
Chapter 8 Wireless communications by Prof.XIAOFENG LI SCIE,UESTC UESTC-Wireless communicatons Prof李晓峰 1

Contents 4 Hr Spread spectrum communication systems Brief introduction to mobile communication systems UESTC-Wireless communicatons Prof李晓峰 3

8.4 Spread spectrum communication systems The major objective is often the efficient ultilization of transmission power and BW.Engineers make tradeoff between them. A spread spectrum (SS)system expands the BW of the signal largely to overcome various interferences.And more,using of the random-like codes in the expansion makes the signal hard to listen for an unintended user. Rooted in military communications,it was developed to provide resistance to jamming and to hide signals from enemies by transmitting at very low power. UESTC-Wireless communicatons Prof李晓峰 4

8.4 Spread spectrum communication systems Direct sequence(DS)and freq-hopped(FH)SS are two main types. 1)The DS system is based on PSK modulation and requires strictly coherent demodulation. 2)The FH system is based on the FSK modulation and often uses non- coherent demodulation. UESTC-Wireless communicatons Prof李晓峰 5
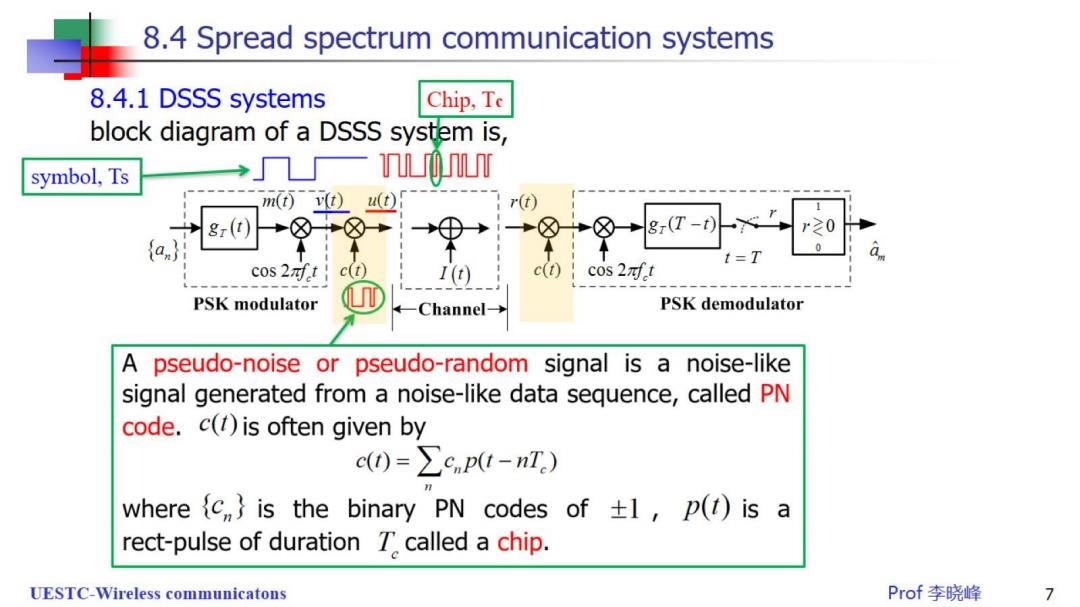
