
自秋转大材 Organic Chemistry,6h Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 7 AlRylHalides:Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Key Notes Nucleophilic Substitution,SN1/SN2,Elimination (E1/E2) Nucleophilicity,Leaving group By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com
By Junru Wang Email: wangjr07@163.com Chapter 7 Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Organic Chemistry, 6h Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Key Notes Nucleophilic Substitution, SN1/SN2, Elimination(E1/E2) Nucleophilicity, Leaving group
0诚钛对 Content 教华魔 Preparation and physical properties Nucleophilic substitution Factorsaffecting SN2 versus SN1 reactions ☐Elimination Elimination versus substitution Reactions of alkyl halides Organometallic reactions
Content ◼Preparation and physical properties ◼Nucleophilic substitution ◼Factors affecting SN2 versus SN1 reactions ◼Elimination ◼Elimination versus substitution ◼Reactions of alkyl halides ◼Organometallic reactions
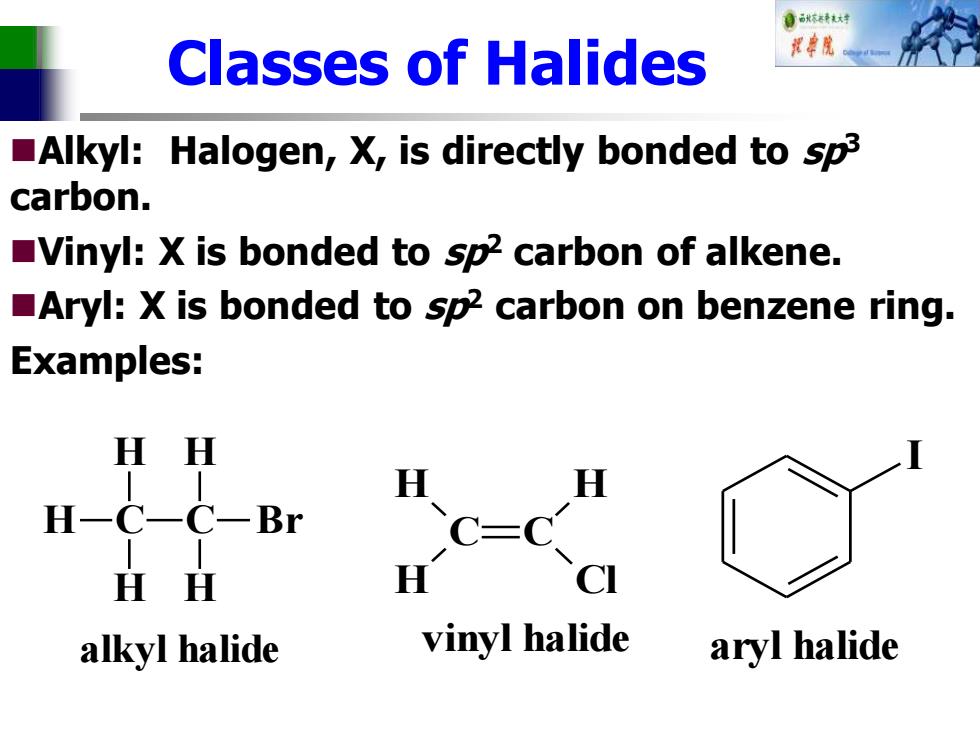
自标不有花大时 Classes of Halides Alkyl:Halogen,X,is directly bonded to sp3 carbon. Vinyl:X is bonded to sp2 carbon of alkene. Aryl:X is bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring. Examples: H H H H-C-C-Br .c-c H H C alkyl halide vinyl halide aryl halide
