
Contents 16 Hrs Introduction Geometric rep.of the sig waveforms Pulse amplitude modulation 2-d signal waveforms M-d signal waveforms ■Opt.reception for the sig.In AWGN ■Optimal receivers and probs of err UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 3

5.5 Opt.reception for the sig.In AWGN In the nth interval,the process is as follows, {,an,} {,an} 5(t) r(t)The topics are: s(1)The Correlation-Demodulators 2)The MF-Demodulators 3)The Theory of Optimum Detectors 5.6 Typical Optimal Receivers r(t) 。 Binary signals Carrier-amp(1-D signals) It is convenient to divide the receiv Carrier-phs (2-D signals) 1)Demodulator:produce an obse QAM (2-D signals) 2)Detector:estimate the sym fror FSK (M-D orthogonal signals) UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 5

5.6.1 Binary modulations Baseband Binary PAM(the antipodal,unipolar) Orthogonal signaling with M=2 Passband ·BPSK(the antipodal) 。 OOK or BASK (the unipolar) BFSK(Orthogonal signaling with M=2) UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 7
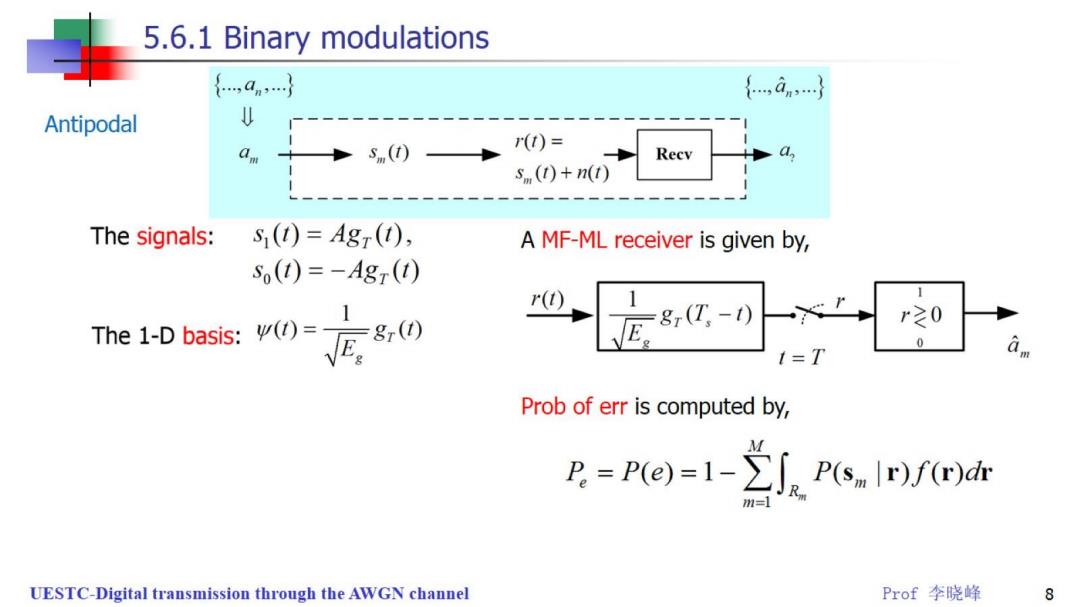
