
呀 Signal Detection and Estimation 2020 edition UESTC 1
UESTC 何子述等 Signal Detection and Estimation 2020 edition 1
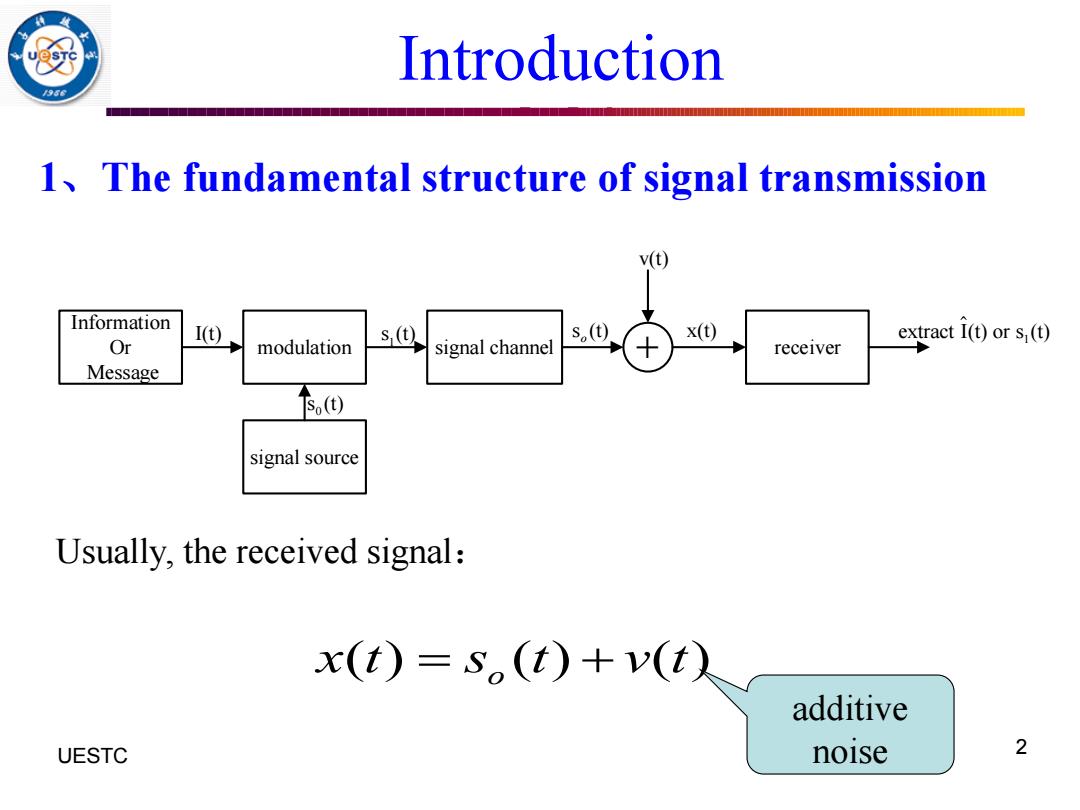
Introduction 1 The fundamental structure of signal transmission v(t Information I(t) s(@ s() x() extract I(t)or s(t) Or modulation signal channel receiver Message 下s(①) signal source Usually,the received signal: x(t)=so(t)+v(t入 additive UESTC noise 2
UESTC 何子述等 2 1、The fundamental structure of signal transmission Usually, the received signal: ( ) ( ) ( ) o x t s t v t = + additive noise 0 s (t) signal channel receiver Information Or Message modulation signal source 1 I(t) s (t) s (t) o v(t) x(t) 1 extract I(t) or s (t) + Introduction
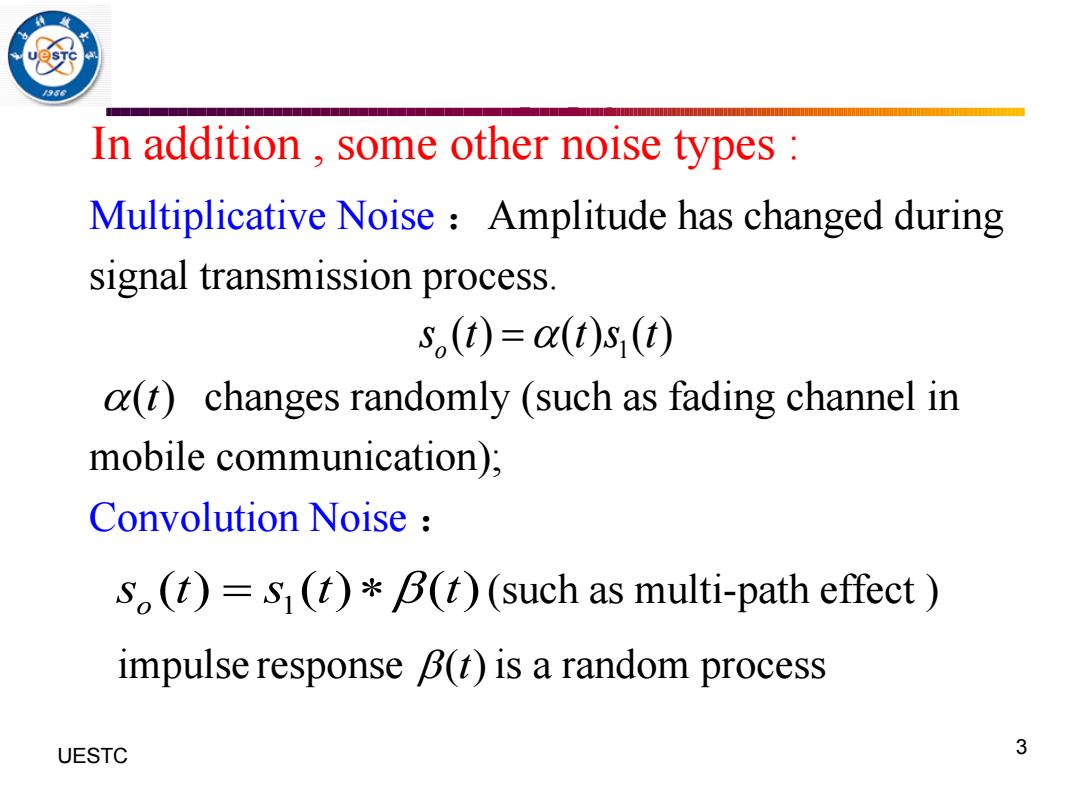
In addition.some other noise types Multiplicative Noise Amplitude has changed during signal transmission process. S,(t)=a(t)s,(t) a(t)changes randomly (such as fading channel in mobile communication); Convolution Noise s.()=s(t)*B()(such as multi-path effect impulse response B(t)is a random process UESTC 3