Classes of Halides ◼Alkyl: Halogen, X, is directly bonded to sp3 carbon. ◼Vinyl: X is bonded to sp2 carbon of alkene. ◼Aryl: X is bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring. Examples: C H H H C H H Br alkyl halide C C H H H Cl vinyl halide I aryl halide

自转达对 Classes of Alkyl Halides Methyl halides:only one C,CHaX Primary:C to which X is bonded has only one C-C bond. Secondary:C to which X is bonded has two C-C bonds. Tertiary:C to which X is bonded has three C-C bonds
Classes of Alkyl Halides ◼Methyl halides: only one C, CH3X ◼Primary: C to which X is bonded has only one C-C bond. ◼Secondary: C to which X is bonded has two C-C bonds. ◼Tertiary: C to which X is bonded has three C-C bonds
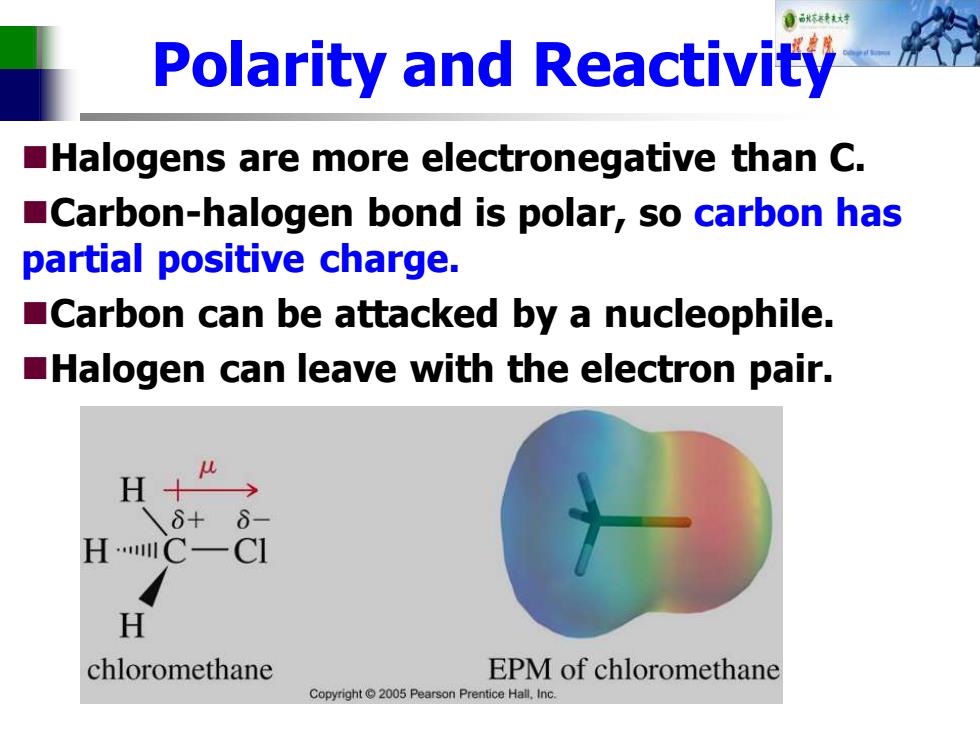
Polarity and Reactivity Halogens are more electronegative than C. Carbon-halogen bond is polar,so carbon has partial positive charge. Carbon can be attacked by a nucleophile. Halogen can leave with the electron pair. H+ 6+ HC一CI H chloromethane EPM of chloromethane Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc
Polarity and Reactivity ◼Halogens are more electronegative than C. ◼Carbon-halogen bond is polar, so carbon has partial positive charge. ◼Carbon can be attacked by a nucleophile. ◼Halogen can leave with the electron pair

