
自标转对 Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 22 Carboxylic Acid ①erivatives http://www.study-organic-chemistry.com/ By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com
By Junru Wang Email: wangjr07@163.com Chapter 22 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. http://www.study-organic-chemistry.com/

Carboxylic Acid Derivatives STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES PREPARATIONS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES ■REACTIONS ■ENOLATE REACTIONS
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives ◼STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES ◼PREPARATIONS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES ◼REACTIONS ◼ENOLATE REACTIONS

Sec 1 Acid Derivatives All can be converted to the carboxylic acid by acidic or basic hydrolysis. Esters and amides common in nature. R-C-NH, R-C≡ acid halide anhydride ester amide nitrile Condensed structure:RCOX (RCO),O RCO,R' RCONH, RCN Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Sec 1 Acid Derivatives ◼All can be converted to the carboxylic acid by acidic or basic hydrolysis. ◼Esters and amides common in nature
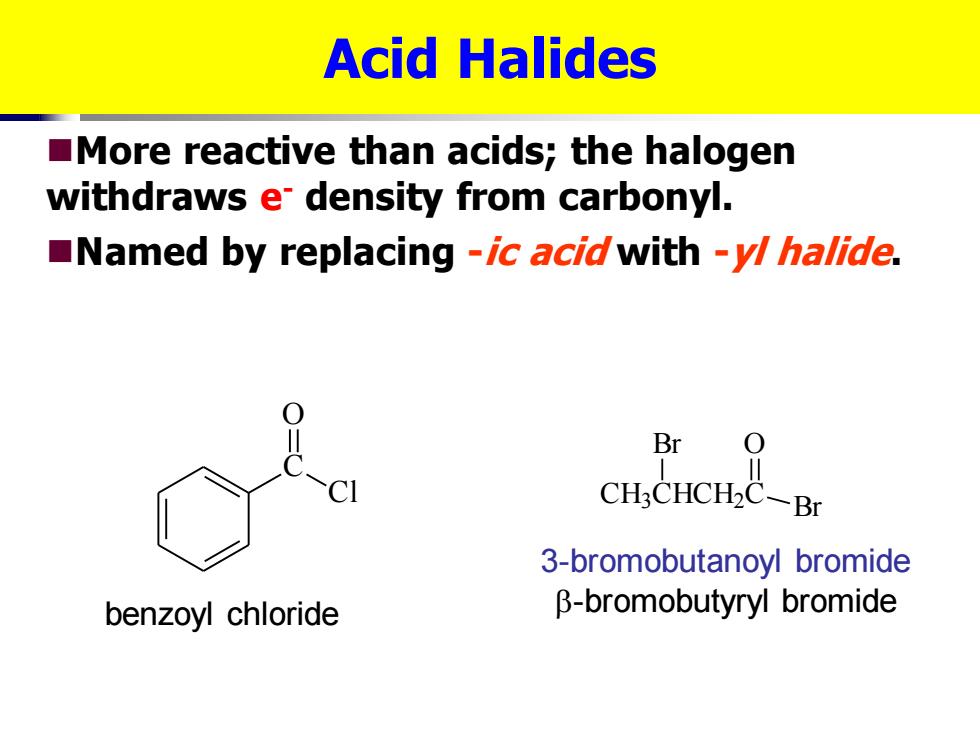
