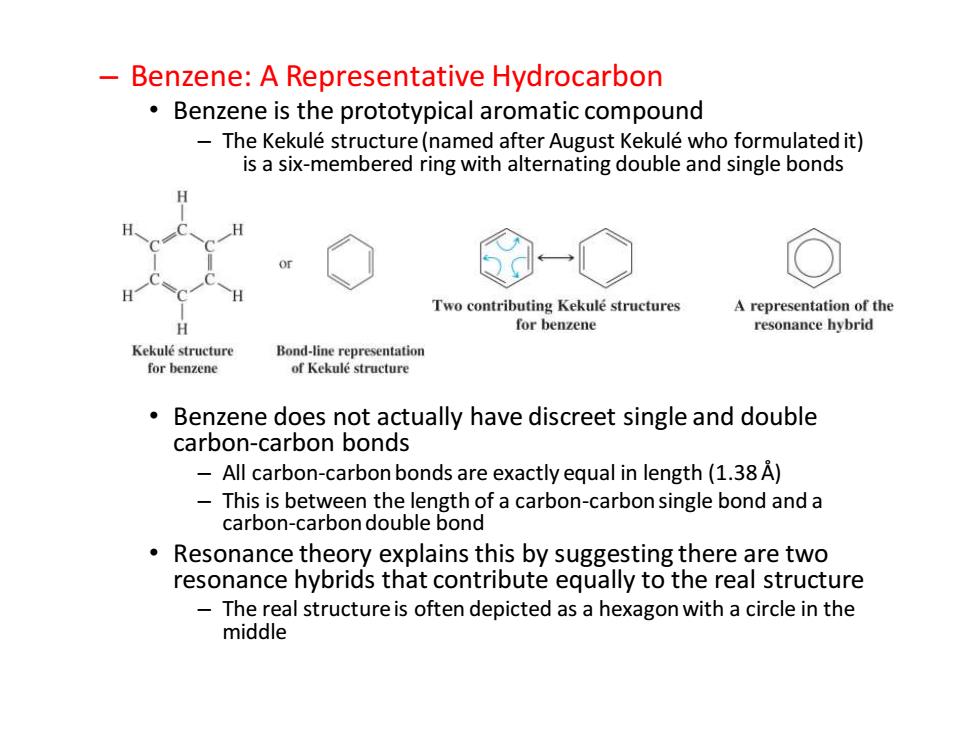
Benzene:A Representative Hydrocarbon Benzene is the prototypical aromatic compound The Kekule structure(named after August Kekule who formulated it) is a six-membered ring with alternating double and single bonds Two contributing Kekule structures A representation of the H for benzene resonance hybrid Kekule structure Bond-line representation for benzene of Kekule structure Benzene does not actually have discreet single and double carbon-carbon bonds 一 All carbon-carbon bonds are exactly equal in length(1.38 A) This is between the length of a carbon-carbon single bond and a carbon-carbon double bond Resonance theory explains this by suggesting there are two resonance hybrids that contribute equally to the real structure The real structure is often depicted as a hexagon with a circle in the middle