5.6.1 Binary modulations {,an} {,an…心} Antipodal am Sm()— r(T)= Recv s (t)+n(t) The signals: S()=Ag(), A MF-ML receiver is given by, So(1)=-Agr(1) r( The 1-basis:) 8(I,-) r之0 0 1=T Prob of err is computed by, P=P(e)=1-∑j。P(snlr)fr)dr UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 8
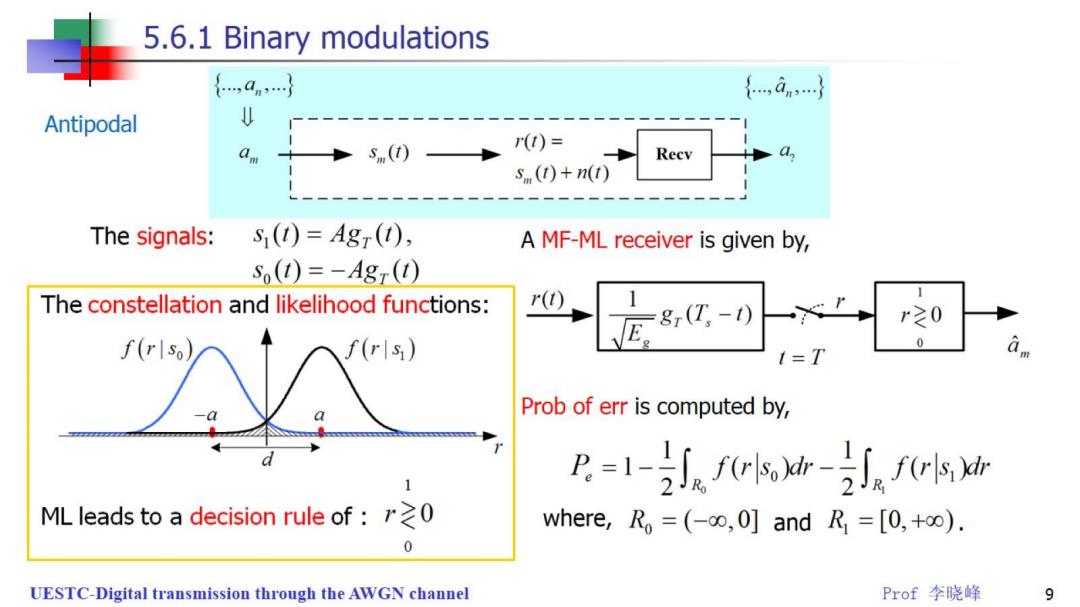
5.6.1 Binary modulations {,an} {,an,} Antipodal s (t)- r(t)= Recv s (t)+n(t) The signals: S,()=Agr(t), A MF-ML receiver is given by, So(1)=-AgT(t) The constellation and likelihood functions: r( E 8(T,-0 r20 f(r1s0) f(rls) 0 I=T Prob of err is computed by, 卫=1-f-afc小sh ML leads to a decision rule of :0 where,Ro=(-0,0]and R=[0,+co). 0 UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 9
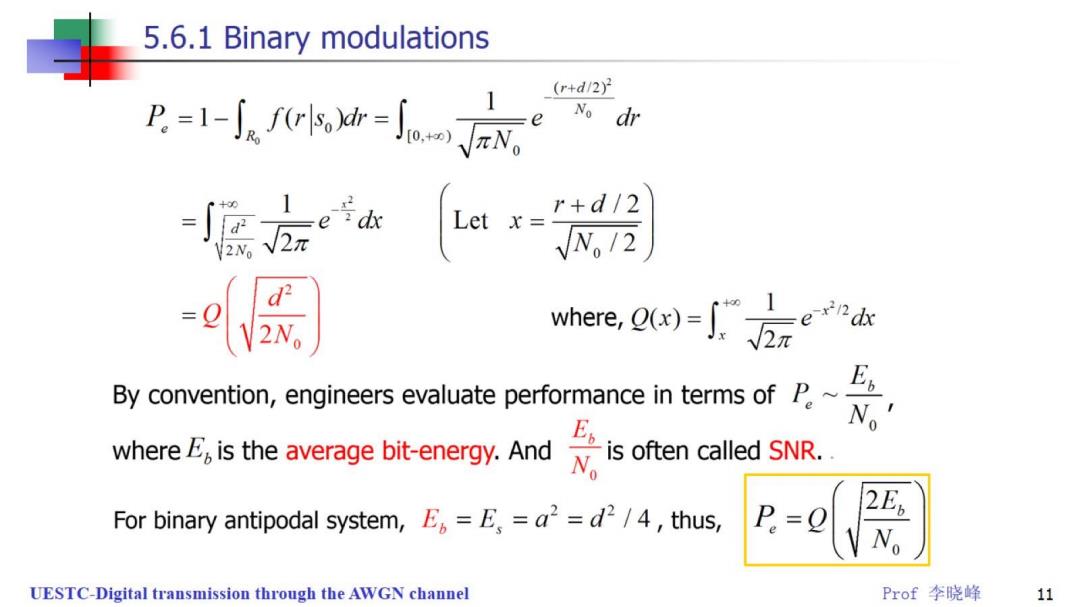
5.6.1 Binary modulations (r+d/2y2 B=1-okh-点 N。dr r+d/2 2N。 By convention,engineers evaluate performance in terms of P.~ Ep N whereE,is the average bit-energy.And is often called SNR. For binary antipodal system,E=E,=a2=d2/4,thus, P.-0 N UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 11
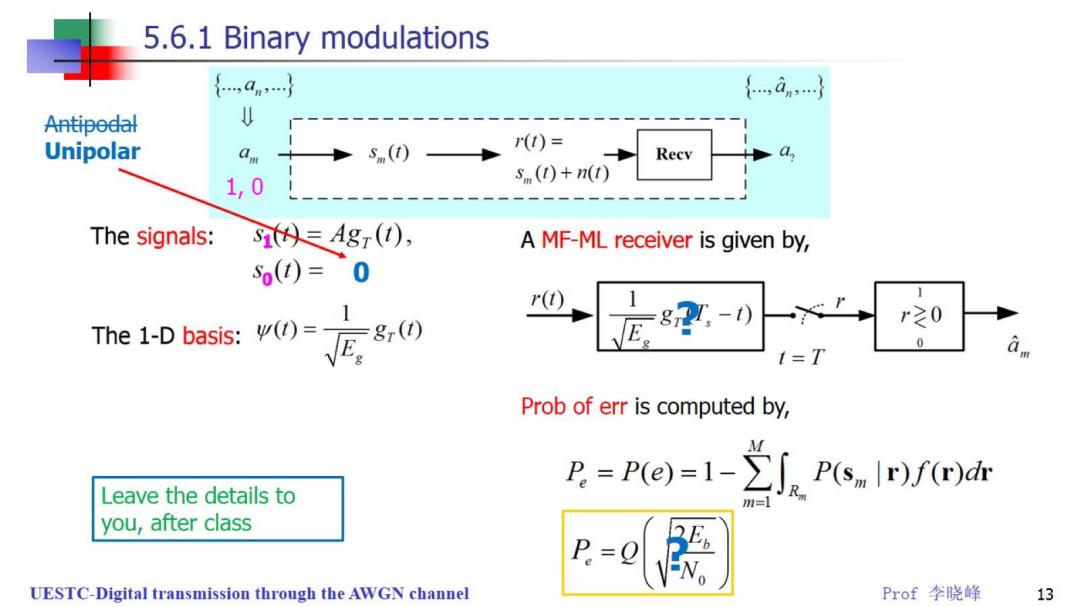
