Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 26 Lipids CH2-0一 0 CH 一0 CH2一O tristearin,mp 72C O- CH2一O一 CH一O一 y Junru Wang CH2-O- r07@163.c0m triolein,mp-4C 0球4试 灌率昆
By Junru Wang Email: wangjr07@163.com Chapter 26 Lipids Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Introduction Classified by solubility,not structure. Can be extracted from cells by nonpolar organic solvents. Complex lipids are easily hydrolyzed. ●Waxes ●Triglycerides Simple lipids are not easily hydrolyzed. ●Steroids ●Prostaglandins ●Terpenes
Introduction ◼Classified by solubility, not structure. ◼Can be extracted from cells by nonpolar organic solvents. ◼Complex lipids are easily hydrolyzed. ⚫Waxes ⚫Triglycerides ◼Simple lipids are not easily hydrolyzed. ⚫Steroids ⚫Prostaglandins ⚫Terpenes
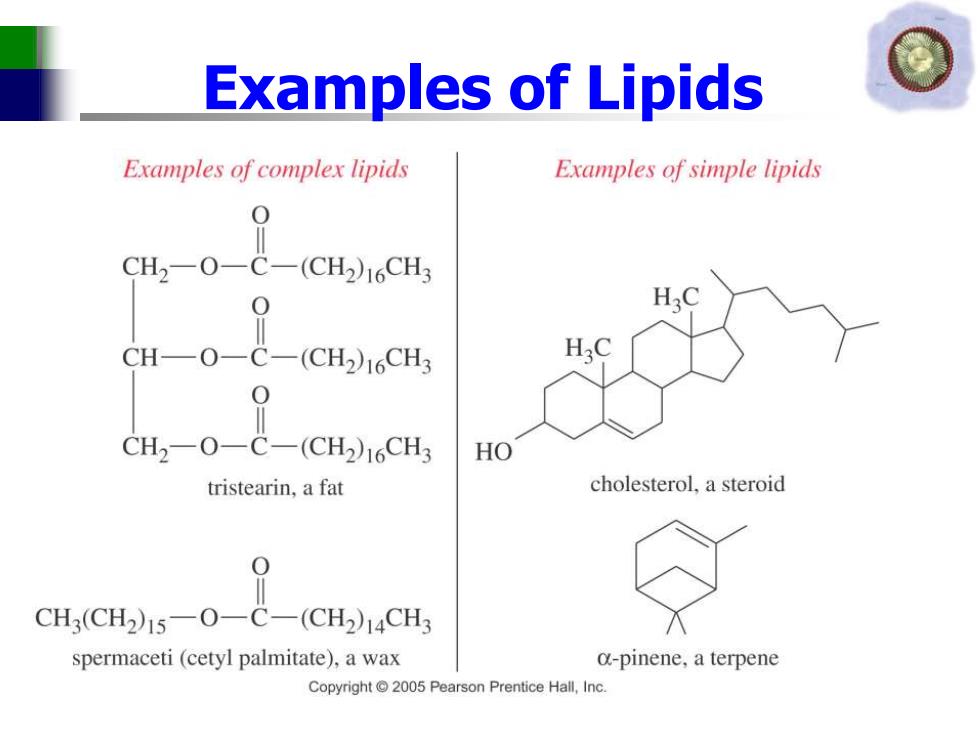
