
Periodic potential & Harmonic oscillator 2011.09.27 何峰
Periodic potential & Harmonic oscillator 2011.09.27 何 峰
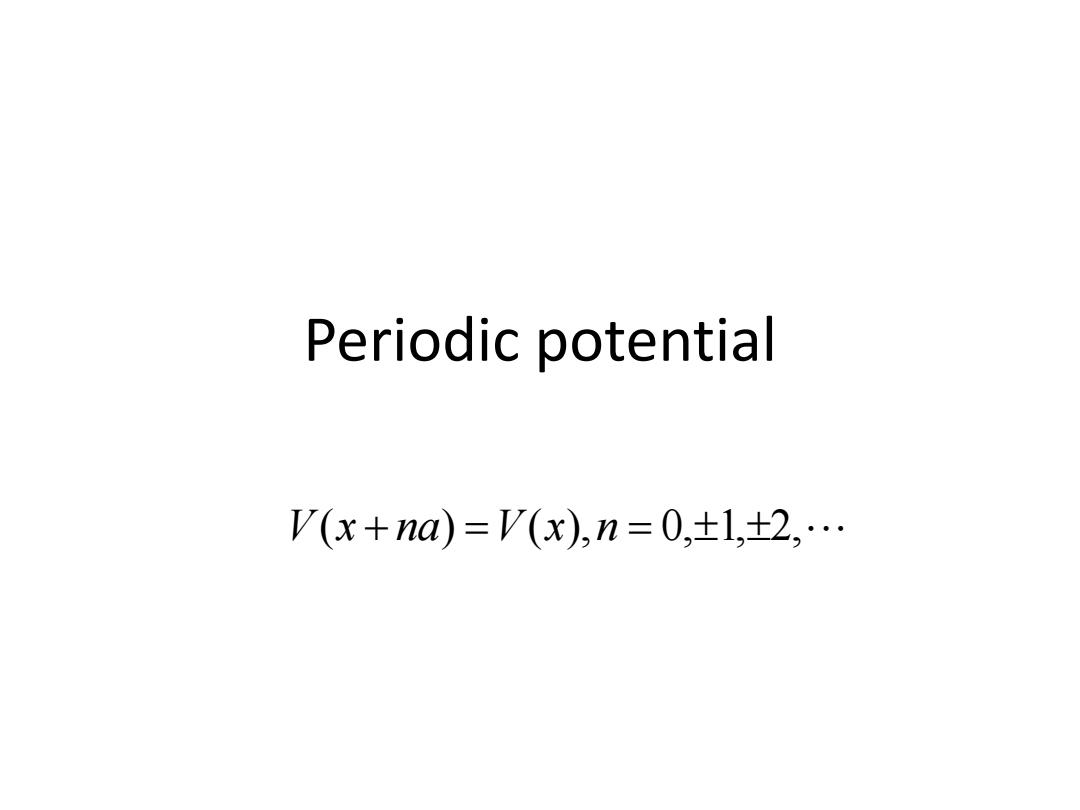
Periodic potential V(x+na=V(x)n=0,±1,±2,…
Periodic potential V(x na) V(x),n 0,1,2,
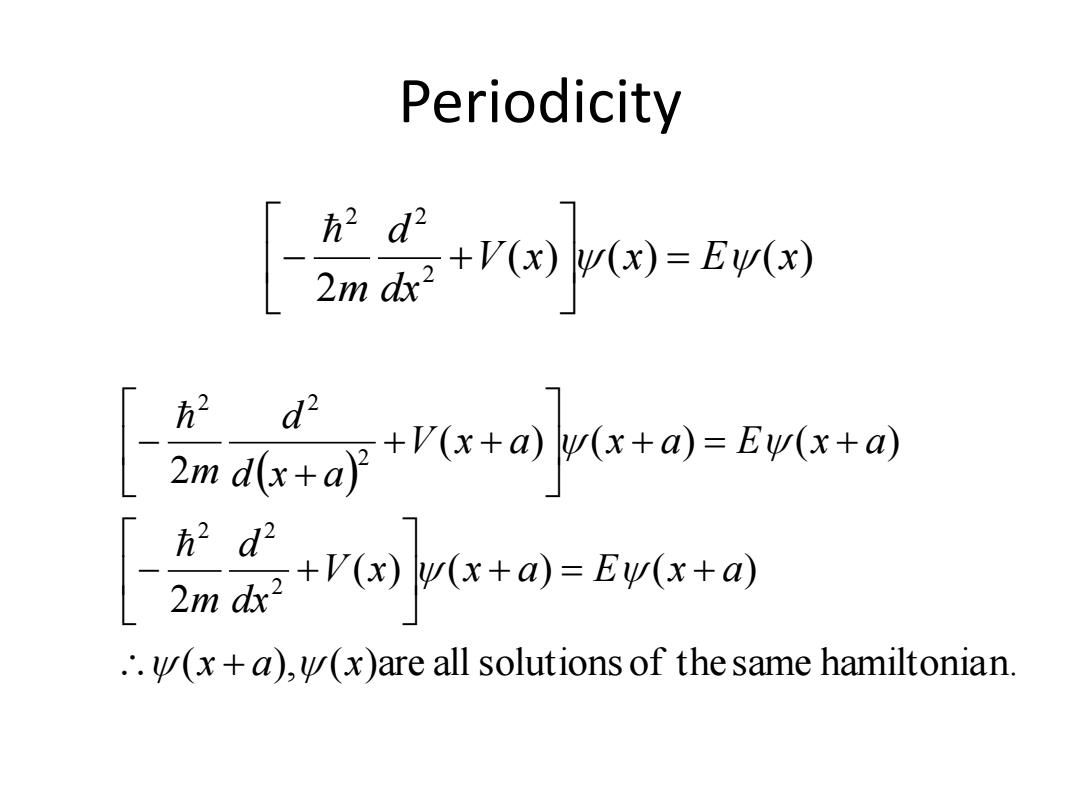
Periodicity 会品-mn-E 式可"ea-o小-5u-w +r闲lr+n-st+a .'.(x+a),(x)are all solutions of the same hamiltonian
Periodicity ( ), ( )are allsolutions of thesame hamiltonian. ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 x a x V x x a E x a dx d m V x a x a E x a d x a d m ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 2 V x x E x dx d m