5.6.1 Binary modulations {,an} {,an,} Antipedal Unipolar am s(t) r(I)= Recv 1,0 s (t)+n(t) The signals: si()=Agr(1), A MF-ML receiver is given by, s()=0 .1 r( The 1-basis;()() E-0 r20 0 I=T Prob of err is computed by, P.=P(e)=1->SP(slr)f(r)dr Leave the details to you,after class P.=0 UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 13

5.6.1 Binary modulations Baseband ·Binary PAM(the antipodal,unipolar) Orthogonal signaling with M=2 Passband ·BPSK(the antipodal) 。 OOK or BASK (the unipolar) BFSK(Orthogonal signaling with M=2) UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 14

5.6.1 Binary modulations {,an} {,an…心} Orthogonal am s,(t) r(t)= Recv 1,0 s (t)+n(t) The 2-D basis:(),v ( 4 A MF-ML receiver is given by, The signals:s(1)=av(1), 4(T-) Min so()=a42(t) Dist 42(T-) t=T Prob of err is computed by, P.=P(e)=1->fP(s,Ir)f(r)dr UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 15

5.6.1 Binary modulations P.=0 2E, {,an} Orthogonal am s,(t) r(0)= Recv s (t)+n(t) MinDist leads to a decision rule of : [(n-a)++(-a) A MF-ML receiver is given by, %(T-) r() Min Dist Ψ2▲ R In terms of P.~。, (0,a) 。r:(5,2)》 Prob P.=9 E6=E,=a2=dP/2 R1 (a,0) Ψ1 =1-∫f(rsoXdr=.= 2No UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 17