
自秋不转大对 视中院 Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter4 Structure and Stereochemistry of AlRanes Key Notes Mechanisms;Conformation;Ring strain Conformers;Cis-trans isomers; By Junru Wang Email:wangjr07@163.com
By Junru Wang Email: wangjr07@163.com Chapter 4 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Key Notes Mechanisms; Conformation; Ring strain; Conformers; Cis-trans isomers;

自秋杯转特 CONTENTS Classification of Hydrocarbons ■Physical properties Reactions Mechanisms of Alkanes Structure Conformation of Alkanes Conformation of Cycloalkanes
CONTENTS ◼Classification of Hydrocarbons ◼Physical properties ◼Reactions & Mechanisms of Alkanes ◼Structure & Conformation of Alkanes ◼Conformation of Cycloalkanes
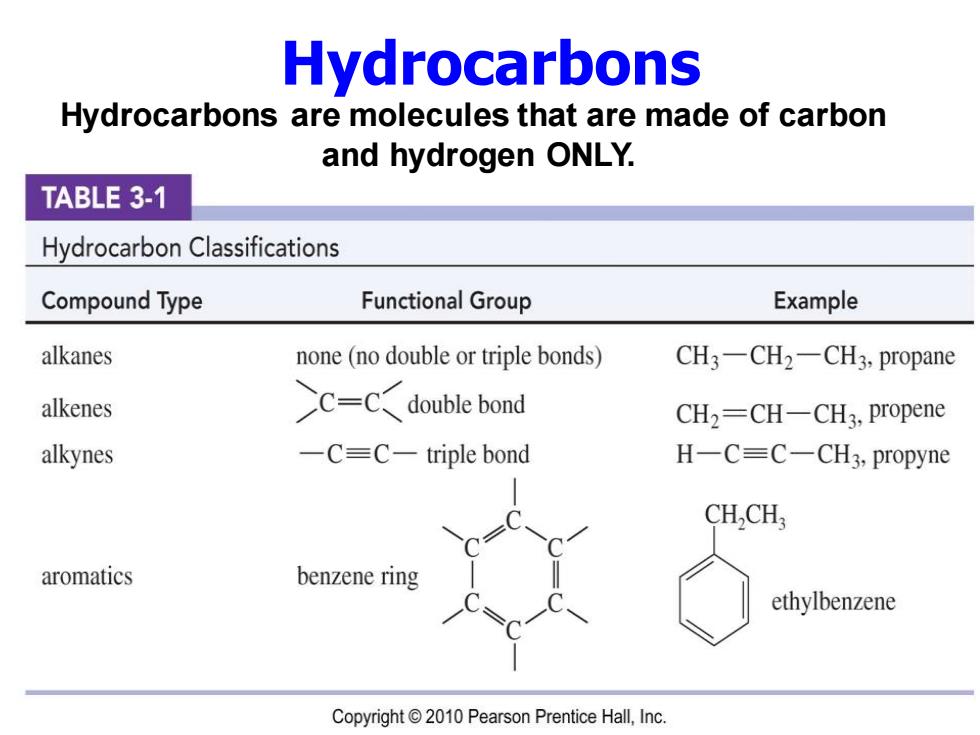
Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are molecules that are made of carbon and hydrogen ONLY. TABLE 3-1 Hydrocarbon Classifications Compound Type Functional Group Example alkanes none(no double or triple bonds) CH3一CH2-CH3,propane alkenes C=Cdouble bond CH2=CH-CH3,propene alkynes -C=C-triple bond H-C=C-CH3,propyne CH,CH, aromatics benzene ring ethylbenzene Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Hydrocarbons are molecules that are made of carbon and hydrogen ONLY. Hydrocarbons
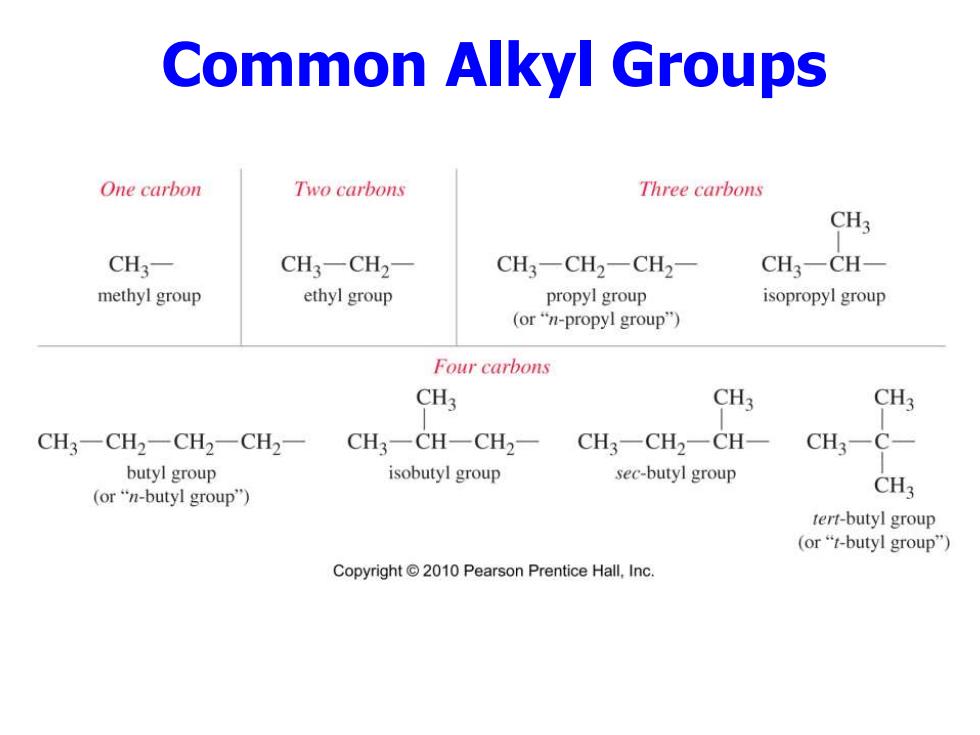
Common Alkyl Groups One carbon Two carbons Three carbons CH3 CH3- CH3-CH2- CH3-CH2一CH2- CH3-CH- methyl group ethyl group propyl group isopropyl group (or“n-propyl group") Four carbons CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3一CH2一CH2-CH2- CH3-CH-CH2- CH3-CH2一CH- CH3-C- butyl group isobutyl group sec-butyl group (or“n-butyl group'") CH3 tert-butyl group (or"t-butyl group") Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Common Alkyl Groups