Examples of Lipids Examples of complex lipids Examples of simple lipids CH2-O-C-(CH2)16CH3 H30 HO tristearin,a fat cholesterol,a steroid CH3(CH2)15-O-C-(CH2)14CH3 spermaceti (cetyl palmitate),a wax a-pinene,a terpene Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Examples of Lipids

Waxes Esters of long-chain fatty acids with long-chain alcohols. Spermaceti is found in the head of the sperm whale and is probably used to control buoyancy. Most natural waxes are protective coats for plants'leaves,insects'exoskeletons, mammals'fur,and birds'feathers
Waxes ◼Esters of long-chain fatty acids with long-chain alcohols. ◼Spermaceti is found in the head of the sperm whale and is probably used to control buoyancy. ◼Most natural waxes are protective coats for plants’ leaves, insects’ exoskeletons, mammals’ fur, and birds’ feathers

Triglycerides Fatty acid esters of glycerol. ■Fats Solid at room temperature oMost are derived from mammals ■Oils Liquid at room temperature Most are derived from plants or cold-blooded animals
Triglycerides ◼Fatty acid esters of glycerol. ◼Fats ⚫Solid at room temperature ⚫Most are derived from mammals ◼Oils ⚫Liquid at room temperature ⚫Most are derived from plants or cold-blooded animals

Fatty Acids Unbranched carboxylic acids with 12-20 carbons. Most contain an even number of carbons because they are built from acetic acid units. Melting points increase with increasing molecular weights. Unsaturation greatly lowers the melting point
Fatty Acids ◼Unbranched carboxylic acids with 12-20 carbons. ◼Most contain an even number of carbons because they are built from acetic acid units. ◼Melting points increase with increasing molecular weights. ◼Unsaturation greatly lowers the melting point
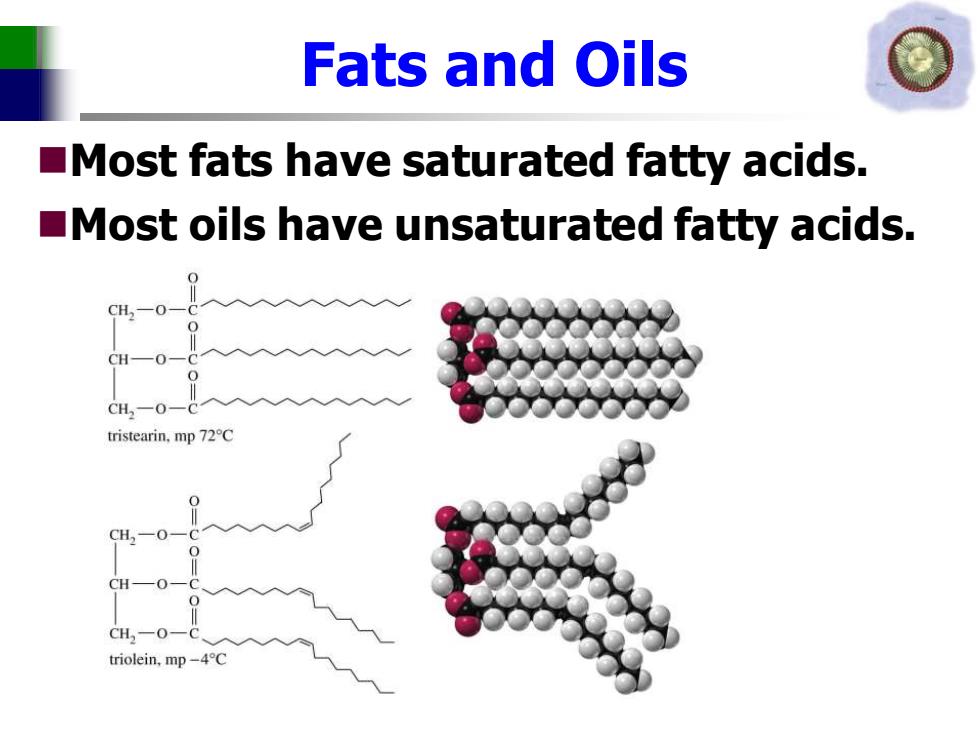
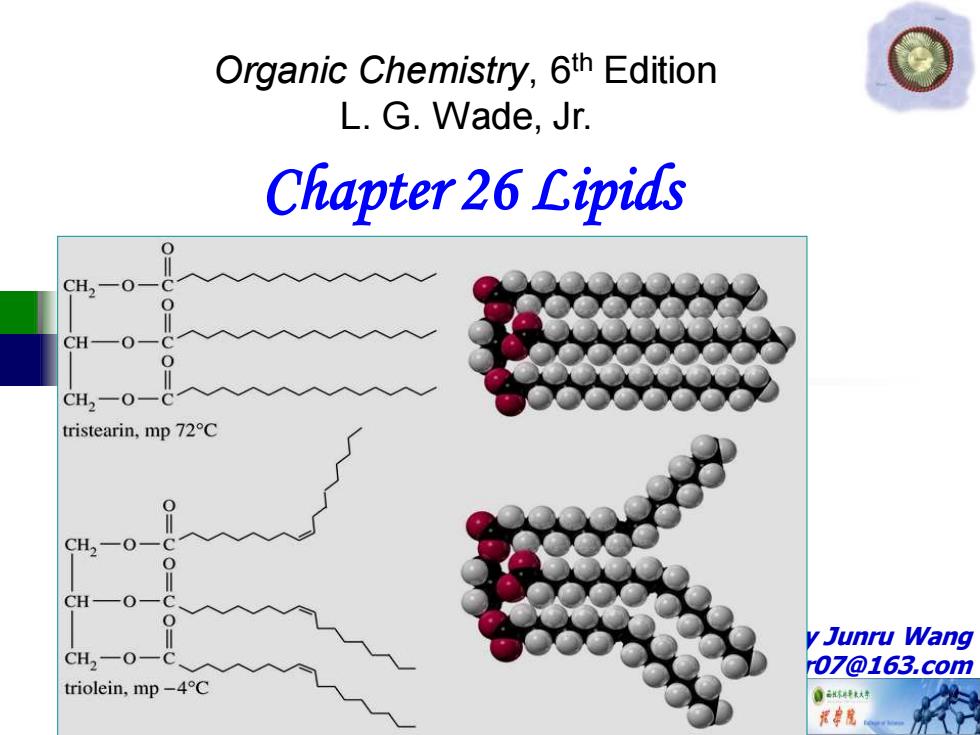
