自秋不转大对 教华税 Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acids http://www.study-organic-chemistry.com/ By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com
By Junru Wang Email: wangjr07@163.com Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acids Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. http://www.study-organic-chemistry.com/

CONTENT ■REVIEW:NAMING STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION ■PREPARATIONS ■REACTIONS ■ENOLATE REACTIONS
CONTENT ◼REVIEW:NAMING ◼STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES ◼NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION ◼PREPARATIONS ◼REACTIONS ◼ENOLATE REACTIONS

Sec 1 STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES Carbon is sp2 hybridized. 1.32A Bond angles are close to 124/2s 1.23A 120°. )106 1.10A 0.97A H O-H eclipsed with C=O,to H 11100 H get overlap of zorbital bond angles bond lengths with orbital of lone pair or. oxygen. Resonance Stabilization R-C-0-H+H,0: R- +H,0t pK=5 (K≡105) acid carboxylate
◼Carbon is sp2 hybridized. ◼Bond angles are close to 120 . ◼O-H eclipsed with C=O, to get overlap of orbital with orbital of lone pair on oxygen. ◼Resonance Stabilization Sec 1 STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES
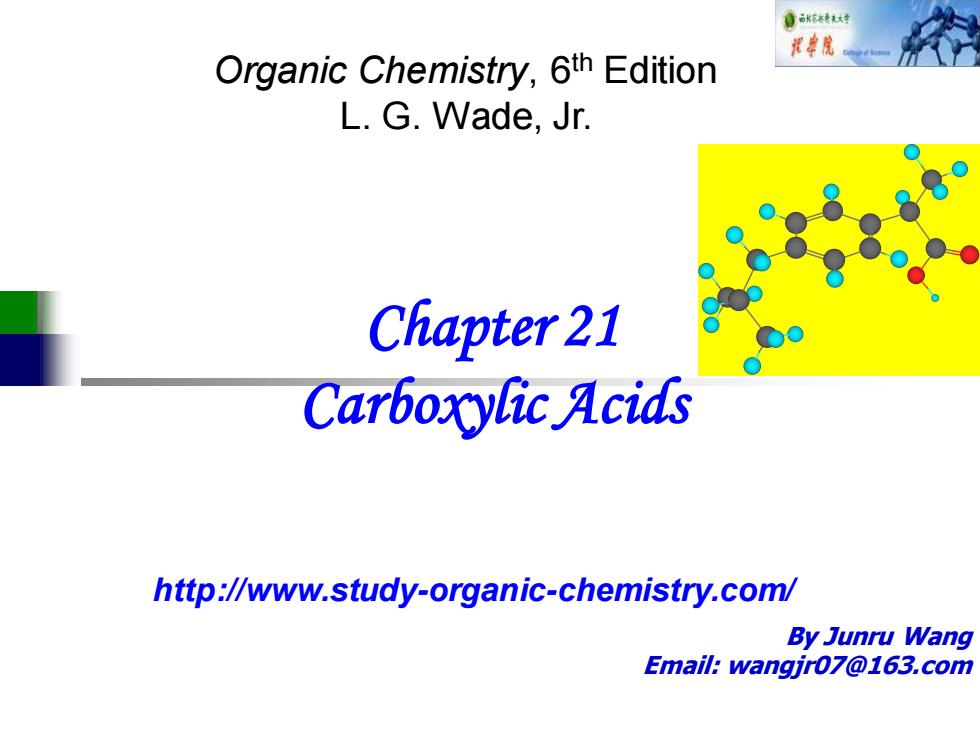
Resonance Structures :0: :0 H←→ H H H H H major very minor minor H CH3
Resonance Structures
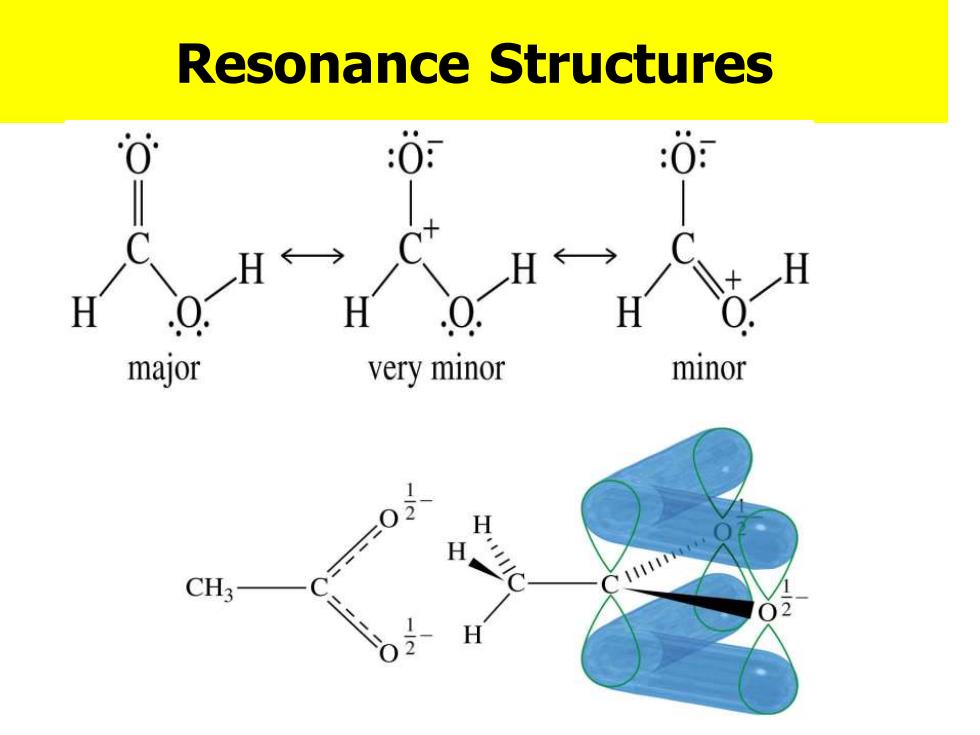
B.P Higher boiling points than similar alcohols,due to dimer formation b.p.°C Formaldehyde -21° Methanol 64° Formic acid 100P Acetaldehyde 21° Ethanol 78 Acetic acid 118 0H一0 R- Acetic acid,b.p.118C hydrogen-bonded acid dimer
❖B.P Higher boiling points than similar alcohols, due to dimer formation Acetic acid, b.p. 118C
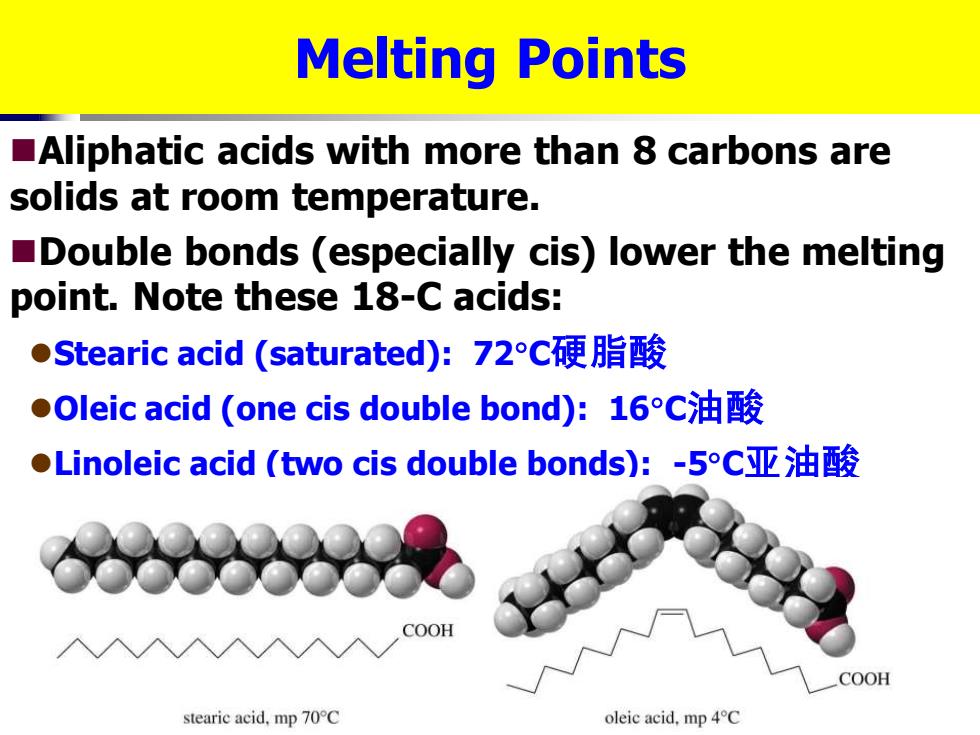
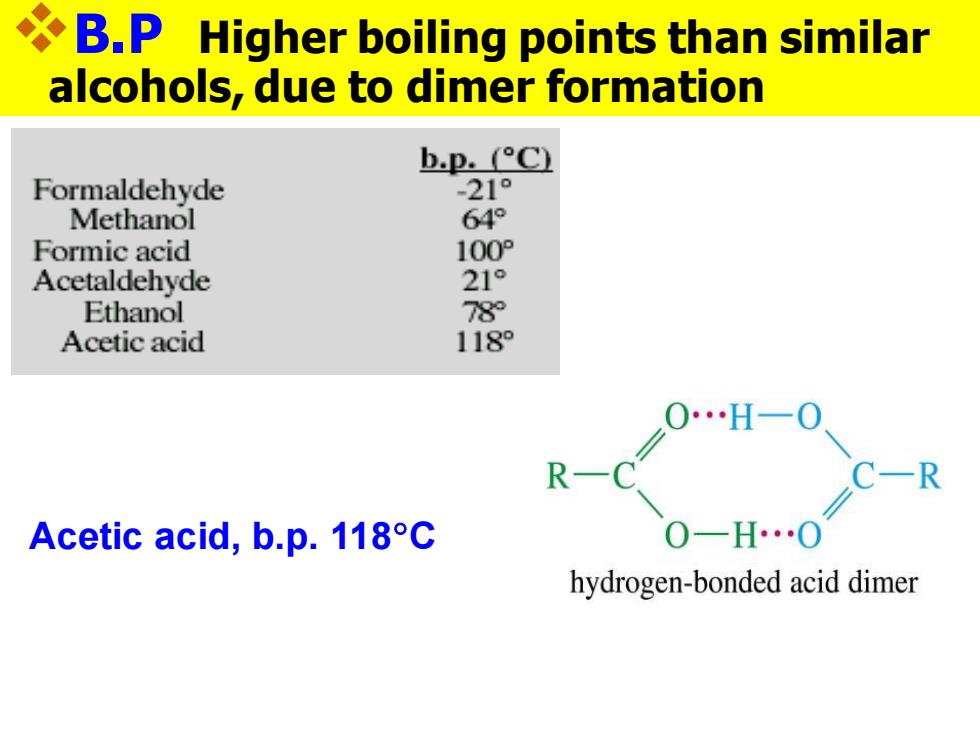