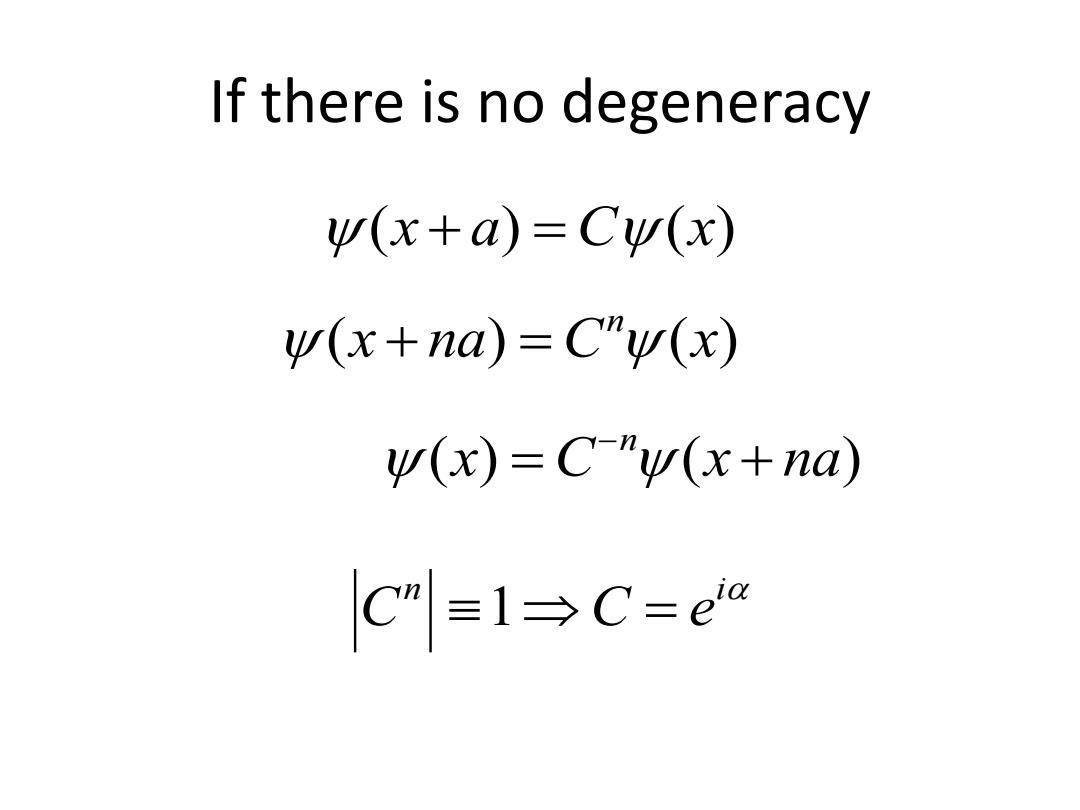
If there is no degeneracy w(x+a)=Cw(x) w(x+na)=C"w(x) y(x)=C"v(x+na) C≡l→C=ea
If there is no degeneracy (x a) C(x) (x na) C (x) n (x) C (x na) n n i C 1C e
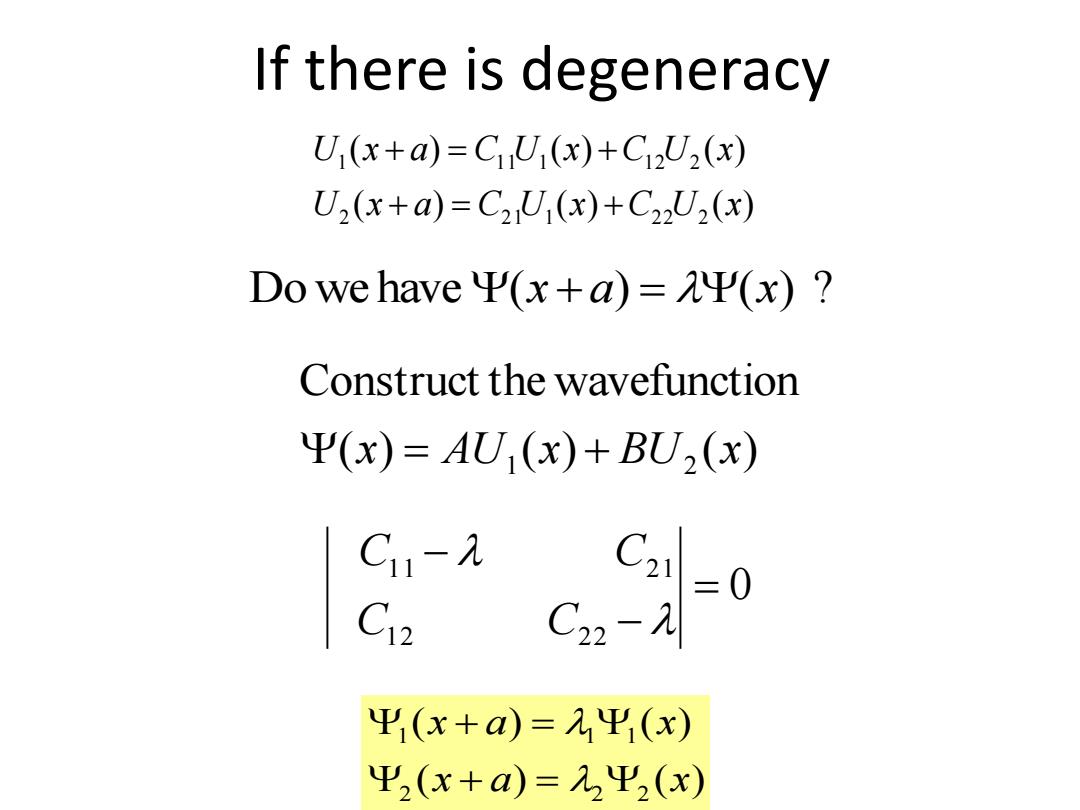
If there is degeneracy U1(x+a)=C1U1(x)+C12U2(x) U2(x+a)=C2U1(x)+C22U2(x) Do we have P(x+a)=(x)? Construct the wavefunction Ψ(x)=AU1(x)+BU2(x) |8c 二0 C12 Ψ1(x+a)=Ψ1(x) Ψ2(x+a)=2Ψ2(x)
If there is degeneracy ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 U x a C U x C U x U x a C U x C U x Do we have (x a) (x) ? ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 1 1 1 x a x x a x 0 