
Chap 16 Sound and hearing
Chap 16 Sound and hearing

Outline Pressure fluctuations ·Sound speed 。Sound intensity Standing sound waves---organ pipe ·Resonance ·Beat ·Doppler effect ·Shock waves
Outline • Pressure fluctuations • Sound speed • Sound intensity • Standing sound waves---organ pipe • Resonance • Beat • Doppler effect • Shock waves
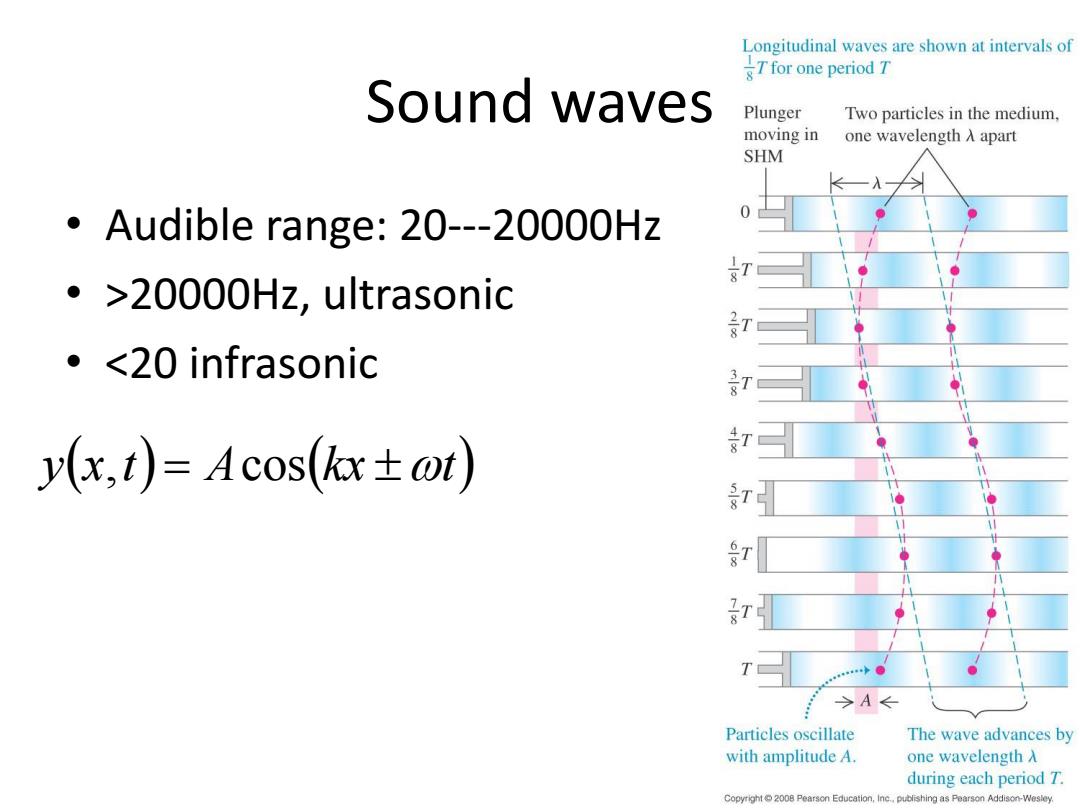
Longitudinal waves are shown at intervals of Tfor one period T Sound waves Plunger Two particles in the medium, moving in one wavelength入apart SHM Audible range:20---20000Hz .>20000Hz,ultrasonic ·A← Particles oscillate The wave advances by with amplitude A. one wavelength入 during each period T. Copyright 2008 Pearson Education,Inc..publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
