
Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Estimation Theory UESTC 1
1 UESTC Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Estimation Theory

10.1 Chapter highlights Parameter estimation problem formulation Properties of estimators ·Bayes estimation ·inimax estimation Maximum-likelihood estimation Comparison of estimators of parameters UESTC 2
2 UESTC 10.1 Chapter highlights • Parameter estimation problem formulation • Properties of estimators • Bayes estimation • Minimax estimation • Maximum-likelihood estimation • Comparison of estimators of parameters
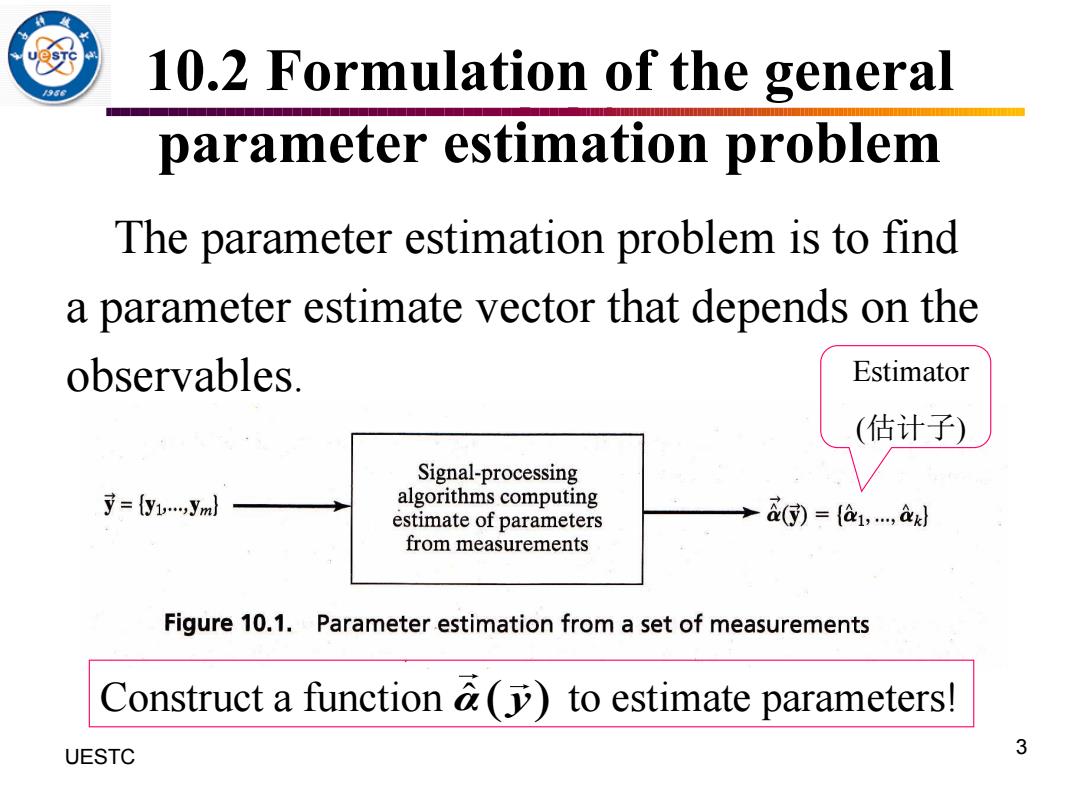
10.2 Formulation of the general parameter estimation problem The parameter estimation problem is to find a parameter estimate vector that depends on the observables. Estimator (估计子) Signal-processing 寸={y1w…,yml algorithms computing estimate of parameters &(G=a,,a from measurements Figure 10.1.Parameter estimation from a set of measurements Construct a function &(to estimate parameters! UESTC 3
3 UESTC 10.2 Formulation of the general parameter estimation problem The parameter estimation problem is to find a parameter estimate vector that depends on the observables. Estimator (估计子) Construct a function to estimate parameters! α ˆ( y)

5 The parameter estimate (depends on the random observables and is itself a random variable. The parameter a may be random vector or a nonrandom parameter vector. Specific cases of parameter estimation occur depending on whether pdf is known or unknown. UESTC 4
4 UESTC • The parameter estimate depends on the random observables and is itself a random variable. • The parameter may be random vector or a nonrandom parameter vector. • Specific cases of parameter estimation occur depending on whether pdf is known or unknown. α ˆ( y) α