– Benzene: A Representative Hydrocarbon • Benzene is the prototypical aromatic compound – The Kekulé structure (named after August Kekulé who formulated it) is a six-membered ring with alternating double and single bonds • Benzene does not actually have discreet single and double carbon-carbon bonds – All carbon-carbon bonds are exactly equal in length (1.38 Å) – This is between the length of a carbon-carbon single bond and a carbon-carbon double bond • Resonance theory explains this by suggesting there are two resonance hybrids that contribute equally to the real structure – The real structure is often depicted as a hexagon with a circle in the middle
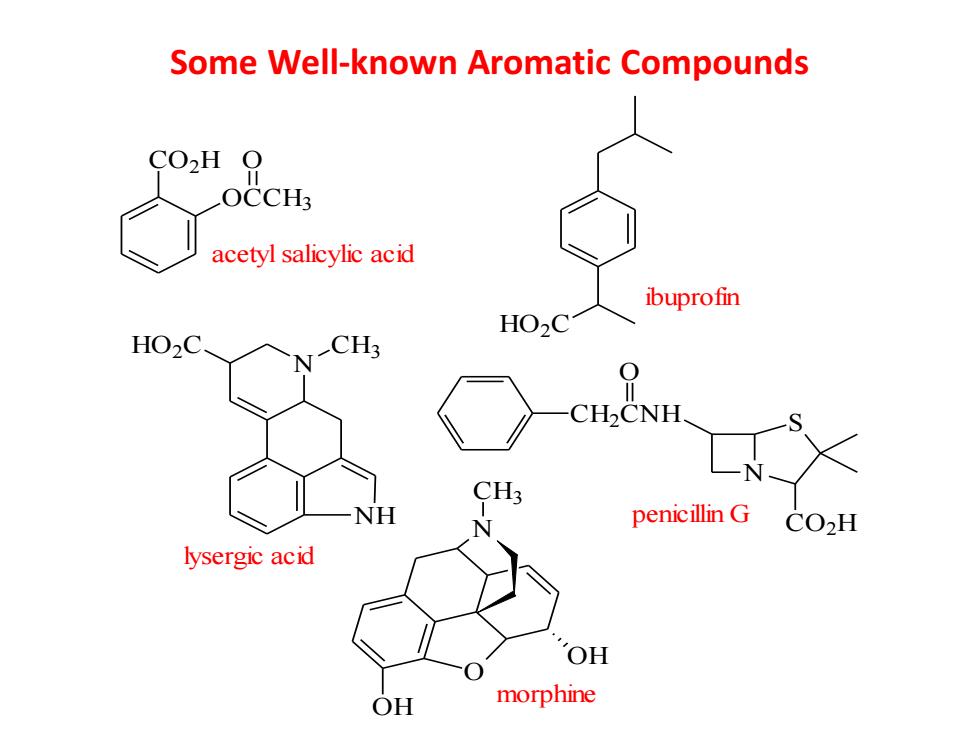