Acid Halides More reactive than acids;the halogen withdraws e density from carbonyl. Named by replacing -ic acid with -y/halide. Br CH3CHCH2C-Br 3-bromobutanoyl bromide benzoyl chloride B-bromobutyryl bromide
Acid Halides ◼More reactive than acids; the halogen withdraws e- density from carbonyl. ◼Named by replacing -ic acid with -yl halide. C O Cl CH3 CHCH2 C Br O Br benzoyl chloride 3-bromobutanoyl bromide -bromobutyryl bromide

Anhydrides The word acidis replaced with anhydride. For a mixed anhydride,name both acids. Diacids may form anhydrides if a 5-or 6- membered ring is the product. ethanoic anhydride acetic anhydride 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic anhydride phthalic anhydride
Anhydrides ◼The word acid is replaced with anhydride. ◼For a mixed anhydride, name both acids. ◼Diacids may form anhydrides if a 5- or 6- membered ring is the product. CH3 C O O C O CH3 ethanoic anhydride acetic anhydride O O O 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic anhydride phthalic anhydride
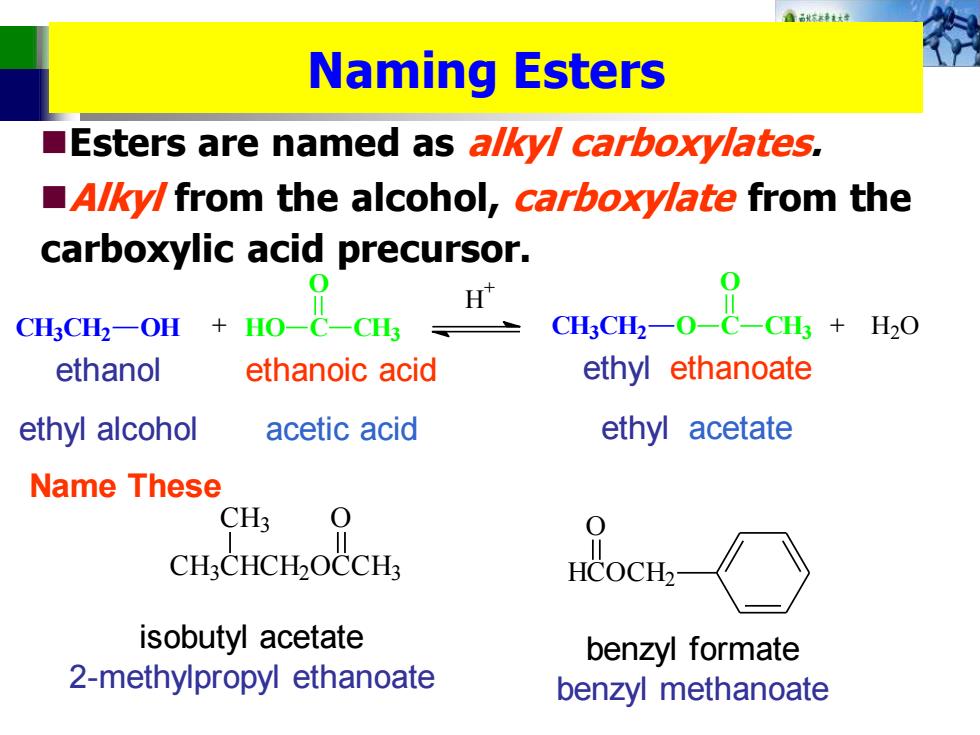
A8秋路k女 Naming Esters Esters are named as a/ky/carboxylates, A/ky/from the alcohol,carboxylate from the carboxylic acid precursor. CHCH:-On Ho-C CH CH3CH2-O- CH3 H2O ethanol ethanoic acid ethyl ethanoate ethyl alcohol acetic acid ethyl acetate Name These CH3 CH:CHCH2OCCH3 HCOCH2 isobutyl acetate benzyl formate 2-methylpropyl ethanoate benzyl methanoate
