
Contents 16 Hrs ■Introduction Geometric rep.of the sig waveforms Pulse amplitude modulation 2-d signal waveforms M-d signal waveforms Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN Optimal receivers and probs of err UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 2
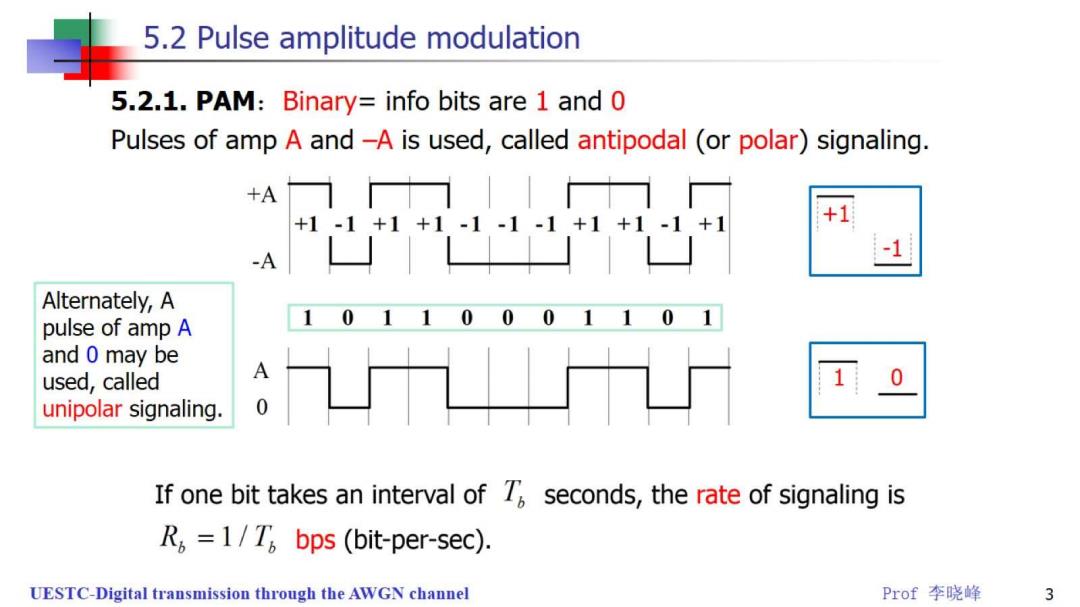
5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation 5.2.1.PAM:Binary=info bits are 1 and 0 Pulses of amp A and-A is used,called antipodal (or polar)signaling. +A一|十一 +1-1+1+1-1-1-1+1+1-1+1 +1 Alternately,A 0 0 pulse of amp A and 0 may be used,called unipolar signaling. If one bit takes an interval of 7 seconds,the rate of signaling is R,=1/T,bps (bit-per-sec). UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 3
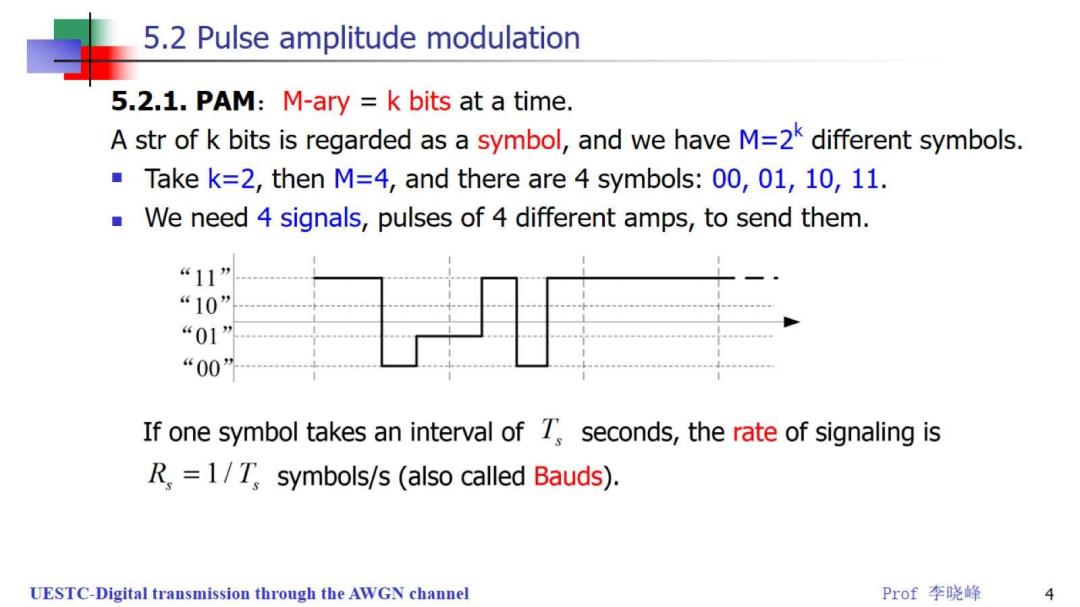
5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation 5.2.1.PAM:M-ary k bits at a time. A str of k bits is regarded as a symbol,and we have M=2k different symbols. Take k=2,then M=4,and there are 4 symbols:00,01,10,11. We need 4 signals,pulses of 4 different amps,to send them. “11” “10” “01” “00” If one symbol takes an interval of 7 seconds,the rate of signaling is R.