Example 10.1 Constant number plus zero mean noise are yi=u+n, i=1,.,m The estimate can be defined by 空小点m m i=1 A direct estimation way (moment based method) 62=2(0y- 1ni1 i=1 UESTC 5
5 UESTC Example 10.1 Constant number plus zero mean noise are , 1,...., i i y n i m = + = The estimate can be defined by 1 1 ˆ m i i y m = = A direct estimation way (moment based method): 1 1 ˆ m i i y m = = ( ) 2 2 1 1 ˆ ˆ m i i y m = = − ( ) ( ) 2 2 1 ; , exp 2 2 i i y p y − = −
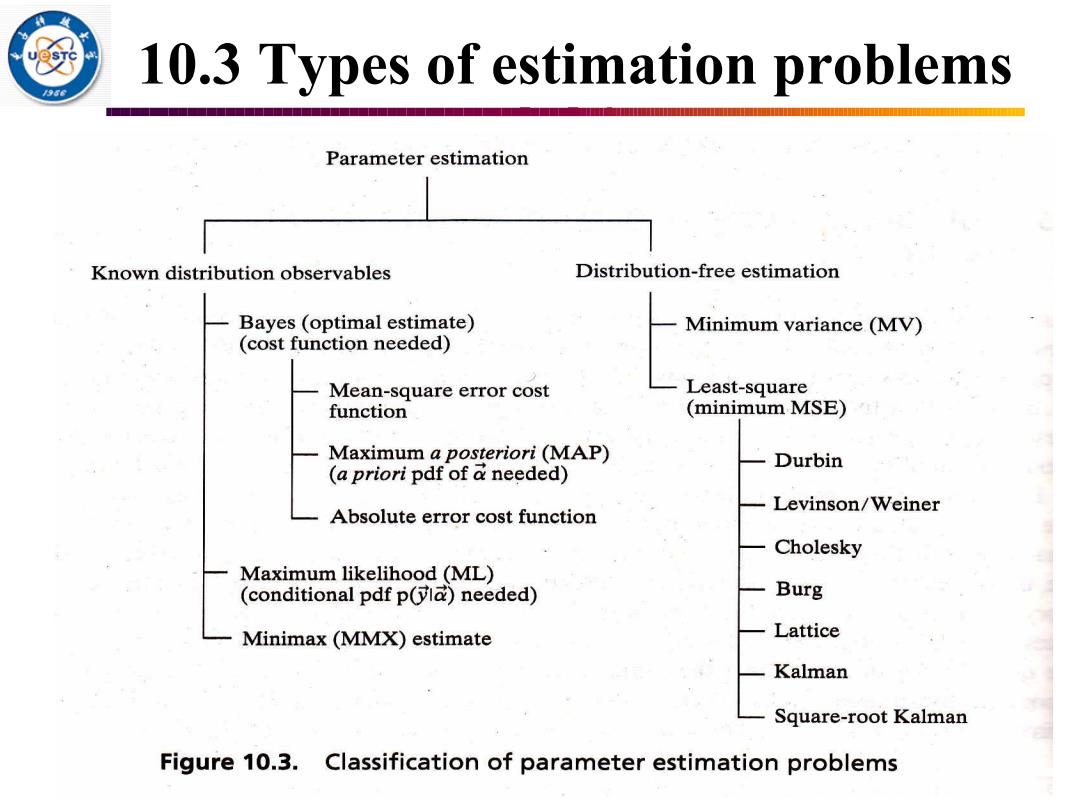
10.3 Types of estimation problems 36 Parameter estimation Known distribution observables Distribution-free estimation Bayes (optimal estimate) Minimum variance (MV) (cost function needed) Mean-square error cost Least-square function (minimum MSE) Maximum a posteriori(MAP) Durbin (a priori pdf of a needed) Levinson/Weiner Absolute error cost function Cholesky Maximum likelihood (ML) (conditional pdf p(la)needed) Burg Minimax (MMX)estimate Lattice Kalman Square-root Kalman Figure 10.3.Classification of parameter estimation problems
6 UESTC 10.3 Types of estimation problems

10.5 Properties of estimators For same observables,we can define different ( How can we comment each a()? ·Unbiased ·Consistent ·Sufficient Minimum-variance estimates (efficient) Asymptotically efficient Asymptotically normal UESTC 7
7 UESTC 10.5 Properties of estimators For same observables, we can define different . How can we comment each ? • Unbiased • Consistent • Sufficient • Minimum-variance estimates (efficient) • Asymptotically efficient • Asymptotically normal α ˆ( y) α ˆ( y)