Some Well-known Aromatic Compounds CO2H O OCCH3 acetyl salicylic acid ibuprofin HO2C HO2C. CH3 CH2CNH CH3 NH penicillin G COH lysergic acid OH OH morphine
Some Well-known Aromatic Compounds CO2H OCCH3 O acetyl salicylic acid HO2C ibuprofin N NH HO2C CH3 lysergic acid N S CO2H CH2CNH O penicillin G O OH OH N CH3 morphine
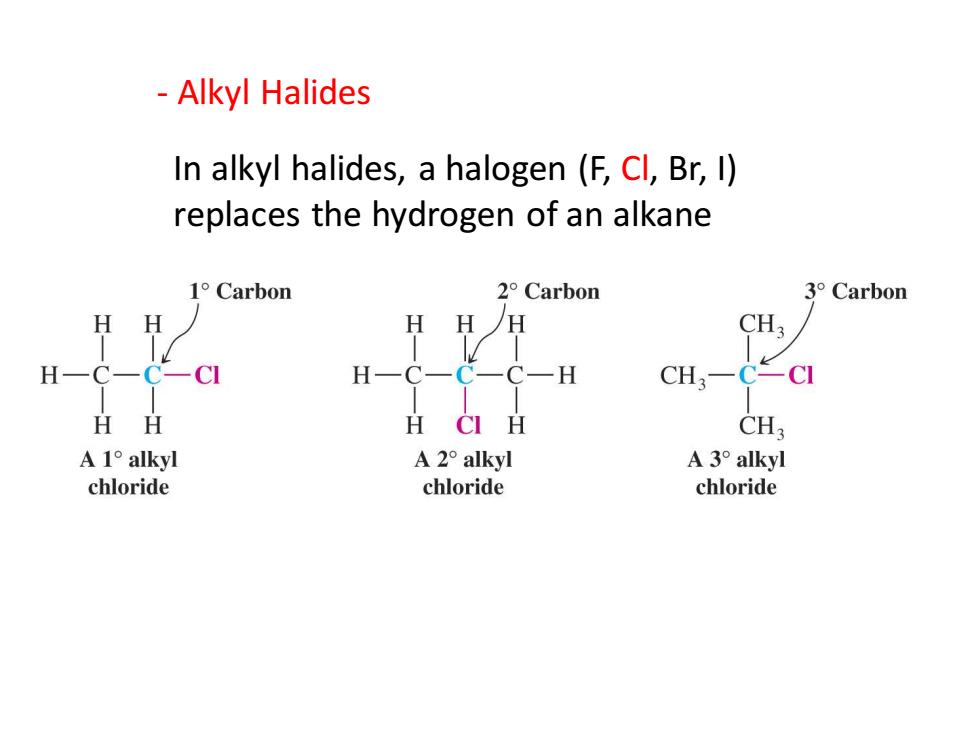
Alkyl Halides In alkyl halides,a halogen (F,Cl,Br,I) replaces the hydrogen of an alkane 1°Carbon 2°Carbon 3°Carbon HH H HH CH3 H-C-C-CI H一C一C一C-H CH3-C-CI HH H CI H CH3 A1°alkyl A2°alkyl A3°alkyl chloride chloride chloride
- Alkyl Halides In alkyl halides, a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces the hydrogen of an alkane
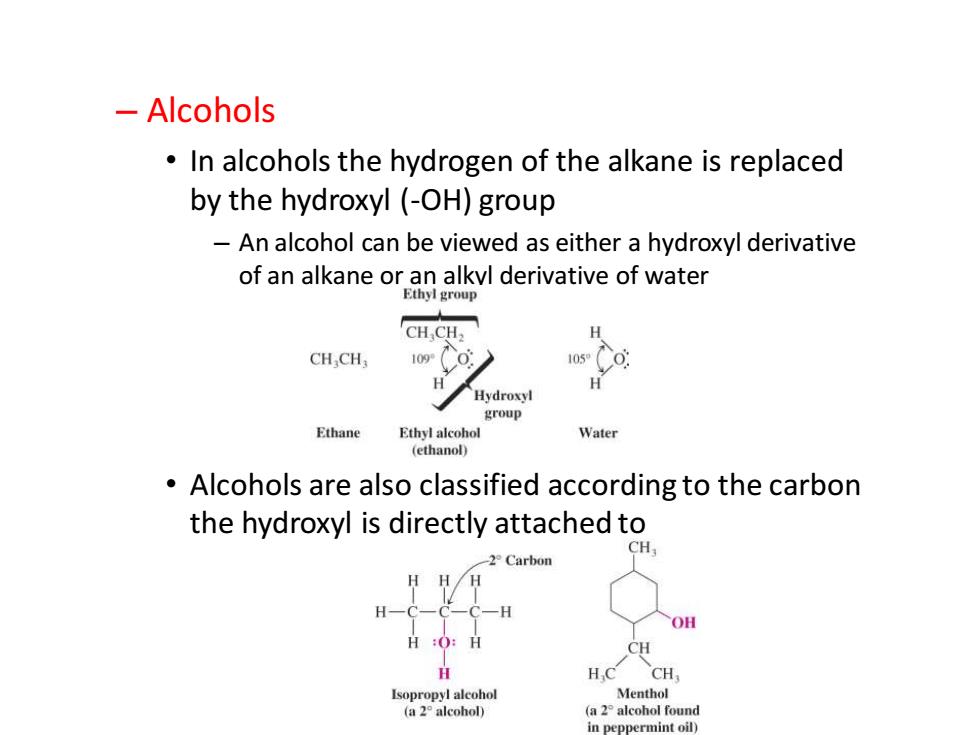