=1/T symbols/s (also called Bauds). UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 4
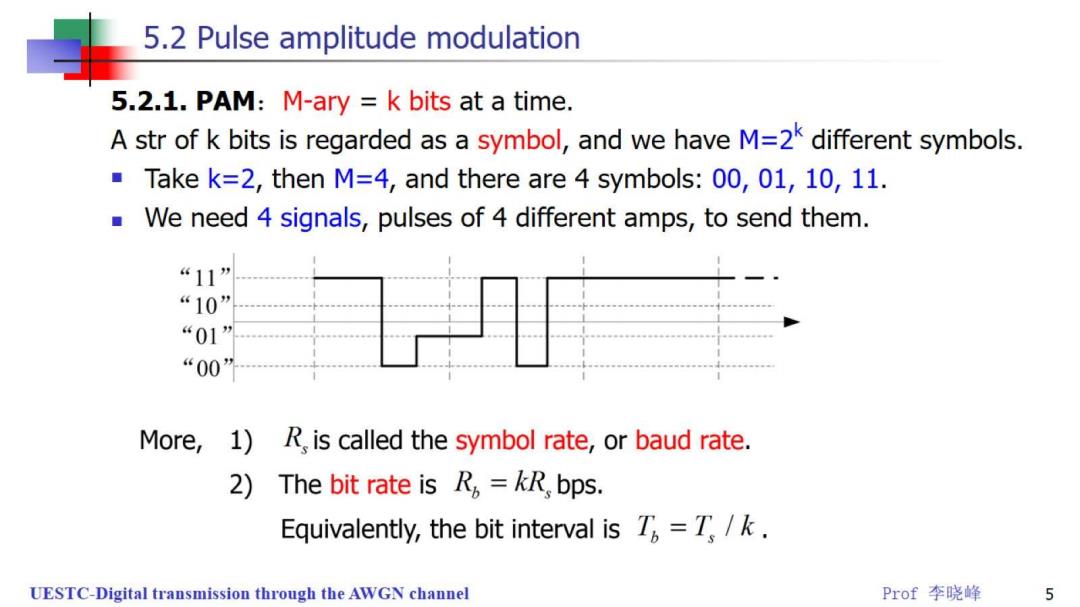
5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation 5.2.1.PAM:M-ary k bits at a time. A str of k bits is regarded as a symbol,and we have M=2k different symbols. Take k=2,then M=4,and there are 4 symbols:00,01,10,11. We need 4 signals,pulses of 4 different amps,to send them. “11” “10” “01” “00” More, 1)R,is called the symbol rate,or baud rate. 2)The bit rate isR,=kRbps. Equivalently,the bit interval is T,=T./k. UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 5
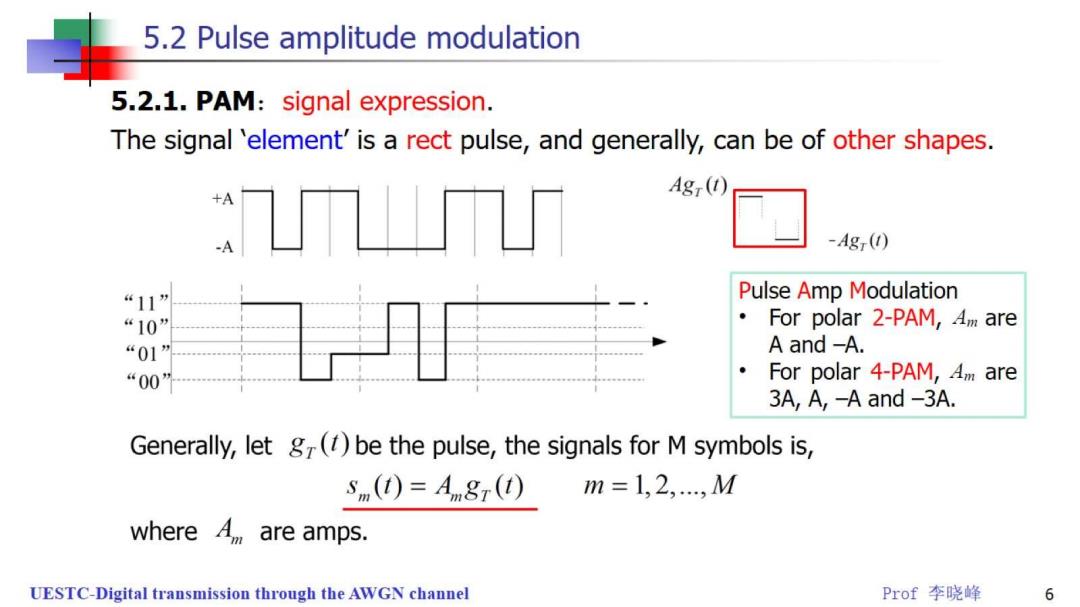
5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation 5.2.1.PAM:signal expression. The signal 'element'is a rect pulse,and generally,can be of other shapes. Agr(1) A -Ag() “11” Pulse Amp Modulation “10” For polar 2-PAM,4 are “01” A and -A. “00” For