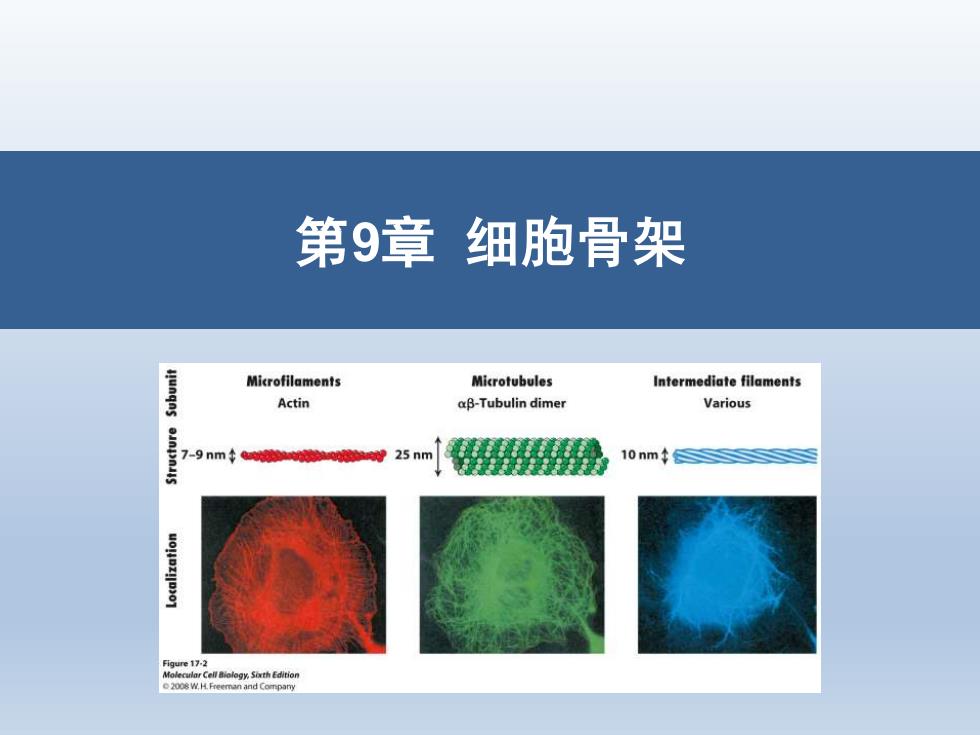
第9章细胞骨架 Microfilaments Microtubules Intermediate filaments Actin aβ-Tubulin dimer Various 7-9nm25nm 10nm
第9章 细胞骨架
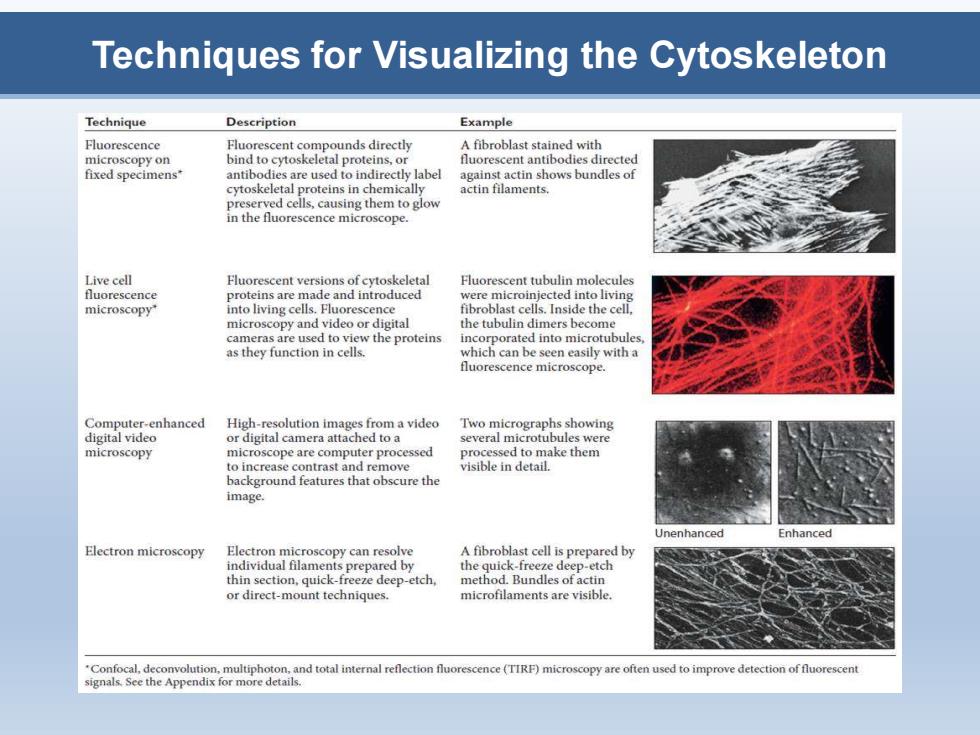
Techniques for Visualizing the Cytoskeleton Technique Description Example Fluorescence Fluorescent compounds directly A fibroblast stained with microscopy on bind to cytoskeletal proteins,or fluorescent antibodies directed fixed specimens* antibodies are used to indirectly label against actin shows bundles of cytoskeletal proteins in chemically actin filaments. preserved cells,causing them to glow in the fluorescence microscope. Live cell Fluorescent versions of cytoskeletal Fluorescent tubulin molecules fluorescence proteins are 1 and introduced re micro ted into living microscopy" into living cells.Fluorescence fibroblast cells.Inside the cell, microscopy and video or digital the tubulin dimers become cameras are used to view the