Fats and Oils Most fats have saturated fatty acids. Most oils have unsaturated fatty acids. CH一O CH2-O一( tristearin,mp 72C CH-0- CH2一O triolein,mp-4C
Fats and Oils ◼Most fats have saturated fatty acids. ◼Most oils have unsaturated fatty acids
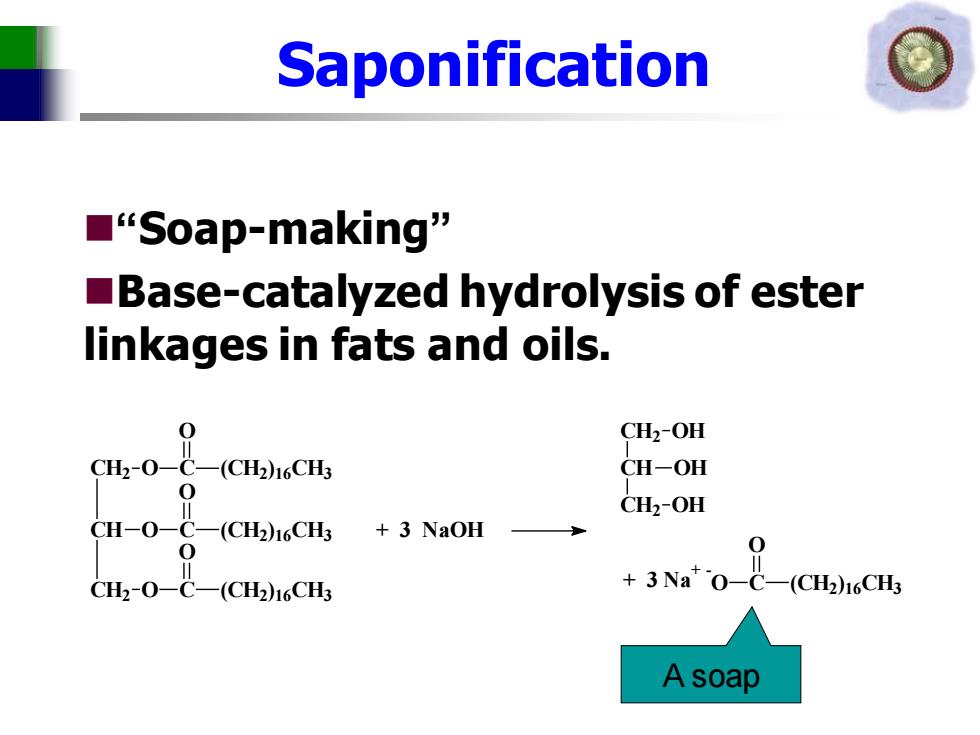
Saponification ■“Soap-making” Base-catalyzed hydrolysis of ester linkages in fats and oils. Ct-0-C(CCHs CH2-OH CH-OH 0 CH-0-C-(CH2)CH CH2-OH 3 NaOH 0 0 CH-0-C-(CH2CH +3Na*O-C- CH2)16CH3 A soap
Saponification ◼“Soap-making” ◼Base-catalyzed hydrolysis of ester linkages in fats and oils. CH O C O (CH2 )16CH3 CH2 O C O (CH2 )16CH3 CH2 O C O (CH2)16CH3 + 3 NaOH CH2 CH CH2 OH OH OH + 3 Na+ - O C O (CH2 )16CH3 A soap
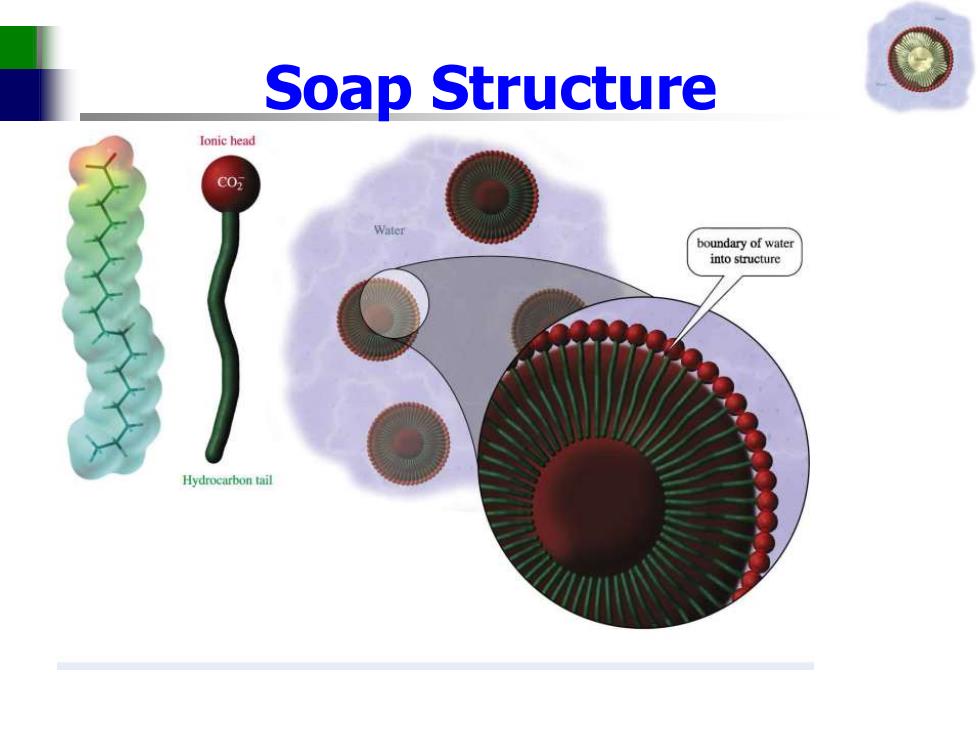
Soap Structure Ionic head C05 boundary of water into structure Hydrocarbon tail
Soap Structure

Soap Structure Ionic head Water c02 Water Grease Water Water Water Hydrocarbon tail 2007 Thomson Higher Education
Soap Structure