Sound waves • Audible range: 20---20000Hz • >20000Hz, ultrasonic • <20 infrasonic yx,t Acoskx t

Pressure fluctuations Undisturbed cylinder of fluid has cross-sectional =y(x,),y2=y(x+△x,t) area S,length Ax,and volume SAx. A sound wave displaces the left ...and the △V=S6y2-y) end of the cylinder right end by by y1=y(x,t)...y2 =y(x Ar,t). dv 1ims0-》_ ov V Ax→0 S△x Ox Bs px,0→Ap(k.=-B.l dv V Ox x+Ax The change in volume of the disturbed If y(x,t)=Acos(kx-ot), cylinder of fluid is S(y2-y). then Ap(x,t)=BAk sin(kx-ot)
Pressure fluctuations ( , ), ( , ) 1 2 y y x t y y x x t 2 1 V S y y x y S x S y y V dV x lim 2 1 0 x y x t p x t B dV V p x t B , , ( , ) px t BAk kx t y x t A kx t then , sin If ( , ) cos( )
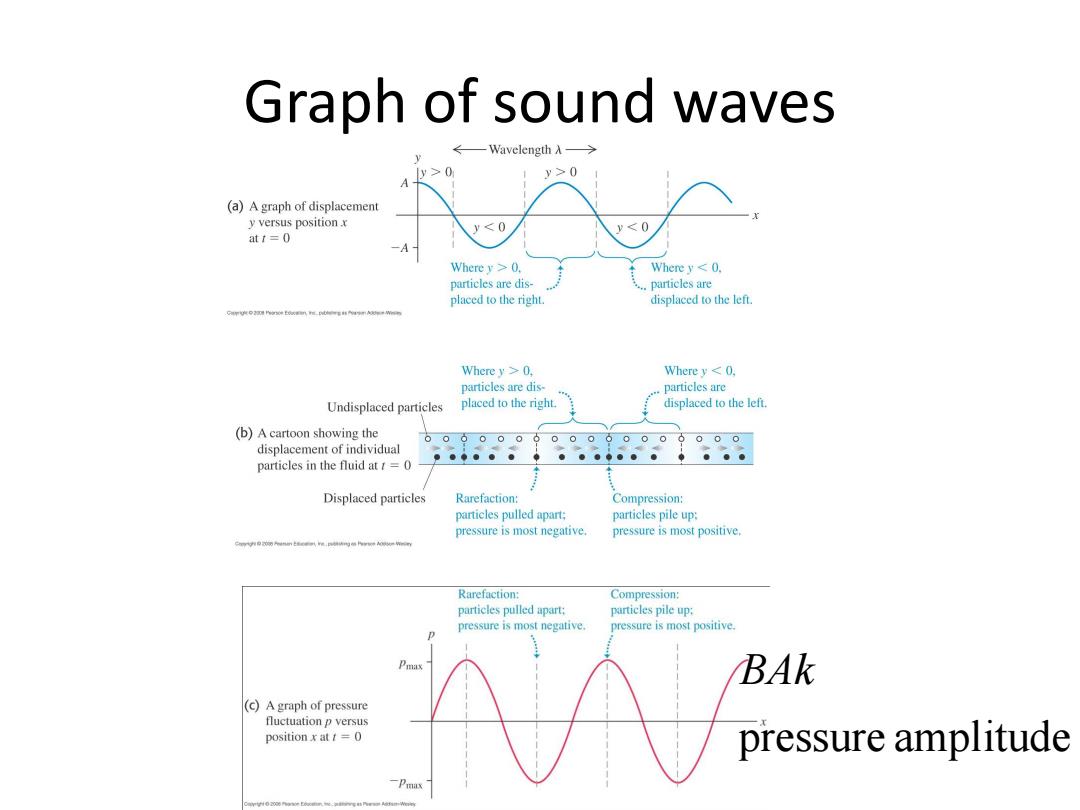
