
Contents 16 Hrs Introduction Geometric rep.of the sig waveforms Pulse amplitude modulation 2-d signal waveforms M-d signal waveforms ■Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN ■Optimal receivers and probs of err UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 3
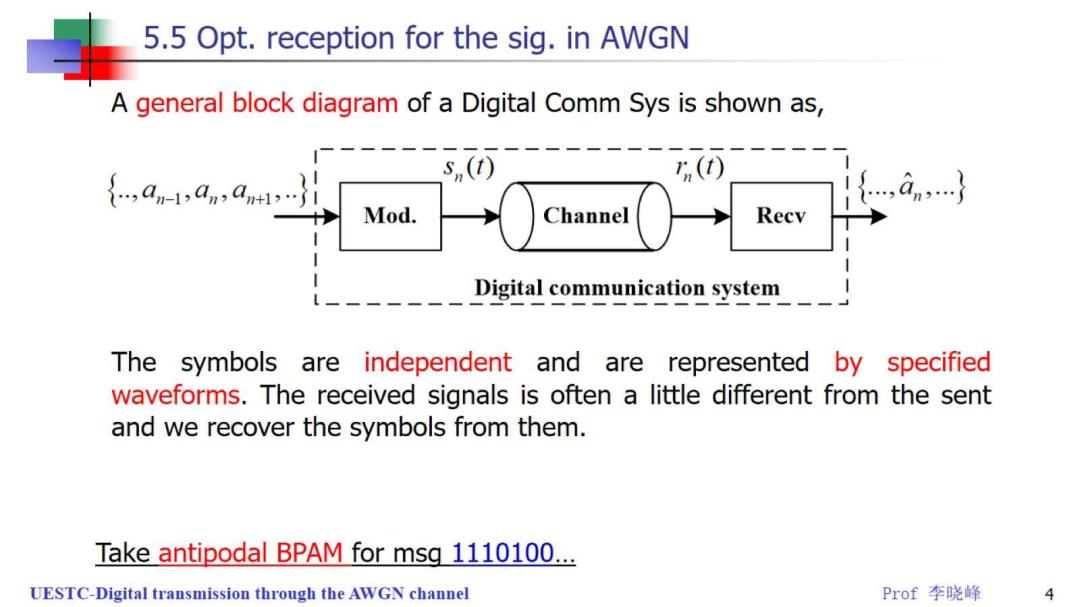
5.5 Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN A general block diagram of a Digital Comm Sys is shown as, s,(t) 5n(t) 十 Mod. Channel Recv Digital communication system The symbols are independent and are represented by specified waveforms.The received signals is often a little different from the sent and we recover the symbols from them. Take antipodal BPAM for msg 1110100... UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 4
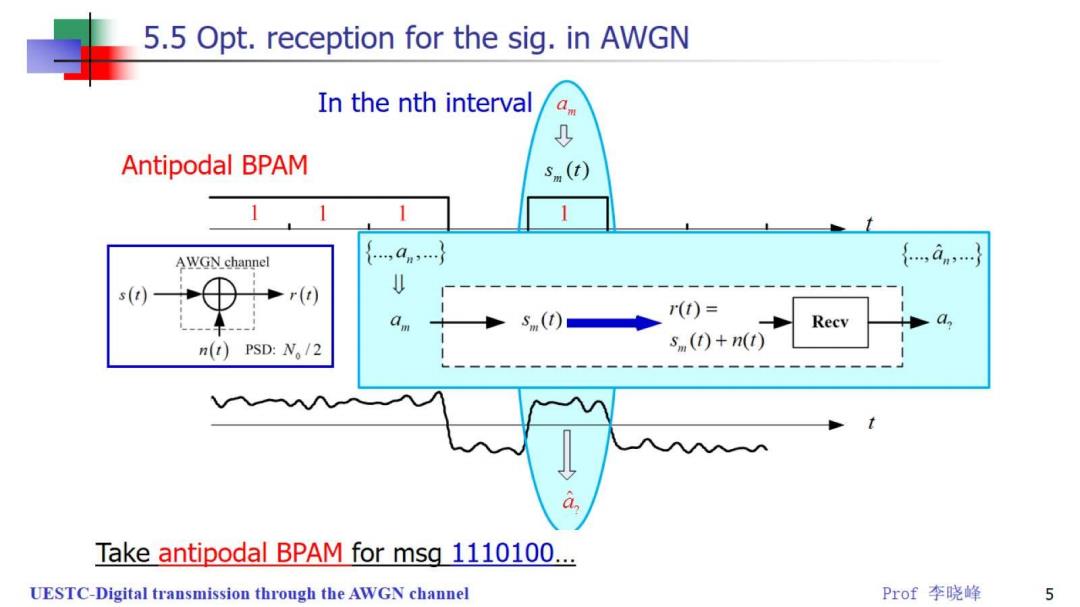