Naming Esters ◼Esters are named as alkyl carboxylates. ◼Alkyl from the alcohol, carboxylate from the carboxylic acid precursor. CH3CH2 OH HO C O CH3 H + + CH3CH2 O C + H2O O CH3 ethanol ethyl alcohol ethanoic acid acetic acid ethyl ethanoate ethyl acetate Name These CH3CHCH2OCCH3 CH3 O HCOCH2 O isobutyl acetate 2-methylpropyl ethanoate benzyl formate benzyl methanoate
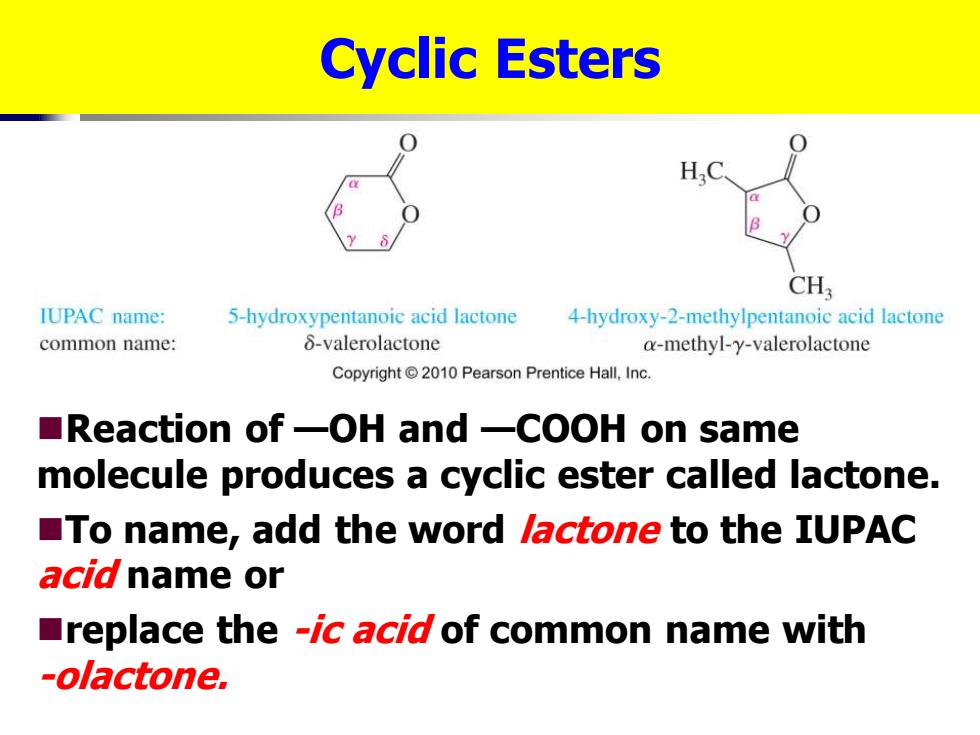
Cyclic Esters H,C CH3 IUPAC name: 5-hydroxypentanoic acid lactone 4-hydroxy-2-methylpentanoic acid lactone common name: 8-valerolactone a-methyl-y-valerolactone Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. ■Reaction of一OH and一COOH on same molecule produces a cyclic ester called lactone. To name,add the word lactone to the IUPAC acid name or replace the -ic acid of common name with -olactone
Cyclic Esters ◼Reaction of —OH and —COOH on same molecule produces a cyclic ester called lactone. ◼To name, add the word lactone to the IUPAC acid name or ◼replace the -ic acid of common name with -olactone
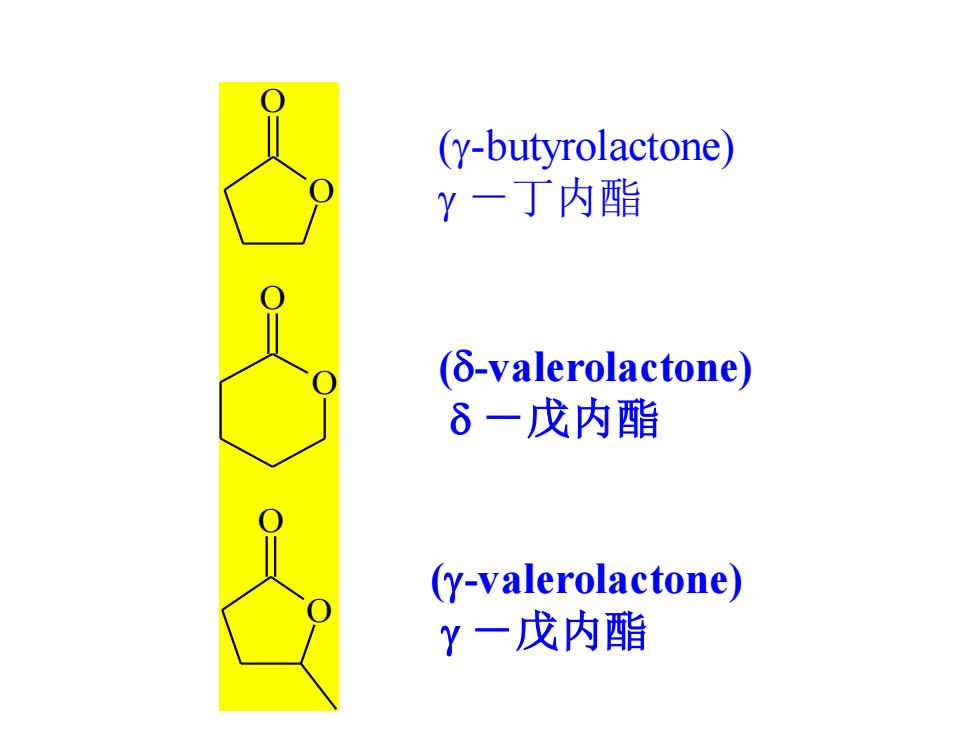