10.5.1 Unbiased estimates An estimate a(y)is unbiased,if Ea-a is a constant vector E{a=E{a}-n。 is a random vector Asymptotically unbiased estimate lim=F)- UESTC 8
An estimate is unbiased, if 8 UESTC 10.5.1 Unbiased estimates ( ) ˆ y ˆ is a constant vector ˆ E = is a random vector = = Asymptotically unbiased estimate ˆ lim = m E → =

10.5.1 Unbiased estimates In the example 10.1 ·the sample mean Unbiased i)2y· m i= ·The sample variance 6=12(y-) m i=l UESTC 9
9 UESTC 10.5.1 Unbiased estimates In the example 10.1 • the sample mean • The sample variance ( ) 1 1 ˆ=ˆ m i m i= α y y = Unbiased ( ) 2 2 1 1 ˆ ˆ m i m i = = − y
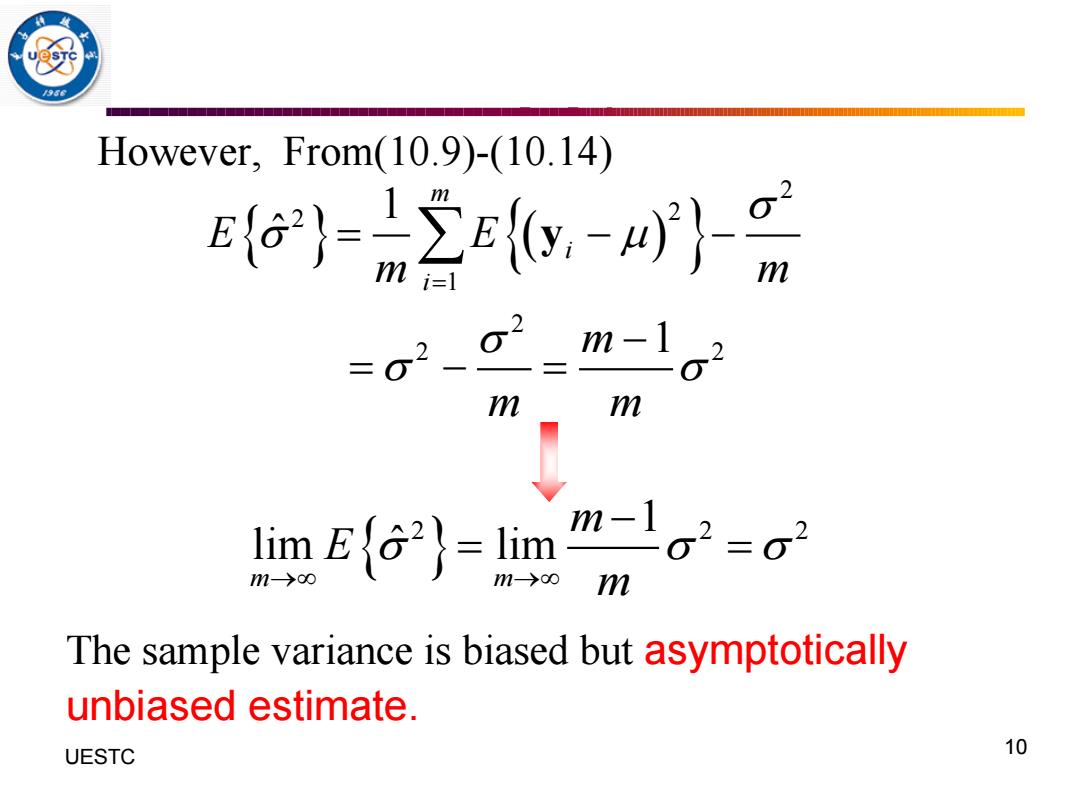
However,From(10.9)-(10.14) Ea}=2c-} m 2 m-1o2 m m lim EG2)-1 lim m-lo2=g2 m→0 m The sample variance is biased but asymptotically unbiased estimate. UESTC 10
10 UESTC However, From(10.9)-(10.14) The sample variance is biased but asymptotically unbiased estimate. ( ) 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 ˆ 1 m i i E E m m m m m = = − − − = − = y 2 2 2 1 lim lim ˆ m m m E m → → − = =