
第三讲 单级放大器 游飞博导,副教授 电子科学与工程学院,feiyou@uestc..edu.cn 03/74
2020/3/24 1 第三讲 单级放大器 游飞 博导,副教授 电子科学与工程学院, feiyou@uestc.edu.cn

Why Amplifiers? Amplifiers are essential building blocks of both analog and digital systems. Amplifiers are needed for variety of reasons including: To amplify a weak analog signal for further processing To reduce the effects of noise of the next stage To provide a proper logical levels(in digital circuits) Amplifiers also play a crucial role in feedback systems We first look at the low-frequency performance of amplifiers.Therefore, all capacitors in the small-signal model are ignored! 705/74
2020/3/24 Set 3: Single-Stage Amplifiers 2 SM 5 Why Amplifiers? • Amplifiers are essential building blocks of both analog and digital systems. • Amplifiers are needed for variety of reasons including: – To amplify a weak analog signal for further processing – To reduce the effects of noise of the next stage – To provide a proper logical levels (in digital circuits) • Amplifiers also play a crucial role in feedback systems • We first look at the low-frequency performance of amplifiers. Therefore, all capacitors in the small-signal model are ignored!
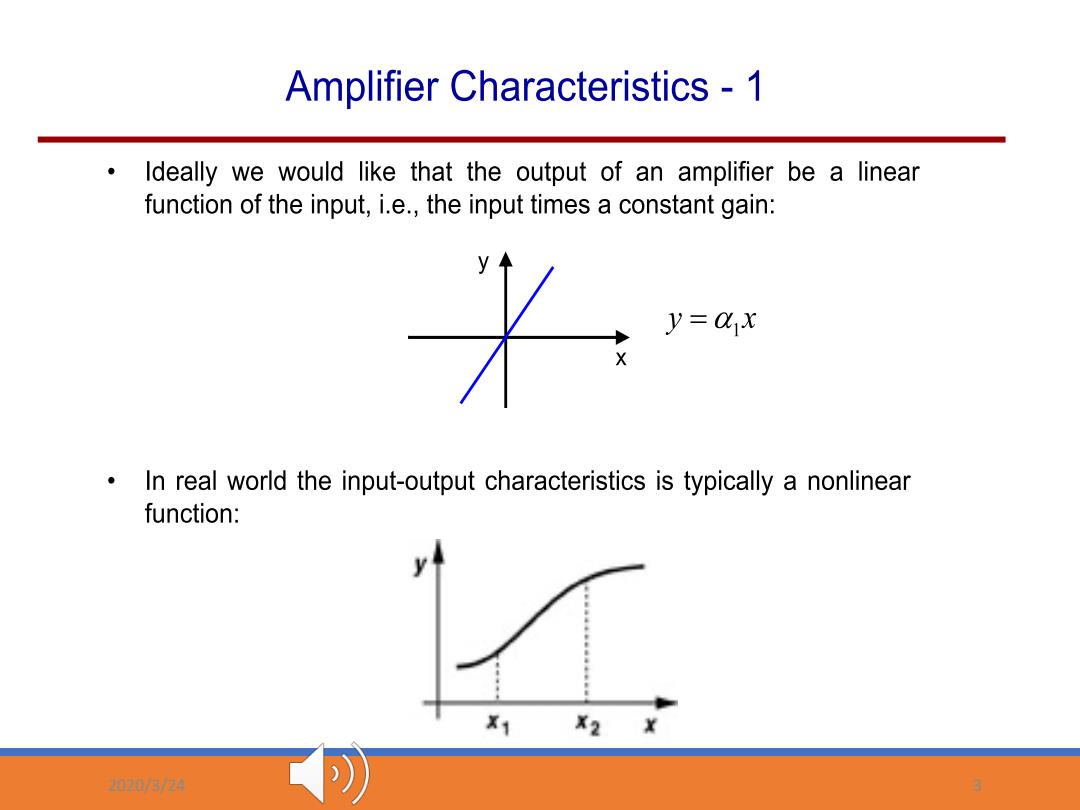
Amplifier Characteristics -1 Ideally we would like that the output of an amplifier be a linear function of the input,i.e.,the input times a constant gain: y=01X In real world the input-output characteristics is typically a nonlinear function: X1 X2 X 03/74
2020/3/24 3
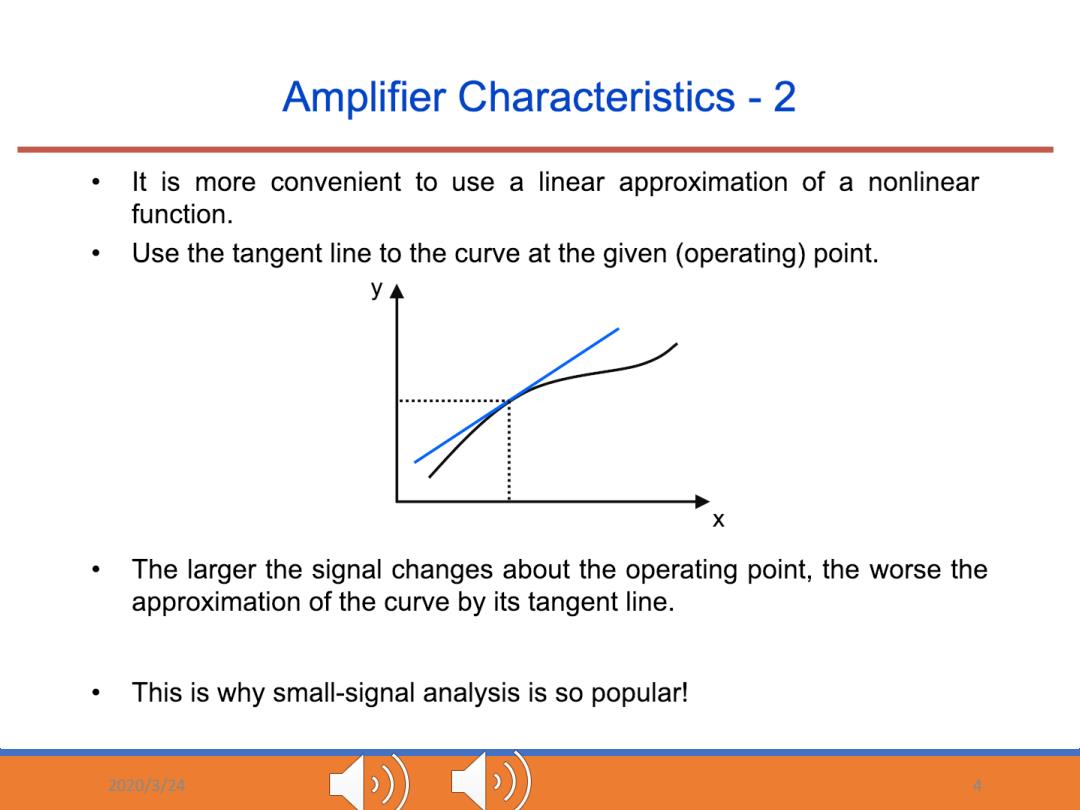
Amplifier Characteristics-2 It is more convenient to use a linear approximation of a nonlinear function. Use the tangent line to the curve at the given(operating)point. y◆ X The larger the signal changes about the operating point,the worse the approximation of the curve by its tangent line. This is why small-signal analysis is so popular! 705/24
2020/3/24 4

Amplifier Characteristics -3 A well-behaved nonlinear function in the vicinity of a given point can be approximated by its corresponding Taylor series: y*x)+fx)-x-x)+".x-x++"G).6x- 2 