(y-butyrolactone) Y一丁内酯 (δ-valerolactone) 6一戊内酯 (y-valerolactone) Y一戊内酯
O O O O O O (g-butyrolactone) g -丁内酯 (d-valerolactone) d -戊内酯 (g-valerolactone) g -戊内酯
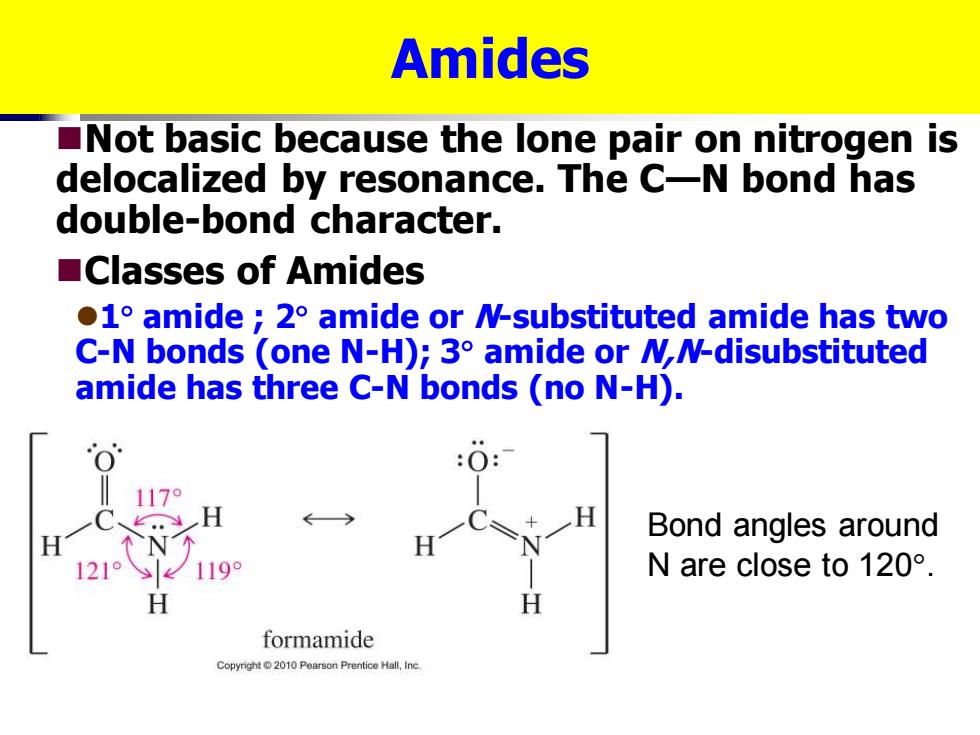
Amides Not basic because the lone pair on nitrogen is delocalized by resonance.The C-N bond has double-bond character. ■Classes of Amides 1 amide 2 amide or N-substituted amide has two C-N bonds (one N-H);3 amide or MN-disubstituted amide has three C-N bonds (no N-H). 170 Bond angles around 1219 1199 N are close to120°. H formamide Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc
Amides ◼Not basic because the lone pair on nitrogen is delocalized by resonance. The C—N bond has double-bond character. ◼Classes of Amides ⚫1 amide ; 2 amide or N-substituted amide has two C-N bonds (one N-H); 3 amide or N,N-disubstituted amide has three C-N bonds (no N-H). Bond angles around N are close to 120

Protonation of Amides H时 :01 concentrated acid R R R very weakly basic protonation on oxygen Copyright010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Under acidic conditions,the double-bonded oxygen will get protonated
Protonation of Amides ◼Under acidic conditions, the double-bonded oxygen will get protonated