UESTC 何子述等 3 Multiplicative Noise :Amplitude has changed during signal transmission process. changes randomly (such as fading channel in mobile communication); Convolution Noise : 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) o s t t s t = 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) o s t s t t = (such as multi-path effect ) impulse response ( )t is a random process ( )t In addition , some other noise types :

0 This course mainly discuss the signal detection and estimation of additive noise. By taking logarithm,the multiplicative noise can be transformed to additive noise. By taking FFT,the convolution noise can be transformed to multiplicative noise ,and t then to additive noise by taking logarithm. So all kinds of noise can transform to additive noise to discuss. UESTC何子述等 4
UESTC 何子述等 4 • This course mainly discuss the signal detection and estimation of additive noise. • By taking logarithm, the multiplicative noise can be transformed to additive noise. • By taking FFT, the convolution noise can be transformed to multiplicative noise ,and then to additive noise by taking logarithm. So all kinds of noise can transform to additive noise to discuss
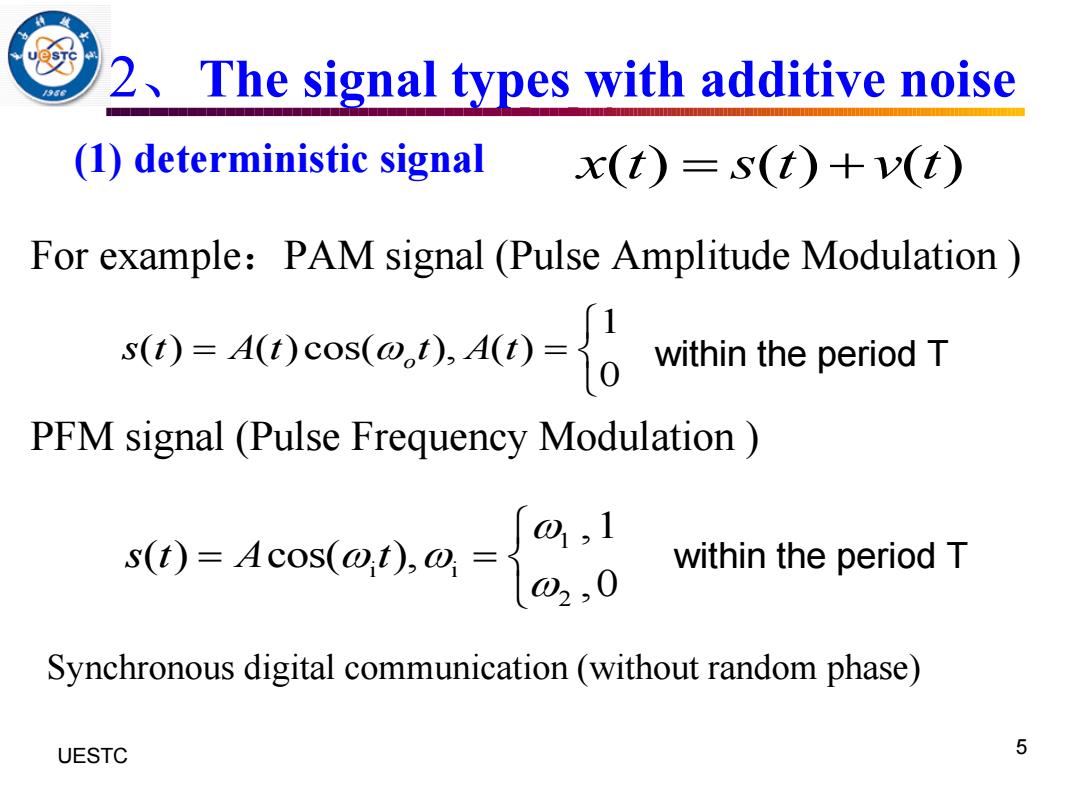
2 The signal types with additive noise (1)deterministic signal x(t)=s(t)+v() For example:PAM signal (Pulse Amplitude Modulation st0=A0cosa40=0 within the period T PFM signal (Pulse Frequency Modulation s(t)=Acos()0 J0,1 within the period T Synchronous digital communication (without random phase) UESTC 5
UESTC 何子述等 5 2、The signal types with additive noise For example:PAM signal (Pulse Amplitude Modulation ) PFM signal (Pulse Frequency Modulation ) x t s t v t ( ) ( ) ( ) = + 1 ( ) ( )cos( ), ( ) 0 o s t A t t A t = = within the period T 1 i i 2 , 1 ( ) cos( ), , 0 s t A t = = within the period T Synchronous digital communication (without random phase) (1) deterministic signal