5.5 Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN In the nth interval ↓ Antipodal BPAM 5m(t) 1 1 1 AWGN channel {,an,} {,an} s() r() am (t)= Recv a n(t)PsD:N。/2 s (t)+n(t) Take antipodal BPAM for msg 1110100... UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 5
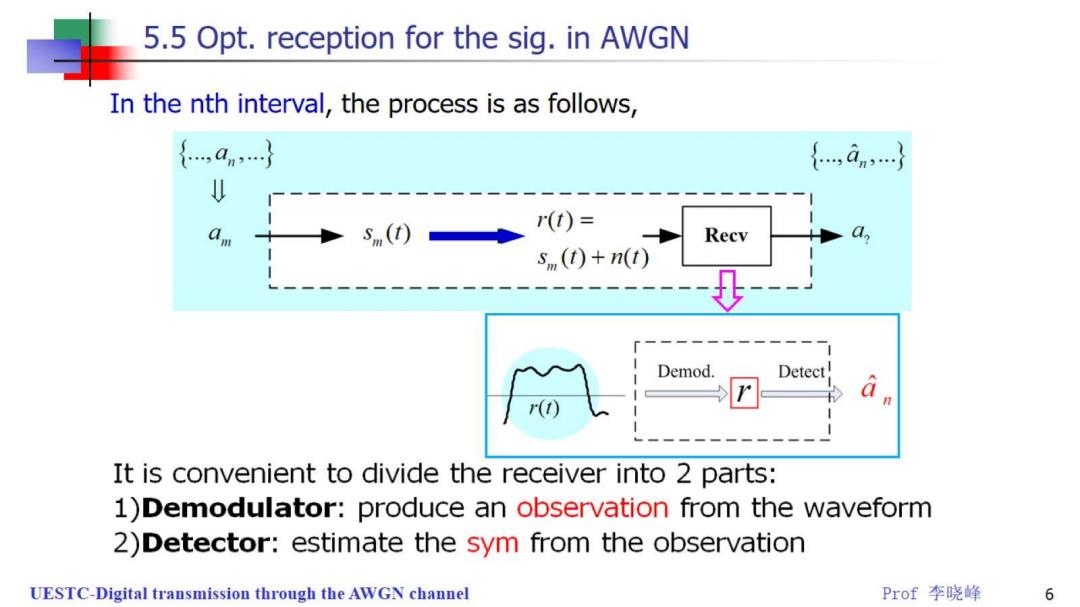
5.5 Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN In the nth interval,the process is as follows, {,an,} {,an…} s (t) r(t)= Recv s,(t)+n(t) Demod. Detect a It is convenient to divide the receiver into 2 parts: 1)Demodulator:produce an observation from the waveform 2)Detector:estimate the sym from the observation UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 6
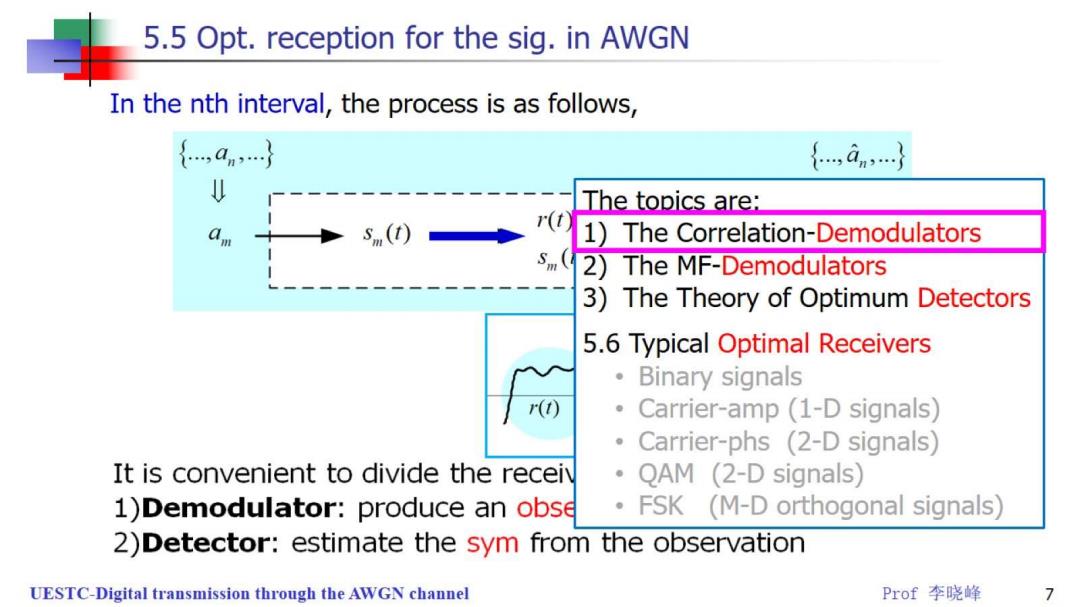