proteins incorporated into microtubules as they function in cells. which can be seen easily with a fluorescence microscope. Computer-enhanced High-resolution images from a video Two micrographs showing digital video or digital camera attached to a several microtubules were microscopy microscope are computer processed processed to make them to increase contrast and remove visible in detail. background features that obscure the image. Inenhanced Enhanced Electron microscopy Electron microscopy can resolve A fibroblast cell is prepared by the quick-freeze deep etch method.Bundles of actin or direct-mount techniques. microfilaments are visible. Confocal,deconvolution,multiphoton. and total internal efle orescence(TIRF)microscopy are c mprove detection of tiuorescent signals.See the Appendix for more details
Techniques for Visualizing the Cytoskeleton
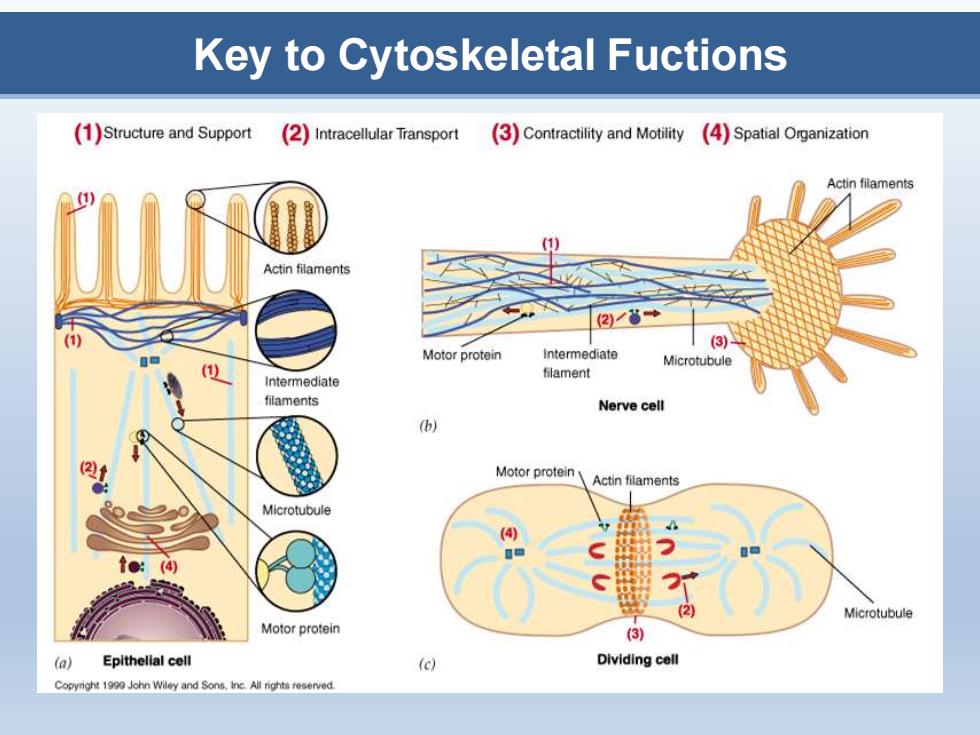