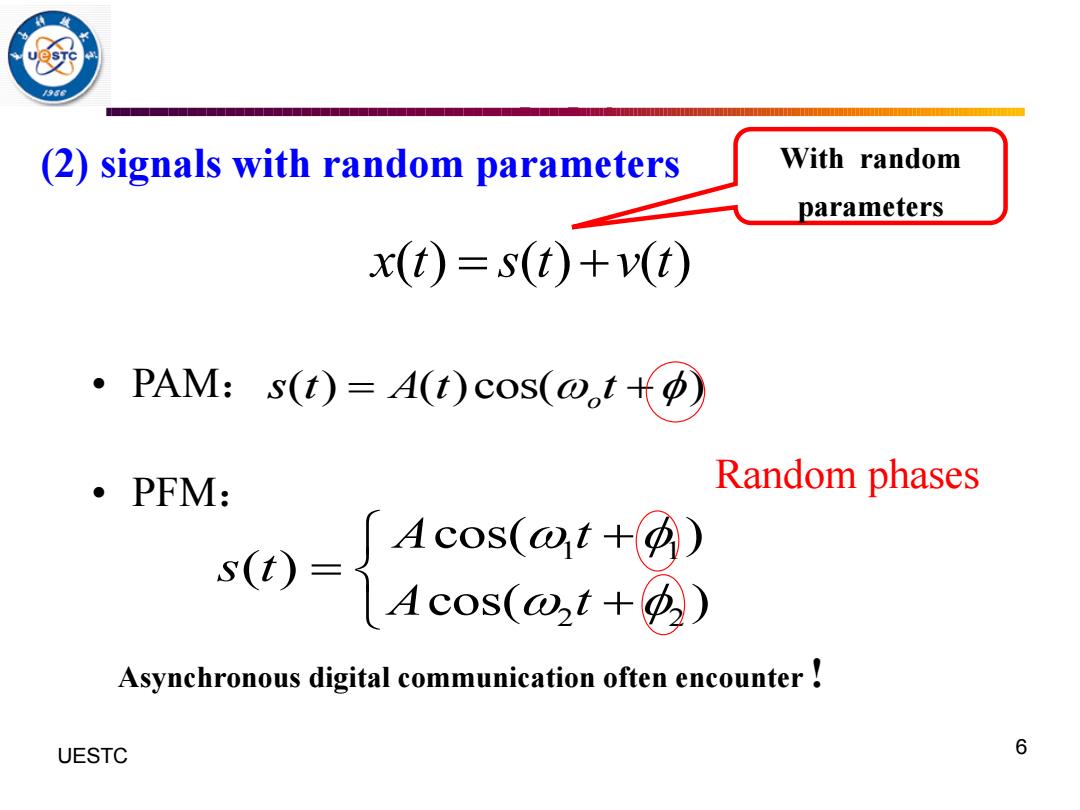
(2)signals with random parameters With random parameters x(t)=s(t)+v(t) ·PAM:s(t)=A(t)Cos(o,t十p) PFM: Random phases -8e】 4cos(@+) Asynchronous digital communication often encounter! UESTC 6
UESTC 何子述等 6 (2) signals with random parameters x t s t v t ( ) ( ) ( ) = + • PAM: ( ) ( )cos( ) o s t A t t = + • PFM: 1 1 2 2 cos( ) ( ) cos( ) A t s t A t + = + Asynchronous digital communication often encounter ! With random parameters Random phases

radar echo signals s(1)=A(t)cos[@(t-t)+) A(t),t,o All are random parameters UESTC 7
UESTC 何子述等 7 ( ) ( )cos[ ( ) )] o s t A t t = − + radar echo signals All are random parameters A t( ), ,
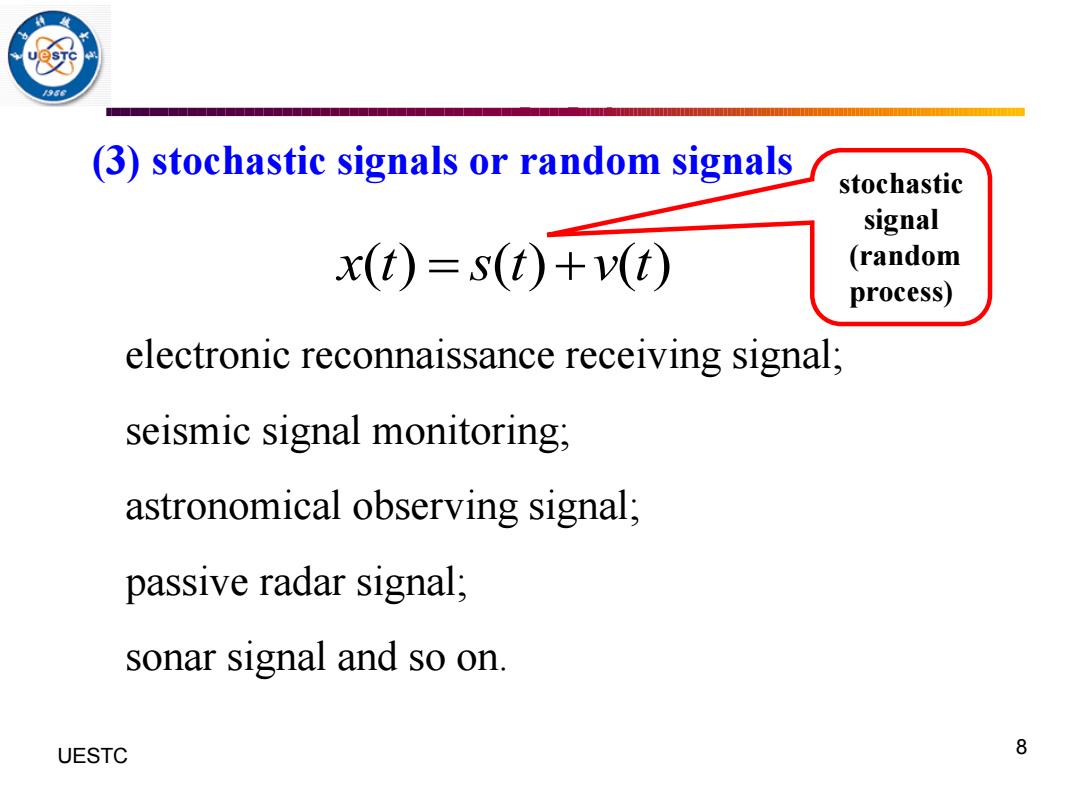