n! .Leta,=f"G)to get n! y≈a+ax(x-xo)+a2(x-x)2+…+an(x-x)月 If x-Xo=Ax is small,we can ignore the higher-order terms (hence the name small-signal analysis)to get: y≈ao+a(x-xo)) do is referred to as the operating (bias)point and a is the small-signal gain. Ay=y-f(xo)=y-ao≈△x 03/74 ))))
2020/3/24 5
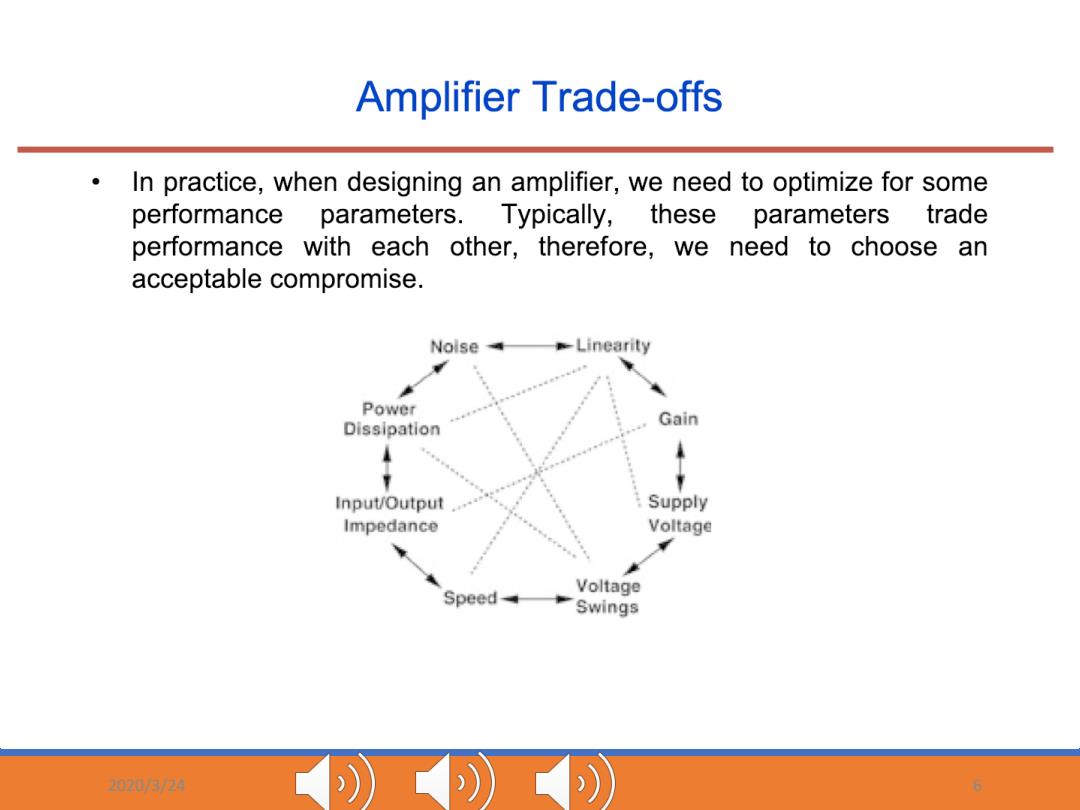
Amplifier Trade-offs In practice,when designing an amplifier,we need to optimize for some performance parameters.Typically,these parameters trade performance with each other,therefore,we need to choose an acceptable compromise. Nolse -Linearity Power Gain Dissipation Input/Output Supply Impedance Voltage Voltage Speed Swings 03/74 )))
2020/3/24 6

Single-Stage Amplifiers We will examine the following types of amplifiers: 1.Common Source 2.Common Drain(Source Follower 3.Common Gate 4.Cascode and Folded Cascode 。 Each of these amplifiers have some advantages and some disadvantages.Often,designers have to utilize a cascade combination of these amplifiers to meet the design requirements. 03/74 ))