Key to Cytoskeletal Fuctions (1)Structure and Support (2)Intracellular Transport 3)Contractility and Motility 4)Spatial Organization Actin filaments Actin filaments (3 Motor protein intermediate Microtubule filament Intermediate filaments Nerve cell (b) Motor protein Actin filaments Microtubule (4) (2 Microtubule Motor protein (3) (a) Epithelial cell (c) Dividing cell Copyright 199 John Wiley and Sons.inc.All rights reserved
Key to Cytoskeletal Fuctions
本章主要内容 ·微丝与细胞运动 ·微管及其功能 B ·中间丝 D
本章主要内容 • 微丝与细胞运动 • 微管及其功能 • 中间丝

第一节微丝与细胞运动 ·微丝 (microfilament,MF) 。 肌动蛋白丝 (actin filament) ·纤维状肌动蛋白 (fibrous actin,F-actin) ·直径7nm 。 存在于所有真核细胞中 Srowth con Stress fibers 6种 ·微丝结合蛋白 (microfilament binding protein) Neuronal growth cone photosSchaefer,Kabir,and Forscher,2002 Originally published in The Joumal of Cell Biology,158:139-152
第一节 微丝与细胞运动 • 微丝 (microfilament, MF) • 肌动蛋白丝 (actin filament) • 纤维状肌动蛋白 (fibrous actin, F-actin) • 直径7 nm • 存在于所有真核细胞中 • 6种 • 微丝结合蛋白 (microfilament