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 1 C C C C ( ) ( ) ( ) Construct the wavefunction 1 2 x AU x BU x
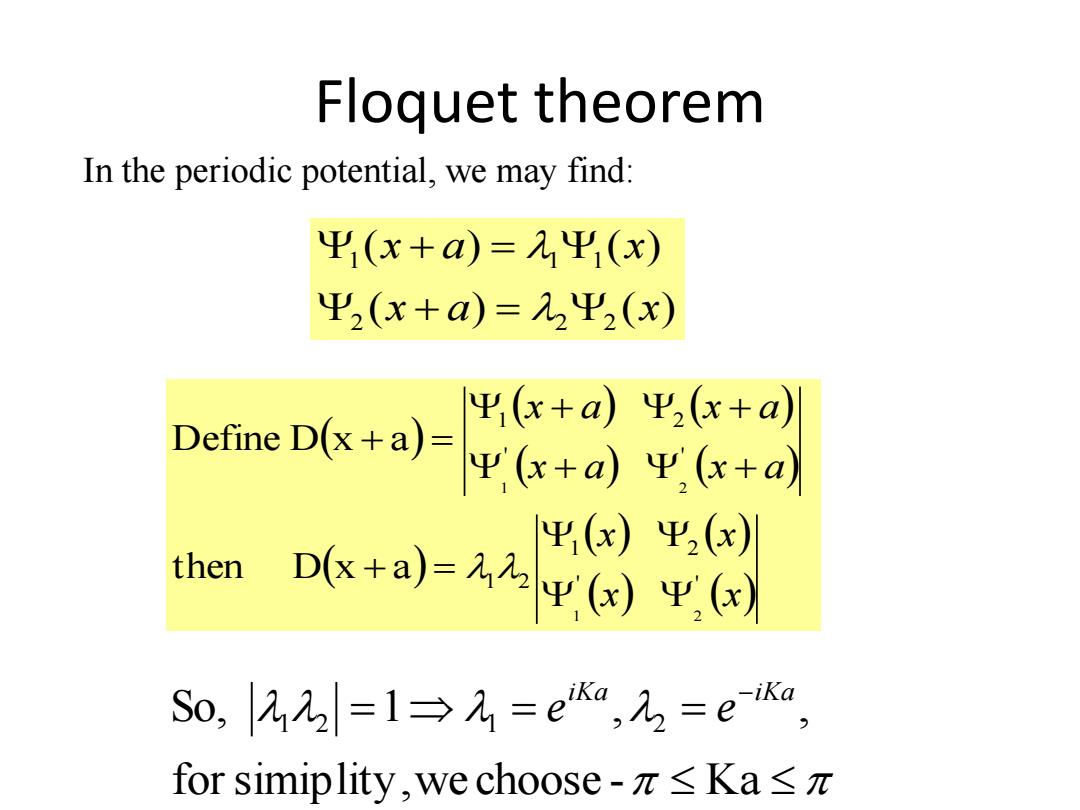
Floquet theorem In the periodic potential,we may find: 出1(x+a)=平(x) Ψ2(x+a)=2Ψ2(x) 出(x+aΨ2(x+a Define Dx+a)d+a 出(x)平(x) then Dx+a)=12Ψ()Ψ(✉ So,22=1→=ea,2=ea for simiplity,we choose-π≤Ka≤π
Floquet theorem In the periodic potential, we may find: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 1 1 1 x a x x a x for simiplity, we choose - Ka So, 1 , , 1 2 1 2 iKa iKa e e x x x x x a x a x a x a ' ' 1 2 1 2 ' ' 1 2 1 2 1 2 then D x a Define D x a
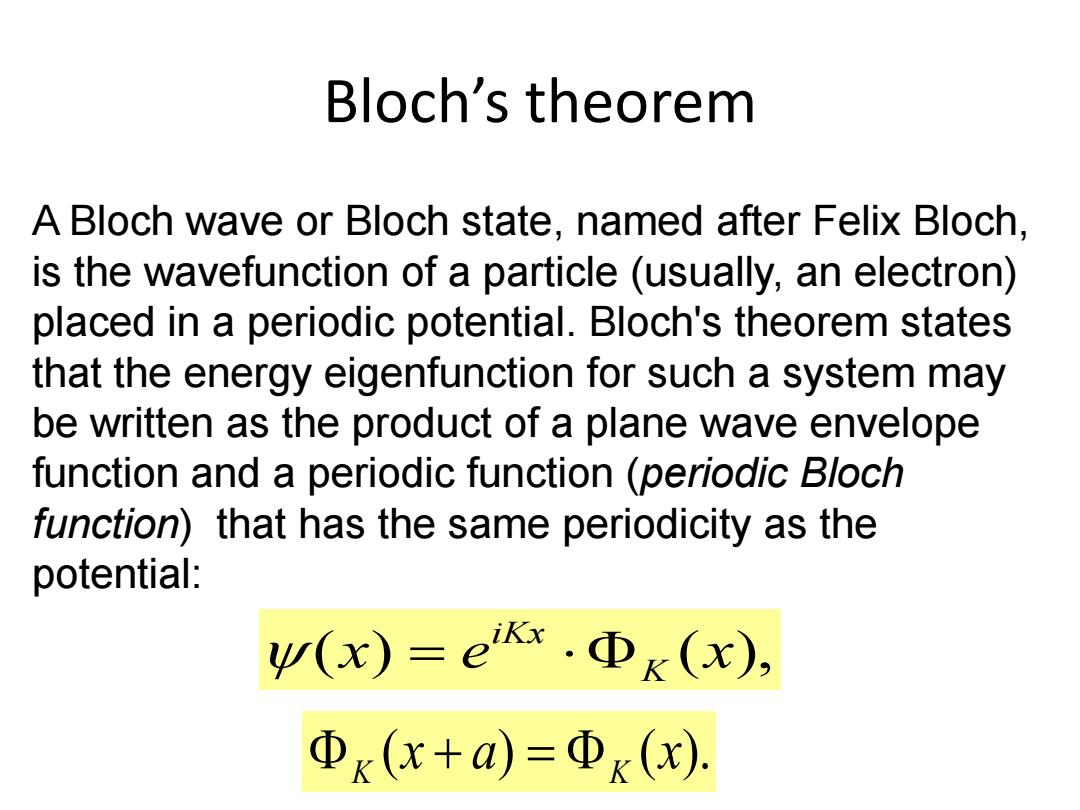