5.5 Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN In the nth interval,the process is as follows, {,an,} {,an} The topics are: s(t) r(t 1)The Correlation-Demodulators Sm( 2)The MF-Demodulators 3)The Theory of Optimum Detectors 5.6 Typical Optimal Receivers 。 Binary signals r(t) Carrier-amp(1-D signals) Carrier-phs (2-D signals) It is convenient to divide the receiv 。 QAM (2-D signals) 1)Demodulator:produce an obse FSK (M-D orthogonal signals) 2)Detector:estimate the sym from the observation UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 77
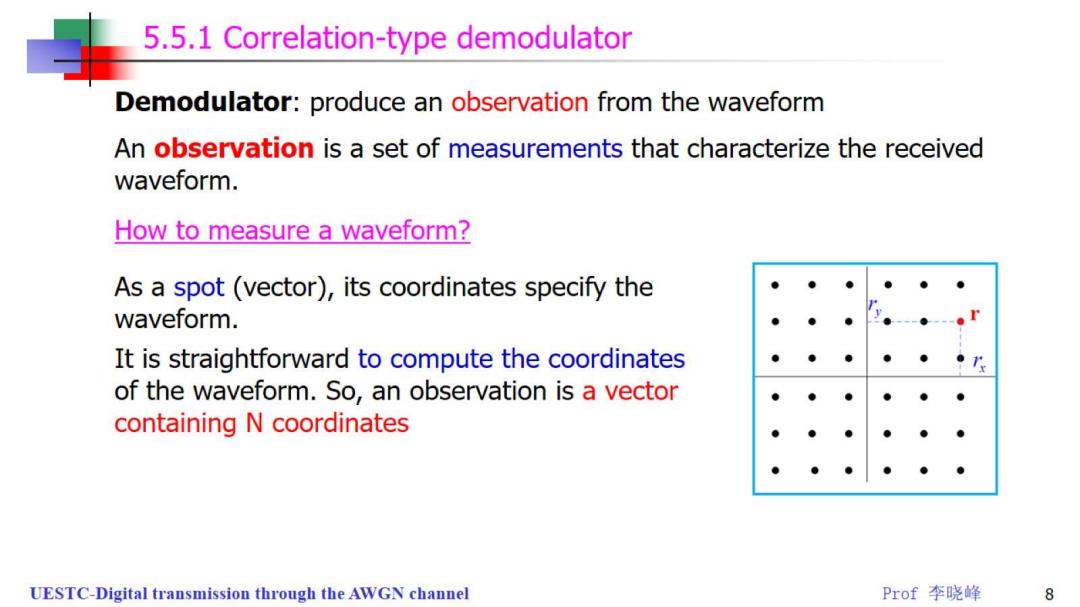
5.5.1 Correlation-type demodulator Demodulator:produce an observation from the waveform An observation is a set of measurements that characterize the received waveform. How to measure a waveform? As a spot(vector),its coordinates specify