binding protein) Neuronal growth cone photos © Schaefer, Kabir, and Forscher, 2002. Originally published in The Journal of Cell Biology, 158: 139-152
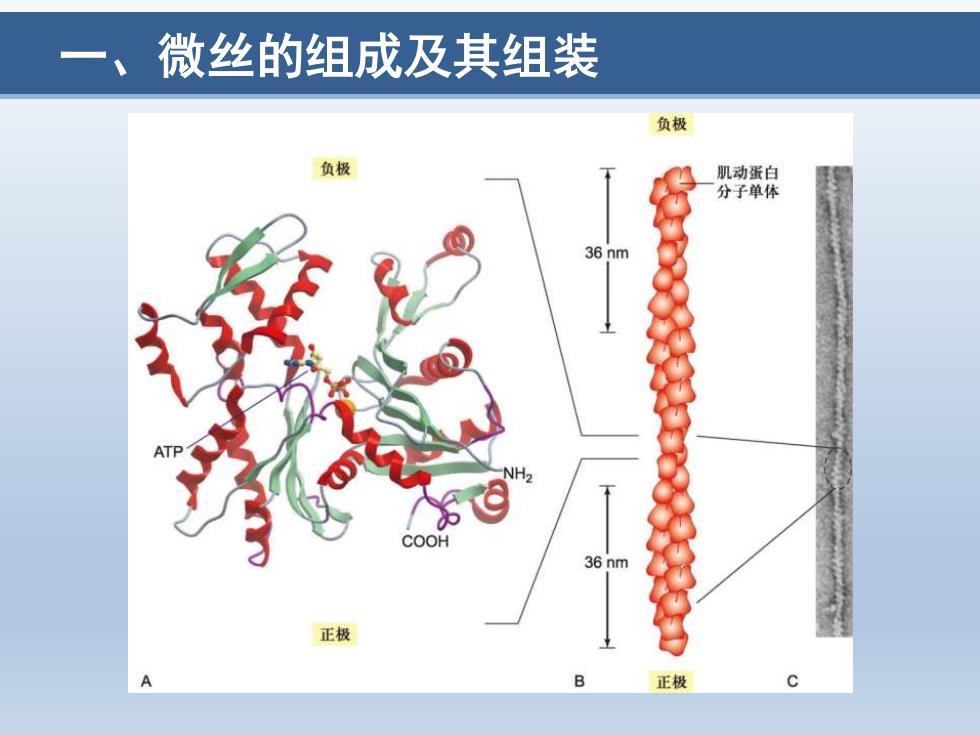
微丝的组成及其组装 负极 负极 肌动蛋白 分子单体 36 nm 2 COOH 36 nm 正极 A 正极
一、微丝的组成及其组装
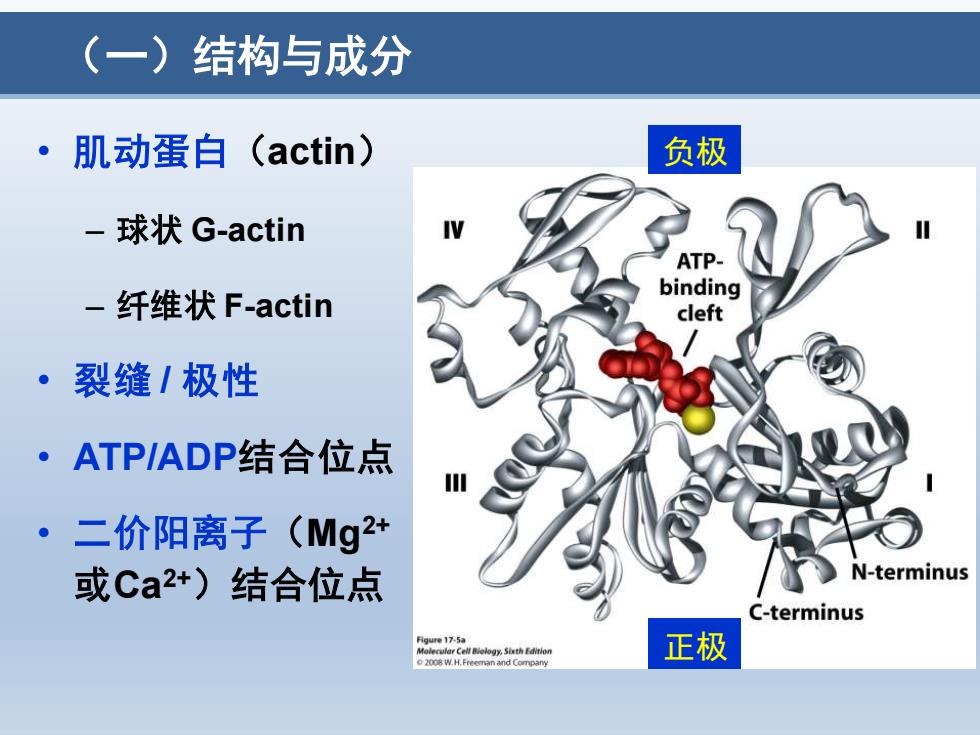
(一)结构与成分 ·肌动蛋白(actin) 负极 -球状G-actin ATP- binding -纤维状F-actin cleft ·裂缝/极性 ·ATP/ADP结合位点 二价阳离子(Mg2+ 或Ca2+)结合位点 N-terminus C-terminus 正极
(一)结构与成分 • 肌动蛋白(actin) – 球状 G-actin – 纤维状 F-actin • 裂缝 / 极性 • ATP/ADP结合位点 • 二价阳离子(Mg2+ 或Ca2+)结合位点 负极 正极

(一)结构与成分 直径约7nm扭链 (-end ·肌动蛋白单体组装 36 nm ·右手螺旋 。极性 AD 一具有裂缝的一端为 36 nm 负极,相反一端为 正极 (+)end 9ur17-56 o2008 W.H.Freeman and Company
(一)结构与成分 • 直径约7 nm 扭链 • 肌动蛋白单体组装 • 右手螺旋 • 极性 – 具有裂缝的一端为 负极,相反一端为 正极
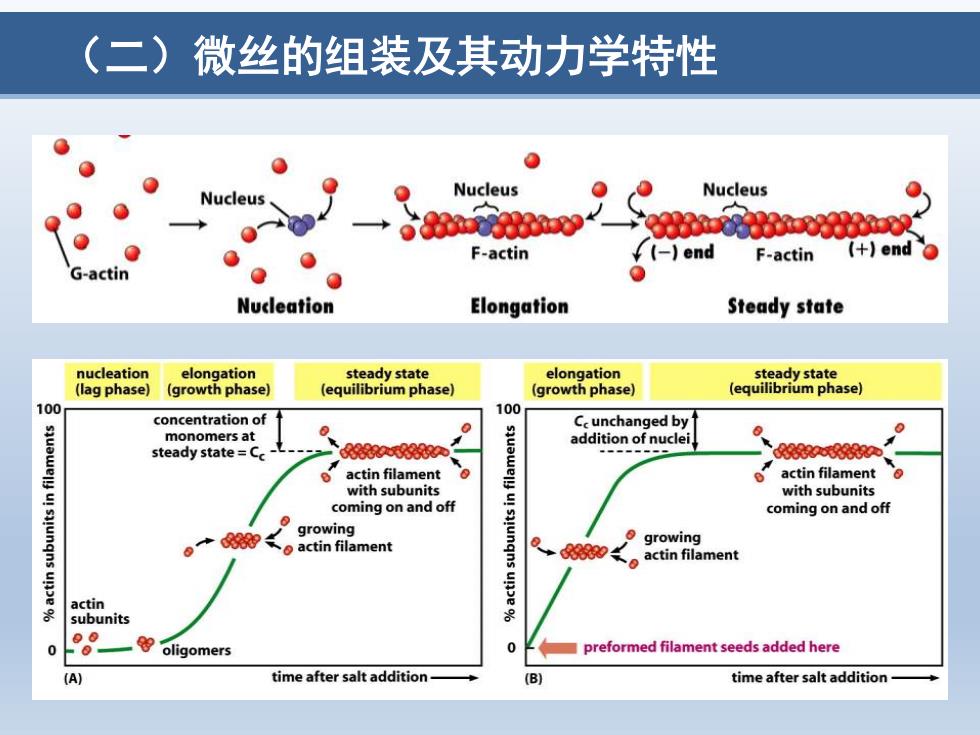
(二)微丝的组装及其动力学特性 e 0 Nucleus Nucleus Nucleus aae义 F-actin ¥(-)end F-actin (+end G-actin 0 Nucleation Elongation Steady state nucleation elongation steady state