-Alcohols In alcohols the hydrogen of the alkane is replaced by the hydroxyl (-OH)group An alcohol can be viewed as either a hydroxyl derivative of an alkane or an alkvl derivative of water Ethyl group CHCH H CHCH H H Hydroxyl group Ethane Ethyl alcohol Water (ethanol) Alcohols are also classified according to the carbon the hydroxyl is directly attached to 2 Carbon HH/H H 一H OH H:O:H CH H H.C CH Isopropyl alcohol Menthol (a 2 alcohol) (a 2 alcohol found in peppermint oil)
Chapter 2 – Alcohols • In alcohols the hydrogen of the alkane is replaced by the hydroxyl (-OH) group – An alcohol can be viewed as either a hydroxyl derivative of an alkane or an alkyl derivative of water • Alcohols are also classified according to the carbon the hydroxyl is directly attached to
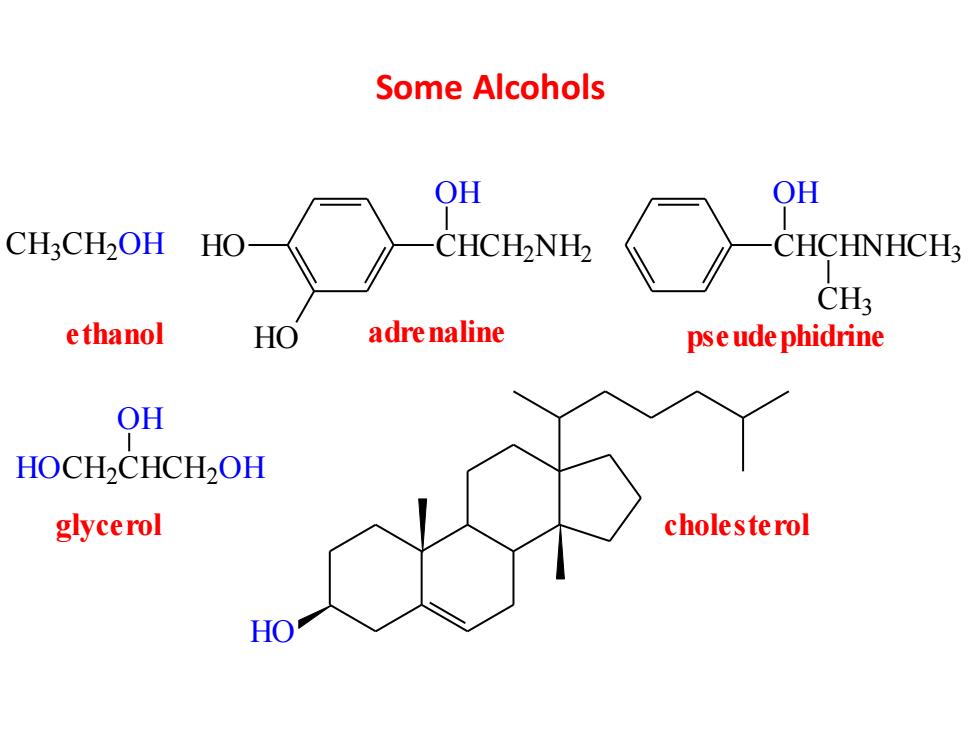
Some Alcohols OH OH CH3CH2OH HO CHCH2NH2 CHCHNHCH3 CH3 e thanol HO adre naline pse ude phidrine OH HOCH2CHCH2OH glycerol cholesterol HO