the waveform. It is straightforward to compute the coordinates of the waveform.So,an observation is a vector containing N coordinates UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 8

5.5.1 Correlation-type demodulator How to compute the coordinates Given an N-d transmission waveform s,()m=1,2,...,M, the received signal is (0 r(t)=s,(t)+n(t) )d山 Let the orthonormal basis be (),...,() )d山 片=∫r()y()dh r(t) =∫」sn0y,(0dh+∫n0y()dh w() In vector language,that is )d山 r=Sm+n (i,,w)=(Snm1,,SmN)+(h,,nw) UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 9
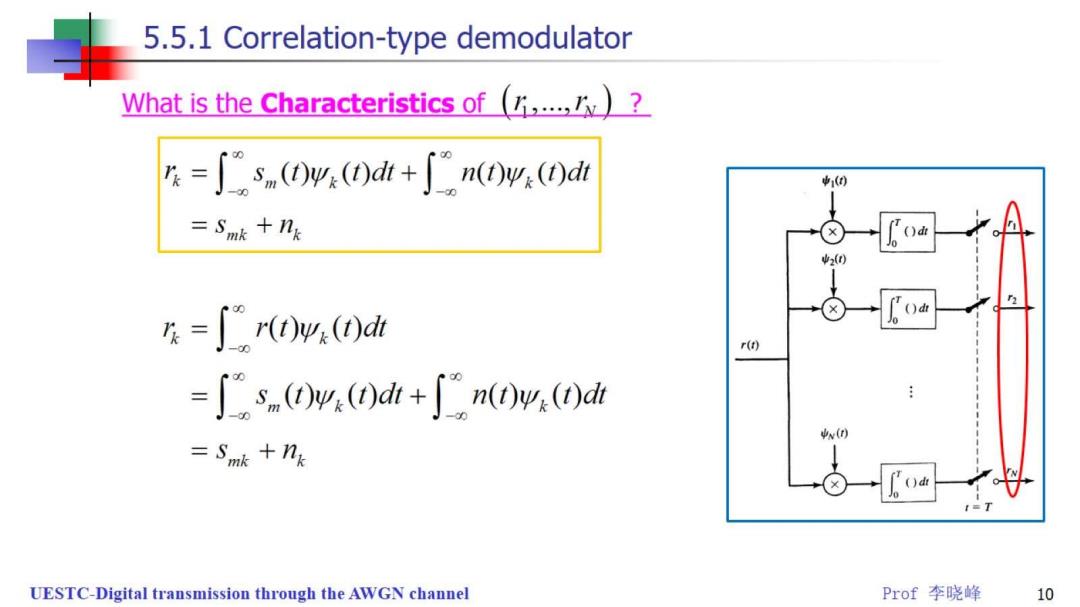
5.5.1 Correlation-type demodulator What is the Characteristics of(? n=∫sn(0ws(0di+∫n0w:(0d 1(0 =Smk +ng )d山 ()d山 片=∫r(0w(0d r(t) =sn0w,0dh+∫n0y,0dh v(r) -Smk +nk ()d山 UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 10