Melting Points Aliphatic acids with more than 8 carbons are solids at room temperature. Double bonds (especially cis)lower the melting point.Note these 18-C acids: ●Stearic acid(saturated):72c硬脂酸 ●Oleic acid(one cis double bond):16C油酸 ●Linoleic acid(two cis double bonds):-5c亚油酸 COOH COOH stearic acid,mp 70C oleic acid,mp 4C
Melting Points ◼Aliphatic acids with more than 8 carbons are solids at room temperature. ◼Double bonds (especially cis) lower the melting point. Note these 18-C acids: ⚫Stearic acid (saturated): 72C硬脂酸 ⚫Oleic acid (one cis double bond): 16C油酸 ⚫Linoleic acid (two cis double bonds): -5C亚油酸 硬脂酸,油酸,亚油酸

Solubility Water solubility decreases with the length of the carbon chain. Up to 4 carbons,acid is miscible in water. More soluble in alcohol. Also soluble in relatively nonpolar solvents like chloroform because it dissolves as a dimer
Solubility ◼Water solubility decreases with the length of the carbon chain. ◼Up to 4 carbons, acid is miscible in water. ◼More soluble in alcohol. ◼Also soluble in relatively nonpolar solvents like chloroform because it dissolves as a dimer
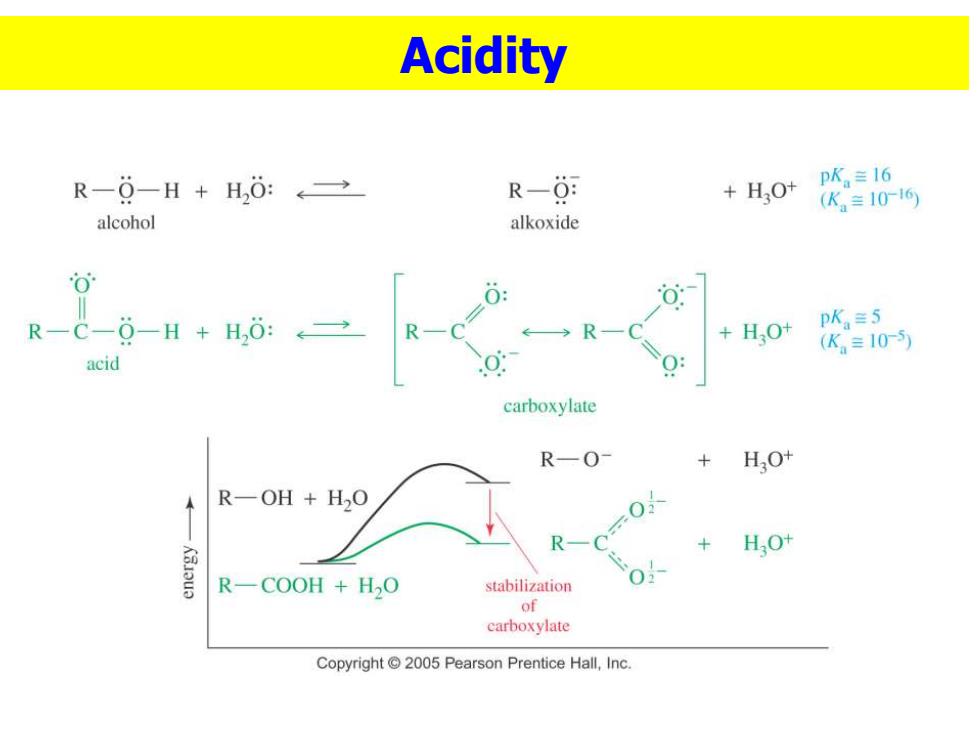
Acidity R-0-H+H,ǒ:→ R-0 +H2O+ pK.≡I6 (K,=1016 alcohol alkoxide 0 R-C-0-H+H,0:←2 HO+ pK≡5 (K。=10-) acid carboxylate R-O- + H.O+ R一OH+H2O 0=0X R- HO+ R一COOH+HO stabilization of carboxylate Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Acidity
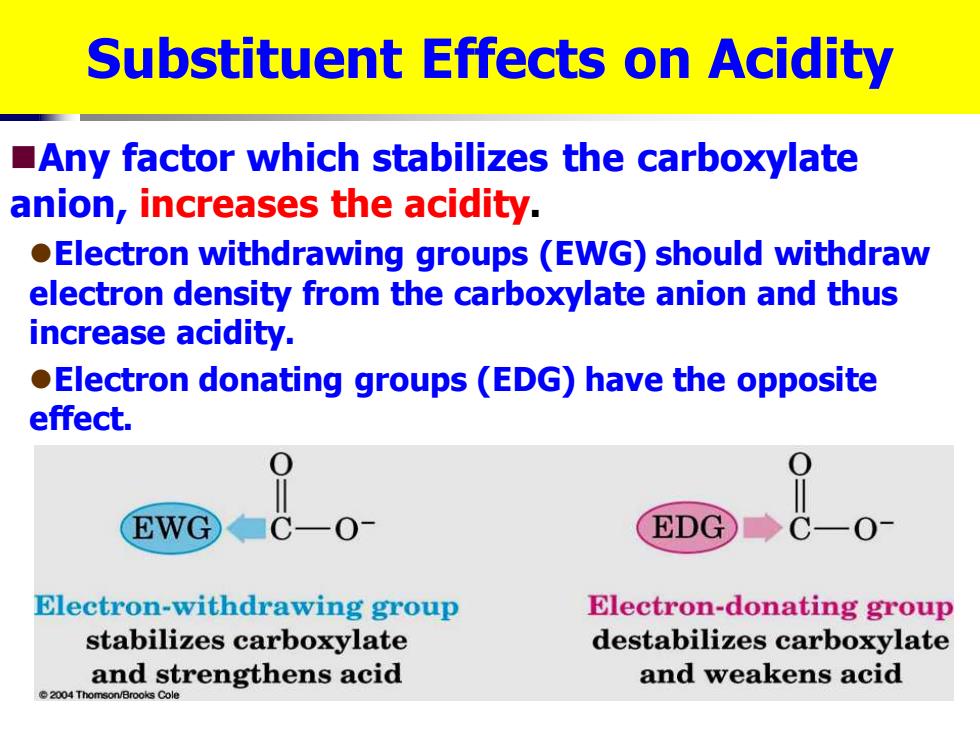
Substituent Effects on Acidity Any factor which stabilizes the carboxylate anion,increases the acidity. Electron withdrawing groups(EWG)should withdraw electron density from the carboxylate anion and thus increase acidity. Electron donating groups(EDG)have the opposite effect. EWG EDG ◆C一O0 Electron-withdrawing group Electron-donating group stabilizes carboxylate destabilizes carboxylate and strengthens acid and weakens acid 2004 Thom son/Brooks Cole