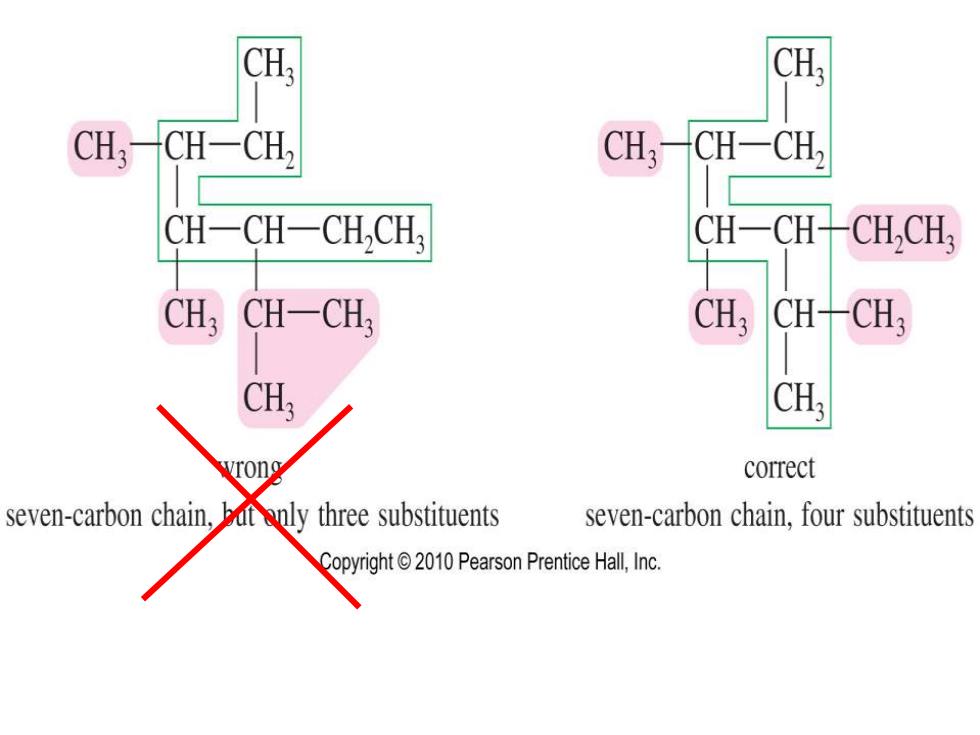
CH. CH: CH-CH-CH, CH: CH-CH, CH-CH-CH,CH CH-CH- CH,CH CH CH-CH, CH, CH-CH3 CH; CH; correct seven-carbon chain,bat only three substituents seven-carbon chain,four substituents Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
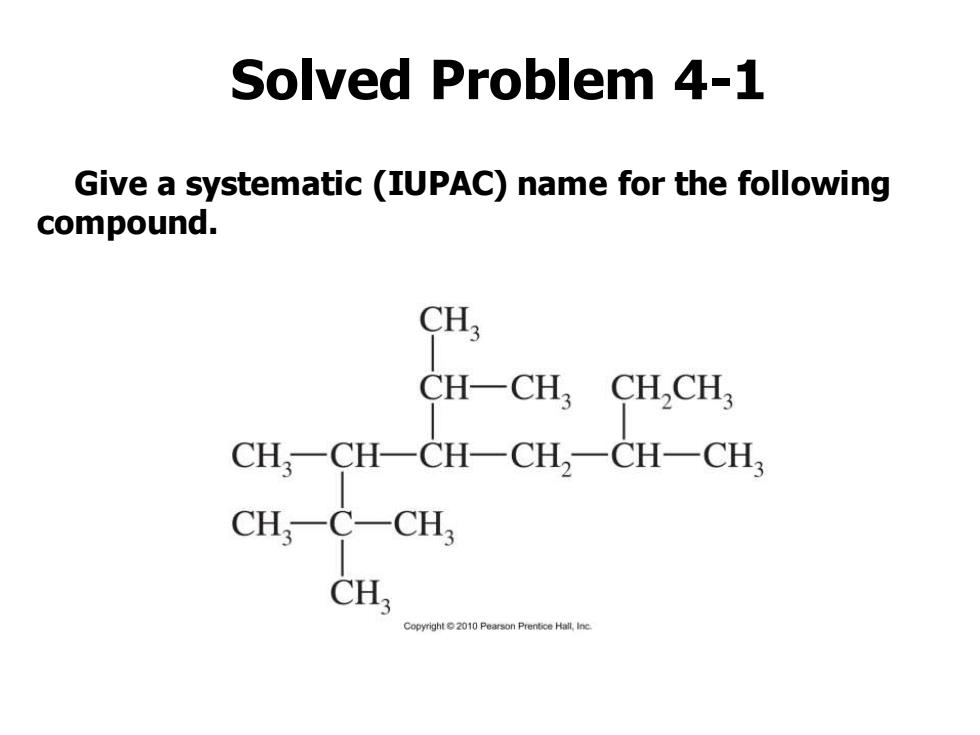
Solved Problem 4-1 Give a systematic (IUPAC)name for the following compound. CH; CH-CH CHCH CH一CH一CH-CH2一CH-CH CHCCH, CH Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Ine
Solved Problem 4-1 Give a systematic (IUPAC) name for the following compound
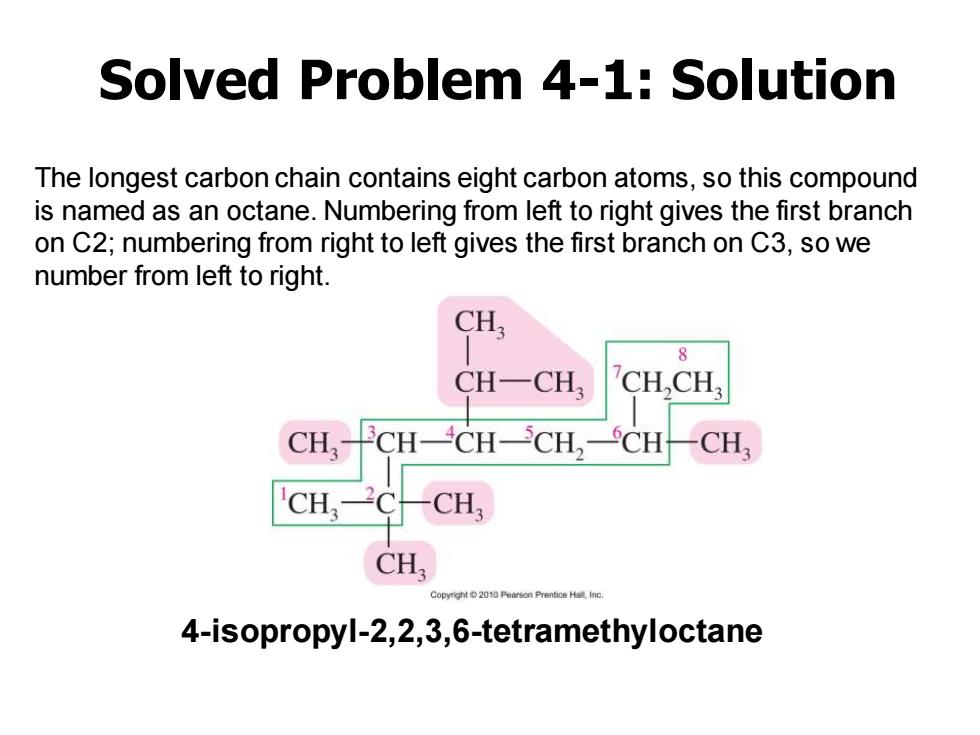
Solved Problem 4-1:Solution The longest carbon chain contains eight carbon atoms,so this compound is named as an octane.Numbering from left to right gives the first branch on C2;numbering from