
Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 17 18 Aromatic chemistry By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com 西北农林科技大学理学院
Chapter 17 & 18 Aromatic chemistry Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. By Junru Wang Email: wangjr07@163.com 西北农林科技大学理学院
CONTENT Structure Physical Properties Aromaticity reactivity Hiickel rule Preparation of Ar compounds Electrophilic substitutions Effects of substituents on E.S. -Synthesis of mono-,di-and tri-substituted benzenes Other reactions -Oxidation and reduction -Nucleophilic Substitution
CONTENT Structure & Physical Properties Aromaticity & reactivity Hückel rule Preparation of Ar compounds Electrophilic substitutions Effects of substituents on E.S. Synthesis of mono-, di- and tri-substituted benzenes Other reactions Oxidation and reduction Nucleophilic Substitution
Keynotes Aromaticity Resonance Structure Hiickel rule Electrophilic substitutions Deactivating group,Deactivating group
Keynotes Aromaticity Resonance Structure Hückel rule Electrophilic substitutions Deactivating group, Deactivating group
Sec 1 Structure Physical Properties Discovery of Benzene -Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. -Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to be C6H6. -Other related compounds with low C:H ratios had a pleasant smell,so they were classified as aromatic
Sec 1 Structure & Physical Properties Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to be C6 H6 . Other related compounds with low C:H ratios had a pleasant smell, so they were classified as aromatic
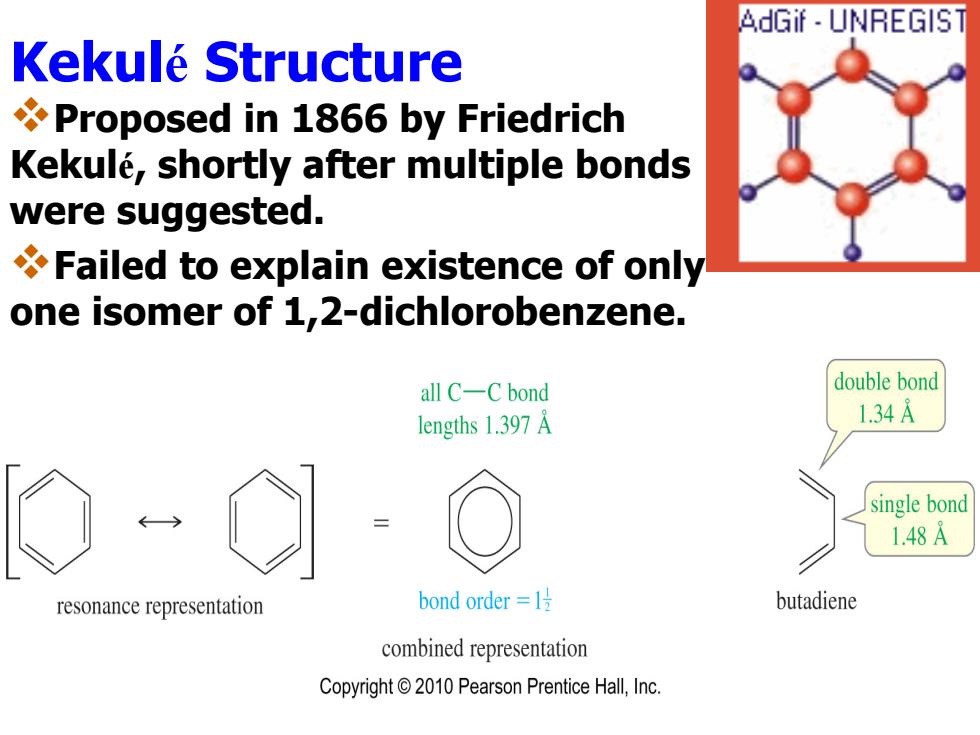
AdGif UNREGIST Kekule Structure Proposed in 1866 by Friedrich Kekule,shortly after multiple bonds were suggested. Failed to explain existence of only one isomer of 1,2-dichlorobenzene. all C-C bond double bond lengths 1.397 A 1.34A single bond 1.48A resonance representation bond order=l号 butadiene combined representation Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Kekulé Structure Proposed in 1866 by Friedrich Kekul é, shortly after multiple bonds were suggested. Failed to explain existence of only one isomer of 1,2-dichlorobenzene