Graph of sound waves ←—Wavelength A> y>0 y>0 (a)A graph of displacement y versus position x v0. Where y0, Wherey <0, particles are dis. particles are Undisplaced particles placed to the right. displaced to the left. (b)A cartoon showing the 0000 00000006 000 displacement of individual particles in the fluid at=0 Displaced particles Rarefaction: Compression: particles pulled apart; particles pile up: pressure is most negative. pressure is most positive, Rarefaction: Compression: particles pulled apart: particles pile up: pressure is most negative. pressure is most positive. BAk (c)A graph of pressure fluctuation p versus position x at=0 pressure amplitude
Graph of sound waves pressure amplitude BAk
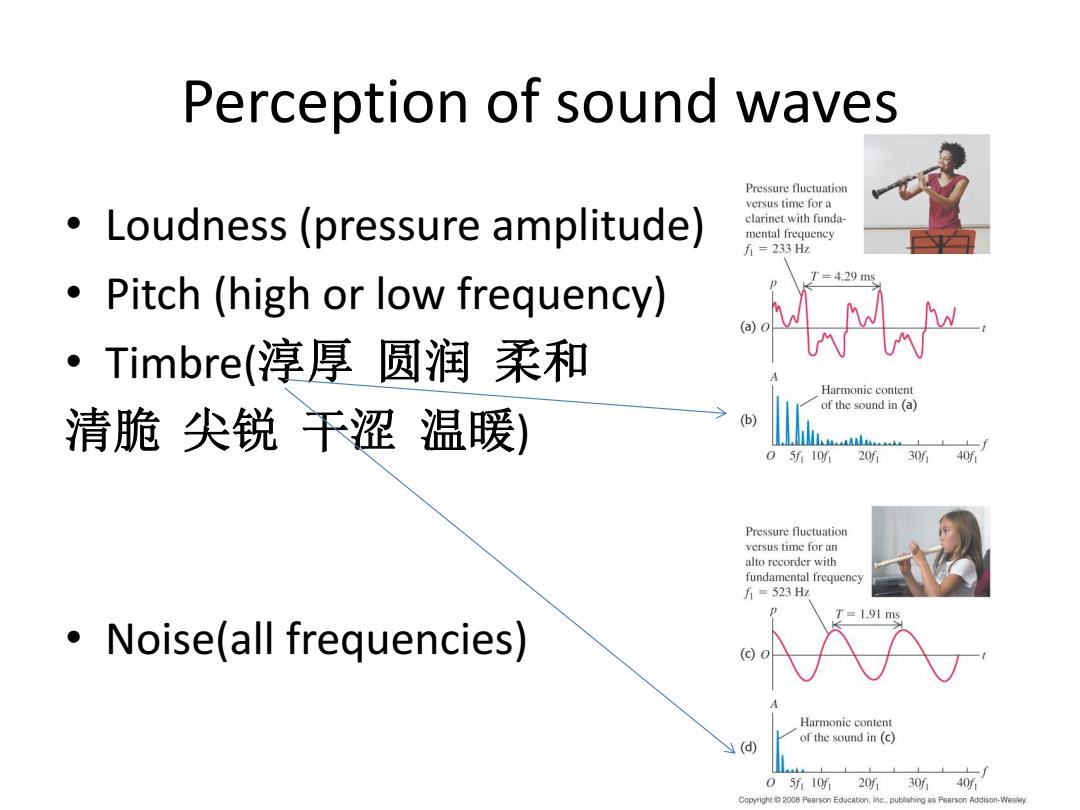
Perception of sound waves Pressure fluctuation versus time for a Loudness(pressure amplitude) clarinet with funda- mental frequency 斤=233Hz =4.29ms Pitch (high