8.4 Spread spectrum communication systems 8.4.1 DSSS systems Chip,Te block diagram of a DSSS system is, symbol,Ts 几一0U m(0u① r(t) 8r(t 8r(T-t r0 0 t=T cos 2nft c(t) I(1) c(t) cos 2nft PSK modulator Channel- PSK demodulator A pseudo-noise or pseudo-random signal is a r noise-like signal generated from a noise-like data sequence,called PN code.c()is often given by c0=∑cnp-nI.) where {c,}is the binary PN codes of +1,p(1)is a rect-pulse of duration 7'called a chip UESTC-Wireless communicatons Prof李晓峰 7
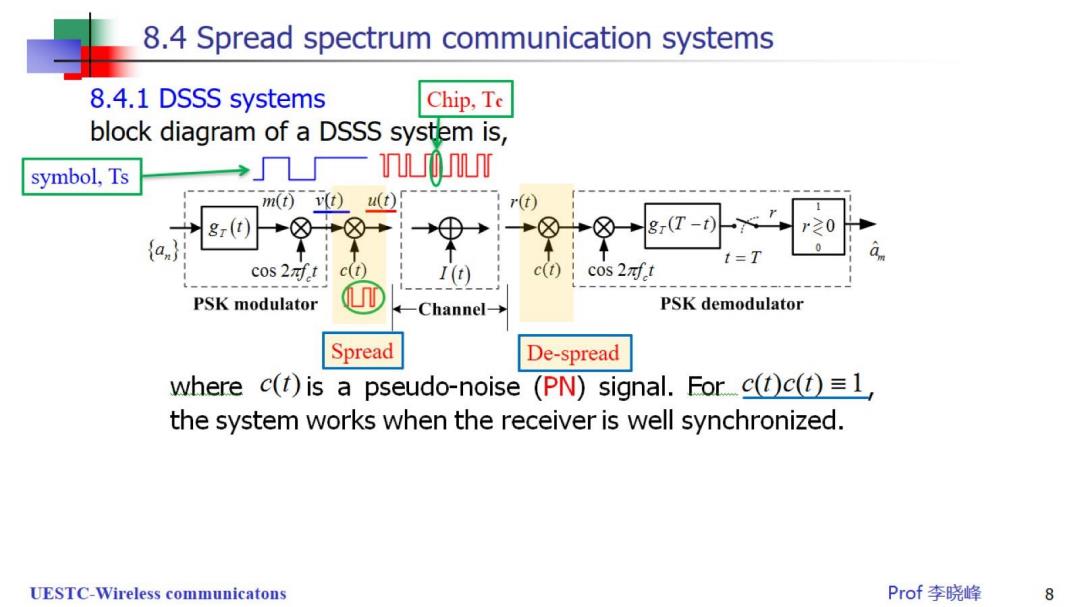
8.4 Spread spectrum communication systems 8.4.1 DSSS systems Chip,Te block diagram of a DSSS system is, symbol,Ts 一0r m⑥v)u① r(t) 8r(t 8r(T-t r20 0 t=T 0 cos2寸t c(t) I(t) c(t) cos 2af t PSK modulator Channe→ PSK demodulator Spread De-spread where c()is a pseudo-noise (PN)signal.Forc()c()=1, the system works when the receiver is well synchronized. UESTC-Wireless communicatons Prof李晓峰 8

8.4 Spread spectrum communication systems 8.4.1 DSSS systems Chip,Te block diagram of a DSSS system is, symbol,Ts 一L0 m⑥v)u① r(t) 8r(T-t) r20 0 t=T a cos 2nft c(t) I(t) c(t) c0s2对ft PSK modulator Channel→ PSK demodulator What happen in SPECTUM? B≈T Spread-factor: B.≈T Bne =B+Be L= B 、 Brsk B T UESTC-Wireless communicatons Prof李晓峰 9