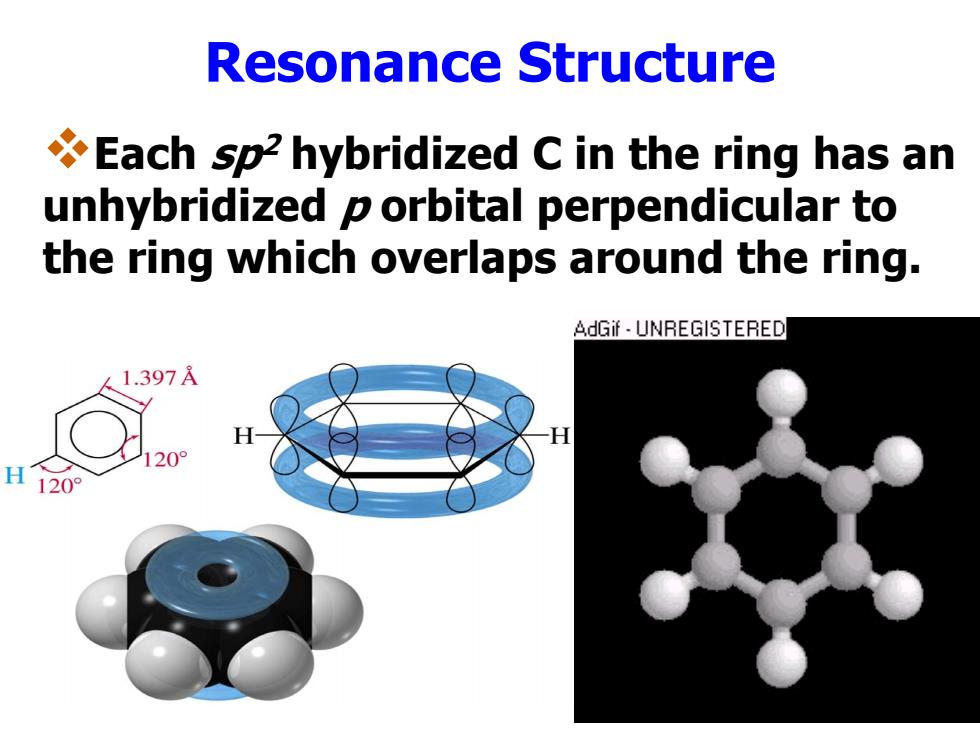
Resonance Structure Each sp2 hybridized C in the ring has an unhybridized p orbital perpendicular to the ring which overlaps around the ring. AdGif UNREGISTERED 1.397A 20 H 120°
Resonance Structure Each sp2 hybridized C in the ring has an unhybridized p orbital perpendicular to the ring which overlaps around the ring
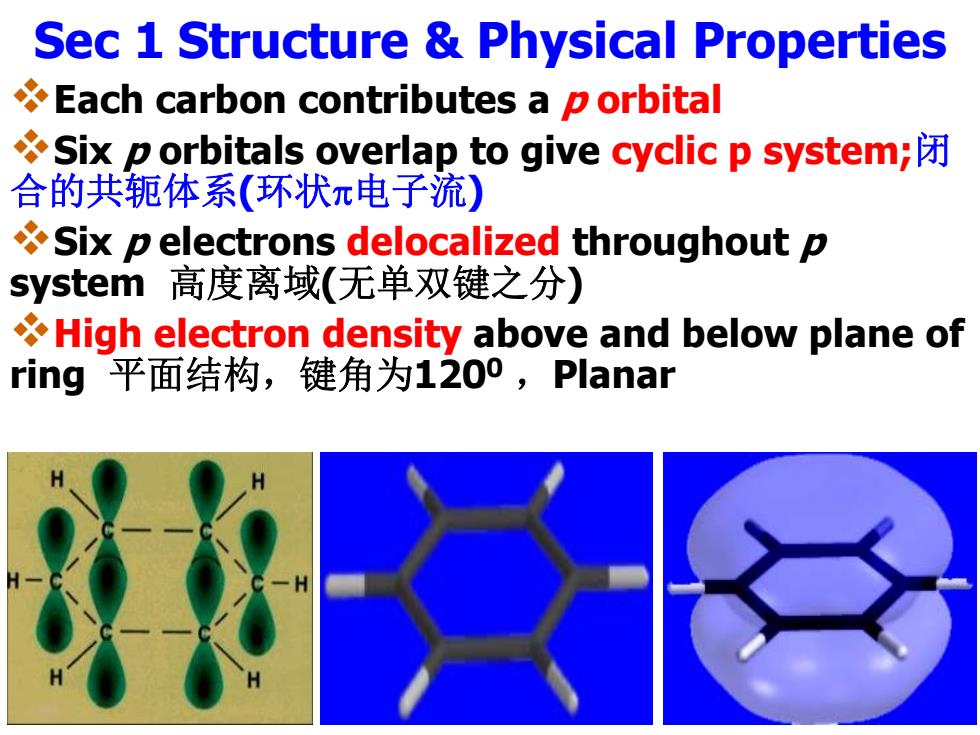
Sec 1 Structure Physical Properties Each carbon contributes a p orbital Six p orbitals overlap to give cyclic p system; 合的共轭体系(环状π电子流) Six p electrons delocalized throughout p system高度离域(无单双键之分) High electron density above and below plane of ring平面结构,键角为1200,Planar
Sec 1 Structure & Physical Properties Each carbon contributes a p orbital Six p orbitals overlap to give cyclic p system; 闭 合的共轭体系 (环状 电子流 ) Six p electrons delocalized throughout p system 高度离域 (无单双键之分 ) High electron density above and below plane of ring 平面结构,键角为1200 ,Planar
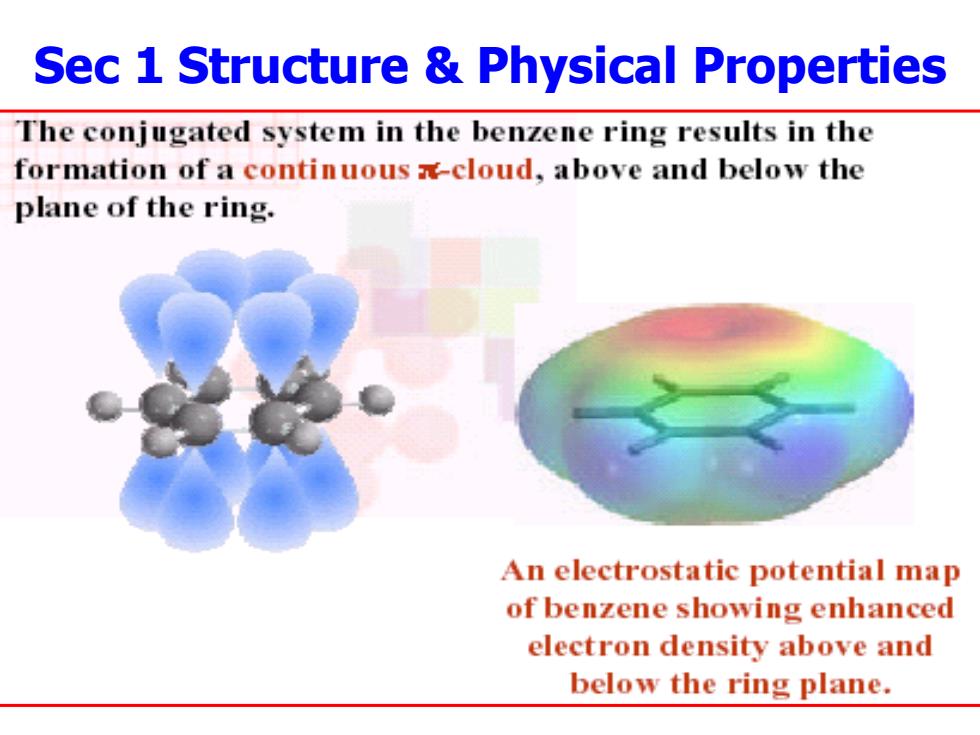