or low frequency) ·Timbre(淳厚圆润柔和 Harmonic content of the sound in (a) 清脆尖锐干涩温暖) (b) 05所10听 20听3040 Pressure fluctuation versus time for an alto recorder with fundamental frequency 万=523Hz T=1.91ms Noise(all frequencies) Harmonic content of the sound in (c) (d) 05f10所20听30听40听 Copyright2008 Pearson Education,inc.pubishing as Paarson Addison-Wesey
Perception of sound waves • Loudness (pressure amplitude) • Pitch (high or low frequency) • Timbre(淳厚 圆润 柔和 清脆 尖锐 干涩 温暖) • Noise(all frequencies)
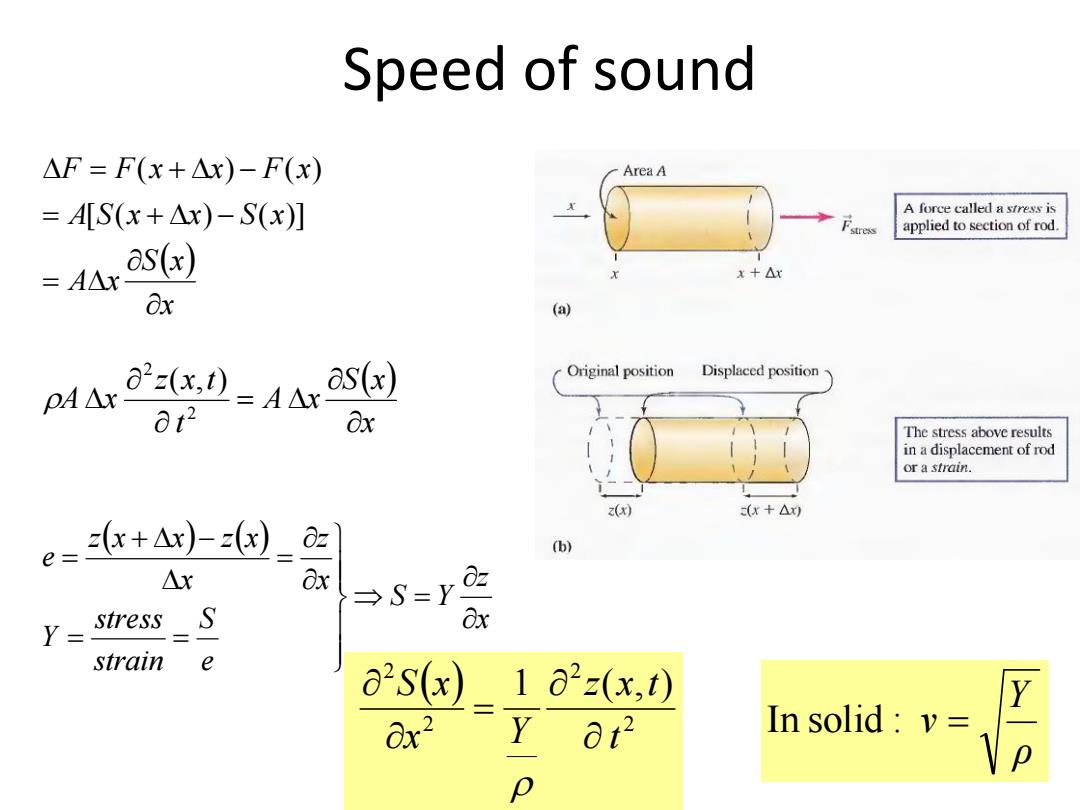
Speed of sound △F=F(x+△x)-F(x) AreaA =A[S(x+△x)-S(x)] A force called a stress is applied to section of rod. =A△ as(x) x+△r Ox (a) a2z(x,)=A△ Original position Displaced position pA△x as(x) 0t2 Ox The stress above results in a displacement of rod or a strain. z(x) (x+△x) e==(x+Ax)-=(x) az (b) △x 8x →S=Y 0z Y= stress S Ox strain e a2S(x)_1∂2z(x,) Ox2 In solid:v= P