Substituent Effects on Acidity ◼Any factor which stabilizes the carboxylate anion, increases the acidity. ⚫Electron withdrawing groups (EWG) should withdraw electron density from the carboxylate anion and thus increase acidity. ⚫Electron donating groups (EDG) have the opposite effect
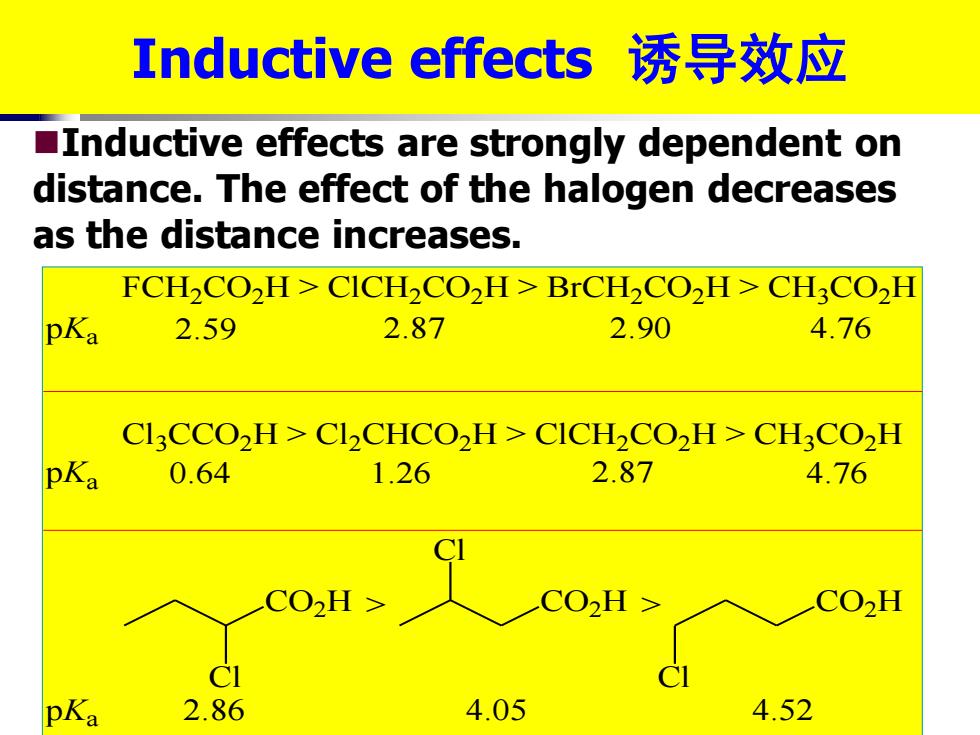
Inductive effects诱导效应 Inductive effects are strongly dependent on distance.The effect of the halogen decreases as the distance increases. FCH2CO2H>CICH2CO2H>BrCH2CO2H>CH3CO2H pKa 2.59 2.87 2.90 4.76 CICCO,H>CICHCO2H>CICH2CO,H>CHCO2H pKa 0.64 1.26 2.87 4.76 CO2H pKa 2.86 4.05 4.52
FCH2CO2H > ClCH2CO2H > BrCH2CO2H > CH3CO2H Cl3CCO2H > Cl2CHCO2H > ClCH2CO2H > CH3CO2H CO2H Cl CO2H Cl CO2H Cl > > pKa pKa pKa 2.59 2.87 2.90 4.76 0.64 1.26 2.87 4.76 2.86 4.05 4.52 Inductive effects 诱导效应 ◼Inductive effects are strongly dependent on distance. The effect of the halogen decreases as the distance increases