(3)stochastic signals or random signals stochastic signal x(t)=s(t)+v(t) (random process) electronic reconnaissance receiving signal; seismic signal monitoring; astronomical observing signal; passive radar signal; sonar signal and so on. UESTC 8
UESTC 何子述等 8 (3) stochastic signals or random signals x t s t v t ( ) ( ) ( ) = + electronic reconnaissance receiving signal; seismic signal monitoring; astronomical observing signal; passive radar signal; sonar signal and so on. stochastic signal (random process)
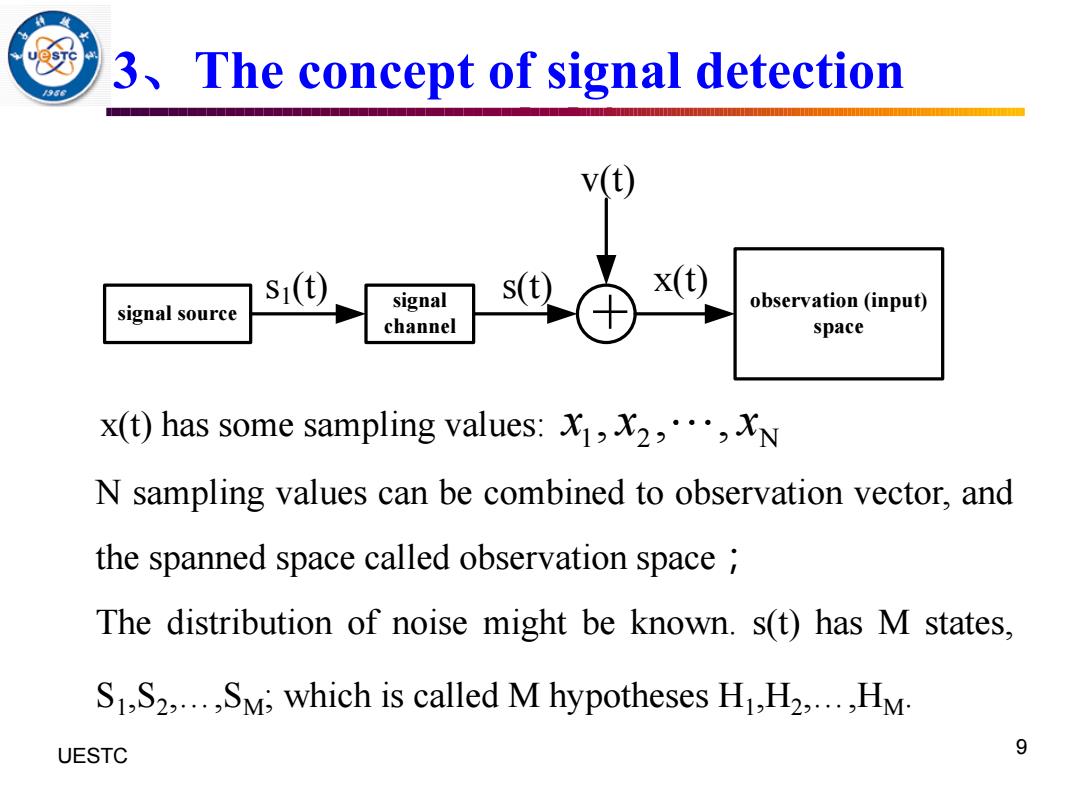
3 The concept of signal detection S1() s(t) x(t) signal observation(input) signal source channel space x(t)has some sampling values:,N N sampling values can be combined to observation vector,and the spanned space called observation space The distribution of noise might be known.s(t)has M states, S1,S2,...,SM;which is called M hypotheses H1,H2,...,HM UESTC 9