2020/3/24 7
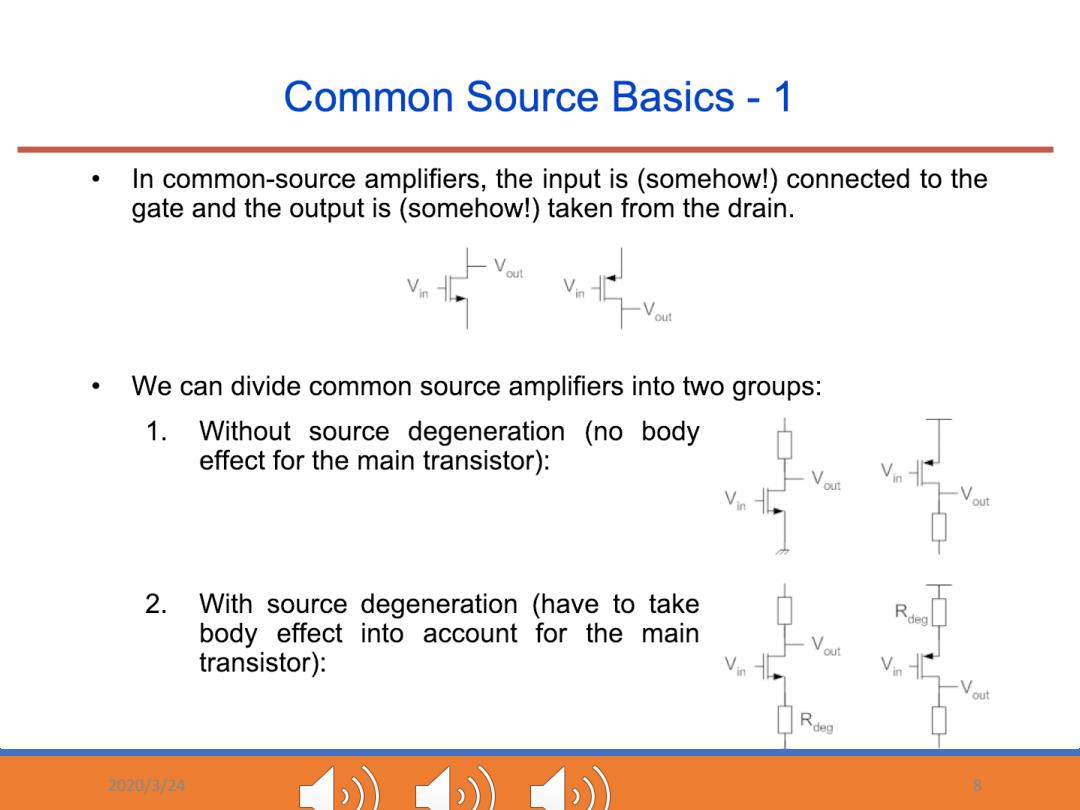
Common Source Basics -1 In common-source amplifiers,the input is (somehow!)connected to the gate and the output is(somehow!)taken from the drain. We can divide common source amplifiers into two groups: 1.Without source degeneration (no body effect for the main transistor): 2. With source degeneration (have to take body effect into account for the main transistor): 尺deg 032W 8
2020/3/24 8
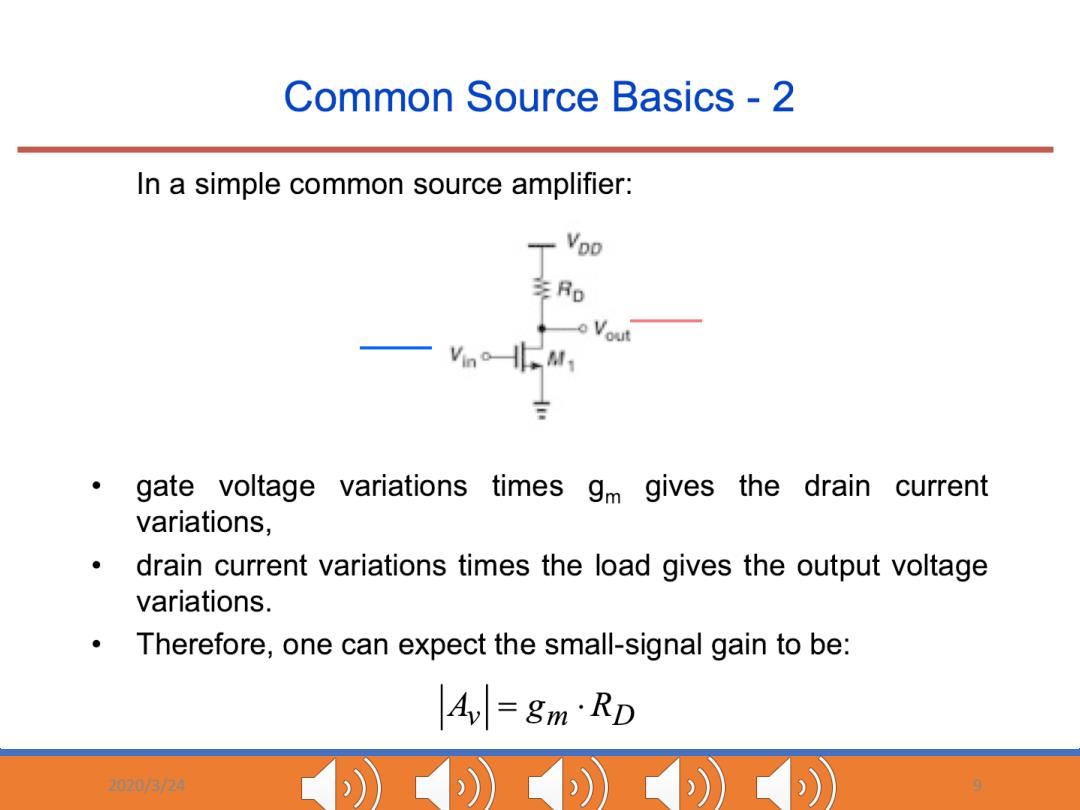
Common Source Basics -2 In a simple common source amplifier: 李Ro gate voltage variations times gm gives the drain current variations, drain current variations times the load gives the output voltage variations. Therefore,one can expect the small-signal gain to be: A=gm·RD 3/4
2020/3/24 9

Common Source Basics-3 Different types of loads can be used in an amplifier: 1.Resistive Load 2.Diode-connected Load 3.Current Source Load 4.Triode Load The following parameters of amplifiers are very important: 1.Small-signal gain 2.Voltage swing 3/7 10
2020/3/24 10