Some Alcohols C H3 C H2 O H HO HO CHCH2 NH2 OH ethanol adrenaline CHCHNHCH3 OH CH3 pseudephidrine HOC H2 CHCH2 O H OH glycerol HO cholesterol
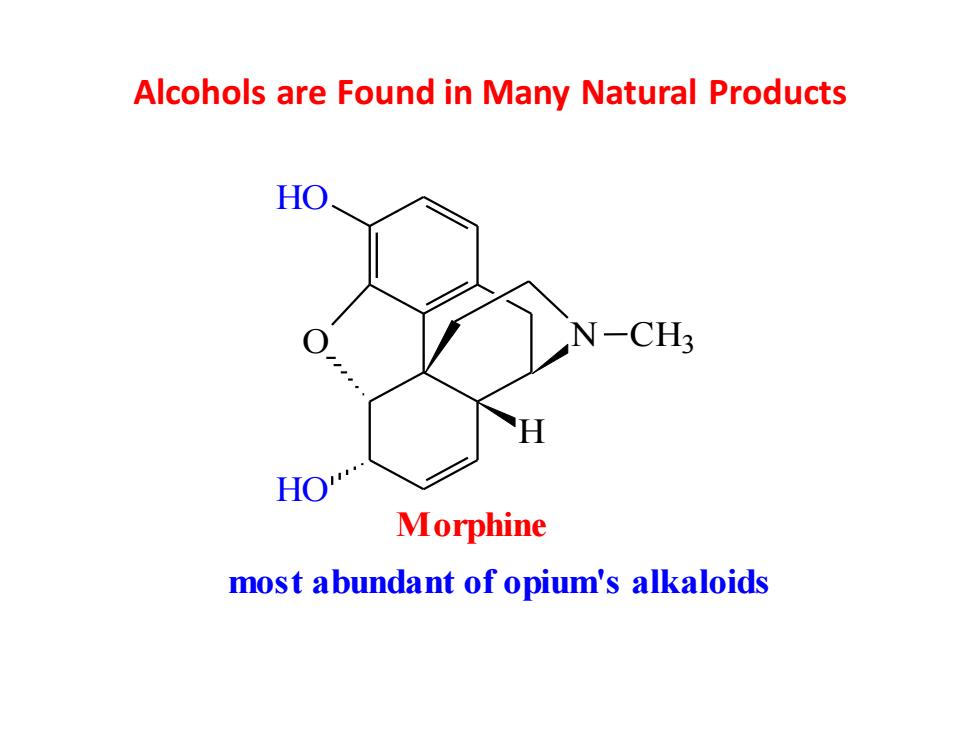
Alcohols are Found in Many Natural Products HO N-CH3 HO Morphine most abundant of opium's alkaloids
Alcohols are Found in Many Natural Products O HO HO N CH3 H Morphine most abundant of opium's alkaloids
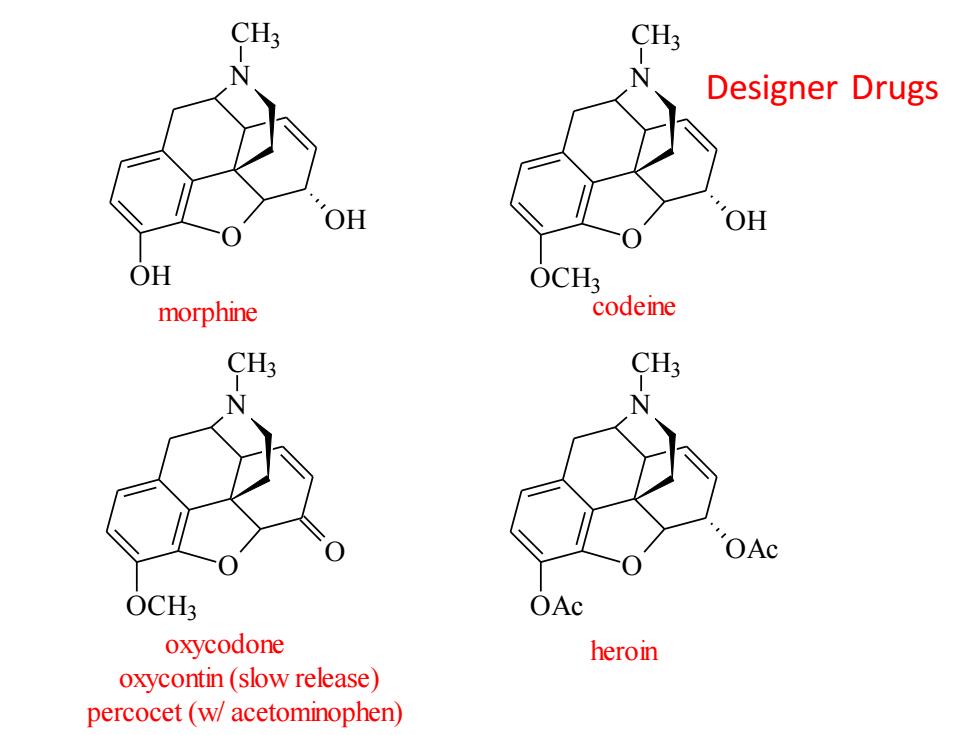
CH3 N Designer Drugs OH OH OH OCH3 morphine codeine CH3 CH3 OAc OCH3 OAc oxycodone heroin oxycontin(slow release) percocet(w/acetominophen)
Designer Drugs O OH OH N CH3 morphine O OH OCH3 N CH3 codeine O OCH3 N CH3 O oxycodone oxycontin (slow release) percocet (w/ acetominophen) O OAc OAc N CH3 heroin