UESTC 何子述等 9 3、The concept of signal detection signal source signal channel observation (input) space s1(t) + s(t) v(t) x(t) x(t) has some sampling values: 1 2 N x x x , , , N sampling values can be combined to observation vector, and the spanned space called observation space ; The distribution of noise might be known. s(t) has M states, S1 ,S2 ,…,SM; which is called M hypotheses H1 ,H2 ,…,HM
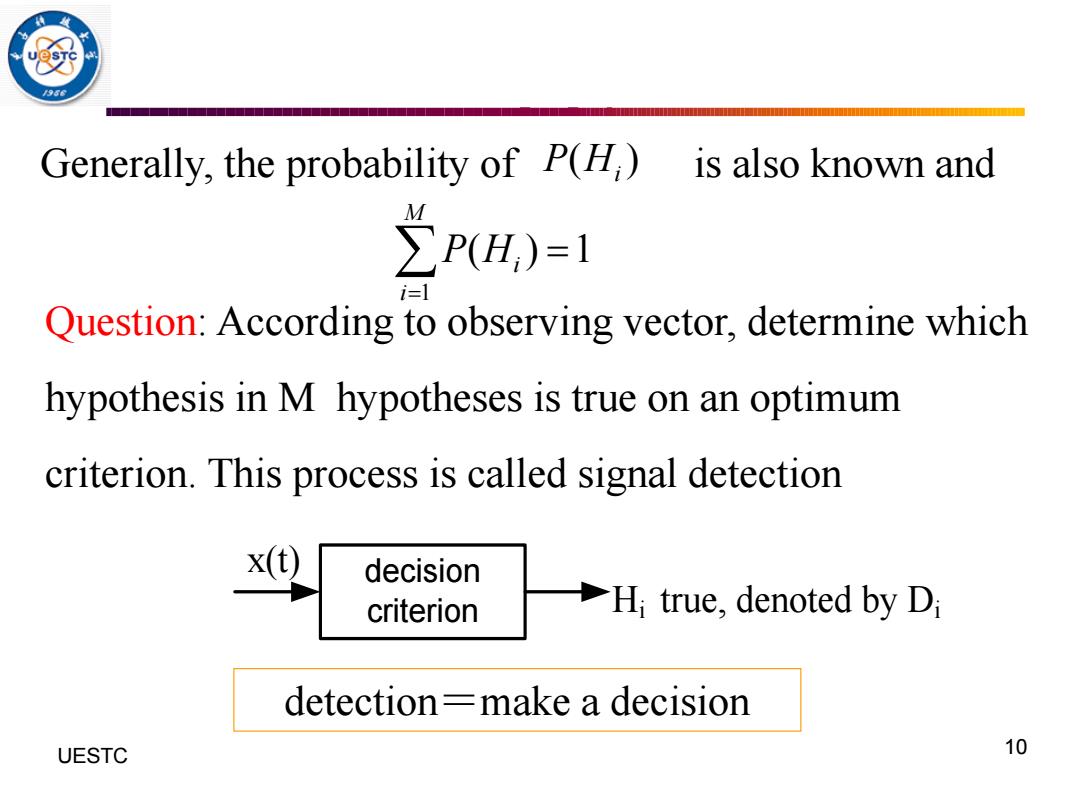
Generally,the probability of P(H) is also known and ∑P(H,)=1 i=l Question:According to observing vector,determine which hypothesis in M hypotheses is true on an optimum criterion.This process is called signal detection x(t) decision criterion H true,denoted by Di detection=make a decision UESTC 10
UESTC 何子述等 10 Question: According to observing vector, determine which hypothesis in M hypotheses is true on an optimum criterion. This process is called signal detection decision criterion x(t) Hi true, denoted by Di detection=make a decision Generally, the probability of is also known and 1 ( ) 1 M i i P H = = ( ) P Hi