right to left gives the first branch on C3,so we number from left to right. CH 8 CH-CH, CH,CH, CH,- CH-CH-CH,-CH-CH3 CH CH CH Copyrgnt 2010 4-isopropyl-2,2,3,6-tetramethyloctane
The longest carbon chain contains eight carbon atoms, so this compound is named as an octane. Numbering from left to right gives the first branch on C2; numbering from right to left gives the first branch on C3, so we number from left to right. Solved Problem 4-1: Solution 4-isopropyl-2,2,3,6-tetramethyloctane

SEC 1 Physical Properties Solubility:hydrophobic Density:less than 1 g/mL Boiling points increase with increasing carbons (little less for branched chains). Melting points increase with increasing carbons(less for odd-number of carbons)
SEC 1 Physical Properties ◼Solubility: hydrophobic ◼Density: less than 1 g/mL ◼Boiling points increase with increasing carbons (little less for branched chains). Melting points increase with increasing carbons (less for odd-number of carbons)
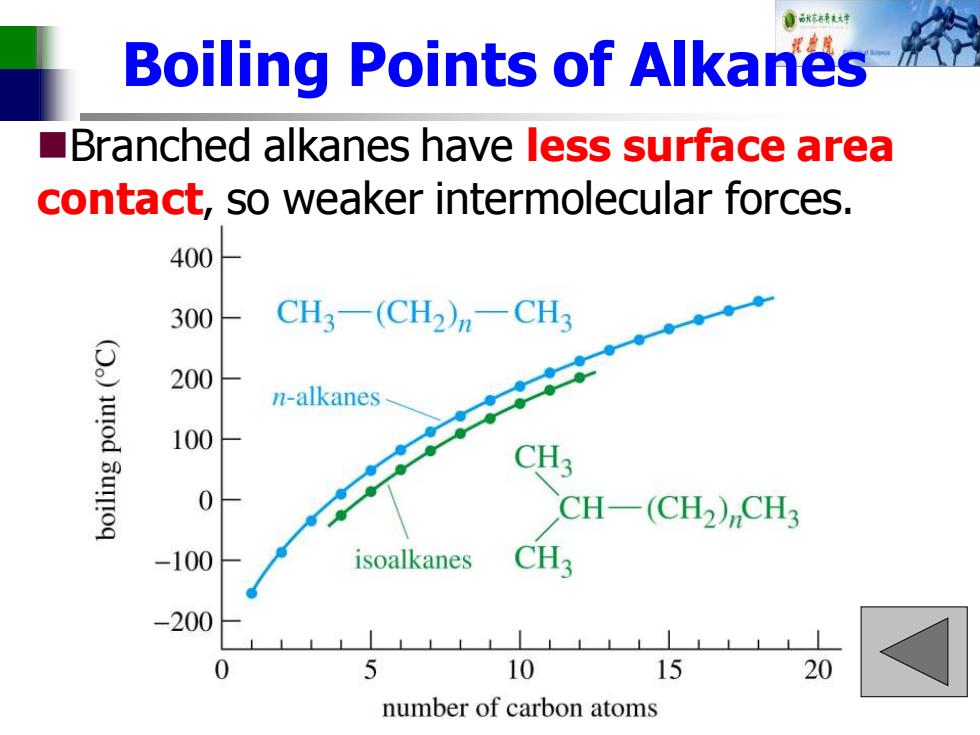
自秋不转大对 Boiling Points of Alkanes ■ Branched alkanes have less surface area contact,so weaker intermolecular forces. 400 300 CH3-(CH2)n-CH3 ()uod 3um!oq 200 n-alkanes 100 0 CH-(CH2)CH3 100 isoalkanes CH3 -200 5 10 15 20 number of carbon atoms
Boiling Points of Alkanes ◼Branched alkanes have less surface area contact, so weaker intermolecular forces
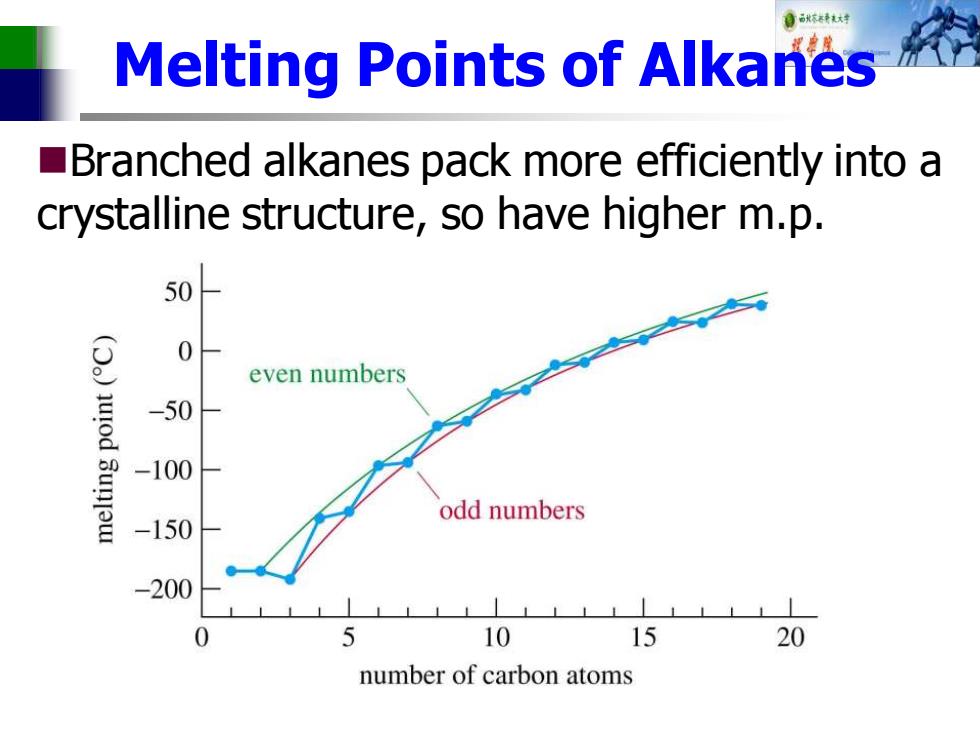
自秋不特大对 Melting Points of Alkanes Branched alkanes pack more efficiently into a crystalline structure,so have higher m.p. 50 0 even numbers -50 -100 -150 odd numbers -200 0 5 10 15 20 number of carbon atoms
Melting Points of Alkanes ◼Branched alkanes pack more efficiently into a crystalline structure, so have higher m.p