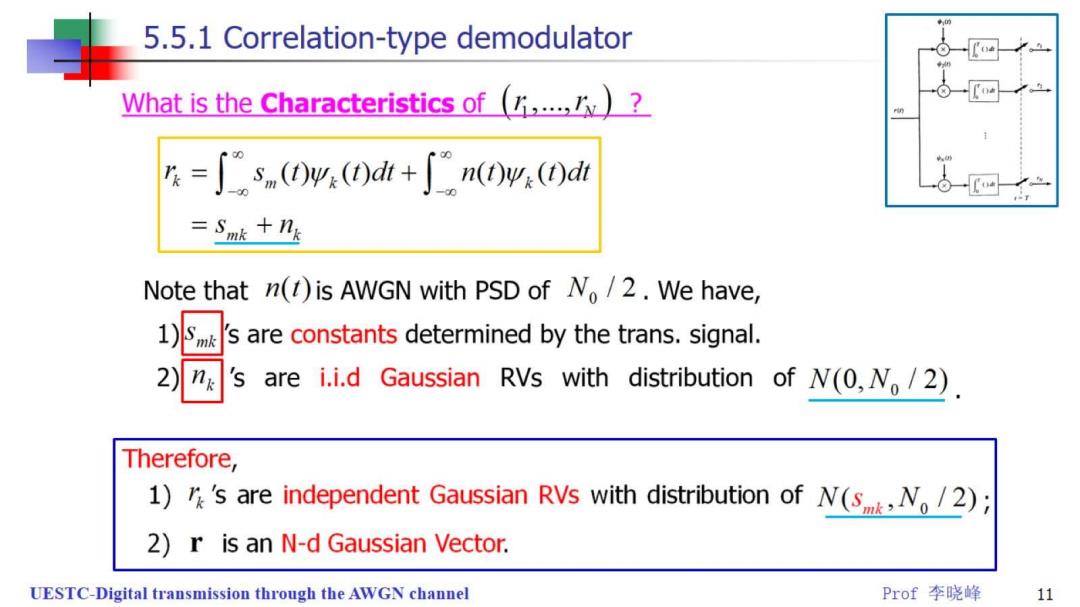
5.5.1 Correlation-type demodulator What is the Characteristics of()? 片=∫sn(04(0dt+∫n(0w.(0d =Smk +nk Note that n()is AWGN with PSD of No/2.We have, are constants determined by the trans.signal. 2) s are i.i.d Gaussian RVs with distribution of N(0,No/2) Therefore, 1)'s are independent Gaussian RVs with distribution of N(sN./2); 2)r is an N-d Gaussian Vector. UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 11
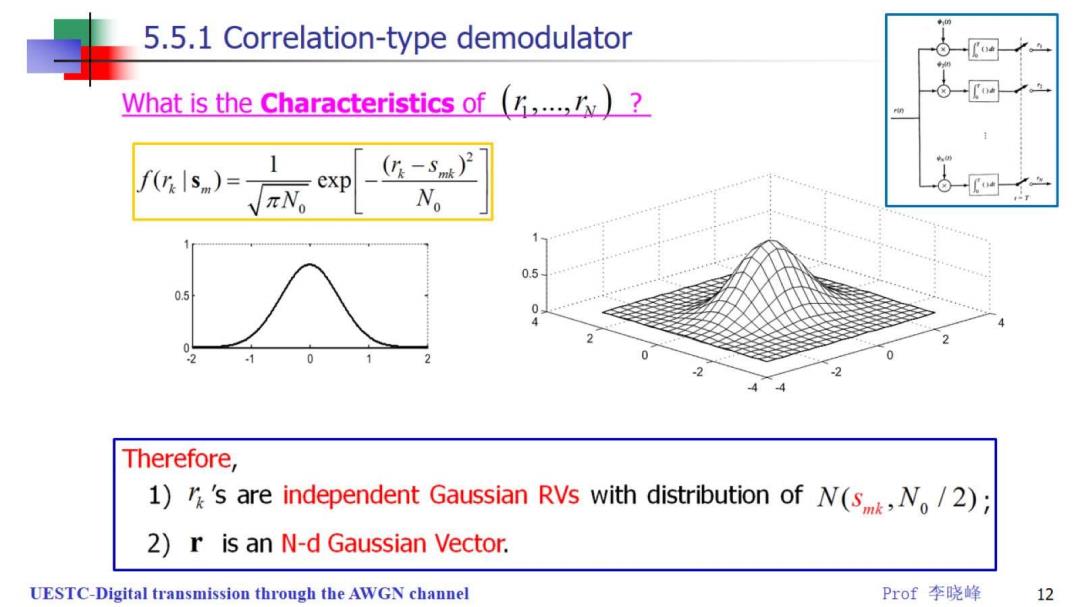
5.5.1 Correlation-type demodulator What is the Characteristics of(.? exp (n-s)2 N 0.5 0.5 2 0 Therefore, 1)'s are independent Gaussian RVs with distribution of N(sN./2); 2)r is an N-d Gaussian Vector. UESTC-Digital transmission through the AWGN channel Prof李晓峰 12