polar 4-PAM,4 are 3A,A,-A and-3A. Generally,let g()be the pulse,the signals for M symbols is, s(t)=Agr(t) m=1,2,.,M where are amps. UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 6
5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation 5.2.1.PAM:geometric representation s(1)=Agr(t) 1)Basis function:()=kog(t) whereko=1E=g()di=the energy of the g(). The space is of 1-d and N=1.. 2)The signal vectors (points):s=(a) m=1,2,M where,,a.=snΨ,-∫Ag,)0dh E =AEs UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 7
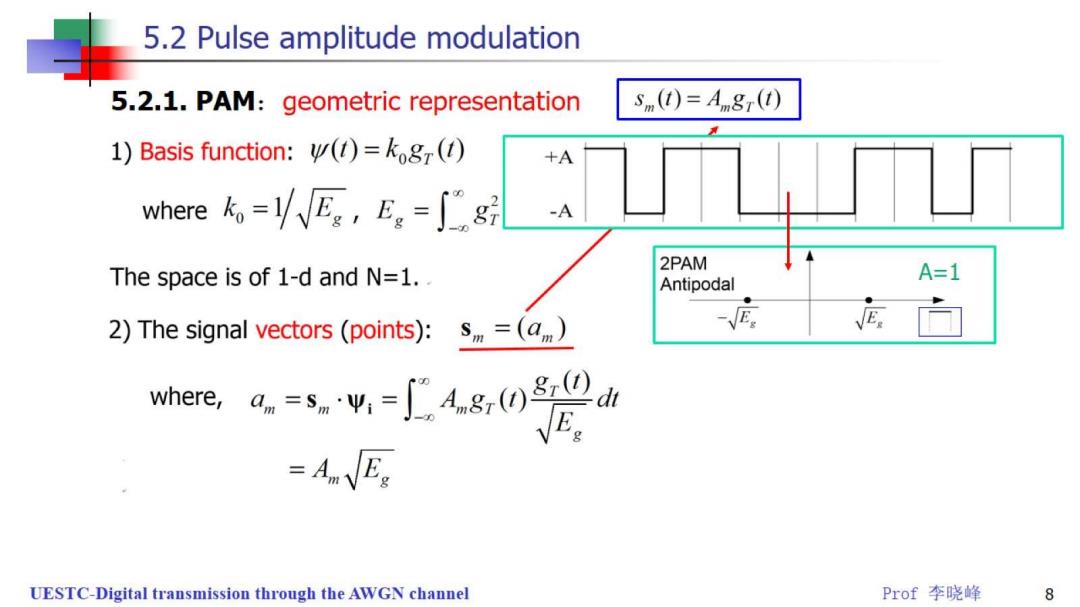
5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation 5.2.1.PAM:geometric representation Snm(t)=An8r(t)) 1)Basis function:()=kog() +A where=VVEe,Eg=∫g -A 2PAM The space is of 1-d and N=1. Antipodal A=1 2)The signal vectors (points):s=(a) 应广向 where,,a.=snΨ,-∫Ag,)0d E =AEs UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 8
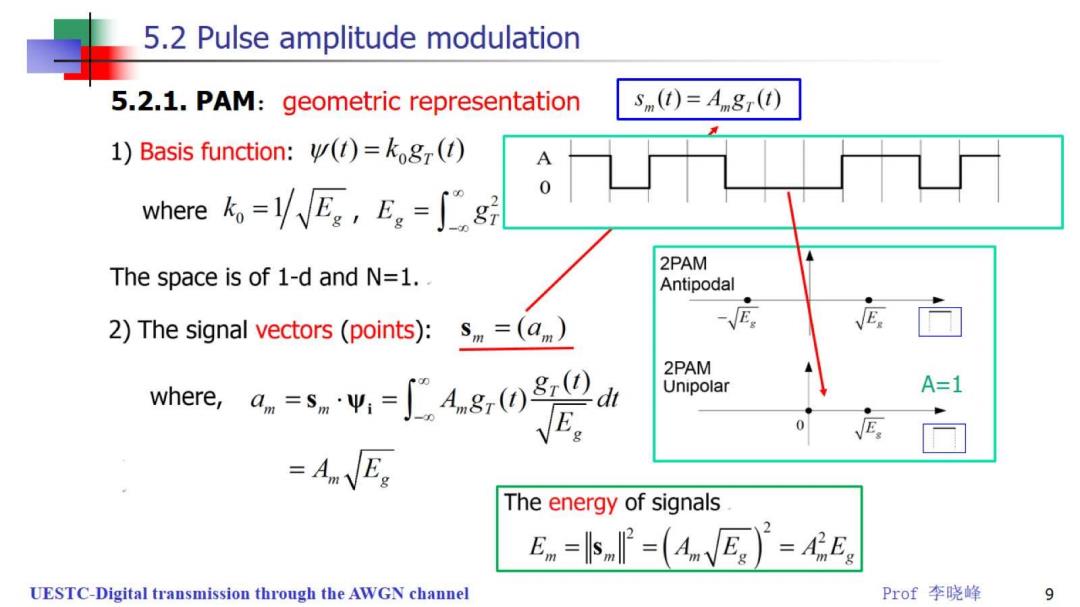
