
Contents 16 Hrs Introduction Geometric rep.of the sig waveforms Pulse amplitude modulation 2-d signal waveforms M-d signal waveforms ■Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN ■Optimal receivers and probs of err UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 2

5.4 Multi-d signal waveforms Sets of multiple dimensional signals are used to transmit M-ary symbols. Common types are 1.Orthogonal signals; 2.*Bi-orthogonal signals; 3.Simplex signals; 4. Binary coded signals; UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 3
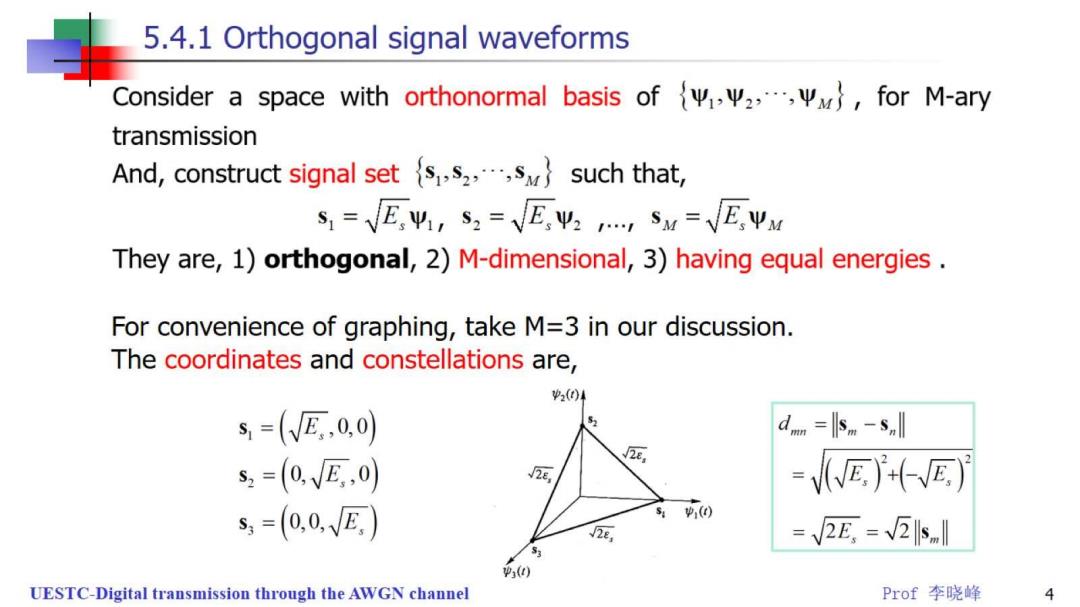
5.4.1 Orthogonal signal waveforms Consider a space with orthonormal basis of{Ψ1,Ψ2,,Ψw},forM-ary transmission And,construct signal set s,s2,,s such that, s,=VE,业1,S,=VE,业,,sw=VEΨu They are,1)orthogonal,2)M-dimensional,3)having equal energies. For convenience of graphing,take M=3 in our discussion. The coordinates and constellations are, 2(04 s=(VE,0,0) dnm=小sm-snl s,=(0VE,0) 2e, =WEE s=(0,0,VE e, =√2E,=2ls p() UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 4
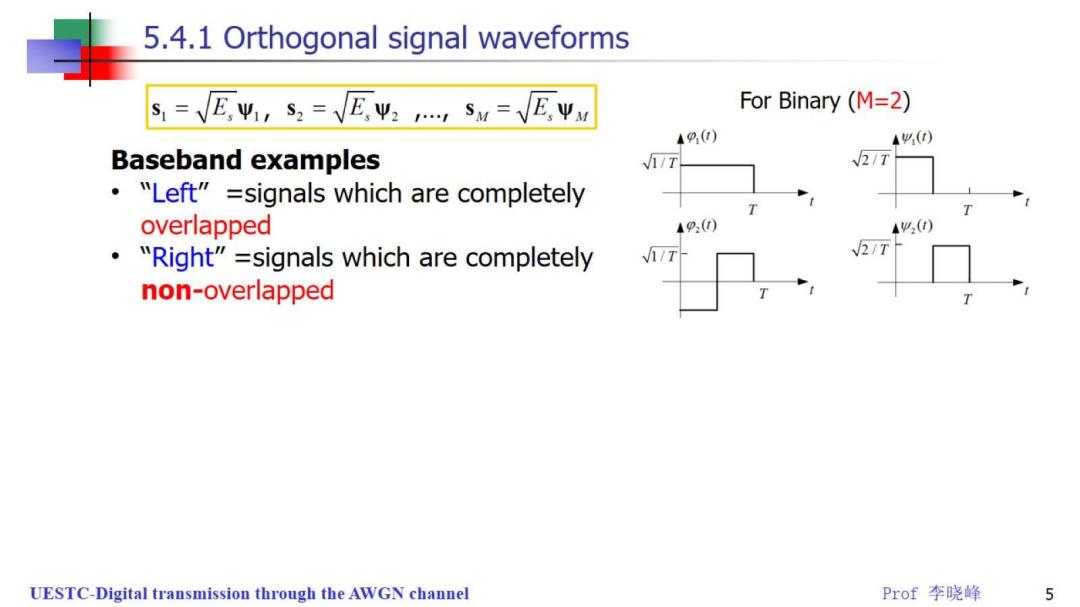
5.4.1 Orthogonal signal waveforms S=VE,Ψ,s,=E,Ψ2,Sw=VEyu For Binary(M=2) 49) 44() Baseband examples /7 IT "Left"=signals which are completely overlapped 9(t) A4() "Right"=signals which are completely 1/T non-overlapped UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 5