Sec 1 Structure Physical Properties The conjugated system in the benzene ring results in the formation of a continuous -cloud,above and below the plane of the ring. An electrostatic potential map of benzene showing enhanced electron density above and below the ring plane
Sec 1 Structure & Physical Properties
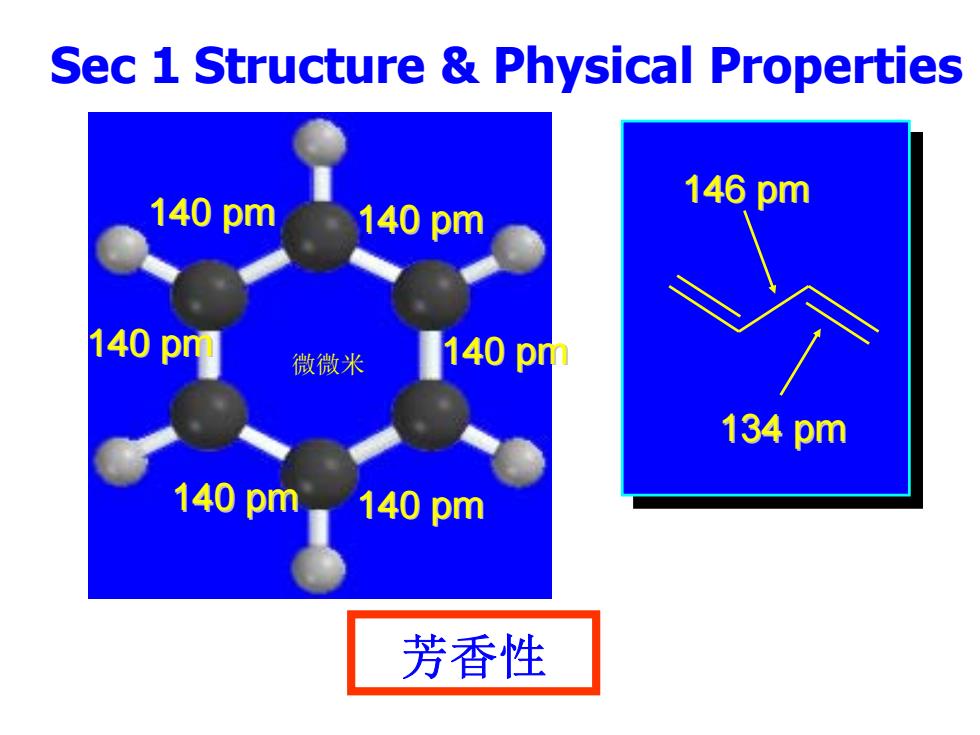
Sec 1 Structure Physical Properties 140pm 146pm 140pm 140pm 微微米 140pm 134pm 140pm 140pm 芳香性
Sec 1 Structure & Physical Properties 芳香性 140 pm 140 pm 140 pm 140 pm 140 pm 140 pm 146 pm 134 pm 微微米
Unusual Reactions Alkene KMnO4>diol (addition) Benzene KMnO4->no reaction. Alkene Br2/CCl4>dibromide (addition) -Benzene Br2/CCl4->no reaction. With FeCl3 catalyst,Br2 reacts with benzene to form bromobenzene HBr (substitution!). -Double bonds remain
Unusual Reactions Alkene + KMnO4 diol (addition) Benzene + KMnO4 no reaction. Alkene + Br2 /CCl4 dibromide (addition) Benzene + Br2 /CCl4 no reaction. With FeCl3 catalyst, Br2 reacts with benzene to form bromobenzene + HBr (substitution!). Double bonds remain