自秋转达对 Uses of Alkyl Halides" Solvents -degreasers and dry cleaning fluid Reagents for synthesis of other compounds Anesthetic:Halothane is CF3CHCIBr ●CHCl3 used originally(toxic and carcinogenic))麻醉剂 >In 1847,the Edinburgh obstetrician James Young Simpson first used chloroform for general anesthesia during childbirth Freons,chlorofluorocarbons or CFC's Freon 12,CF2Cl2,now replaced with Freon 22,CF2CHCI, not as harmful to ozone layer. Pesticides-DDT banned in U.S. eextremely toxic to insects but not as toxic to mammals
Uses of Alkyl Halides ◼Solvents - degreasers and dry cleaning fluid ◼Reagents for synthesis of other compounds ◼Anesthetic: Halothane is CF3CHClBr ⚫CHCl3 used originally (toxic and carcinogenic)麻醉剂 ➢In 1847, the Edinburgh obstetrician James Young Simpson first used chloroform for general anesthesia during childbirth ◼Freons, chlorofluorocarbons or CFC’s ⚫Freon 12, CF2Cl2 , now replaced with Freon 22, CF2CHCl, not as harmful to ozone layer. ◼Pesticides - DDT banned in U.S. ⚫extremely toxic to insects but not as toxic to mammals
目可秋5转大对 Uses of Alkyl Halides 杀虫剂、杀灭蚊子(疟疾) DDT1939年后广泛使用(残留高) Srilanka ●1934-1935150万(8万died) ●1963:仅15例 ●1968-1969第二季度60万例 1972:环境保护组织(EPA) 废除 ■冷却液和喷气燃料推进剂
Uses of Alkyl Halides ◼杀虫剂、杀灭蚊子(疟疾) DDT 1939年后广泛使用(残留高) Srilanka : ⚫1934-1935 150万(8万 died) ⚫1963:仅15例 ⚫1968-1969第二季度60万例 1972:环境保护组织(EPA)废除 ◼冷却液和喷气燃料推进剂
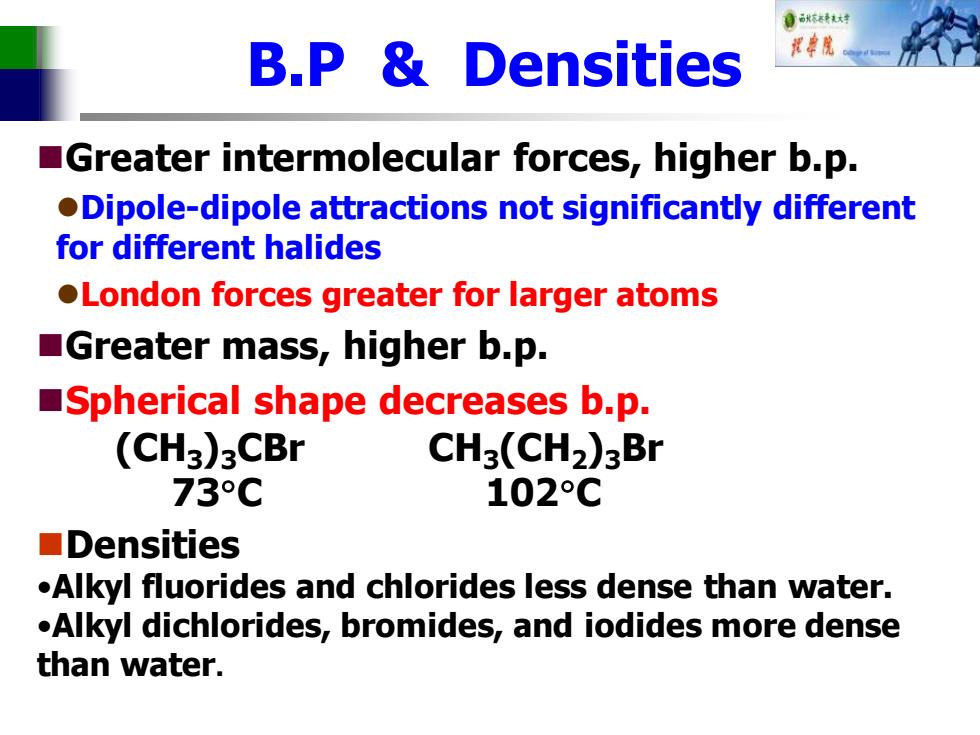