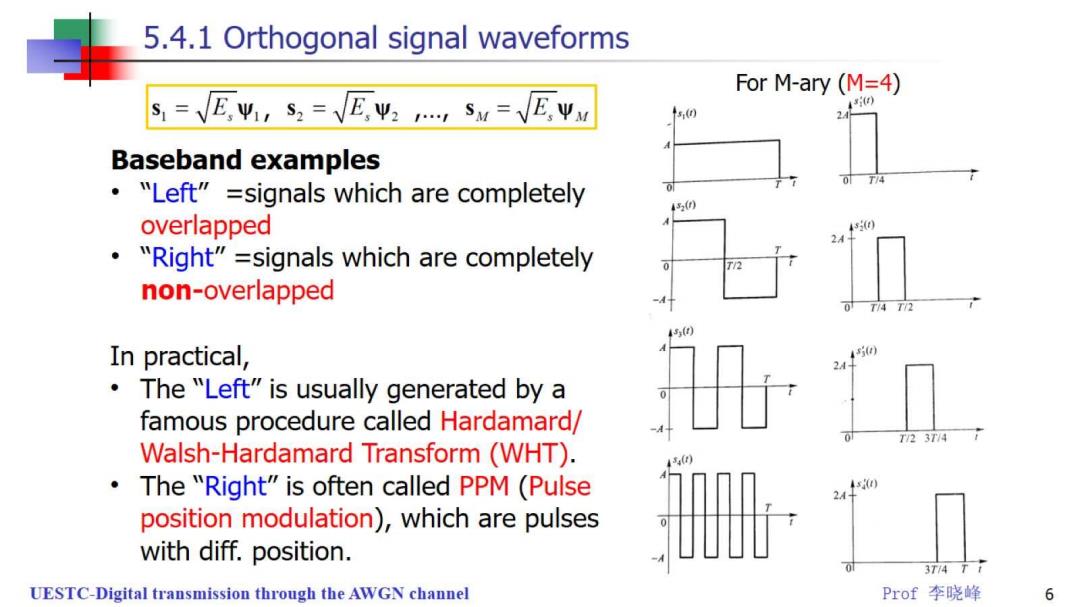
5.4.1 Orthogonal signal waveforms For M-ary(M=4) S=E,Wir S2 =E.W2 S=E.Wx s (n Baseband examples "Left"=signals which are completely 4320 overlapped 50 24- "Right"=signals which are completely T/2 non-overlapped T/4 Th T(I In practical, The "Left"is usually generated by a famous procedure called Hardamard/ T/23T/4 Walsh-Hardamard Transform(WHT). The "Right"is often called PPM (Pulse 5() position modulation),which are pulses with diff.position. 3T74T UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 6

5.4.1 Orthogonal signal waveforms S=VE,Ψ,S,=VE,Ψ2,Sw=VEVu Passband examples A very common type is call FSK(Freq shift keying) The signals are given by, u()=Acos[2π(f+m×△f)] t∈[0,T],m=0,1,,M-1 Note that: 1. Afis the freq separation which is some value making the signals orthogonal. 2. With same amplitude the signals are all of equal energy. Take M=4 (4FSK)a 0 32 0 AAAWAAAA- UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 7
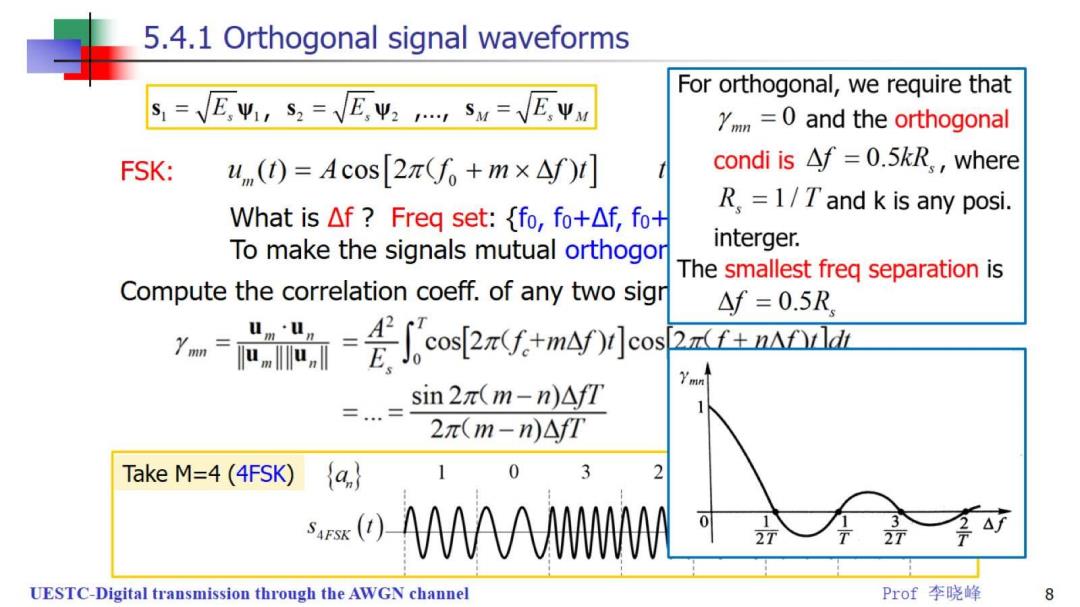
5.4.1 Orthogonal signal waveforms For orthogonal,we require that S=VEΨ,s,=VE,Ψ2,Sw=VEyy Ymm=0 and the orthogonal FSK: um()=Acos[2π(f0+m×△f)] condi is Af=0.5kR,,where What is△f?Freq set:{fo,fo+△f,fot R.