5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation 5.2.1.PAM:geometric representation s(t)=Augr(t) 1)Basis function:()=kog() where。=lVEe,Eg=∫g 2PAM The space is of 1-d and N=1. Antipodal 2)The signal vectors (points):s=(a) E 2PAM where,d.=(d Unipolar A=1 =AEs The energy of signals Em=小P=(AnEs)=AEe UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 9

5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation 5.2.1.PAM:geometric representation s(t)=Augr(t) 1)Basis function:()=kog() “11” “10” where。=VEe,Eg=∫g “01” “00” 2PAM The space is of 1-d and N=1. Antipodal ● 2)The signal vectors (points):s=(a) -E. 2PAM where,ds(d Unipolar =AEs 4PAM A=1 -3E.-E E UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 10
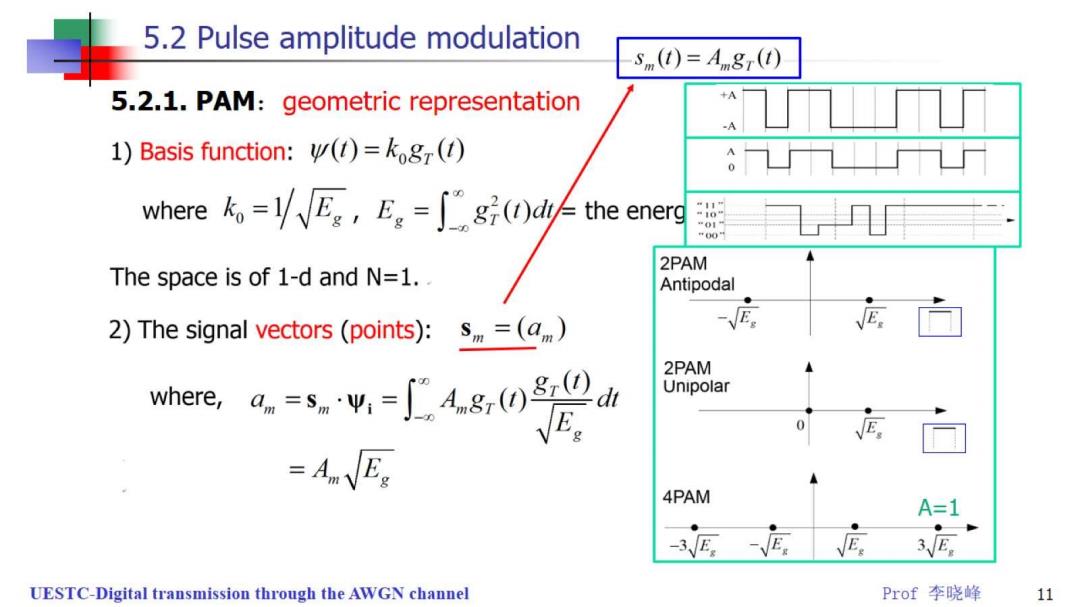
5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation s(t)=Agr(t) 5.2.1.PAM:geometric representation 1)Basis function:()=kog() where。=/√Eg,E。=∫'ng()dthe energ 11 10 01 00 2PAM The space is of 1-d and N=1.. Antipodal 2)The signal vectors (points):s=(a) E 2PAM where,d(d Unipolar VE。 =AEs 4PAM A=1 E UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 11