0东转大对 B.P Densities Greater intermolecular forces,higher b.p. .Dipole-dipole attractions not significantly different for different halides London forces greater for larger atoms Greater mass,higher b.p. Spherical shape decreases b.p. (CH3)3CBr CH3(CH2)3Br 73C 102°C ■Densities .Alkyl fluorides and chlorides less dense than water. .Alkyl dichlorides,bromides,and iodides more dense than water
B.P & Densities ◼Greater intermolecular forces, higher b.p. ⚫Dipole-dipole attractions not significantly different for different halides ⚫London forces greater for larger atoms ◼Greater mass, higher b.p. ◼Spherical shape decreases b.p. (CH3)3CBr CH3(CH2)3Br 73C 102C ◼Densities •Alkyl fluorides and chlorides less dense than water. •Alkyl dichlorides, bromides, and iodides more dense than water

Sec 1 PREPARATION AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ■PREPARATION .Halogenation(Allylic Halogenation) ●With HX ●From alcohol .Diazonium coupling (for aryl halide only) ■Use
Sec 1 PREPARATION AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ◼PREPARATION ⚫Halogenation(Allylic Halogenation) ⚫With HX ⚫From alcohol ⚫Diazonium coupling (for aryl halide only) ◼Use
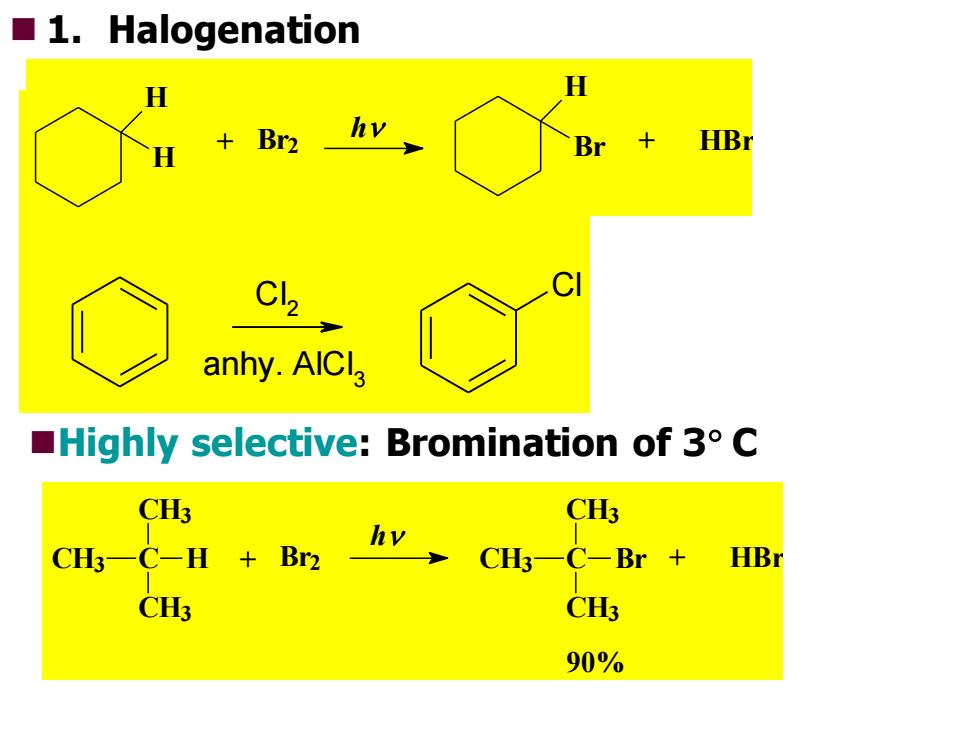
■l.Halogenation H H h +Br2 Br HB anhy.AICla Highly selective:Bromination of 3 C CH3 CH3 CH一C-H +Br2 hv CHC-Br HBr CH3 CH3 90%
◼Highly selective: Bromination of 3 C 90% CH3 C + HBr CH3 CH3 Br h CH3 C + Br2 CH3 CH3 H RH + Cl 2 RCl + HCl u.v. C Cl l 2 anhy. AlCl 3 ◼ 1. Halogenation + HBr H Br h + Br2 H H