
Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 08 09 AlRenes Key Notes Electrophile;Electrophilic addition; Carbocation stability;Conjugated dienes By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com 西北农林科技大学理学院
西北农林科技大学理学院 By Junru Wang Email: wangjr07@163.com Chapter 08 & 09 Alkenes Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Key Notes Electrophile; Electrophilic addition; Carbocation stability; Conjugated dienes

Content Introduction Properties Preparation Reactions of alkenes Electrophilic addition -Carbocation stabilization -Free-Radical Addition of HBr Reduction and oxidation -Allylic halogenation Conjugated dienes
Content ❖Introduction & Properties ❖Preparation ❖Reactions of alkenes ◼Electrophilic addition ◼Carbocation stabilization ◼Free-Radical Addition of HBr ◼Reduction and oxidation ◼Allylic halogenation ❖Conjugated dienes
Key Notes Electrophile Electrophilic addition Carbocation stability Conjugated dienes
Key Notes ❖Electrophile ❖Electrophilic addition ❖Carbocation stability ❖Conjugated dienes

Sec 1 Introduction Properties Hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds Sometimes called olefins,oil-forming gas” Pi bond is the functional group. More reactive than sigma bond. Bond dissociation energies: C=C BDE 611 kJ/mol C-C BDE -347 kJ/mol Pi bond 264k灯/mol
Sec 1 Introduction & Properties ❖Hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds ❖Sometimes called olefins, “oil-forming gas” ❖Pi bond is the functional group. ❖More reactive than sigma bond. ❖Bond dissociation energies: ◼C=C BDE 611 kJ/mol ◼C-C BDE -347 kJ/mol ◼Pi bond 264 kJ/mol
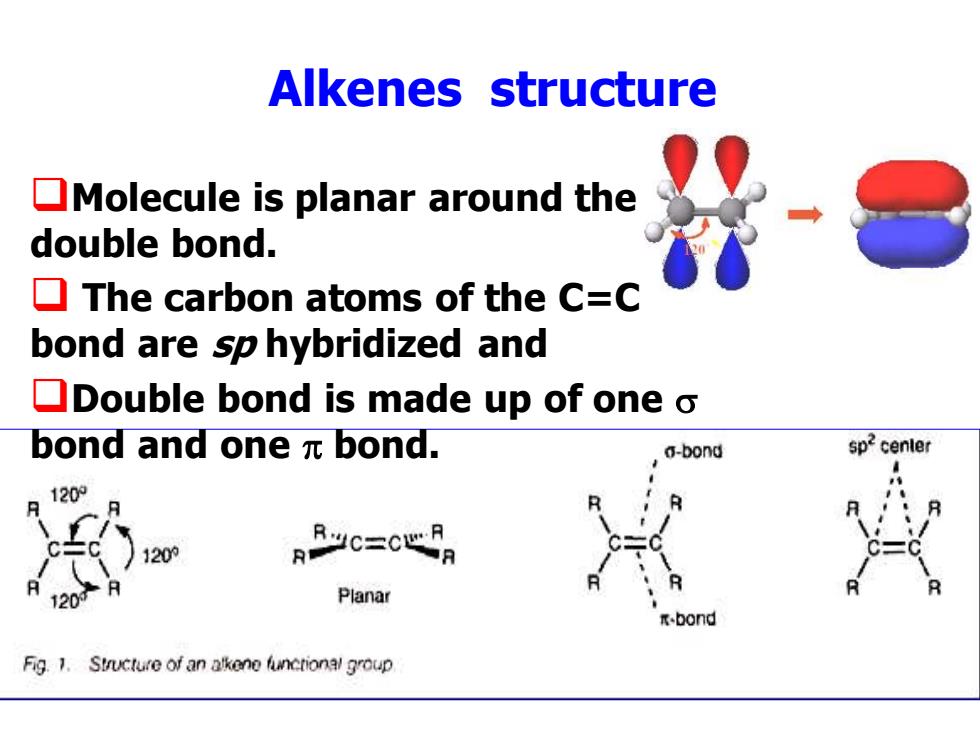
Alkenes structure Molecule is planar around the double bond. The carbon atoms of the C=C bond are sp hybridized and Double bond is made up of one o bond and one元bond. a-bond sp2center 120 120的 RR.JC-CLP 120 Planar bond Fig.1.Structure of an alkene functional group
Alkenes structure ❑Molecule is planar around the double bond. ❑ The carbon atoms of the C=C bond are sp hybridized and ❑Double bond is made up of one bond and one bond
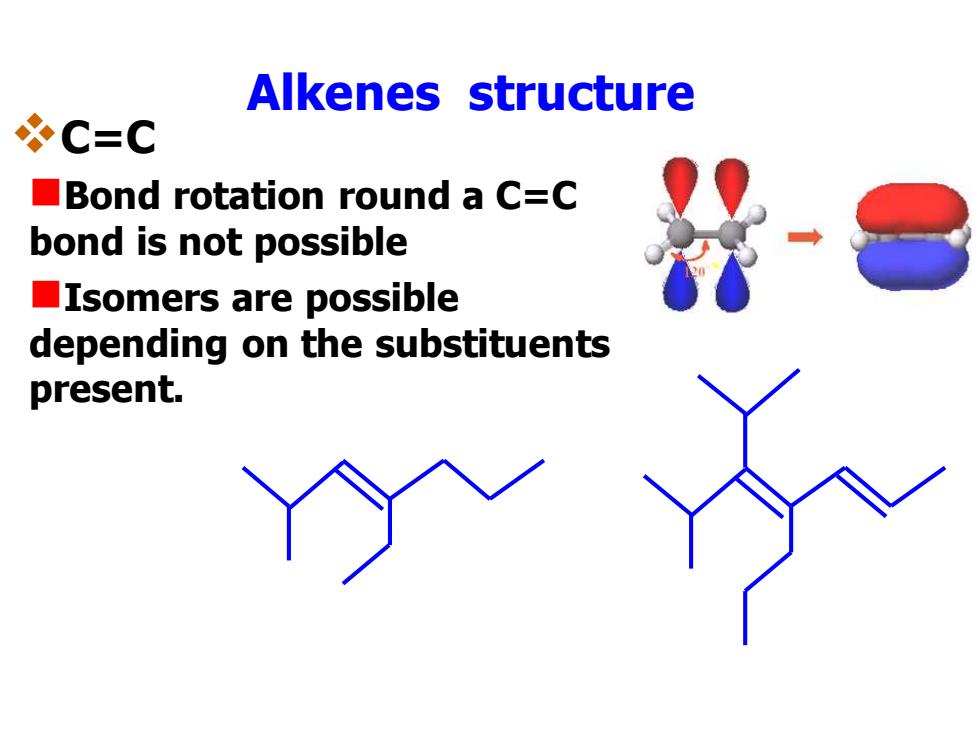