elongation steady state (lag phase) (growth phase (equilibrium phase】 (growth phase) (equilibrium phase】 100 100 concentration of Ce unchanged by monomers at 0 addition of nuclei steady state=C 8众66 d58n actin filament actin filament with subunits with subunits coming on and off coming on and off growing actin filament growing actin filament actin subunits 0 oligomers preformed filament seeds added here (A) time after salt addition time after salt addition-
(二)微丝的组装及其动力学特性
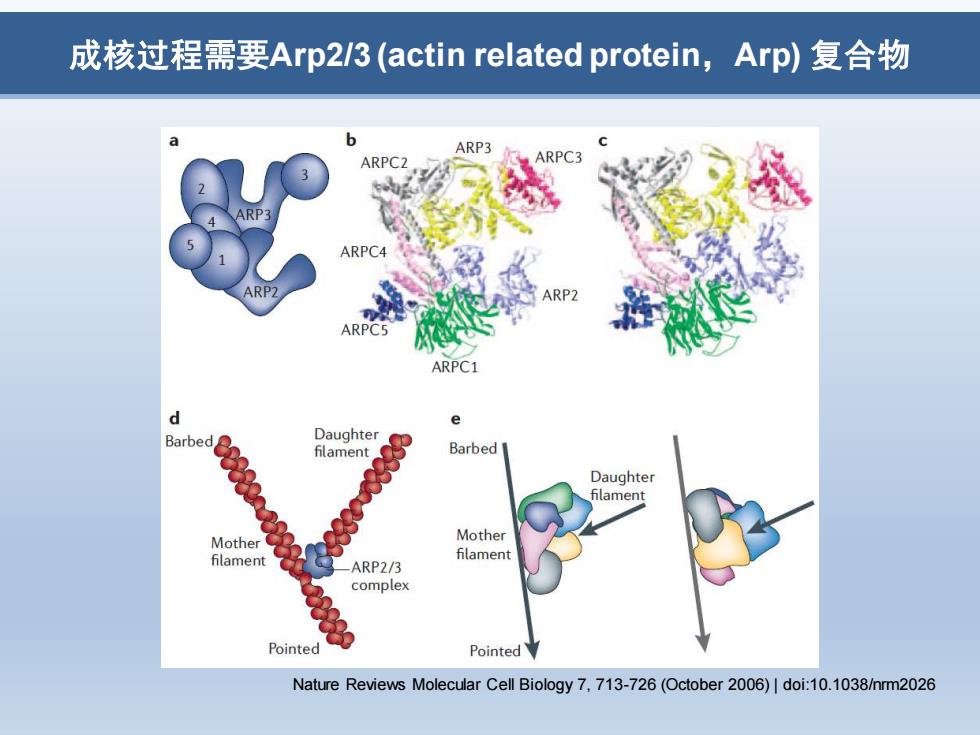
成核过程需要Arp23(actin related protein,Arp)复合物 ARP3 ARPCZ ARPC4 ARP2 ARPC5 ARPC1 Barbed Daughter Barbed Daughter filament Mother Mother filament filament ARP2/3 complex Pointed Pointed Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 7,713-726(October 2006)|doi:10.1038/nrm2026
成核过程需要Arp2/3 (actin related protein,Arp) 复合物 Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 7, 713-726 (October 2006) | doi:10.1038/nrm2026