Bloch's theorem A Bloch wave or Bloch state,named after Felix Bloch. is the wavefunction of a particle (usually,an electron) placed in a periodic potential.Bloch's theorem states that the energy eigenfunction for such a system may be written as the product of a plane wave envelope function and a periodic function (periodic Bloch function)that has the same periodicity as the potential: w(x)=e.Φk(x), Φx(x+a)=Φx(x)
Bloch’s theorem A Bloch wave or Bloch state, named after Felix Bloch, is the wavefunction of a particle (usually, an electron) placed in a periodic potential. Bloch's theorem states that the energy eigenfunction for such a system may be written as the product of a plane wave envelope function and a periodic function (periodic Bloch function) that has the same periodicity as the potential: (x) e (x), K iKx (x a) (x). K K
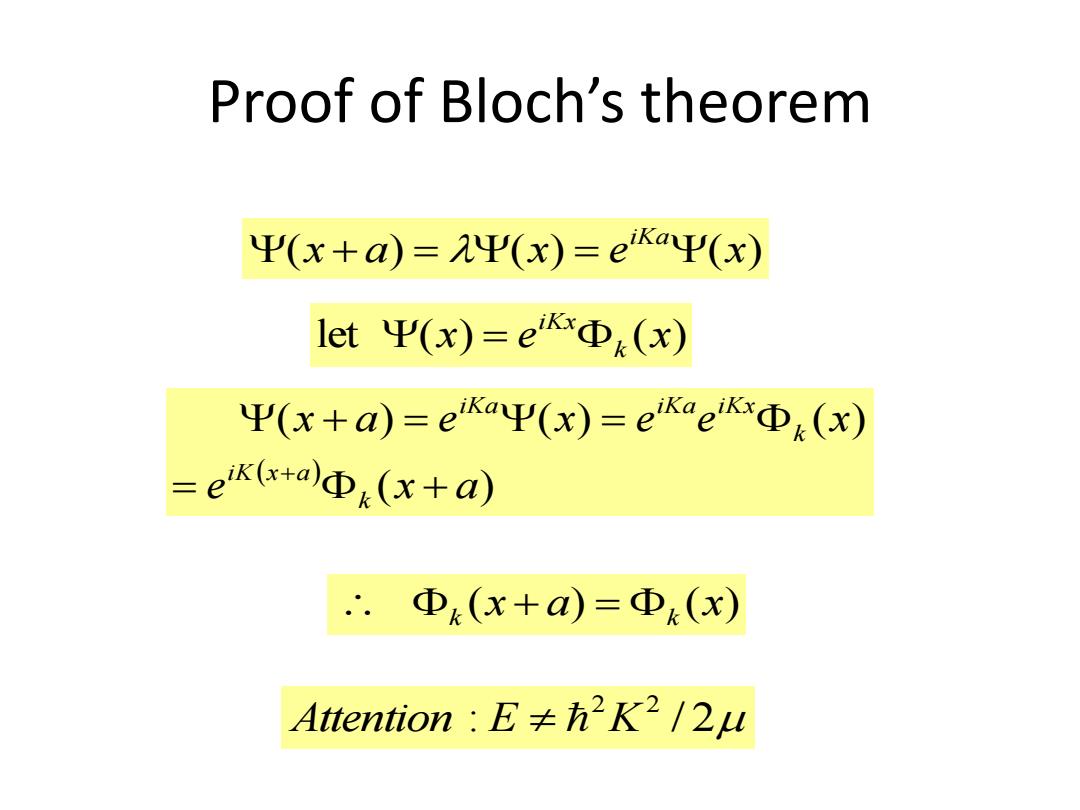
Proof of Bloch's theorem Ψ(x+a)=Ψ(x)=ekaΨ(x) letΨ(x)=eKxΦk(x) Ψ(x+a=eKaΨ(x)=eikaeikx④k(x) =eKx+aΦ(x+a) ∴.Φk(x+a)=Φk(x) Attention:E≠h2K2/2u
Proof of Bloch’s theorem (x a) (x) e (x) iKa let (x) e (x) k iKx ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) e x a x a e x e e x k iK x a k iKa iKa iKx (x a) (x) k k : / 2 2 2 Attention E K
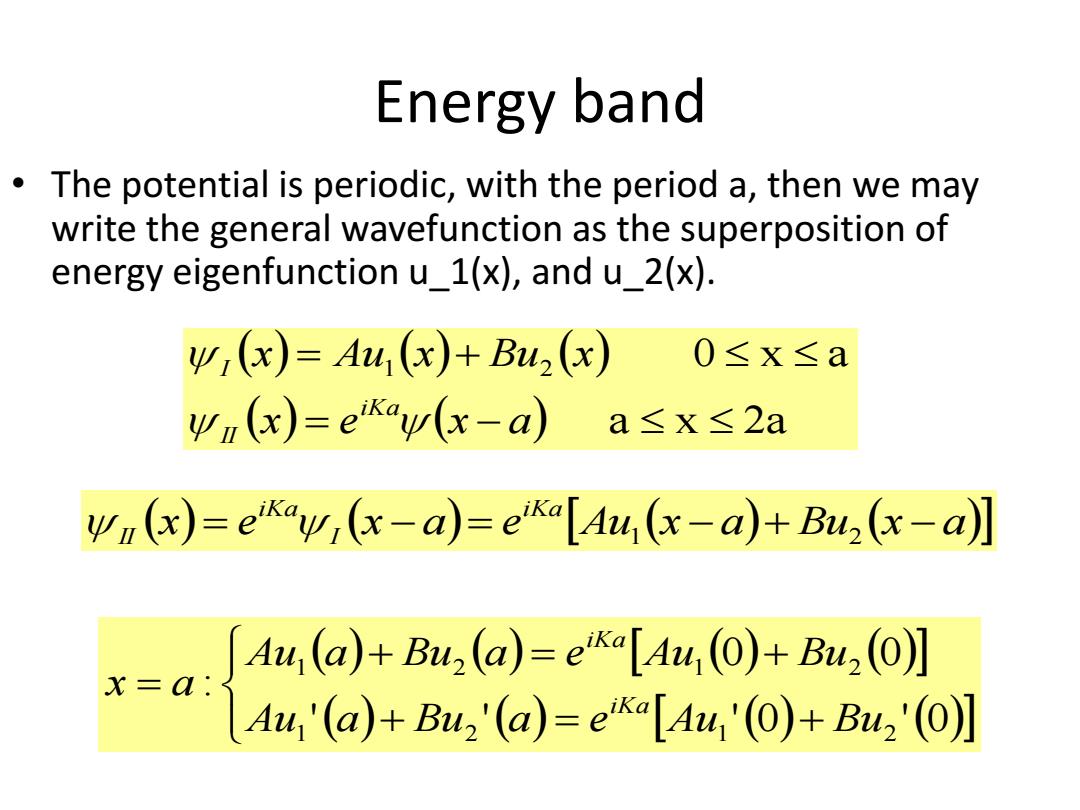