Alkenes structure *C=C Bond rotation round a C=C bond is not possible ■Isomers are possible depending on the substituents present
Alkenes structure ❖C=C ◼Bond rotation round a C=C bond is not possible ◼Isomers are possible depending on the substituents present
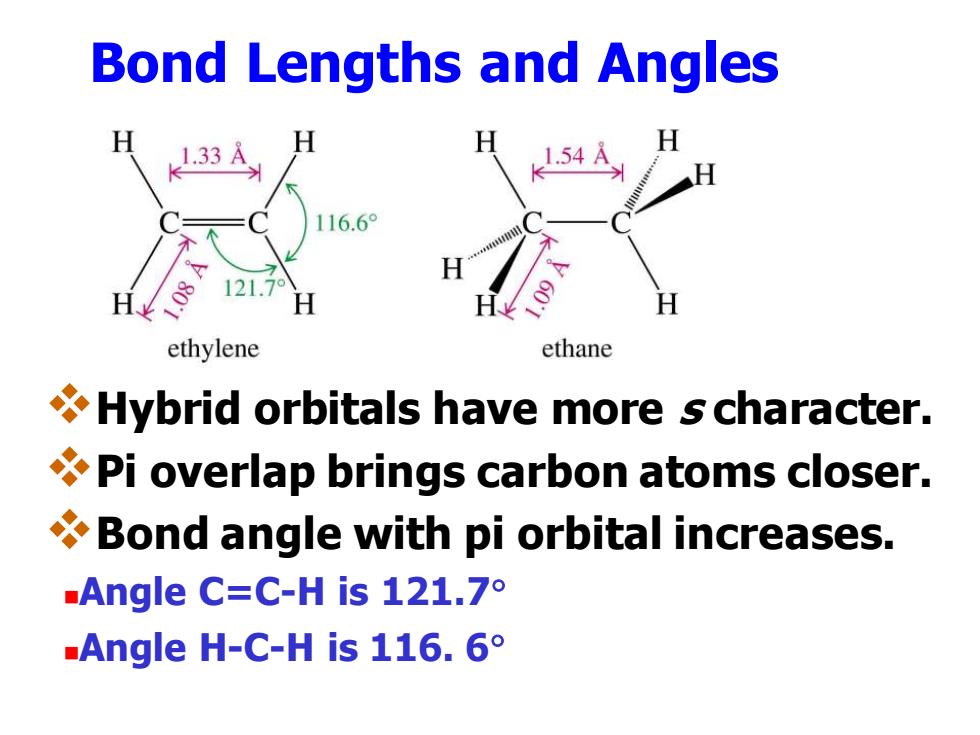
Bond Lengths and Angles 1.33 54 116.6° 121.7 ethylene ethane Hybrid orbitals have more s character. Pi overlap brings carbon atoms closer. Bond angle with pi orbital increases. Angle C:=C-His121.7° Angle H-C-His116.6°
Bond Lengths and Angles ❖Hybrid orbitals have more s character. ❖Pi overlap brings carbon atoms closer. ❖Bond angle with pi orbital increases. ◼Angle C=C-H is 121.7 ◼Angle H-C-H is 116. 6
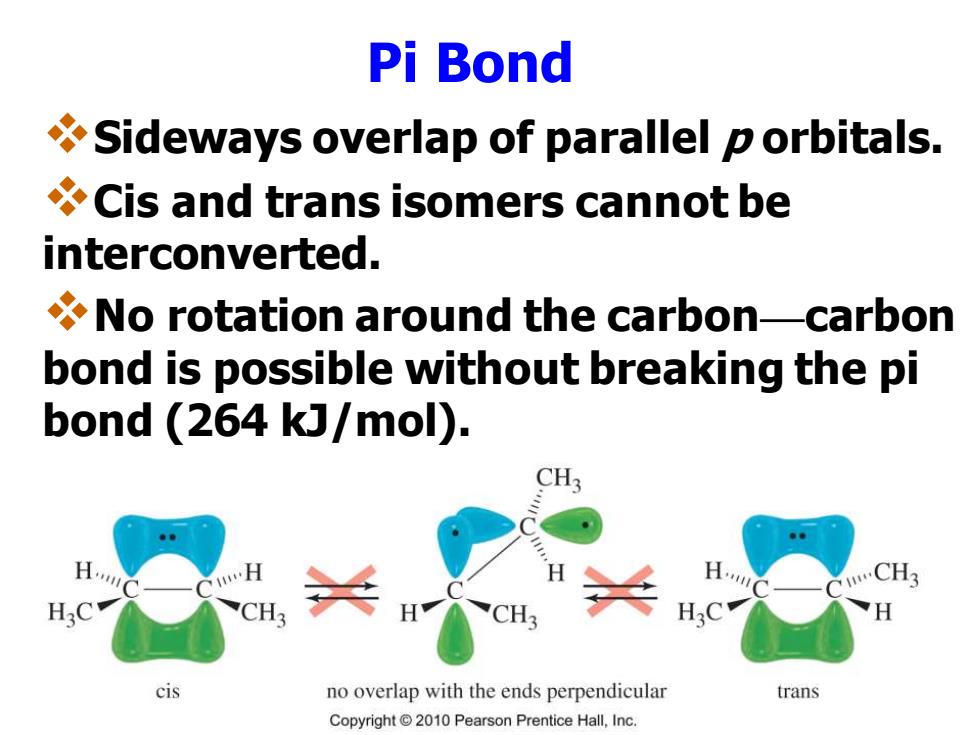
Pi Bond Sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals. Cis and trans isomers cannot be interconverted. No rotation around the carbon-carbon bond is possible without breaking the pi bond (264 kJ/mol). CH3 CH3 H:C CH cis no overlap with the ends perpendicular trans Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Pi Bond ❖Sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals. ❖Cis