x S x A x A S x x S x F F x x F x [ ( ) ( )] ( ) ( ) x S x A x t z x t A x ( , ) 2 2 x z S Y e S strain stress Y x z x z x x z x e 2 2 2 2 1 ( , ) t z x t x Y S x Speed of sound ρ Y In solid : v
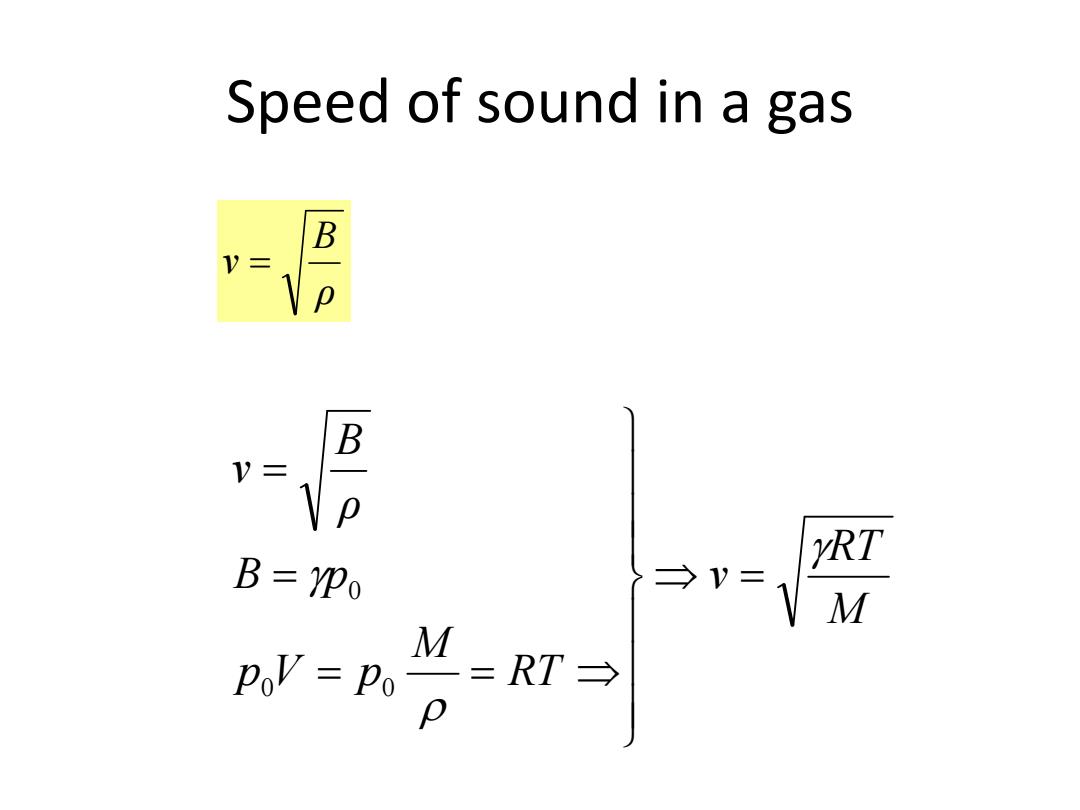
Speed of sound in a gas B B y= B=YPo rRT →V= M M Pov=Po =RT→
Speed of sound in a gas M RT v RT M p V p B p ρ B v 0 0 0 ρ B v
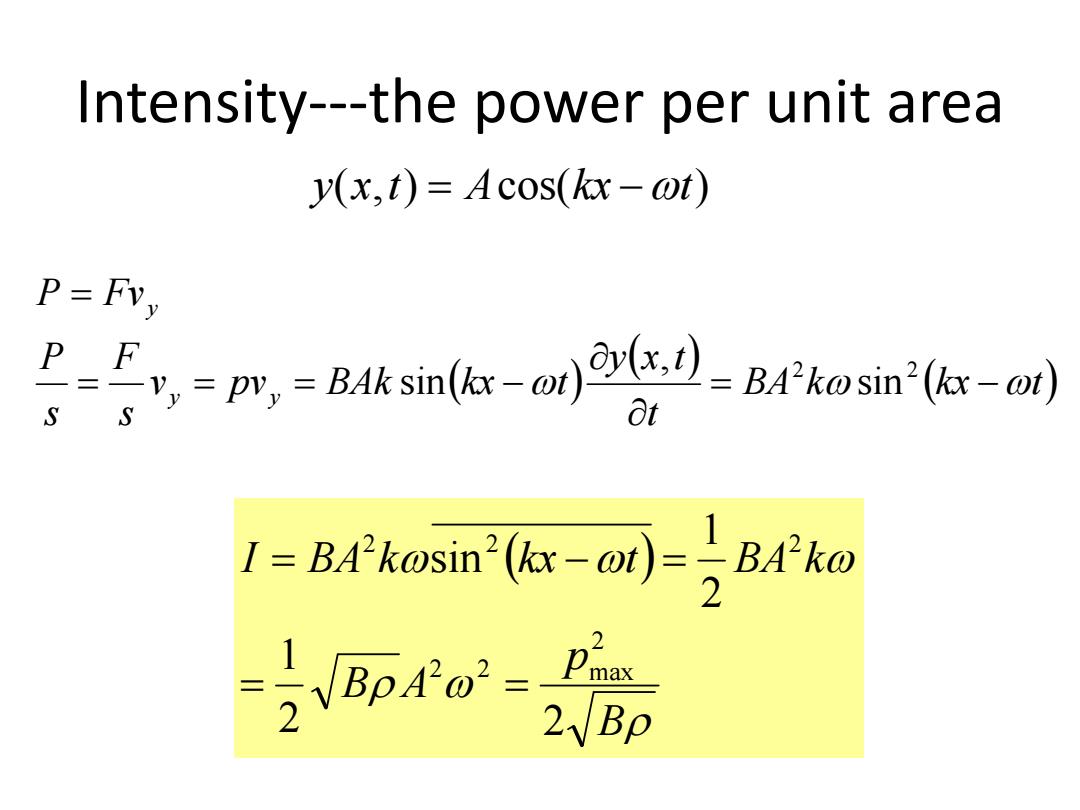
Intensity---the power per unit area y(x,t)=Acos(kx-@t) P P F ,-p,=B4ksin(xo)-BAkosin(x-o) S at 1=Bsnc-o侧-号BMko 项o
Intensity---the power per unit area BA k kx t t y x t v pv BAk kx t s F s P P Fv y y y 2 2 sin , sin y(x,t) Acos(kx t) B p B A I BA k kx t BA k 2 2 1 2 1 sin 2 2 2 max 2 2 2
Inverse-square law
Inverse-square law