Energy band The potential is periodic,with the period a,then we may write the general wavefunction as the superposition of energy eigenfunction u_1(x),and u_2(x). W,(x)=Au,(x)+B2(x) 0≤x≤a wn(x)=e"kow(x-a) a≤x≤2a Wu(x)=ekav,(x-a)=ekaLAu (x-a)+Buz(x-a) Au(a)+Buz(a)=e"ka[Au (O+Buz (O] xAu(a)Buz"(a)u)+Bus
Energy band • The potential is periodic, with the period a, then we may write the general wavefunction as the superposition of energy eigenfunction u_1(x), and u_2(x). a x 2a 0 x a 1 2 x e x a x Au x Bu x iKa II I x e x a e Au x a Bu x a iKa I iKa II 1 2 ' ' ' 0 ' 0 0 0 : 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 Au a Bu a e Au Bu Au a Bu a e Au Bu x a iKa iKa

Energy band 4,(a)-ek4,(O) u,(a-e4,0)=-0 4'(a)-ea4'(0)42'(a-ekau2'(0) 4(a4,(a)-4'(a,(a-4(a,(O)+4O4,(aa +e2au(O)h4,0)-u'0hu,(0)】+u'(a4,(0)+u'(0h4,(ala=0 U-U2 264242-4,4) cos Ka, whereU=u O)uz(a)+u(a)uz(0). U2=4,(04(a+42(a)4(O)
Energy band 0 0 where 0 0 , cos , 2 ' 2 1 ' 2 2 1 ' 1 2 ' 1 1 2 ' 2 1 ' 1 2 1 2 U u u a u a u U u u a u a u Ka u u u u U U 0 ' - ' 0 ' - ' 0 - 0 - 0 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 u a e u u a e u u a e u u a e u iKa iKa iKa iKa 0 0 '0 0 ' 0 '0 0 ' 0 0 1 2 1 2 1 2 ' 1 2 2 ' 1 2 ' 1 2 1 2 ' 1 2 i K a iKa iKa e u u u u u a u u u a e u a u a u a u a u a u u u a e