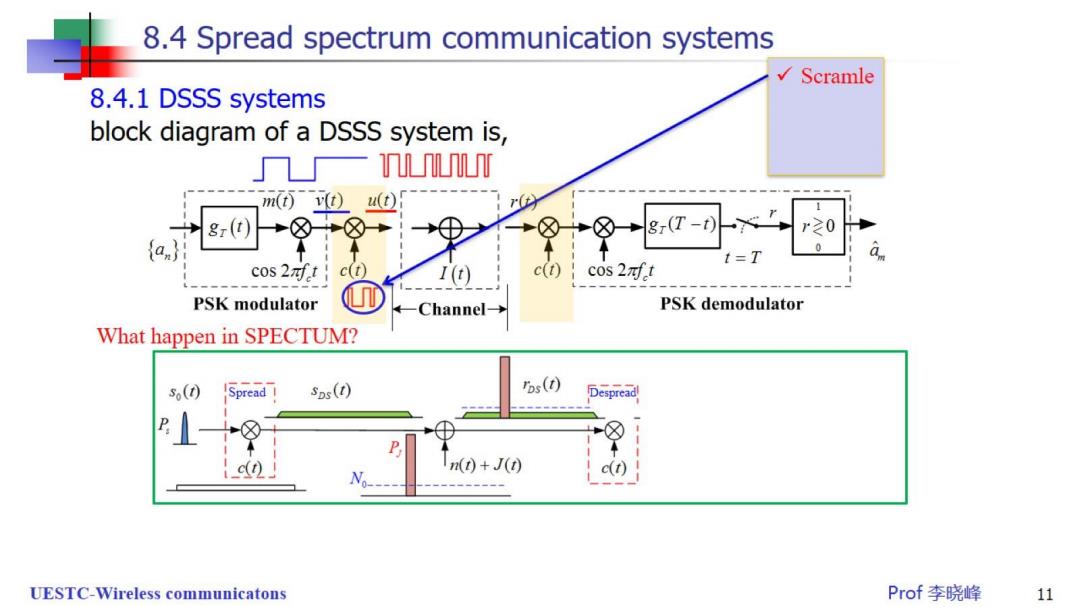
8.4 Spread spectrum communication systems √Scramle 8.4.1 DSSS systems block diagram of a DSSS system is, nm m(v0u① 8r(T-t) r20 0 t=T a cos 2nft c(t) I (t c(t) c0s2对ft PSK modulator Channel- PSK demodulator What happen in SPECTUM? (0 sps(t) bs(0) Despread c(t) n(0+J() UESTC-Wireless communicatons Prof李晓峰 11
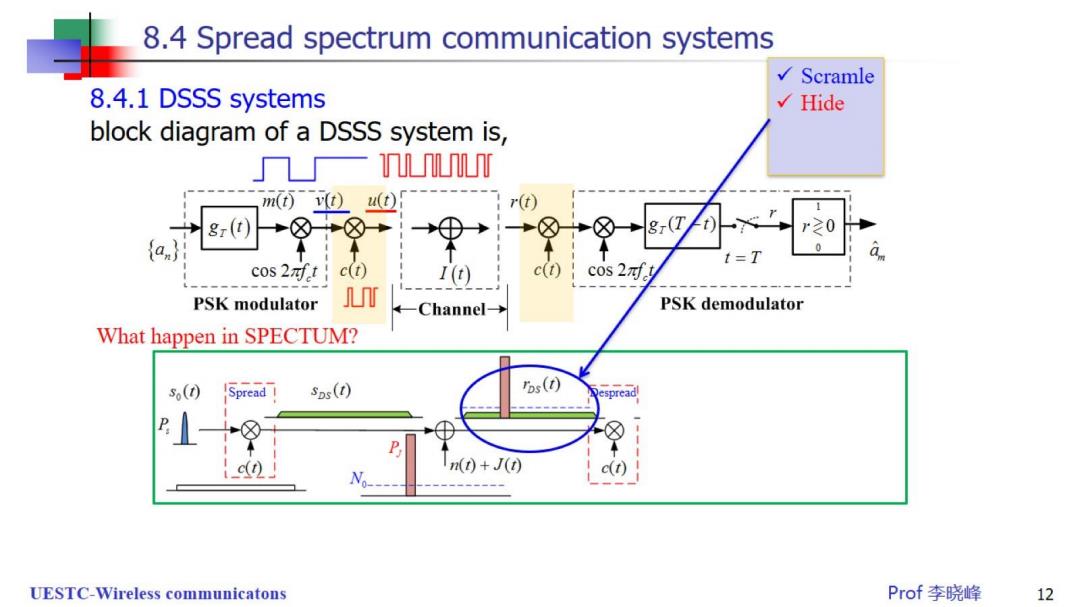
8.4 Spread spectrum communication systems Scramle 8.4.1 DSSS systems √Hide block diagram of a DSSS system is, U m(v0u① r(t) 8(T r≥0 0 t=T 0 cos 2nft c(t) I(t) c(t) cos 2nf PSK modulator T Channel- PSK demodulator What happen in SPECTUM? (0 sps(t) Tos(t) espread c(t) ()+J(t) UESTC-Wireless communicatons Prof李晓峰 12
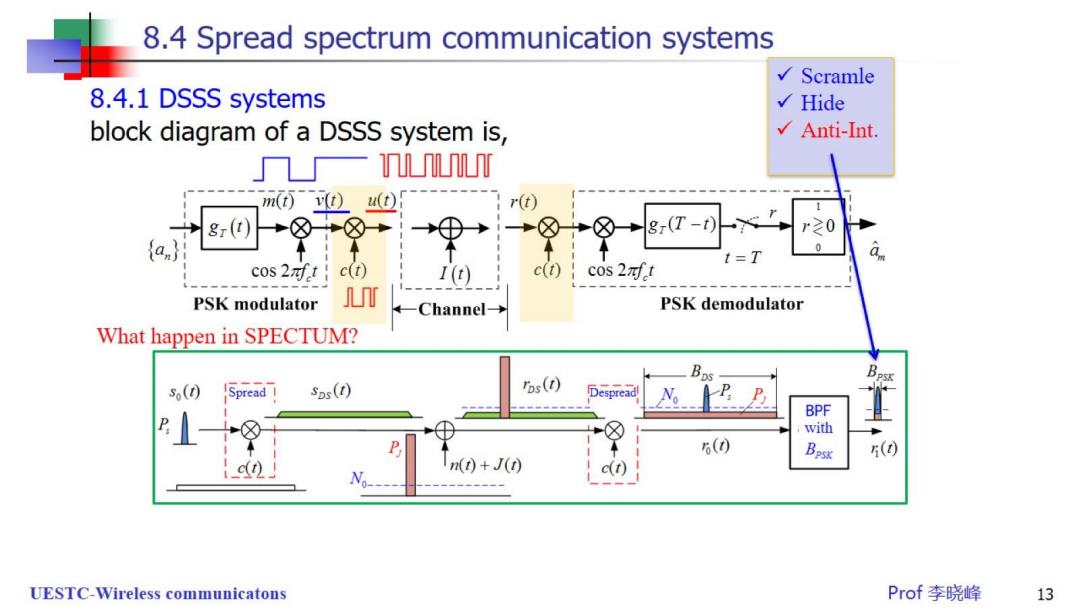
8.4 Spread spectrum communication systems Scramle 8.4.1 DSSS systems √Hide block diagram of a DSSS system is, Anti-lnt U m(v0u① r(t) 8(T-t) r20 0 t=T a. cos 2nft c(t) I(t) c(t) c0s2对ft PSK modulator Channel-→ PSK demodulator What happen in SPECTUM? 5(0 sps(t) ros(t) Despread No BPF with 6(0 5() c(t) ()+J() B c(t) UESTC-Wireless communicatons Prof李晓峰 13