=1/T'and k is any posi. To make the signals mutual orthogor interger. The smallest freq separation is Compute the correlation coeff.of any two sigr △f=0.5R =尚=fco2+m4W小eo s2(f+n△fOdL sin2π(m-n)△fT 2π(m-n)△fT Take M=4(4FSK) a 2 AAAAMW A UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 8

5.4.1 Orthogonal signal waveforms FSK:un(t)=Acos[2π(f+m×△f)t] t∈[0,T],m=0,1,,M-1 The Binary example is called BFSK(or 2FSK). u(t)=Acos2πfo f=f+f/2 where, 4,()=Acos2πft 6=f6-△f12 And,f&=[f6+f]/2 The MSK is the BFSK with minimum freq separation and continuous phase. Thus, f=f。+R/4, f0=f6-R,/4 Take M=4(4FSK)a, 0 WM- UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 9

5.4.2 Bi-Orthogonal signal waveforms A set of M-ary bi-orthogonal signals is constructed from a set of M/2-ary orthogonal signals. Given M=6 and 3 orthogonal signals s,s2,s;),the set of bi-orthogonal signals is simply given by, {1,2,3,S1,-52,-3 (04 Or expressed as, s=(VE,0,0 s,=(0E,0) s,=(0,0,VE) s,=(-E,0,0)s=(0,-√E,0 s6=(0,0,-√E) We have the followings: 中3() M-ary bi-orthogonal signals are M/2 dimensional. The energy of signals are equal.Two distances between signals are,2E,and 2E,. Baseband bi-orthogonal signals are from baseband orthogonal signals,Bandpass signals from bandpass ones. UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 10