and trans isomers cannot be interconverted. ❖No rotation around the carbon—carbon bond is possible without breaking the pi bond (264 kJ/mol)
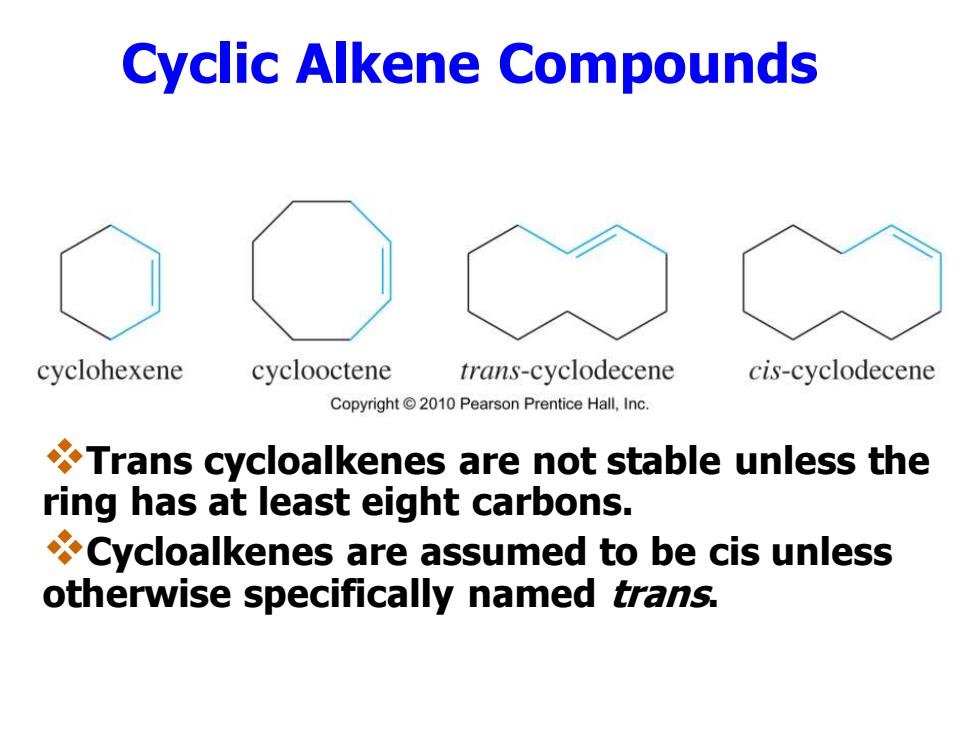
Cyclic Alkene Compounds cyclohexene cyclooctene trans-cyclodecene cis-cyclodecene Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Trans cycloalkenes are not stable unless the ring has at least eight carbons. Cycloalkenes are assumed to be cis unless otherwise specifically named trans
Cyclic Alkene Compounds ❖Trans cycloalkenes are not stable unless the ring has at least eight carbons. ❖Cycloalkenes are assumed to be cis unless otherwise specifically named trans
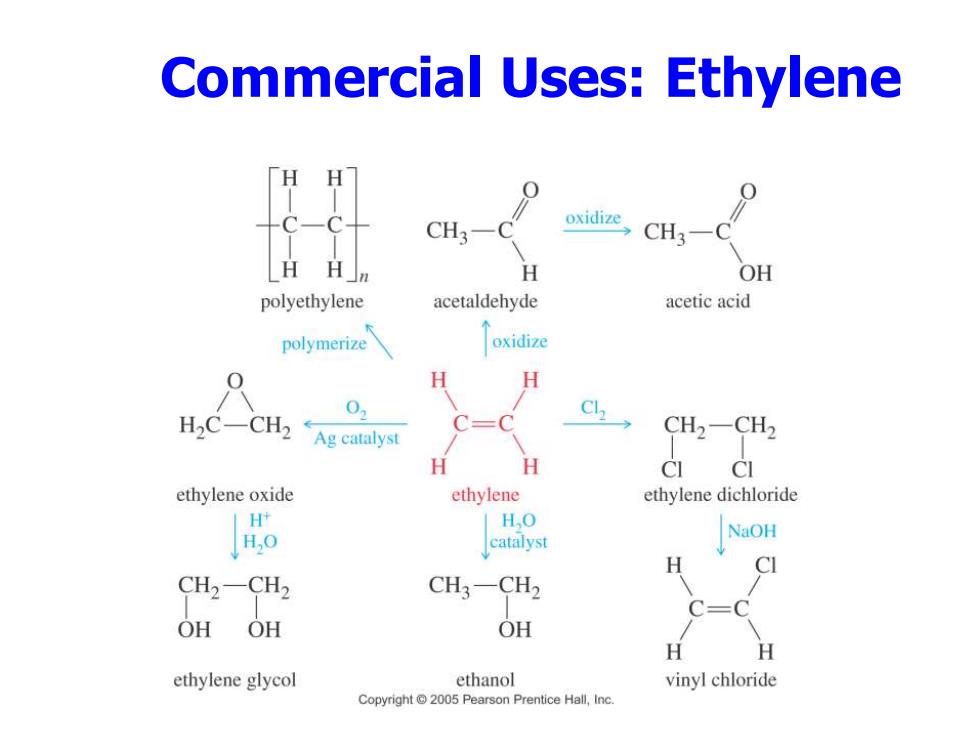
Commercial Uses:Ethylene CH3- oxidize CH3-C H H H OH polyethylene acetaldehyde acetic acid polymerize oxidize H H H2C-CH2 0 Ag catalyst CH2-CH2 H H CI CI ethylene oxide ethylene ethylene dichloride I H,O H,0 catalyst NaOH H C CH2-CH2 CH3-CH2 OHOH OH H H ethylene glycol ethanol vinyl chloride Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Commercial Uses: Ethylene